蘋果GRF基因家族在非生物脅迫下的表達分析
高明剛 李明 段高飛 王滕飛 馮曉健 許瑞瑞

摘 要 GRF(Growth Regulating Factor)基因家族是一類植物特有的轉錄因子,它在調控植物的生長發育、滲透脅迫等方面發揮重要作用,主要通過調控細胞增殖過程促進植物組織器官的生長,提高植物對環境脅迫的適應性,因此,研究GRF基因家族在逆境條件下的表達調控具有重要意義。利用生物信息學分析和實時熒光定量PCR技術研究蘋果中12個 GRF 基因在干旱、鹽害和溫度脅迫條件下的表達情況。結果表明:蘋果MdGRFs基因參與響應非生物脅迫,干旱、鹽害、高溫和低溫條件下MdGRFs表達量多數有明顯變化。分別用干旱、鹽害處理蘋果幼苗后有相同的4 個MdGRFs基因呈上調表達趨勢;分別用干旱、低溫處理后也有4 個基因有相似的誘導表達;MdGRF05和MdGRF07受到干旱、鹽害和低溫的誘導表達;鹽脅迫處理后,12 個MdGRFs基因中有8個明顯上調,4個明顯下調;高溫條件下,MdGRF04、MdGRF05、MdGRF07、MdGRF09和MdGRF11基因表達上調略明顯,MdGRF02、MdGRF03和MdGRF10表達均下調,其中高溫12 h 后,幾乎檢測不到MdGRF10的表達。
關鍵詞 蘋果;GRF基因家族;非生物脅迫;表達分析
生長調節因子(Growth Regulated Factor,GRF)是一種植物特有的轉錄因子,不僅可以調控植物的生長發育,也可在不利環境條件下的生長發育過程中發揮重要作用[1-3]。研究表明,GRF的N端區域包含兩個保守結構域:谷氨酰胺Gln、亮氨酸Leu、谷氨酰胺Gln組成的QLQ保守域和色氨酸Trp、精氨酸Arg、半胱氨酸Cys組成的WRC保守域,WRC結構域具有核定位信號和鋅指結構;除此之外,有些GRF轉錄因子的C端區域還含有TQL、GGPL和FFD共3個保守結構域[4-6]。
2000年,水稻 OsGRF1作為第一個成員被鑒定出在赤霉素(Gibberellic acid,GA)誘導的莖伸長中發揮著重要的調控作用[2],隨后,研究者發現大量GRF基因參與植物的生長發育調控[7-8]。 AtGRF1和 AtGRF2的過表達導致葉片和子葉增大[1]; AtGRF1、 AtGRF2和 AtGRF3在葉片發育過程中起到細胞增殖的正調控作用[9]; AtGRF4是葉細胞增殖、子葉胚胎發育和莖尖分生組織(SAM)發育所必需的[10]; AtGRF1調節種子的重量和大小[11]; AtGRF7作為滲透脅迫響應基因的抑制因子,防止在脅迫條件下的生長抑制[6]。
甘藍型油菜 BnGRF2可以通過提高光合效率促進種子質量和產油[12];玉米 GRF10則是通過降低細胞增殖來控制葉片大小和株高[13];水稻 GRF4是調控粒質量和產量的關鍵轉錄因子[14-15]; OsGRF6通過IAA途徑調控花序構型,通過GA途徑調控植株高度[16-17];此外,在各種非生物脅迫誘導下,miR396負調控 AtGRF、 OsGRF和 ZmGRF的表達[18-22]。然而,目前關于蘋果MdGRFs在非生物脅迫條件下的表達調控機制還不清楚。
蘋果是全球廣泛種植的水果作物之一,富含人體所需的多種元素和營養成分[23]。中國是世界上最大的蘋果生產國和消費國,種植面積和產量均占世界總量的40%以上,在世界蘋果產業中占有重要地位[24]。近年來,非生物脅迫嚴重影響著蘋果的生理生化反應和代謝過程,對蘋果果實的產量和品質造成顯著負面影響[25-26]。因此,探索蘋果非生物脅迫的基因資源,對培育耐高溫新品種和蘋果生產具有重要的現實意義。蘋果全基因組共鑒定到12個GRF基因成員[27],本研究采用實時熒光定量PCR技術,分別對12個MdGRFs基因進行表達檢測,分析它們在干旱、鹽害和溫度脅迫條件下的表達調控特點,擬為今后進一步探究MdGRFs基因的逆境生物學功能奠定一定的試驗基礎。
1 材料與方法
1.1 試驗材料
所用植物材料由山東農業大學園藝科學與工程學院提供,‘嘎拉蘋果組培苗每隔30 d繼代培養1次,25 ℃,光照16 h/暗8 h無菌培養。繼代20 d后,將生長良好的‘嘎拉組培苗轉移到生根培養基(1/2MS+0.1 mg/L IAA)中,組培生根生長45 d后移栽于營養土里,置于25 ℃溫室中,光照16 h/暗8 h。生長2個月后,選擇發育均勻的幼苗進行脅迫處理后取樣。對照組置于25 ℃正常培養,用1/2霍格蘭營養液澆灌;干旱脅迫和鹽害分別用含有200 mmol/L甘露醇和300?? mmol/L氯化鈉的1/2霍格蘭營養液澆灌3 h、? 12 h;溫度脅迫處理選擇高溫39 ℃和低溫4 ℃進行,分別處理3 h、12 h。樣品迅速用液氮冷凍,存放于-80 ℃冰箱,備用。
1.2 引物設計
在蘋果基因組數據庫中檢索MdGRFs的基因序列,使用Beacon Designer 7軟件設計引物(表1)。
1.3 主要試劑
Trizol試劑(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA)用于RNA提取;反轉錄試劑盒和熒光定量PCR試劑盒購于Takara公司;甘露醇和NaCl等試劑均為國藥集團藥品。
1.4 蘋果MdGRFs基因啟動子序列提取
從TAIR數據庫(https://www.arabidopsis.org)下載擬南芥GRF家族的基因序列。蘋果基因組序列從GDR數據庫(https://www.rosaceae.org)下載。利用hmmer程序[28]搜索蘋果所有潛在的GDR轉錄因子家族成員。從Pfam數據庫(http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk)下載WRC(PF08879.8)和QLQ(PF08880.9)結構域的隱馬爾可夫文件對蘋果GDR家族進行鑒定。提取蘋果所有GDR家族成員轉錄起始位點上游1 500 bp的DNA序列作為啟動子序列進行后續分析。利用PlantCARE在線程序(http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/ webtools/plantcare/html/)對蘋果MdGRFs基因的啟動子序列進行響應元件預測與分析。
1.5 蘋果MdGRFs基因在非生物脅迫條件下的表達分析
采用Trizol法提取總RNA,用DNaseI除去基因組DNA后,根據反轉錄試劑盒說明書合成cDNA,用于qRT-PCR表達分析。熒光定量PCR使用的儀器為BIO-RAD IQ5,所有PCR反應均設3次重復。采用Md18S為內參基因。熒光定量PCR反應體系為:SYBR Green Ⅰ Master 10 μL,上、下游引物各1 μL,模板2 μL,加去離子水至20 μL。反應條件為94? ℃ 10 min;94? ℃ 10 s,60? ℃ 60 s,40個循環。采用2-ΔΔCT法對數據進行定量分析,用Excel 2010作圖。
2 結果與分析
2.1 蘋果MdGRFs轉錄因子基因上游的啟動子序列分析
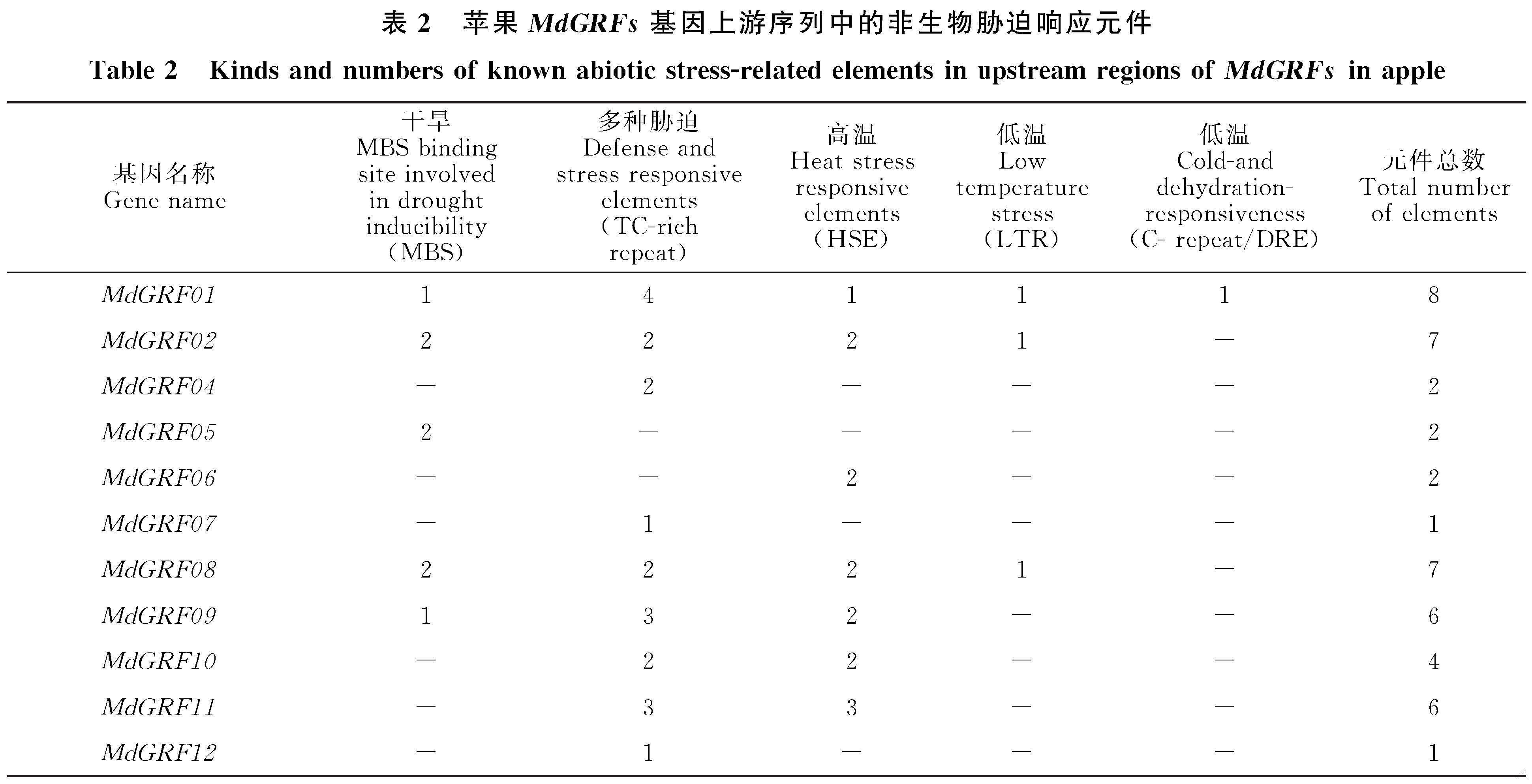
利用PlantCARE在線程序對12個MdGRFs轉錄因子基因上游1 500 bp啟動子區域包含的非生物脅迫響應元件進行預測和分析,如表2所示,除MdGRF03外,11個MdGRFs的啟動子區域存在多個響應元件,如MBS(MBS binding site involved in drought inducibility)、TC-rich repeat(Defense and stress responsive elements)、HSE(Heat stress responsive elements)、LTR(Low temperature stress)和C-repeat/DRE(Cold- and dehydration-responsiveness)等,非生物脅迫響應元件共46個,其中,MdGRF01、MdGRF02、MdGRF08、MdGRF09和MdGRF11分別含有8、7、7、6和6個元件,這些元件說明以上5個基因可能響應干旱、高溫和低溫等不同脅迫(表2)。
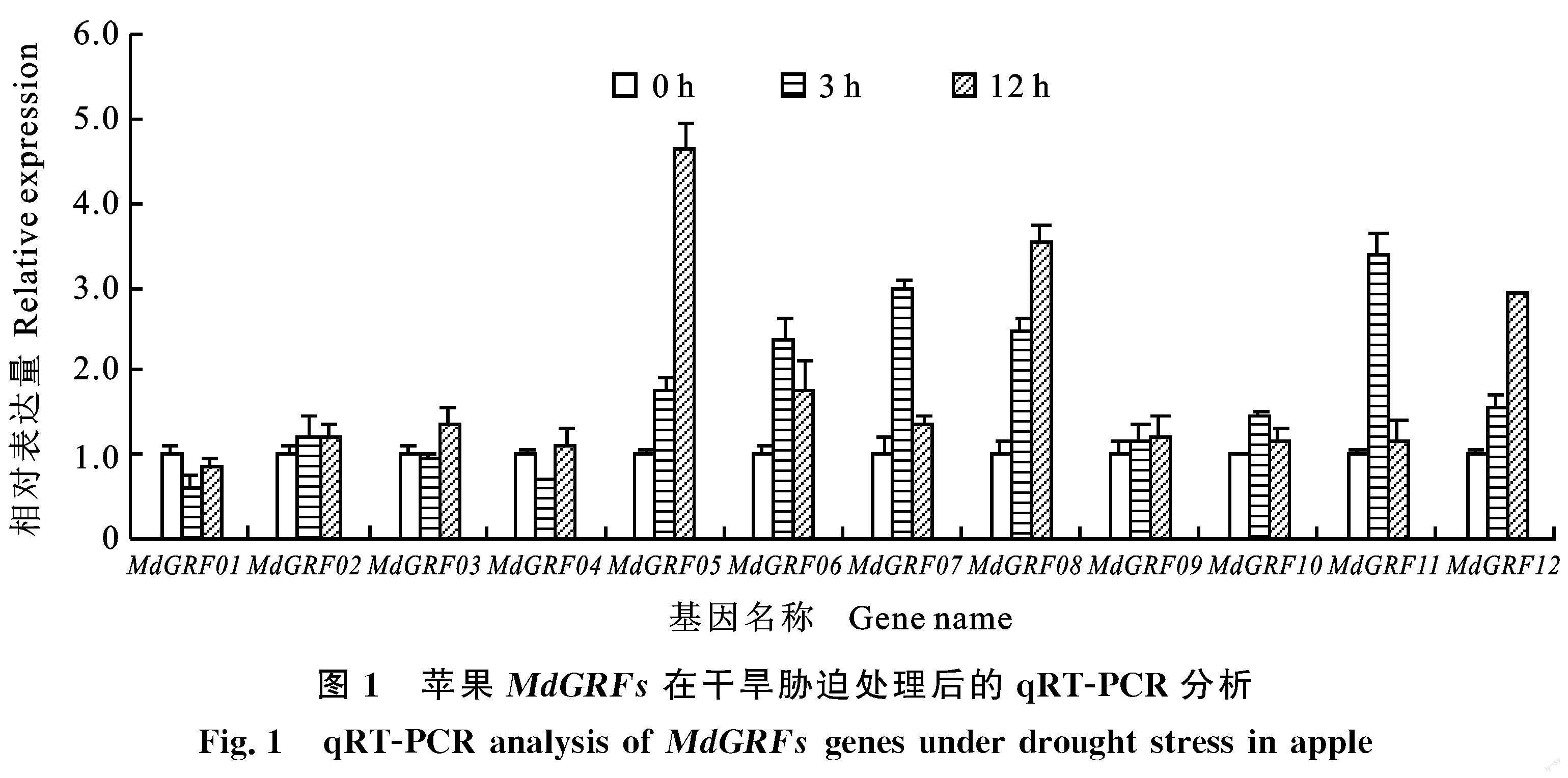
2.2 蘋果MdGRFs在干旱脅迫條件下的表達? 分析
12個MdGRFs基因的表達量均有不同程度變化,但是干旱脅迫條件下基因下調的情況并沒有檢測到。結果表明,MdGRF05、MdGRF06、MdGRF07、MdGRF08、MdGRF11和MdGRF12 6 個基因的表達明顯上調,上調倍數為2.39~4.64(圖1),其中,5個基因的啟動子預測分析均包含相關響應元件,只有MdGRF06的啟動子中無干旱相關響應元件(表2),MdGRF05經過12 h甘露醇處理后表達量升高至對照的4.64倍,表明該基因明顯受到干旱誘導(圖1)。
2.3 蘋果MdGRFs在鹽脅迫條件下的表達分析
由圖2可知,蘋果MdGRF02、MdGRF03、MdGRF05、MdGRF07、MdGRF11和MdGRF12共6個基因的表達明顯上調,基因表達量均達到對照的2.0倍以上,最高的達到4.15倍,同時MdGRF01、MdGRF08和MdGRF09的表達量變化也很明顯,鹽脅迫處理后,表達量降低至不足對照的1/2。
2.4 蘋果MdGRFs在高溫條件下的表達分析
近年來,全球溫室效應導致極端天氣增加,氣候反常,尤其是高溫天氣嚴重影響著蘋果的生理生化反應和代謝過程,對蘋果果實的產量和品質造成顯著負面影響[23]。由圖3可知,MdGRF04和MdGRF11的表達量明顯增加,高溫處理3 h后MdGRF11的表達量達到對照的3.33倍;檢測到基因表達量下調的有4個基因,包括MdGRF01、MdGRF02、MdGRF03和MdGRF10,高溫處理12 h后,MdGRF10的表達量降至對照的1/20,表明以上6個基因的表達量均不同程度響應高溫脅迫。MdGRF01、MdGRF02、MdGRF10和MdGRF11均含有1~3個HSE元件(表2)。
2.5 蘋果MdGRFs在低溫條件下的表達分析
MdGRF01、MdGRF02和MdGRF04的表達有明顯下降趨勢,該趨勢在低溫處理12 h時顯現;MdGRF05~MdGRF10 6 個基因啟動子區域內只有MdGRF08包含1個LTR元件,但是6 個基因經過低溫處理后表達均有明顯上調,最高達5.47倍(表2和圖4),說明低溫處理時基因表達的變化趨勢與基因內的LTR響應元件數量相關性不大。
3 討? 論
植物GRFs基因在根和地上部組織中有不同程度的表達,在細胞增殖的組織部位的表達較高[1,9,12]。蘋果MdGRFs基因在根、莖、葉、花和果實等多種組織中表達,但在幼苗葉片中的表達水平高于成熟葉片,也符合GRF在不同組織生長發育早期發揮作用的結果[27];NtGRFs和BnGRFs在不同的器官或組織中存在差異表達[3,29-30],很多GRF基因也具有組織特異性的表達模式,表明它們可能在調控植物生長發育方面具有不同的功能。
研究表明,響應非生物脅迫和激素處理的GRF基因通常包含脅迫相關的順式響應元件[3,22,31]。本研究分析得知11個蘋果MdGRFs基因的啟動子區域分別包含1~8個非生物脅迫響應順式元件(表2),因此,初步預測蘋果MdGRFs基因可能參與非生物脅迫信號通路。結合qRT-PCR分析得知,干旱和高溫脅迫處理后,基因表達量的變化與含有的MBS、HSE等響應元件的相關性分別為83.3%和66.7%,而低溫處理后蘋果MdGRFs的表達量變化與基因啟動子區域含有的LTR元件并沒有緊密聯系。
通過深入分析qRT-PCR結果還發現,很多非生物脅迫條件下的調控模式有相似性,比如:干旱、鹽害脅迫后,MdGRF05、MdGRF07、MdGRF11和MdGRF12均有上調表達趨勢(圖1和圖2);同時,干旱、低溫處理后,MdGRF05、MdGRF06、MdGRF07和MdGRF08的基因表達量增加,以上兩種情況相似基因數占總上調基因數的2/3(圖1和圖4);MdGRF05和MdGRF07兩個基因受到干旱、鹽害和低溫的誘導表達(圖1、圖2和圖4),可作為今后重點研究的非生物脅迫響應途徑的關鍵基因;另外,分析還發現MdGRF01多呈現下調模式,鹽害、溫度脅迫都會降低該基因的表達,MdGRF04受到高溫誘導,低溫處理后表達量下降;MdGRF10則正好相反(圖2、圖3和圖4),以上結果說明:MdGRFs基因家族響應非生物脅迫是大多數基因具有相似性和少數基因多樣化共存。
綜合上述研究結果,MdGRFs參與蘋果響應干旱、鹽脅迫、高溫及低溫信號途徑,在調控蘋果逆境響應機制中可能發揮著重要作用,但詳細的逆境生物學功能以及分子調控機制需進一步探索。本文為今后研究蘋果MdGRFs在干旱、鹽脅迫及溫度等非生物脅迫過程中的具體功能和抗性機理提供了一定的理論基礎,也為培育抗逆蘋果新品種提供了關鍵的候選基因資源。
參考文獻 Reference:
[1] KIM J H,CHOI D,KENDE H.The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis[J].The Plant Journal,2003,? 36(1):94-104.
[2] OMIDBAKHSHFARD M A,PROOST S,FUJIKURA U,et al.Growth-regulating factors (GRFs):a small transcription factor family with important functions in plant biology[J].Molecular Plant,2015,8(7):998-1010.
[3] MA J Q,JIAN H J,YANG B,et al.Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the GRF gene family in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.)[J].Gene,2017,620:36-45.
[4] VAN DER KNAAP E,KIM J H,KENDE H.A novel gibberellin-induced gene from rice and its potential regulatory role in stem growth[J].Plant Physiology,2000,122(3):695-704.
[5] CHOI D,KIM J H,KENDE H.Whole genome analysis of the OsGRF gene family encoding plant-specific putative transcription activators in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J].Plant & Cell Physiology,2004,45(7):897-904.
[6] KIM J S,MIZOI J,KIDOKORO S,et al.Arabidopsis growth-regulating factor7 functions as a transcriptional repressor of abscisic acid- and osmotic stress-responsive genes,including DREB2A[J].The Plant Cell,2012,24(8):3393-3405.
[7] HORIGUCHI G,KIM G T,TSUKAYA H.The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana[J].The Plant Journal,2005,43(1):68-78.
[8] KUIJT S J,GRECO R,AGALOU A,et al.Interaction between the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and KNOTTED1-LIKE HOMEOBOX families of transcription factors[J].Plant Physiology,2014,164(4):1952-1966.
[9] KIM J H,KENDE H.A transcriptional coactivator,AtGIF1,is involved in regulating leaf growth and morphology in Arabidopsis[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2004,? 101(36):13374-13379.
[10]KIM J,LEE B.GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR4 of Arabidopsis thaliana is required for development of leaves,cotyledons,and shoot apical meristem[J].Journal of Plant Biology,2006,49(6):463-468.
[11] VAN DAELE I,GONZALEZ N,VERCAUTEREN I,? et al.A comparative study of seed yield parameters in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants and transgenics[J].Plant Biotechnology Journal,2012,10(4):488-500.
[12] LIU J,HUA W,YANG H L,et al.The BnGRF2? gene ( GRF2-like? gene from Brassica napus) enhances seed oil production through regulating cell number and plant photosynthesis[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2012,63(10):3727-3740.
[13] WU L,ZHANG D F,XUE M,et al.Overexpression of the maizeGRF10,an endogenous truncated growth-regulating factor protein,leads to reduction in leaf size and plant height[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2014,? 56(11):1053-1063.
[14] HU J,WANG Y X,FANG Y X,et al.A rare allele of?? GS2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice[J].Molecular Plant,2015,8(10):1455-1465.
[15] SUN P Y,ZHANG W H,WANG Y H,et al. OsGRF4 controls grain shape,panicle length and seed shattering in rice[J].Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,2016,? 58(10):836-847.
[16] GAO F,WANG K,LIU Y,et al.Blocking miR396 increases rice yield by shaping inflorescence architecture[J].Nature Plants,2015,2:15196.
[17] TANG Y Y,LIU H H,GUO S Y,et al.OsmiR396d miRNA affects gibberellin and brassinosteroid signaling to regulate plant architecture in rice[J].Plant Physiology,2018,176(1):946-959.
[18] LIU H H,GUO S Y,XU Y Y,et al.OsmiR396d-regulated OsGRFs function in floral organogenesis in rice through binding to their targets OsJMJ706? and OsCR4[J].Plant Physiology,2014,165(1):160-174.
[19] SCHOMMER C,DEBERNARDI J M,BRESSO E G,? et al.Repression of cell? proliferation by miR319-Regulated TCP4[J].Molecular Plant,2014,7(10):1533-1544.
[20] KIM J H,TSUKAYA H.Regulation of plant growth and development by the GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR duo[J].Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(20):6093-6107.
[21] NELISSEN H,EECKHOUT D,DEMUYNCK K,et al.Dynamic changes in ANGUSTIFOLIA3 complex composition reveal a growth regulatory mechanism in the maize leaf[J].The Plant Cell,2015,27(6):1605-1619.
[22] 何 彬,王俞丹,宋世威.miR396-GRF模塊參與植物逆境脅迫響應的研究進展[J].植物科學學報,2022,40(3):437-447.
HE B,WANG Y D,SONG SH W,et al.Research progress on miR396-GRF module regulating plant stress response[J].Plant Science Journal,2022,40(3):437-447.
[23] LEE S Y,CHANG S S,SHIN J H,et al.Membrane filtration method for enumeration and isolation of Alicyclobacillus spp. from apple juice[J].Letters in Applied Microbiology,2007,45(5):540-546.
[24] 趙政陽,馮寶榮,王雷存,等.我國蘋果產業向優勢區域集中的戰略思考[J].西北農業學報,2004,13(4):195-199.
ZHAO ZH Y,FENG B R,WANG L C,et al.The strategic thinkings on the concentrating apple industry in the superior district of China[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2004,13(4):195-199.
[25] CHALLINOR A,WATSON J,LOBELL D,et al.A meta-analysis of crop yield under climate change and adaptation[J].Nature Climate Change,2014,4:287-291.
[26] 趙明玉,李 宏,武勝利,等.果實膨大期干旱脅迫對'紅富士'蘋果樹生理特性的影響[J].西北農業學報,2020,? 30(12):1839-1847.
ZHAO M Y,LI H,WU SH L,et al.Effect of drought stress on physiological characteristics of ‘Red Fuji? apple trees during fruit expansion period[J].Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2020,30(12):1839-1847.
[27] XU R R,GAO M G,LI M,et al.Identification of MdGRF genes and the necessary role of MdGRF02 in apple root growth regulation[J].Scientia Horticulturae,2022,295:110866.
[28] JOHNSON L S,EDDY S R,PORTUGALY E.Hidden Markov model speed heuristic and iterative HMM search procedure[J].BMC Bioinformatics,2010,11:431.
[29] 韋燕紅,劉 楨,李 珂,等.蘋果miR396家族鑒定及在不定根發育過程中的表達分析[J].園藝學報,2020,? 47(7):1237-1252.
WEI Y H,LIU ZH,LI K,et al.Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of miR396 family during adventitious root development in apple[J].Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2020,47(7):1237-1252.
[30] ZHANG J F,LI Z F,JIN J J,et al.Genome wide identification and analysis of the growth-regulating factor family in tobacco(Nicotiana tabacum) [J].Gene,2018,639:117-127.
[31] ZOU X Y,XIANG W,LI K,et al.MdGRF11,a growth-regulating factor,participates in the regulation of flowering time and interacts with MdTFL1/MdFT1 in apple[J].Plant Science,2022 321:111339.
Expression Analysis of? GRF Gene Family under Abiotic Stress in Apple
Abstract Growth Regulating Factor (GRF) gene family is a kind of plant-specific transcription factors,which play an important role in regulating the growth and development of plants and osmotic stress,mainly the role in promoting the growth of plant tissues and organs by regulating the cell proliferation process,and improving the adaptability to environmental stress in plants.Therefore,it is of great significance to study the expression regulation of GRF gene family under abiotic stress in plant.In this study,bioinformatics analysis and quantitative real-time PCR were used to detect the expression of 12 MdGRFs genes under drought,salt and temperature stress in apple.The results showed that MdGRFs were involved in response to abiotic stress,and the expression level of MdGRFs changed significantly under drought,salt injury,high temperature and low temperature.MdGRF05,MdGRF06,MdGRF07,MdGRF08 and MdGRF11 showed similar regulation pattern,and the regulation of MdGRF09 and MdGRF12 was different under drought and cold stress.After salt stress,eight MdGRFs were significantly up-regulated and four MdGRFs were significantly down-regulated.Under high temperature stress,the expression of MdGRF04,MdGRF05,MdGRF07,MdGRF09 and MdGRF11 genes were slightly up-regulated,and the expression of MdGRF02,MdGRF03 and MdGRF10 were down-regulated.The expression of MdGRF10 could hardly be detected after 12? h of high temperature.
Key words Apple; GRF? gene family; Abiotic stress; Expression analysis

