章丘區2022年食源性疾病監測分析
于燊 劉毅 李士超
摘 要:對2022年山東省濟南市章丘區23所哨點醫院食源性疾病病例信息進行采集、匯總,通過對時間、人群、空間流行病學三間分布以及引起病例發病的可疑食品類型的分析,了解重要食源性疾病的發病及流行趨勢,及時發現食源性疾病聚集性病例和暴發線索,提高食源性疾病暴發和食品安全隱患的早期識別、預警和防控能力。結果表明,病例多發期為6月(516例)、7月(549例)、8月(357例),共報告1 422例,占報告病例總數的47.89%(1 422/2 969);各年齡段發病主要集中在青年(19~35歲)、中年(36~59歲)和老年(≥60歲),發病病例占比分別為27.25%(809/2 969)、31.19%(926/2 969)和22.84%(678/2 969)。說明食源性疾病在章丘區廣泛存在,夏季是食源性疾病多發季節,中年病例較多。相關部門要根據發病特點、流行趨勢及時進行防控,加強學校集體配餐各流通環節管理。
關鍵詞:食源性疾病;監測分析;章丘區
Surveillance and Analysis of Foodborne Diseases in Zhangqiu District in 2022
YU Shen, LIU Yi, LI Shichao
(Zhangqiu District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jinan City, Jinan 250299, China)
Abstract: Collect and summarize information on foodborne disease cases from 23 sentinel hospitals in Zhangqiu district, Jinan city, Shandong province in 2022. By analyzing the distribution of time, population, and spatial epidemiology, as well as the suspicious food types that cause the onset of cases, understand the incidence and epidemic trends of important foodborne diseases, timely detect clustered cases and outbreak clues of foodborne diseases, and improve the early identification of foodborne disease outbreaks and food safety hazards early warning and prevention and control capabilities. The results showed that the frequent periods of cases were June (516 cases), July (549 cases), and August (357 cases), with a total of 1 422 cases reported, accounting for 47.89% of the total reported cases (1 422/2 969); the incidence of various age groups is mainly concentrated in young people (19~35 years old), middle-aged people (36~59 years old), and elderly people (≥60 years old), with a proportion of 27.25% (809/2 969), 31.19% (926/2 969), and 22.84% (678/2 969), respectively. It shows that foodborne diseases are widespread in Zhangqiu district. Summer is the season of frequent occurrence of foodborne diseases, with more middle-aged cases. Relevant departments should timely carry out prevention and control based on the characteristics and trends of the disease, and strengthen the management of various circulation links in school collective catering.
Keywords: food-borne diseases; surveillance and analysis; Zhangqiu district
對2022年山東省濟南市章丘區23所哨點醫院食源性疾病病例信息進行采集、匯總,通過對對流行病學在時間、人群、空間上的發布以及引起病例發病的可疑食品類型的分析,了解重要食源性疾病的發病及流行趨勢,及時發現食源性疾病聚集性病例和暴發線索,提高食源性疾病暴發和食品安全隱患的早期識別、預警和防控能力[1-2]。
1 材料與方法
1.1 資料來源
2022年章丘區23家食源性疾病哨點醫院上報的所有病例。
1.2 方法
所有食源性疾病病例的上報、審核均按照《濟南市衛生健康委員會關于印發2022年濟南市食品安全風險監測方案的通知》(濟衛監督食安發〔2022〕2號)相關要求進行[3-6]。
2 結果與分析
2.1 食源性疾病監測病例構成
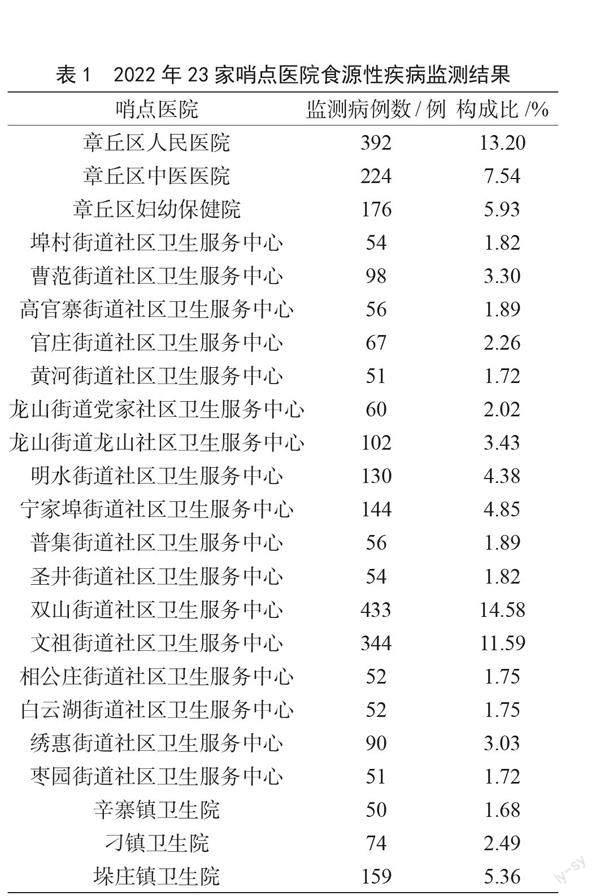
2022年,章丘區23家食源性疾病監測哨點醫院共報告監測病例2 969例,無異常病例報告,詳見表1。
2.2 食源性疾病監測病例報告時間分布
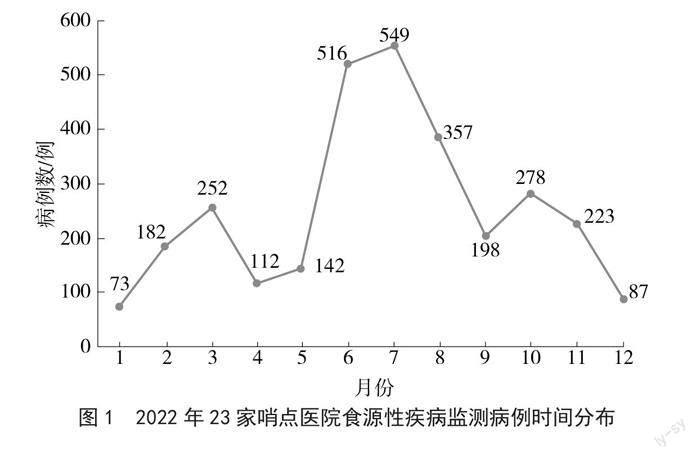
2022年1—12月各月份均有食源性疾病監測病例報告,病例報告數分別為73例、182例、252例、112例、142例、516例、549例、357例、198例、278例、223例和87例。病例報告時間主要集中在6—8月,共報告1 422例,占報告病例總數的47.89%。2022年食源性疾病病例發病時間分布見圖1。
2.3 食源性疾病監測病例年齡分布
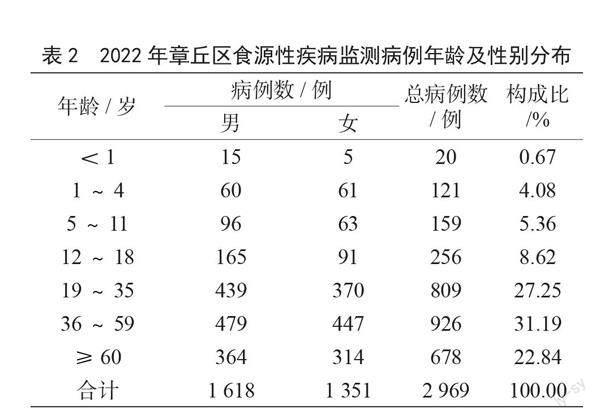
章丘區食源性疾病監測病例年齡及性別分布見表2。不同年齡病例占比分別為嬰兒(<1歲)0.67%
(20/2 969)、幼兒(1~4歲)4.08%(121/2 969)、兒童(5~11歲)5.36%(159/2 969)、少年(12~18歲)8.62%(256/2 969)、青年(19~35歲)27.25%(809/2 969)、中年(36~59歲)31.19%(926/2 969)、老年(≥60歲)22.84%(678/2 969),病例主要集中在中年(36~59歲)年齡段。其中男性病例占比54.50%(1 618/2 969)、女性病例占比45.50%(1 351/2 969),男性病例多于女性。
2.4 食源性疾病監測病例職業分布
2022年章丘區食源性疾病監測病例職業分布情況見表3。病例職業分布集中在農民、學生、工人,分別占報告病例總數的58.75%(1 743/2 969)、17.69%(525/2 969)、6.57%(195/2 969)。
2.5 食源性疾病監測病例地域分布
病例地域分布顯示,雙山、文祖、明水街道社區的病例分布較多,分別占報告病例總數的23.71%(704/2 969)、12.19%(362/2 969)、10.95%(325/2 969)。具體病例地域分布見圖2。
3 結論
對2022年章丘區23所哨點醫院食源性疾病病例報告情況進行收集、匯總發現,食源性疾病在章丘區廣泛存在,病例多發期為6—8月;中年發病比例較高。結合實際情況,提出以下建議。①不食用來歷不明的食品,不購買無廠名、廠址和保質期等標識不全的食品。②不光顧無證無照的流動攤檔和衛生條件不佳的飲食店;不隨意購買、食用街頭小攤販出售的劣質食品、飲料,這些劣質食品、飲料往往衛生質量不合格,食用后會危害身體健康。③直接食用的瓜果應用潔凈的水徹底清洗并盡可能去皮。④不吃腐爛變質的食物,容易造成食物中毒。⑤在進食的過程中如發現感官性狀異常,應立即停止
進食。
參考文獻
[1]李慶梅.冕寧縣食源性疾病監測分析[J].中國保健營養,2017,27(5):81-82.
[2]趙云清,殷鋒科.2013-2019年開封市鼓樓區食源性疾病監測分析[J].河南預防醫學雜志,2020,31(8):643-645.
[3]陳錦鐘,洪舒萍,蔡茂榮,等.漳州市2016—2020年食源性疾病監測分析[J].江蘇預防醫學,2022,33(3):
332-333.
[4]陳安明,楊軍鵬,李梅基.2013年白銀市食源性疾病監測分析[J].甘肅科技,2015,31(2):124-125.
[5]張靜,張秉慧.南寧市2002-2014年食源性疾病監測分析[J].實用預防醫學,2017,24(4):486-488.
[6]孫曄,韓彥明,馬蓮春.2016年昌吉市食源性疾病監測分析研究[J].中國保健營養,2017,27(6):278.

