Effect of oral premedication of midazolam, ketamine, and dexmedetomidine on pediatric sedation and ease of parental separation in anesthesia induction for elective surgery: A randomized clinical trial
Aref Zarei, Hesameddin Modir, Behnam Mahmoodiyeh, Alireza Kamali, Farzad Zamani-Barsari
1Student Research Committee, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
2Anesthesiology Department, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
3Department of ENT Surgery, Arak University of Medical Sciences, Arak, Iran
ABSTRACT Objective: To compare effect of midazolam, dexmedetomidine, and ketamine as oral premedication on pediatric sedation and ease of parental separation anxiety in anesthesia induction.Methods: This multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, clinical trial focused on a pediatric population aged 2-7 years (n=153) with the American Society of Anesthesiologists I-Ⅱ who required elective surgery. The patients were stratified into three intervention groups: midazolam, ketamine, and dexmedetomidine. Hemodynamic parameters (blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation) every 5 min until induction of anesthesia along with non-hemodynamic factors, comprised of sedation score before the administration and at the time of being separated from the parents, as well as parental separation anxiety scale, acceptance of anesthesia induction, and side effects were recorded and compared. Results: No statistically significant difference in oxygen saturation, heart rate, blood pressure, duration of surgery, time to achieve an Aldrete score of 9-10, or sedation score was noted in the study groups. More patients in the dexmedetomidine and midazolam groups could better ease parental separation anxiety than the ketamine group (P=0.001). Moreover, fewer patients accept anesthesia induction (P=0.001) and more had side effects in the ketamine group (P=0.047).Conclusions: Our findings indicate that compared to the ketamine group, dexmedetomidine and midazolam are better in easing parental separation anxiety and accepting induction of anesthesia with fewer side effects. Dexmedetomidine and midazolam may be considered better choices. However, the final choice hinges on the patient's specific physical condition and the anesthesiologist's preference.
KEYWORDS: Dexmedetomidine; Ketamine; Midazolam; Premedication; Sedation
1. Introduction
Many pediatric patients fear anesthesia rather than surgery. Indeed, it is thought that children per se could not distinguish loss of consciousness from death[1]. People undergoing surgery usually are stressed during the preoperative period, in particular children, among whom roughly sixty percent experience preoperative anxiety[2-4]. Preoperative anxiety has been described as an unpleasant state of anxiety or stress due to concerns about illness, hospitalization, anesthesia, surgery, or other unknown[5,6]. Many pediatric patients are extremely uncooperative, fearful, anxious, and physically resistant when being separated from their parents, performing a venipuncture procedure, or using an anesthesia mask[7,8]. Failure to address the anxiety can lead to difficult anesthesia induction, more postoperative pain, higher analgesic requirement, agitation, and even postoperative psychological effects and behavioral difficulties[7,8].
Despite numerous huge advances in non-pharmacological interventions, physicians continue to rely on sedatives. Sedative premedication aims to relieve preoperative anxiety of pediatric patients, ease parental separation anxiety, minimize emotional trauma, help to accept masks, and facilitate anesthesia induction[2-4]. Midazolam, a water-soluble benzodiazepine, is known to be the most popular sedative premedication in children and has numerous benefits, such as a rapid onset of action, effective relief, anterograde amnesia, anxiety relief, and reduced postoperative vomiting[9]. However, potential unwanted and adverse effects including agitation, hiccups, and paradoxical hyperactive reactions to benzodiazepines render it less than an ideal sedative drug[9,10]. Midazolam is reported to be preferred over long-acting drugs such as diazepam and lorazepam[11]. As a highly selective and potent α-2 adrenoceptor agonist, dexmedetomidine possesses both sedative and analgesic effects[2,4,12].
Unlike conventional GABAergic sedatives like midazolam which affect the cerebral cortex, the site of action of dexmedetomidine is primarily in the locus coeruleus[13]. Thus, it is characterized by easy and quick arousal from sedation resembling natural sleep. Numerous trials describe acceptable efficacy of pediatric sedation with dexmedetomidine, demonstrating a similar effect to that with midazolam[2,4,12,14].
Ketamine is a water-soluble phencyclidine derivative formulated as a slightly acid (pH 3.5-5.5) solution, and mostly metabolized by hepatic microsomal enzymes. Norketamine, a metabolite of ketamine, is speculated to have 20%-30% of the potency of ketamine[15]. Following oral administration, ketamine has good sedative properties and appears to be a suitable and safe alternative to midazolam, and a dose of ketamine, ranging from 3 to 6 mg/kg has been reported to offer a high success rate with no significant complications. However, therapeutic use of intravenous ketamine, even at sub-anesthetic doses, could result in hallucinations and psychological disturbances[16,17]. As evidenced by the literature, ketamine has been proven to be a safe and effective choice for sedation in children, easing parental separation anxiety, and was associated with better mask acceptance[16,17].
This trial aims to compare midazolam, dexmedetomidine, and ketamine as oral premedication to find the drug with the best sedative effects and minimal adverse effects.
2. Patients and methods
2.1. Study setting
This study is a randomized double-blind clinical trial and enrolled 153 patients (aged 2 to 7 years) undergoing elective surgery admitted to the affiliated hospitals of Arak University of Medical Sciences from August 2021 to March 2022.
2.2. Ethical statement and trial registration
All patients obtained written informed parental or legal guardian consent. The study protocol was approved by the ethical committee of Arak University of Medical Sciences with code IR.ARAKMU.REC.1400.155 and is registered in the Iranian Registry Clinical Trial center with the clinical trial code of IRCT20211007052693N1.
2.3. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
This study included patients aged 2 to 7 years, of both genders, weight between 10 to 30 kg, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) physical status I or Ⅱ, undergoing elective surgery (not including fractures), no fractures, no history of allergies, no hepatic/renal/cardiopulmonary disorder, no long-term use of anticonvulsant drugs, absence of sleep disorders, no speech or communication issues, no gastrointestinal disorders (because intervention drugs are administered orally), and finally duration of surgery less than 120 min. Moreover, exclusion criteria included the unwillingness of children's parents or guardians to continue the study, and any unpredictable complications around the site of surgery that affect the variables being evaluated.
2.4. Grouping
The study was double-blind. Patients were not aware of the type of drug given. Besides, the intern who was responsible for filling up the questionnaires and registering the data was unaware of the patient grouping and the type of oral solution and only completed the questionnaires according to the numbers assigned by the anesthesiologist leading the study. Therefore, patients were randomized using block randomization. The subjects were randomly divided into three groups (Figure 1) using blocks of 6 that were generated using a random number table. Groups were labeled in a de-identified fashion (A, B, C) and concealed by using similar color, consistency, volume, and packaging.
2.5. Intervention
All subjects who received breast milk as the last preoperative feed had nothing by mouth (NPO) for 4 h, and who were given any milk other than breast milk or liquid foods (like Cerelac and porridge) had a 6-hour course of NPO, while NPO status was imposed 8 hours before the procedure on the children who consumed solid foods. None of the children received sedatives before entering the operating room and the participants were assigned into 3 groups using the block randomization method. All of the patients were cared for and monitored physiologically 30 min before anesthesia, while vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation were measured.
The first group received 0.5 mg/kg midazolam (midazolam ampule, Caspian Tamin Pharmaceutical Company, Rasht, Iran)[18], the second group was given 5 mg/kg ketamine (Rotexmedica, Germany)[19], and the third group with 4 μg/kg of oral dexmedetomidine (Iran Eksir, Tehran, Iran)[20]. The medicine was given in a syringe and sublingually by an intern who was not aware of the type of drug administered and was swallowed after a short space of time. The dose of intervention drug for each group was calculated based on the weight of the child and then one mL of 20% dextrose solution was added to the intervention drug calculated for each patient to standardize the intervention and to provide an acceptable taste, and finally, for group matching, the volume of the intervention drug with distilled water was increased to 5 mL.
2.6. Measurements
Vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation) were recorded every 5 min until induction of anesthesia. Then, the sedation score before the administration and then at the time of being separated and parental separation anxiety scale was recorded. Scores of 1 and 2 were considered unsatisfactory, while scores of 3 to 5 were considered satisfactory[21]. All children were transferred to the operation room and then inhaled induction with sevoflurane at a concentration of 4%-8% using mask ventilation[18].
The acceptance of anesthesia induction was scored based on the following criteria: 1, poor; 2, moderate or somewhat difficult; and 3, good acceptance[21]. Following an inhalation induction, medication was administered intravenously to maintain anesthesia during surgery. Surgery under general anesthesia was performed by endotracheal intubation and the drugs administered for general anesthesia were the same for all groups. Vital signs were noted every 15 min throughout the surgery.
Subjects were shifted to the recovery room after extubation where the mentioned signs were measured until they are completely awake. Patients could only be transferred to the ward when they obtained a score of 9 or higher on the recovery score (Aldert Score of Modification)[18], and the time required to obtain this score was recorded. In the postoperative period, patients were monitored and followed up for 24 h for possible complications. Furthermore, side effects such as nausea, vomiting, hypotension (a decrease in arterial pressure greater than 20% from baseline), and bradycardia (heart beats fewer than 70 times a minute) were also noted, and remedial action was taken if required.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Sample size calculation was conducted based on the results of our recent study[22] considering a study power of 80% and confidence interval of 95%. Normally distributed measurement data were expressed as mean±SD, and categorical data were described as frequency and percentage. The data were analyzed using a chi-square test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures, whereas the software used in the analysis was IBM?SPSS?version 20 (IBM Corp., Armonk, USA), with a significance level of 5%.
3. Results
Of all 168 eligible patients, 15 patients were excluded and 153 patients were assigned to groups as shown in Figure 1. The mean age of patients was (5.07±1.06) years and the mean weight was (21.55±3.21) kg. A total of 77 (50.3%) were boys and 76 (49.7%) were girls (Table 1). Three study groups were similar regarding age, sex, and weight, and had no statistically significant difference in mean blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, time to achieve an Aldrete score of 9 or 10, or duration of surgery (P>0.05) (Table 1, Fgure 2-4).
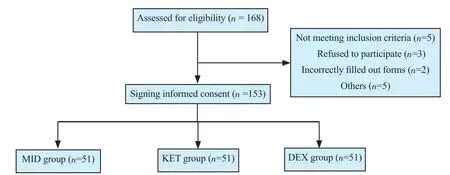
Figure 1. The study flowchart. MID: midazolam; KET: ketamine; DEX: dexmedetomidine.
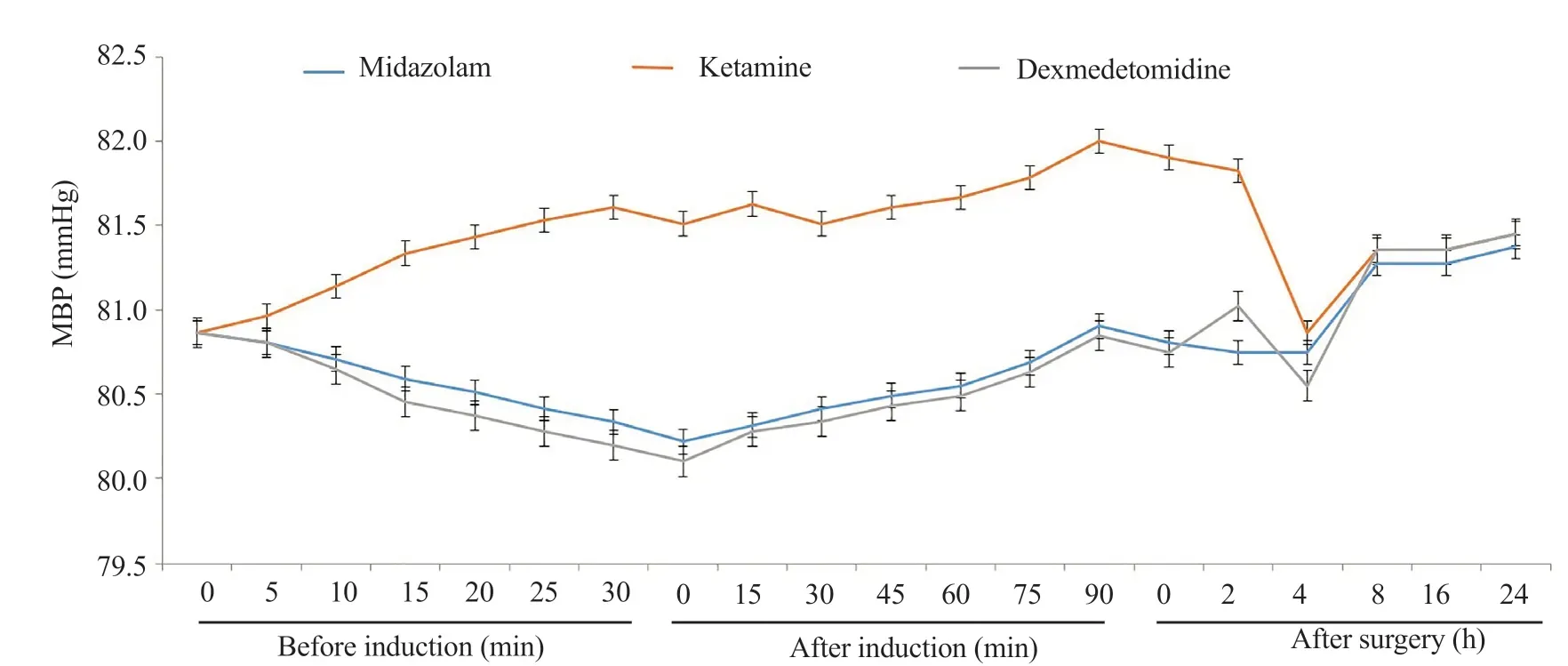
Figure 2. Mean blood pressure (MBP) in the studied objectives.
Figure 3. Mean oxygen saturation (SpO2) in the studied objectives.
Figure 4. Mean heart rate (HR) in the studied objectives.
The study reported no statistically significant intergroup difference in sedation score (Table 2) before and after intervention administration (P>0.05).
The results in Table 3 demonstrate a statistically significant difference in the parental separation anxiety scale (P=0.001), more patients in the dexmedetomidine and midazolam groups had relief separation anxiety and better acceptance of anesthesia induction (P=0.001) than those in the ketamine group.
Besides, more patients in the ketamine group had side effects (P=0.047), and the most common side effects were nausea and dizziness (Table 4).
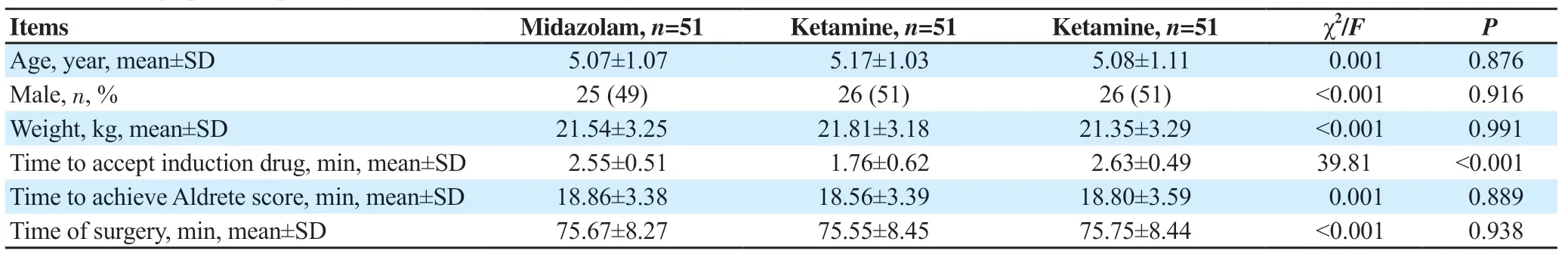
Table 1. Demographic and primary outcomes in the studied objectives.
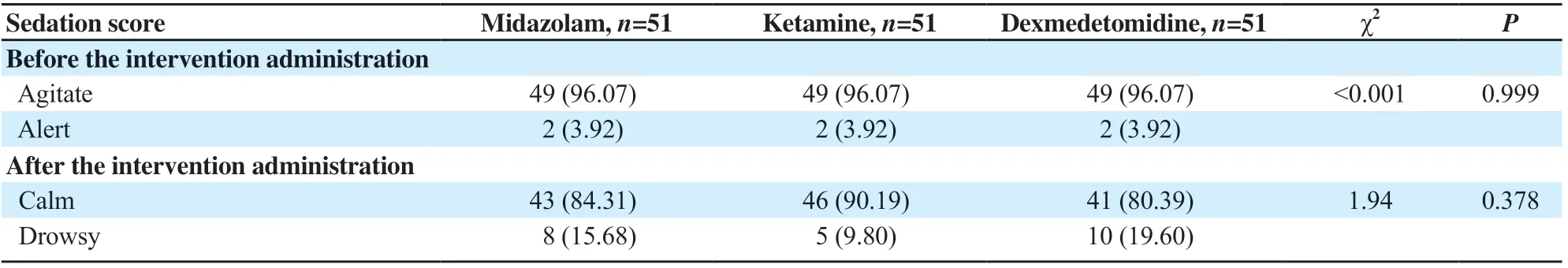
Table 2. Sedation score in the studied objectives (n, %).
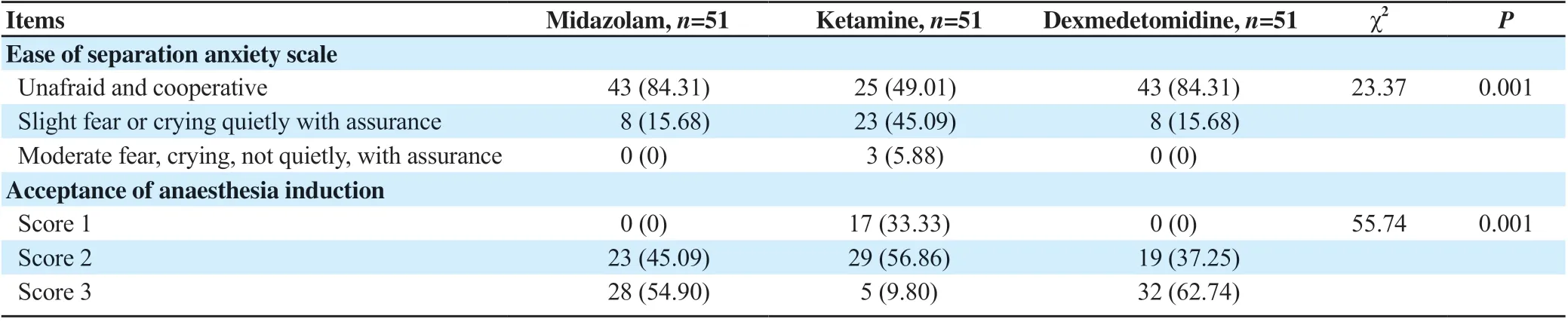
Table 3. Ease of separation anxiety scale and acceptance of anaesthesia induction in the studied objectives (n, %).

Table 4. Side effects in the studied objectives (n, %).
4. Discussion
Based on our results, no statistically significant difference was found in oxygen saturation, heart rate, blood pressure, duration of surgery, Aldrete score, or sedation score. Ease of parental separation anxiety was more satisfactory in the dexmedetomidine and midazolam groups than in the ketamine group. Acceptance of anesthesia induction differed statistically significantly among the three groups and more patients refused in the ketamine group. Besides, more patients in the ketamine group had side effects, and the most common side effects were nausea and dizziness. Overall, dexmedetomidine and midazolam can improve the conditions for parental separation anxiety and acceptance of induction of anesthesia, while no side effect was observed in both.
Yazdi et al. concluded that dexmedetomidine was more effective in accepting induction of anesthesia, while the midazolam and dexmedetomidine groups showed better ease of separation anxiety and sedation scores than the melatonin group[23], whose findings were similar to ours. A comparison of oral dexmedetomidine and oral midazolam as premedication in children proved that oral dexmedetomidine premedication is as effective as oral midazolam premedication in providing sedation and anxiolysis in pediatric patients and reduces the incidence and severity of emergence agitation[24].
Kumari et al. compared oral clonidine, dexmedetomidine, and midazolam for premedication in pediatric patients undergoing elective surgery and concluded that oral midazolam is associated with a faster onset of sedation, higher sedation score, lower anxiety score, and a greater number of children with easy separation anxiety and excellent mask acceptance, compared to the oral clonidine and dexmedetomidine[20]. Jannu et al. compared oral midazolam and dexmedetomidine as premedication in pediatric anesthesia and found that pretreatment with oral administration of dexmedetomidine provided an equally effective preoperative sedation and a better quality of anesthesia in children[25].
Oyedepo et al. assessed the efficacy of oral ketamine premedication in children and suggested that oral ketamine is an acceptable and safe premedication for pediatric patients, whereas treatment with oral ketamine at the studied doses provided effective sedation and relieved anxiety, without any side effects[19]. However, our trial showed that ketamine was less effective.
A meta-analysis of the efficacy of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam as premedication in 2014 by Sun et al. observed that compared with midazolam, dexmedetomidine premedication provided better satisfactory effects on parent separation anxiety and mask acceptance, and has clinical benefits, including reducing the need for analgesic administration, reducing agitation or delirium, and shivering during the postoperative period[10]. Similar to our study, another meta-analysis evaluated the efficacy of dexmedetomidine versus midazolam as pre-anesthetic medication in improving preoperative sedation and analgesia and in decreasing postoperative agitation and showed that the first was more effective in alleviating anxiety during parental separation and postoperative agitation, and providing more effective postoperative analgesia[3].
In line with our study in terms of the effect of midazolam, Deshmukh et al. compared oral midazolam syrup and intranasal midazolam spray as painless, needle-free methods of preanesthetic sedation in pediatric patients and suggested that both produce similar sedation and anxiolysis, but oral midazolam had better acceptance of drug and response to drug administration[21]. A review showed that dexmedetomidine is comparatively better than midazolam because it enhances preoperative sedation and relieves postoperative pain, while, as they stated in their paper, more studies are needed to assess dosing and long-term consequences[4,26].
Our study reveals that dexmedetomidine and midazolam, rather than ketamine, are recommended as the first and second choices with better ease of parental separation and acceptance of anesthesia induction without any side effects, though the final choice depends upon the patient physical status and the anesthesiologist's preference.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study received no extramural funding.
Acknowledgments
Hereby, we would like to extend a special debt of gratitude to the Valiasr Hospital’s clinical research council for its assistance and guidance and to thank the research deputy of Arak University of Medical Sciences for his contributions and support throughout the development of this study.
Authors’ contributions
A.Z.: contributions to the conception or design of the interpretation of data for the work and final approval of the article; H.M.: contributions to the conception or design of the interpretation of data for the work and final approval of the article; B.M.: contributions to the conception or design of the work and final approval of the articles; A.K.: contributions the acquisition and analysis of data for the work and drafting the article; F.Z.: contributions the acquisition and analysis of data for the work and drafting the article.
 Journal of Acute Disease2022年4期
Journal of Acute Disease2022年4期
- Journal of Acute Disease的其它文章
- Challenges of COVID-19 prevention and control: A narrative review
- Delayed post-hypoxic leukoencephalopathy following barbiturate overdose: A case report
- Severe progression of autoimmune hepatitis in a young COVID-19 adult patient: A case report
- Associated risk factors for post-COVID-19 mucormycosis at a tertiary care centre: A cross-sectional study
- Hematological indices as predictors of mortality in dengue shock syndrome: A retrospective study
- Different routine laboratory tests in assessment of COVID-19: A casecontrol study
