Omadacycline for the treatment of Legionella pneumophila pneumonia caused by drowning: a case report
Xiao Lu, Wenqi Qi, Haizhen Wang, Zhongjun Zheng, Libing Jiang, Shanxiang Xu
Department of Emergency Medicine, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310009, China
Drowning is a major cause of preventable death and pathology worldwide.Every year, more than 295,000 people die from accidental drowning.Ninety percent of accidental drowning deaths occur in low- and middleincome countries, and nearly half occur in people under the age of 25.[1,2]Drowning mechanisms include inhaling water into the lungs with subsequent damage to lung surfactants.It destroys alveolar capillary membranes,leading to alveolar edema, and resulting in local acute respiratory distress syndrome.The majority of drowning patients display low oxygen levels or hypoxia,and their PaO2/FiO2ratio is typically <300 mmHg (1 mmHg=0.133 kPa).[3]The treatment of lung injury and associated torsional hypoxia forms the basis for the current standards of care for drowning.
Legionellais an environmental organism found in various water bodies (e.g., lakes, streams, and artificial reservoirs).[4]Fulminant pneumonia or mild Pontiac fever pneumonia can be caused byLegionella pneumophila(L.pneumophila)and other Legionella bacteria in community-acquired or hospital-acquired infections.Such infections often lead to high hospitalization rate and mortality rate, especially in immunodeficient patients.When Legionella pneumonia causes severe acute respiratory failure, the use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) should be considered.[5]Omadacycline is a new aminomethylcycline antibiotic that overcomes the efflux and ribosomal protection mechanisms of tetracycline resistance.[6]Omadacycline can be used to treat community-acquired bacterial pneumonia, includingL.pneumophilapneumonia.
This case report focuses on a patient withL.pneumophilapneumonia caused by drowning who was treated with veno-venous ECMO (V-V ECMO) and omadacycline as the antibiotic treatment.
CASE
The patient, a 46-year-old male, was admitted to the hospital on January 21, 2022, with “7 h of dyspnea due to drowning.” The patient had fallen into the chemical material sewage of a printing factory 7 h ago, while the specific composition of the sewage was unknown.The patient remained in the sewage for approximately 10 min prior to rescue.No obvious nausea, vomiting, chills,or fever was noted.He was sent to the local hospital for treatment.An initial blood gas showed an oxygen partial pressure of 70 mmHg (1 mmHg=0.133 kPa).The patient was intubated and subjected to mechanical ventilation.However, the patient’s SpO2did not improve,and the oxygenation index remained less than 100 mmHg.The patient was then transferred to our center for further treatment.On arrival, the patient’s blood pressure was 116/78 mmHg, peripheral SpO2was 93%(FiO2of the mechanical ventilation 100%; positive endexpiratory pressure 8 cmH2O, 1 cmH2O=0.098 kPa),and oxygenation index was 97 mmHg.Chest computed tomography (CT) imaging showed multiple subpleural infectious lesions in both lungs and a small amount of pleural effusion on both sides (Figure 1A).
The patient was given a sedative, muscle relaxant,and other treatments for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.However, no improvement in the oxygenation index was noted.V-V ECMO treatment (Xenios Console,Fresenius Medical Care, Germany) was initiated in the resuscitation room via the placement of catheters to the right femoral and right jugular veins by the emergency ECMO team.The patient was admitted to the emergency intensive care unit subsequently.Physical examination revealed the following: heart rate 80 beats/min, respiratory rate 12 breaths/min, blood pressure 130/81 mmHg (maintained with norepinephrine, 0.06 μg/[kg·h]), and temperature 36.3 °C.The patient was under sedation and analgesia with a Richmond Agitation-Sedation Scale of -2 points.The ventilator mode was set at volume control, the tidal volume was 250 mL, the FiO2was 35%, the respiratory rate was 8 breaths/min, and the positive end-expiratory pressure was 8 cmH2O.The patient was negative for β-(1,3)-glucan, galactomannan,and influenza A and B.The patient was treated with V-V ECMO at a flow rate of 2.9 L/min, a rotation speed of 7,200 r/min, and an airflow rate of 5 L/min.Moxifloxacin(single intravenous infusion of 0.4 g/d), cefoperazone sulbactam sodium (single intravenous infusion of 2.0 g every 8 h), and voriconazole (first dose of 400 mg given intravenously) were administered.Analysis of a sample of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) using metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS)showed onlyL.pneumophilaandBurkholderiainfection(BALF reads 117 and 2,217).The antibiotic therapy was adjusted to moxifloxacin, cefoperazone sodium,and sulbactam sodium.A laboratory examination showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 3.8×109/L, neutrophil rate of 92.7%, aspartate transaminase level of 137.0 U/L, interleukin-6 level of 1,797 pg/mL, C-reactive protein level of 125 mg/L, and procalcitonin level of >5.1 ng/mL.After a 3-day course of antibiotics, the patient’s heart rate decreased to 35–50 beats/min.An electrocardiogram showed a prolonged QT interval, and the levels of potassium and magnesium in the blood were normal (K+3.9 mmol/L;Mg2+0.92 mmol/L).Moxifloxacin was discontinued out of an abundance of caution.Antibiotic therapy was modified to macycline tosylate (single intravenous infusion of 0.1 g daily), cefoperazone sodium, and sulbactam sodium.This was followed by stabilization of the patient’s heart rate and normalization of the electrocardiogram.Figure 2 summarizes the antibiotic therapy.A chest CT scan (Figure 1B) showed significant improvement, and a sputum smear was negative for bacteria or fungi.Likewise, sputum and blood cultures were negative.Legionella antibodies were not detected.A second BALF mNGS showedBurkholderiainfection, and omacycline tosylate was replaced with cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium.The patient was weaned from ECMO and mechanical ventilation.On a high-flow nasal cannula, the oxygenation index was maintained at >300 mmHg.The patient was discharged shortly after with no complaints of discomfort.A chest CT scan at the time of discharge is shown in Figure 1C.
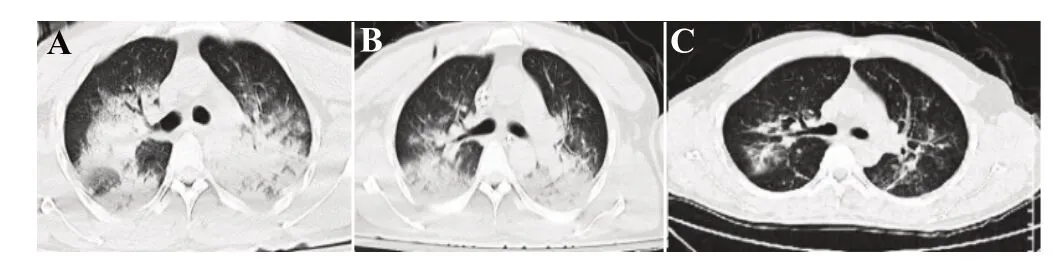
Figure 1.Images of chest CT scans acquired overtime showing changes associated with therapeutic interventions.A: on arrival, chest CT showed multiple subpleural infectious lesions in both lungs and a small amount of pleural effusion on both sides; B: after treatment,significant improvement was revealed; C: chest CT scans at discharge.
DISCUSSION
A review of the literature suggests that 39.8% of drowning victims developed presumed pneumonia.[7]Interestingly, freshwater drowning reported higher rates of multidrug-resistant microorganisms in lung fluid samples from subjects than seawater drowning.[8]The use of ECMO to support severe acute respiratory syndrome has become more frequent.However, guidelines for the use of ECMO in individuals with severe acute respiratory failure secondary to Legionella pneumonia are yet to be promulgated.A review of 144 drowning cases found the survival rate to be 69%.[9]Additionally, a retrospective analysis of data from the Register of the Organization of European Life Scientists analyzed the total survival rate of 194 individuals treated with ECMO due to severe respiratory failure caused by Legionella pneumonia and found that the mortality rates of children (64%) and newborns (88%) were significantly higher than those of adults (27%).[5]

Figure 2.Summary of the antibiotic therapy rendered.V-V ECMO: veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; MV: mechanical ventilation; BALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; mNGS: metagenomic next-generation sequencing.
Legionella pneumonia is mostly caused byL.pneumophila type 1 and can progress rapidly to acute respiratory distress syndrome.The clinical diagnosis of Legionella infection remains difficult, which contribute to a delay in appropriate care.The current approach to diagnosis of Legionella infection includes culturing of body fluids,antibody detection in serum and urine, and polymerase chain reaction.[10]Accurate diagnosis using NGS technology and a precise antibiotic regimen can maximize survival in individuals after a drowning episode.
The use of omadacycline for the treatment of severe pneumonia due toL.pneumophilamakes this case uncommon.Omadacycline, a new oncedaily aminomethylcycline antibiotic agent that can be administered intravenously or orally, reaches high concentrations in pulmonary tissues and is active against pathogens that cause community-acquired bacterial pneumonia.[11]In vitro, omadacycline has reported activity againstStreptococcus pneumoniae,Haemophilus influenzae,Staphylococcus aureus, and atypical pathogens such asL.pneumophila,Mycoplasma pneumoniae, andChlamydia pneumoniae.[12]Omadacycline demonstrated relative intracellular penetrance againstL.pneumophilaserogroup 1, comparable to other antibiotics used for the treatment of community- acquired bronchial pneumonia (CABP).In a phase III trial, omadacycline was found to be comparable to moxifloxacin, with an early clinical success rate of 87%among 37 individuals withL.pneumophilapneumonia.[12]Thus, omadacycline may be an option for empirical therapy for CABP, particularly when atypical bacteria such asL.pneumophilaare suspected.
Fluoroquinolones or macrolide drugs are the first choices to treat Legionella pneumonia and are recommended for the combined treatment of patients with critical or low immune function.However, these drugs carry serious adverse reaction, such as nausea,vomiting, and diarrhea and may induce liver insufficiency or arrhythmias.[13]
CONCLUSION
The present study described a drowning patient with severe Legionella pneumonia who was diagnosed early by mNGS.He was successfully treated with V-V ECMO support and omadacycline as the antibiotic treatment.NGS technology has shown remarkable effectiveness in the early detection of the etiological basis in freshwater critically ill drowning patients.Meanwhile,omadacycline was a reasonable alternative antibiotic.
Funding:None.
Ethical approval:This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, and informed consent and permission to use the illustrations were obtained from the patient.
Conflicts of interest:The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author contribution:All authors contributed to the design,research, writing and review of this paper.
 World journal of emergency medicine2023年6期
World journal of emergency medicine2023年6期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- The effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity after cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a case series
- The effect of prophylactic antibiotics in acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding patients in the emergency department
- Uterine artery pseudoaneurysm after subtotal hysterectomy: a case report
- Tension urinothorax as a reversible cause of cardiac arrest: a case report
- Hemorrhagic pancreatitis from fenofibrate and metformin toxicity: a case report
- Pyopneumothorax caused by Parvimonas micra and Prevotella oralis: a case report
