Multi-Attention Fusion and Fine-Grained Alignment for Bidirectional Image-Sentence Retrieval in Remote Sensing
Qimin Cheng, Yuzhuo Zhou, Haiyan Huang, and Zhongyuan Wang
Dear editor,
Cross-modal retrieval in remote sensing (RS) data has inspired increasing enthusiasm due to its merit in flexible input and efficient query. In this letter, we address to establish semantic relationship between RS images and their description sentences. Specially, we propose a multi-attention fusion and fine-grained alignment network,termed MAFA-Net, for bidirectional cross-modal image-sentence retrieval in RS. While multiple attention mechanisms are fused to enhance the discriminative ability of visual features for RS images with complex scenes, fine-grained alignment strategy is introduced to study the hidden connection between RS observations and sentences.To validate the capability of MAFA-Net, we leverage four captioning benchmark datasets with paired RS images and descriptions, i.e.,UCM-Captions, Sydney-Captions, RSICD and NWPU-Captions.Experimental results on the four datasets demonstrate that MAFANet can yield better performance than the current state-of-the-art approaches.
Related work: The accelerated advancement in earth observation technology witnesses an explosive growth of multi-modal and multisource remote sensing data. Cross-modal retrieval in RS facilitates flexible and efficient query, which has attracted extensive interest in recent years and can be applied to natural disaster early-warning and military intelligence generation, etc.
Significant efforts have been devoted to cross-modal retrieval for natural images. To probe fine-grained relationships among images and sentences, Chenet al. [1] proposed a cross-modal retrieval model(IMRAM) based on a recurrent attention technique. Leeet al. [2]proposed a stacked attention mechanism-based graphic retrieval model (SCAN) to learn more discriminative textual and visual feature representations. Wanget al. [3] proposed a multi-modal tensor fusion network (MTFN) to directly measure the similarity between different modalities through rank-based tensor fusion. Wanget al. [4] proposed a position focused attention network (PFAN) to improve cross-modal matching performance. Besides, to satisfy industrial requirement, Wuet al. [5] proposed a hashing approach to achieve large-scale cross-modal retrieval via learning a unified hash representation and deep hashing functions for different modalities in a self-supervised way. Although these achievements gained inspiring results for retrieval tasks in natural images, their robustness and generalization ability need to be verified when transfer to RS fields due to the intrinsic and extrinsic properties of RS data.
Motivated by the burgeoning demands for multi-modal requests in RS like military intelligence generation, researchers have paid more attention to RS cross-modal retrieval during the recent several years.To explore semantic correlation between visual features and textual description of RS data, Abdullahet al. [6] proposed a novel deep bidirectional ternary network (DBTN) for Text-to-Image (T2I)matching task through features fusion strategy. With regard to Image-to-Text (I2T) retrieval for RS data, Chenget al. [7] proposed to use a cross-attention mechanism and a gating mechanism to enhance the association between RS images and descriptions, which is the first attempt to prove the possibility of bidirectional T2I and I2T retrieval in RS. Afterwards, Lvet al. [8] proposed a fusion-based correlation learning model (FCLM) to capture multi-modal complementary information and fusion features and to further supervise the learning of the feature extraction network. Yuanet al.[9] proposed an asymmetric multimodal feature matching network(AMFMN) to extract the salient visual features of RS images through a multi-scale visual self-attention technique, and exploited it to guide textual feature extraction. Moreover, they further designed a concise and efficient version of their cross-modal retrieval model, namely LW-MCR [10] on the basis of knowledge distillation. For fast and efficient retrieval on large-scale RS data, Mikriukovet al. [11]introduced a novel deep unsupervised cross-modal contrastive hashing model. Except for image-sentence retrieval, there has been some work on visual-audio retrieval [12], image-sketch retrieval[13], cross-source panchromatic-multispectral image retrieval [14],[15] and zero-shot image-word matching [16].
It is no doubt that all the above work partly advances the crossmodal retrieval in RS from different aspects including visual feature representation and description optimization strategy, etc. However,current work on bidirectional image-sentence retrieval in RS is deficient in 1) Achievements on bidirectional image-sentence retrieval for RS data are very limited and comprehensive analysis is still lacking. Current work [6]?[11] conducts comparative experiments with the baseline for natural images unexceptionally; 2) The generalization of existing approaches on much larger and more challenging RS captioning datasets needs to be verified. The size of the datasets applied by existing approaches [6], [8]?[11] is limited(with the maximum of 24 333 original captions in RSICD [17] and 23 715 granular captions in RSITMD [9]); 3) Semantic ambiguity of complex scenes of RS data remains unsolved.
To address these limitations, we propose a novel cross-modal network for bidirectional T2I and I2T retrieval in RS. The contribution of our work lies in: 1) We aim to differentiate visual features for complex scene representation through fusing multiple attention mechanisms and reinforce the intra-modality semantic association through fine-grained alignment strategy. 2) We evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of our proposed network on a much larger dataset, NWPU-Captions with 157 500 captions in total, along with the several popular benchmark datasets.
MAFA-Net: The motivation of MAFA-Net includes two aspects.The first one is to depict RS images, especially those complex scenes, with more abstract and discriminative feature representation.The second one is to address semantic ambiguity existed in different modality of RS data through establishing fine-grained relevance between RS image region and visual words.
To this end, MAFA-Net consists of two main parts: a multiattention fusion module and a fine-grained alignment module. The multi-attention fusion module aims to weaken interference from background noise in RS images and enhance the salient objects,thereby to improve the discriminative ability of the visual features.The fine-grained alignment module exploits sentence features as context information to further optimize and update the visual features of RS images. The overall architecture of MAFA-Net is shown in Fig. 1.
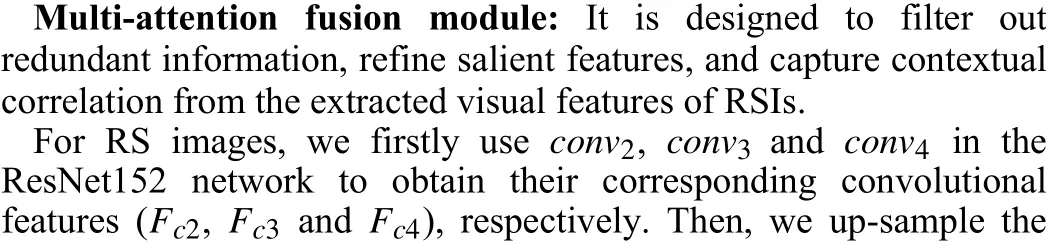
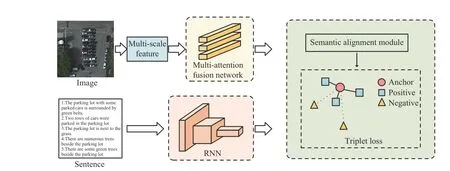
Fig. 1. The overall architecture of MAFA-Net.
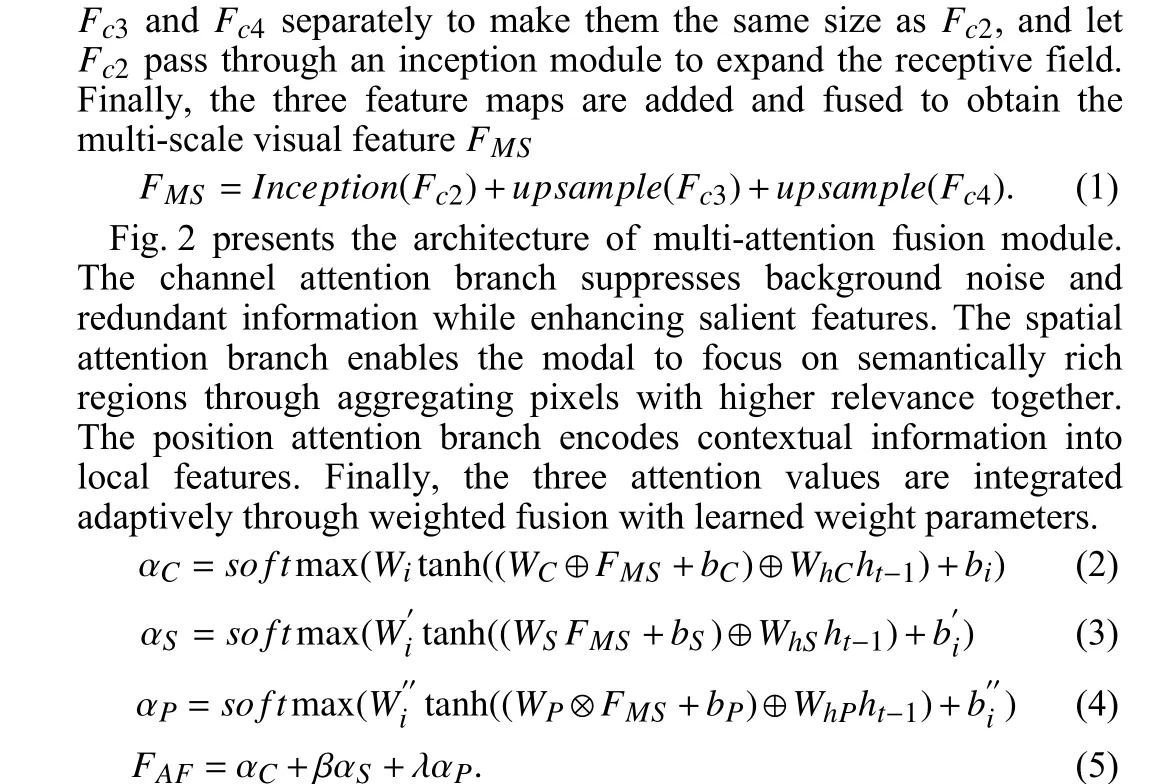
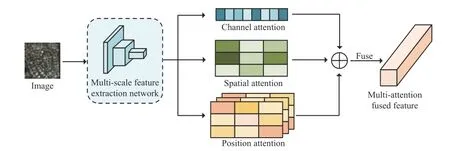
Fig. 2. The architecture of multi-attention fusion module.
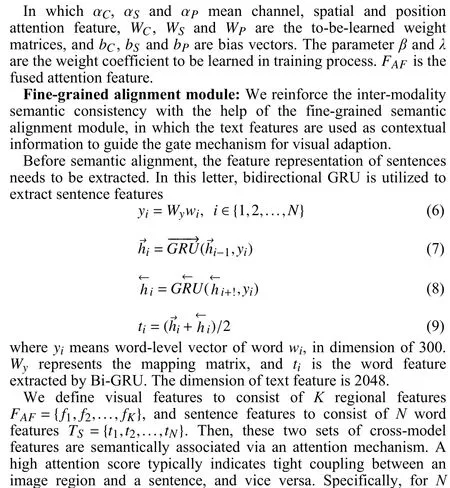

Dataset and metrics: Four RS datasets are selected to evaluate the performance of different approaches in the cross-modal imagesentence retrieval task.
1) UCM-Captions: This dataset is released by [18] based on the UCMerced dataset. The size of each image is 256×256, and the pixel resolution is 0.3048 m. Each image is described with five different sentences and hence contains 10 500 descriptions in total.
2) Sydney-Captions: This dataset is released by [18] based on the Sydney dataset and includes 3065 descriptions for 613 cropped images. The original images in it are with size of 18 000×14 000 and pixel resolution of 0.5 m. Each cropped image is described by five varied sentences.
3) RSICD: There are totally 10 921 RS images and 24 333 original descriptions in this dataset [17], the scale of which is larger than the aforementioned two datasets. Images in it are resized to 224×224 pixels, meanwhile 54 605 sentences are utilized by randomly duplicating existing descriptions.
4) NWPU-Captions: NWPU-Captions is provided by Wuhan University and Huazhong University of Science and Technology based on the NWPU-RESISC45 dataset. It incorporates 45 different labels with each one including 700 instances. Each image is described by five sentences according to certain annotated rules and the total number of descriptions is 157 500. This dataset is challenging due to its large scale and big variations.
We use the criteria R@K (K = 1, 5, 10) to evaluate the performance of different approaches. Larger R@K indicates better performance.
Experimental settings: In the training process, we set the batch size to 16 and the learning rate to 0.0005 which decreases by 0.7 after every 20 epochs. Totally, 120 epochs are conducted. The margin thresholdδin the loss function is set to 0.2. The visual feature of image region is of 2048-dimensional while the word feature is of 300-dimensional. The hidden dimension of Bi-GRU is 2048. During training, word features are initialized randomly and fed to Bi-GRU.
Results and analysis: We conduct experiments on the four benchmark datasets and Tables 1?4 report the experimental results of various methods including representative cross-modal models for natural images like IMRAM [1], SCAN [2], MTFN [3], PFAN [4]and latest models for RS data like FCLM [8], AMFMN [9] and LWMCR [10].
It can be seen from Tables 1?4 that generally MAFA-Net achieves better retrieval performance than other models on four datasets.Although, on the first three datasets, MAFA-Net occasionally slightly underperforms others on some metrics. This might be related to the relatively small amount of data in the UCM-Captions dataset and the Sydney-Captions dataset, and the unbalanced distribution of data categories in the Sydney-Captions dataset itself. However, on the much larger and challenging NWPU-Captions dataset, MAFANet achieves best on all evaluation metrics. The results of MAFANet on four different datasets also demonstrate its robustness.
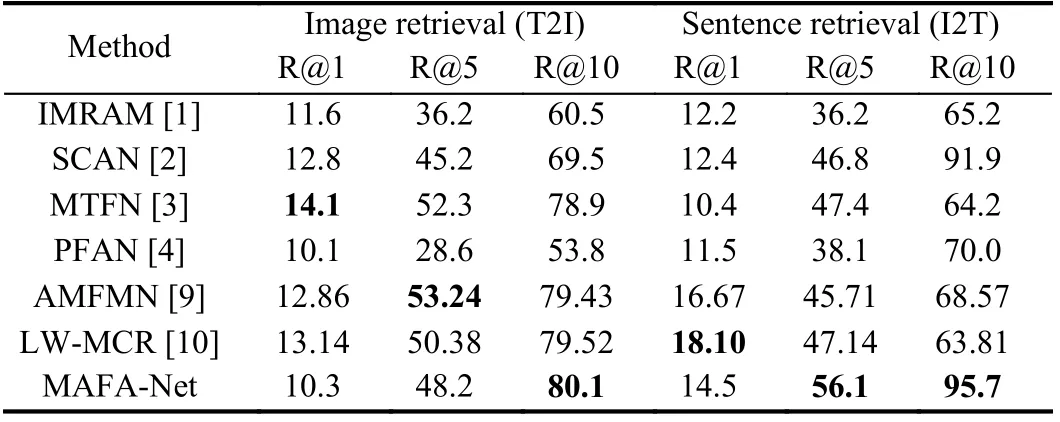
Table 1.Comparative Experimental Results on UCM-Captions
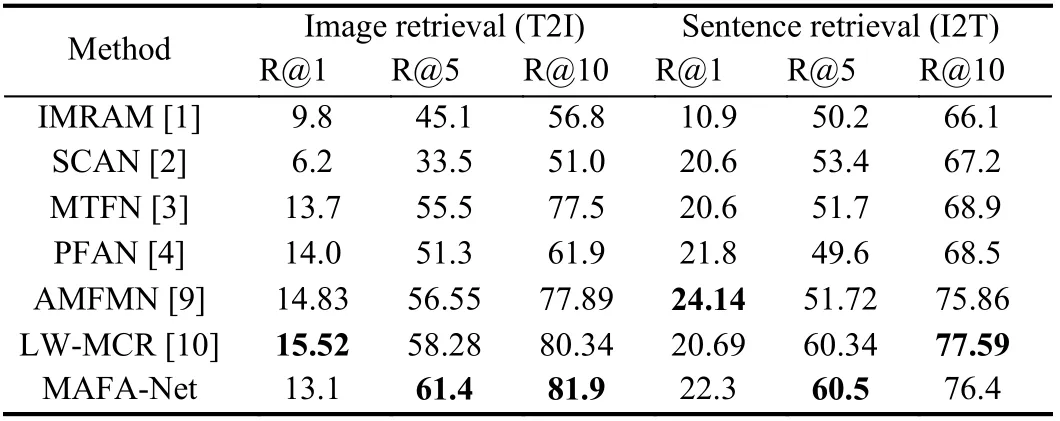
Table 2.Comparative Experimental Results on Sydney-Captions
We also conduct ablation experiments to evaluate the contribution of multi-attention fusion module (MA) and fine-grained alignment module (FA) to MAFA-Net. Table 5 reports the results on NWPUCaptions, in which _nMA_nFA means the basic network without the two modules, _nMA means the network without MA module and_nFA means the network without FA module. It can be seen that the two modules can significantly improve the retrieval performance of the MAFA-Net separately, while their contributions are relatively close. Table 5 also tabulates the training and testing time for executing different models on NWPU-Captions.
We further show the visualization results of our MAFA-Net in Figs. 3?6.
It can be seen that most of the retrieval results match the input,which indicates that the MAFA-Net proposed in this letter can maintain a good semantic correspondence between RS images and sentences. It is worth mentioning that even for the challenging highdensity scenes with a great of small and clustered objects, MAFANet still performs well (see Fig. 6).
Conclusion: In this letter, we propose a multi-attention fusion and fine-grained alignment network (MAFA-Net) to conduct the crossmodal image-sentence retrieval task in the remote sensing domain.MAFA-Net aims at addressing the properties of multiscale properties and the problem of semantic ambiguity existed in cross-modalretrieval of RS data. Specifically, we design a multi-attention fusion module to improve the feature representation ability. Meanwhile, a fine-grained alignment module is designed to make the information between two different modalities (e.g., visual and textural) interact.Besides the three public available benchmark datasets, a much larger captioning dataset, NWPU-Captions, is utilized to evaluate the performance of MAFA-Net. Experimental results prove that MAFANet outperforms current approaches and even for challenging highdensity scenes, MAFA-Net can get satisfying results. In the future,we would like to consider more modalities like LiDAR or multispectral images and domain adaption [19] for RS visual applications.
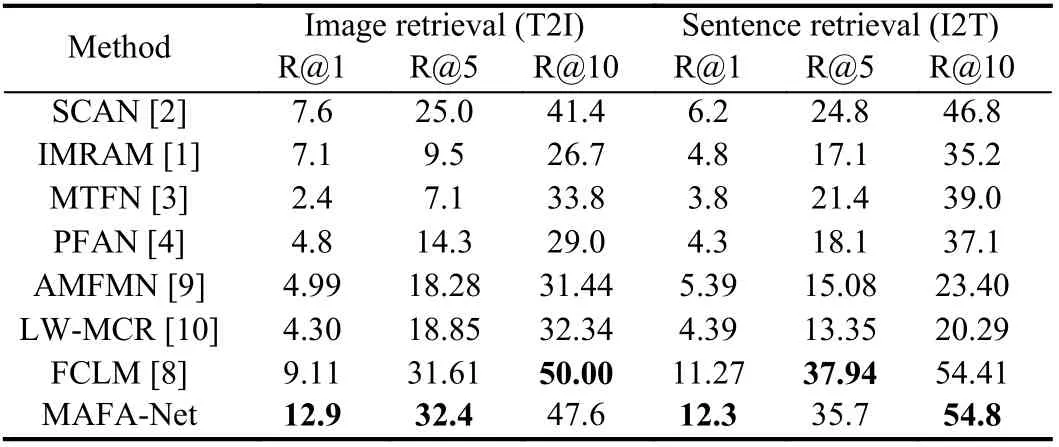
Table 3.Comparative Experimental Results on RSICD
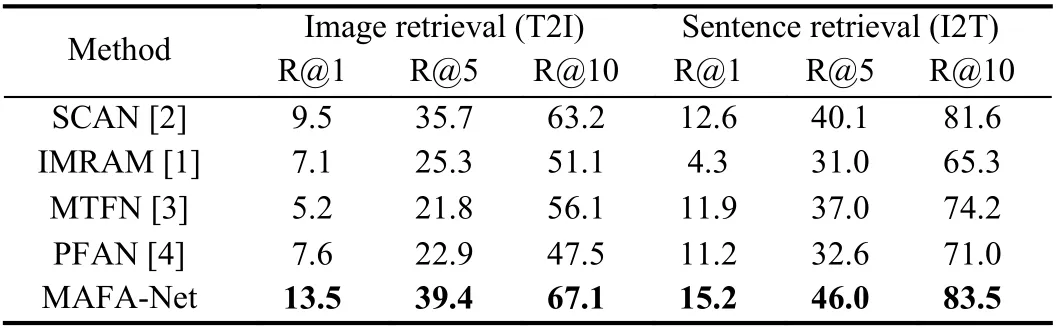
Table 4.Comparative Experimental Results on NWPU-Captions
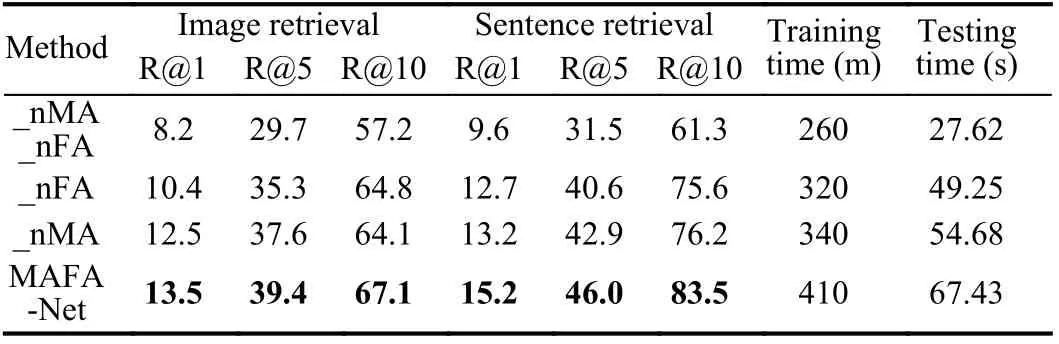
Table 5.Ablation Experimental Results on NWPU-Captions
Acknowledgments: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42090012), Special Research and 5G Project of Jiangxi Province in China (20212ABC03A09),Guangdong-Macao Joint Innovation Project (2021A0505080008),Key R & D Project of Sichuan Science and Technology Plan(2022YFN0031), and Zhuhai Industry University Research Cooperation Project of China (ZH22017001210098PWC).

Fig. 3. Visualization results of MAFA-Net on UCM-Captions.

Fig. 4. Visualization results of MAFA-Net on Sydney-Captions.

Fig. 5. Visualization results of MAFA-Net on RSICD.

Fig. 6. Visualization results of MAFA-Net on NWPU-Captions.
 IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica
2022年8期
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica
2022年8期
- IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Complex-Valued Neural Networks:A Comprehensive Survey
- Visuals to Text: A Comprehensive Review on Automatic Image Captioning
- Cyberbullying and Cyberviolence Detection: A Triangular User-Activity-Content View
- Networked Knowledge and Complex Networks: An Engineering View
- Battery Full Life Cycle Management and Health Prognosis Based on Cloud Service and Broad Learning
- Estimation Based Adaptive Constraint Control for a Class of Coupled String Systems
