基于混沌反向學習和水波算法改進的白鯨優化算法
王亞輝 張虎晨 王學兵 胡繼明 李婭
摘 要:針對原始的白鯨算法(beluga whale optimization,BWO)在某些情況下,中后期的探索和開發能力不足、多樣性和求解精度降低、容易陷入局部最優等問題,提出一種基于混沌反向學習和水波算法改進的白鯨優化算法(TWBWO),進一步提高白鯨算法的計算精度和收斂速度,增強全局搜索和跳出局部最優能力。結合混沌映射和反向學習策略提高種群的質量和多樣性,加快收斂速度。引入水波算法(water wave optimization,WWO)的折射操作,避免尋優時輕易陷入局部最優,提高計算精度。實驗結果表明,TWBWO算法較之原始算法和其他經典算法在收斂速度和求解精度以及穩定性方面更為優秀,性能和尋優能力更強。
關鍵詞:白鯨優化算法; 水波算法; 混沌映射; 反向學習; 算法改進
中圖分類號:TP301?? 文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:1001-3695(2024)03-013-0729-07
doi:10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.07.0332
Improved beluga whale optimization algorithm based onchaotic inverse learning and water wave algorithm
Wang Yahui, Zhang Huchen, Wang Xuebing, Hu Jiming, Li Ya
(College of Mechanical, North China University of Water Resources & Electric Power, Zhengzhou 450045, China)
Abstract:To address the problems of the original BWO algorithm,such as insufficient exploration and exploitation ability in the middle and late stages in some cases, reduce the diversity and solution accuracy, easy to fall into local optimality,this paper proposed a white whale optimization algorithm (TWBWO) based on chaotic backward learning and water wave algorithm improvement. Further it improved the computational accuracy and convergence speed of Moby Dick algorithm, enhanced the ability of global search and jumping out of local optimum. Combining chaotic mapping and backward learning strategies,it improved the quality and diversity of populations and speeded up the convergence rate. It introduced the refraction operation of the WWO to avoid the algorithm from repeatedly falling into local optima and improve the computational accuracy. The experimental results show that the TWBWO algorithm is superior to the original algorithm and other classical algorithms in terms of convergence speed and solution accuracy as well as stability, with better performance and better finding ability.
Key words:BWO; WWO; chaotic mapping; reverse learning; algorithm improvement
0 引言
尋得問題的最佳處理方案一直是各學科的焦點,受自然界生物的啟發,學者們提出了很多群智能優化算法來解決最優問題[1]。白鯨算法(BWO)是由Zhong等人[2]觀察白鯨群體的生活行為后于2022年提出的一種元啟發式優化算法,該算法具有結構設計簡單、收斂速度快、求解精度高等優點。黃欣等人[3]使用白鯨算法優化密度聚類算法(density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise,DBSCAN)實現全局參數的自適應選取,提升了效率和聚類結果的可信度,并應用于變電站數據流異常檢測。Houssein等人[4]將動態候選解(dynamic candidate solutions,DCS)和K-最近鄰(K-nearest neighbor,KNN)分類器結合,通過給潛在候選者一個機會,提高了選擇解的多樣性和一致性。蔡海良等人[5]利用白鯨算法優化極限學習機(extreme learning machine,ELM)初始參數,用于電力光纜故障診斷及定位。
針對傳統白鯨算法在一些情況下多樣性和求解精度降低、容易陷入局部最優等問題,本文提出一種基于混沌反向學習和水波算法(WWO)改進的白鯨算法(TWBWO)。混沌映射和反向學習用于前期的種群初始化來提升種群的質量和多樣性,加快收斂速度。引入水波算法的折射理念,折射當前迭代尋到的最優解,提高計算精度,避免陷入局部最優。通過多組測試函數、多維度、多算法進行對比實驗。結果表明,改進后的算法較原始算法性能有明顯提升。
1 原始白鯨優化算法(BWO)
BWO算法是通過觀察白鯨生活行為提出的元啟發式算法,如圖1所示。
1.1 初始化
基于白鯨種群的機制,白鯨被視為搜索代理,每條白鯨都代表一個候選方案,在優化過程中不斷更新,其模型被建立為
2.2 水波算法(WWO)
Zheng受淺水波理論的啟發,模擬水波運動中的傳播、折射、碎浪運動,于2015年提出了水波優化算法(WWO)[14]。該算法中水波的適應度值與海底深度和波長成反比,距離靜止水位越近,適應度值越高,波長越短[15]。通過波長控制水波的搜索范圍,適應度低的水波進行大范圍的搜索,最大可能尋找更優解,適應度高的水波進行小范圍局部搜索,保證解的質量,如圖4[16]所示。
每一次迭代,種群中首先會進行傳播操作,水波個體x通過在每一維d上增加隨機的位移來產生新的個體解[17]。每次的傳播操作更新波長之后會衰減水波個體的波高,當波高逐漸降低為0時,算法進入折射操作,使其向當前最優個體學習,避免算法停滯[18]。在搜索到新的最優水波后進行碎浪操作,并將其分解,進行更細致的局部搜索,保證解的優越性。
為了提升BWO算法跳出局部最優的能力,提高收斂速度與計算精度,將WWO與BWO算法結合。在BWO算法尋到當前全局最優解后,引入折射操作,對最優解進行折射學習,對比新個體與當前最優個體適應度值,選擇優值替代進入下一次迭代。改進后公式如下:
Xd=N(Xbest+Xm2,|Xbest-Xm|2)(14)
Xm=mean(Xbest+Xworst)(15)
其中:Xbest、Xworst分別為當前種群中最優和最差個體;Xm是兩者的平均位置;N(μ,σ)是均值為μ、標準差為σ的高斯隨機數。
圖5為水波算法優化后的BWO算法與原始BWO算法在同一測試函數上的迭代曲線對比。可以看出,結合水波算法后,白鯨算法跳出局部最優的能力明顯提升,加快了收斂速度,提升了計算精度。
2.3 TWBWO算法
混沌反向學習和水波算法都能對白鯨算法進行有效的優化,在一定程度上提升算法性能,但兩者各自所優化BWO算法的方式并不沖突且互不影響。混沌反向學習策略優化BWO算法的初始化階段,提升種群質量。水波算法影響的是勘探、開發、鯨落階段的當前最優值。因此,將兩者互補結合,進一步提升BWO算法的性能。在同一測試函數上的實驗對比結果如圖6所示。可以看出,TWBWO算法充分繼承了前兩者的優點,進一步提升了BWO算法的性能。
TWBWO算法流程如圖7所示。TWBWO算法實現步驟如下:
a)對參數P、dim、lb、ub、T進行初始化,P為種群中個體數量,dim為個體維度,lb、ub為解的下限和上限,T為最大迭代次數。
b)使用混沌反向學習策略進行初始化,獲得新的初始種群,檢驗是否超出搜索邊界,計算適應度值并排序,得到當前最優個體解和最差個體解。
c)根據式(3)(10)計算平衡因子Bf和鯨落概率Wf。
d)如果Bf<0.5,進入開發階段,按照式(5)更新個體位置;如果Bf>0.5,進入勘探階段,按照式(4)更新個體位置。
e)在步驟c)d)結束后,對比平衡因子Bf和鯨落概率Wf。若Bf
f)在所有個體經歷過一次迭代后,計算適應度值,找出新的當前最優解和最差解,根據式(14)(15)對最優解進行折射操作,計算適應度值并對比保存最優解。
g)判斷是否滿足最大迭代次數或停止條件,不滿足則返回步驟c),直至滿足后輸出最終結果。
3 實驗與分析
3.1 實驗設計
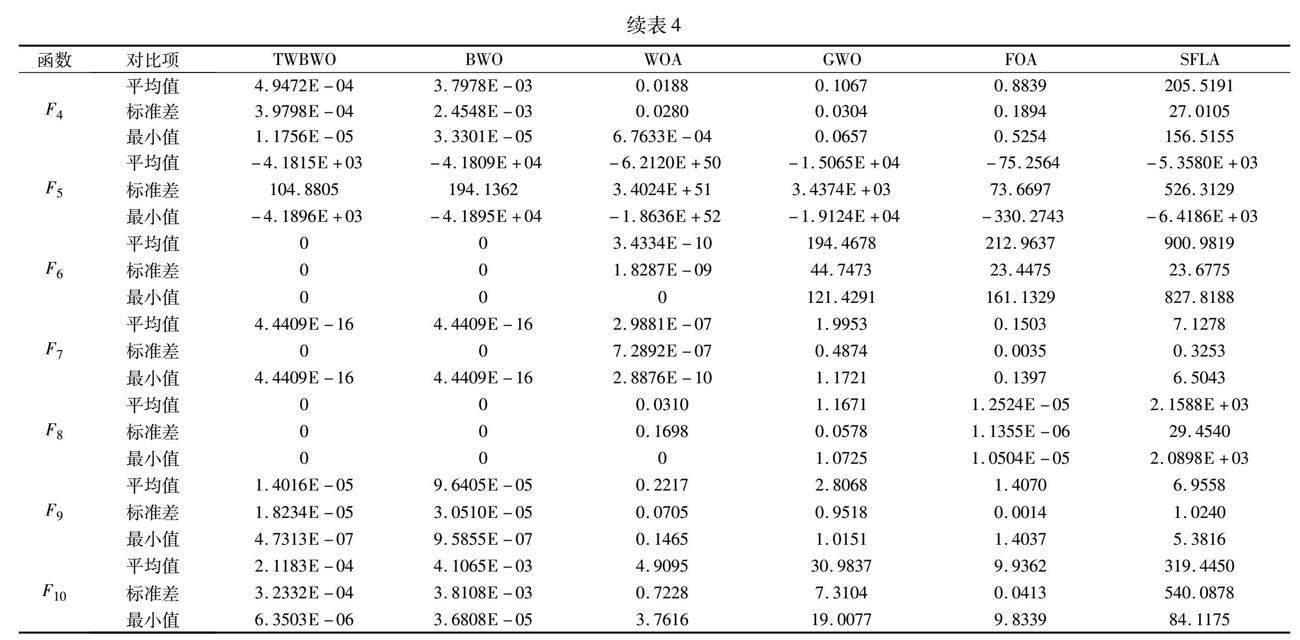
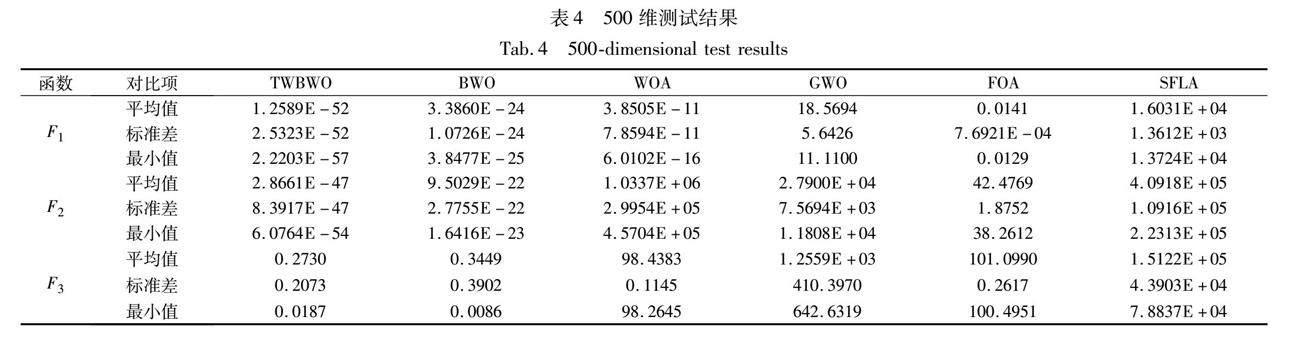
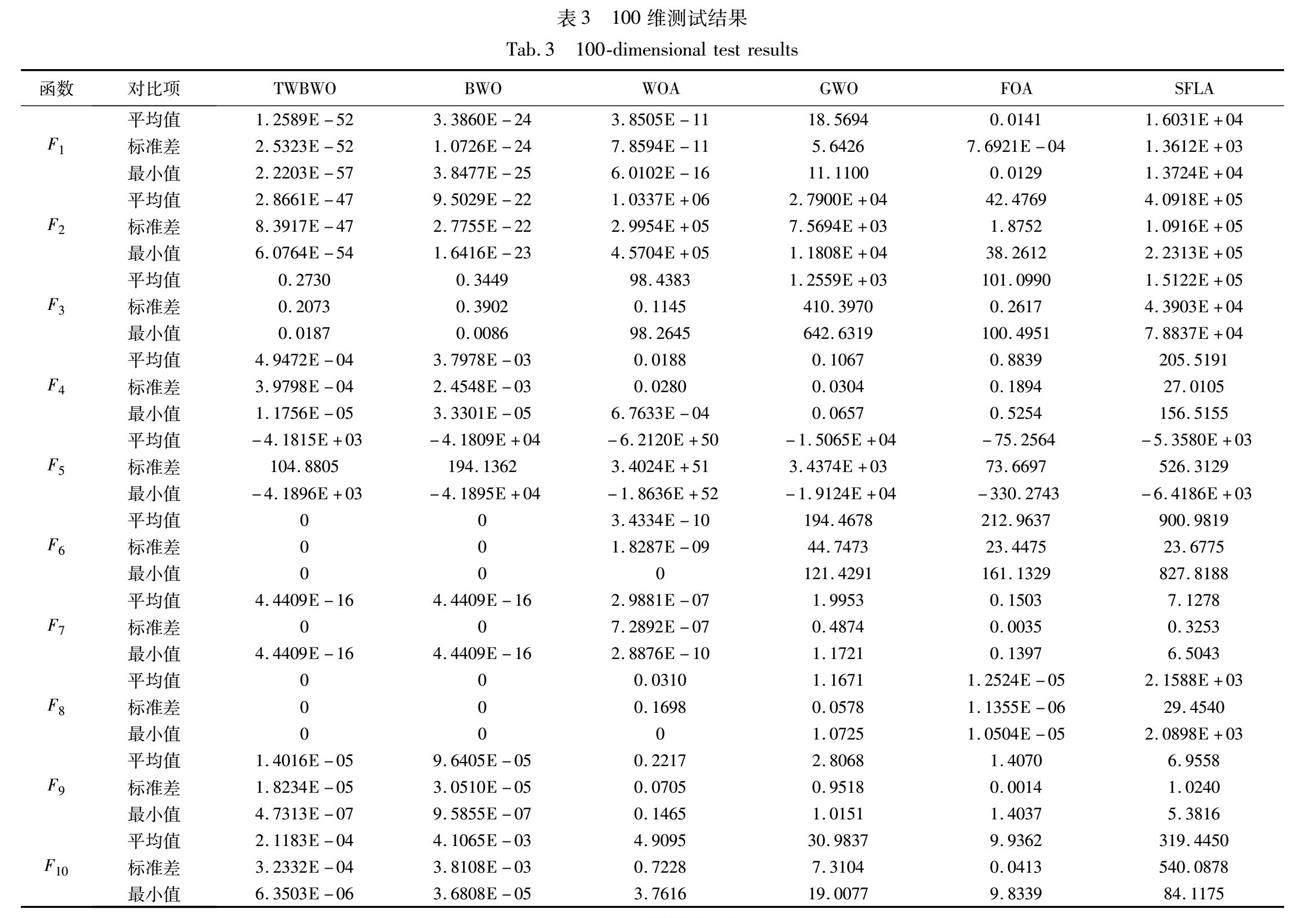
選擇十個基準測試函數進行實驗,測試改進算法的性能。同時,為對比TWBWO算法的優越性,將其與原始白鯨算法(BWO)、鯨魚算法(whale optimization algorithm,WOA)[19]、灰狼算法(grey wolf optimizer,GWO)[20]、混合蛙跳算法(grey wolf optimizer,SFLA)[21]、果蠅算法(fruit fly optimization algorithm,FOA)[22]進行對比實驗。實驗中種群規模為50,最多迭代100次,分別進行30次獨立實驗。測試函數如表1所示。
表1給出了測試函數的表達式、維度、范圍以及理論最優值,其中F1~F4為單模態測試函數,用于測試算法是否能快速搜尋到最優解;F5~F10為多模態測試函數,用于測試算法能否有效跳出局部最優[23]。為了更好地體現算法在不同維度上的性能,將測試函數的維度分別設置為30、100、500維。
3.2 實驗結果
表2~4分別列出了TWBWO、BWO、WOA、GWO、FOA和SFLA算法在十個測試函數的30、100、500維度上獨立運行30次,每次迭代100步的實驗結果。實驗結果統計了每個算法運行30次的最優值(best)、平均值(mean)、標準差(std),在尋找最優解的問題中,平均值越小表明算法尋優精度越高,而標準差越小則證明算法越穩定[24]。
由表中結果可知,通過平均值的比較,無論是在4個單模態測試函數,還是6個多模態測試函數中,TWBWO算法在尋優精度上都表現出了更好的性能,證明結合水波算法的折射操作可以有效提升白鯨算法的局部搜索能力。通過標準差的比較,驗證了TWBWO算法的穩定性更好。而在面對高維問題時,求解過程更加復雜,算法尋找最優解的難度不斷提升,TWBWO算法仍保持較高的尋優精度和魯棒性,較之其他算法更加穩定。
為了驗證TWBWO算法在收斂速度方面的性能,針對本文使用的十個測試函數,選擇尋優維度為30,以迭代次數為x軸,適應度值為y軸,繪制TWBWO、BWO、WOA、GWO、FOA、SFLA六個算法的迭代曲線進行對比[25],如圖8所示。
在十個測試函數中,TWBWO算法的收斂速度明顯優于其他算法。在單模態測試函數中,TWBWO算法在函數F1、F2明顯收斂更快,雖無法收斂,但得到的最終結果在10-40上下,已無限接近最優解。函數F3未在100次迭代后收斂,但相較其他算法,在都無法收斂的情況下,前期搜索效率更高、速度更快且更接近最優解。在多模態測試函數中,TWBWO算法只需20次迭代便可在函數F5收斂得到最優解,且精度最好,更是只需38次迭代和42次迭代便得到了函數F6和F8的理論最優解,在函數F7、F9、F10的收斂速度也都有明顯提高。
通過混沌反向學習策略加強了初始種群的質量和多樣性,使得算法一開始便能找到優秀的初始值,在迭代初期就有較高的精度。折射操作的存在也能保證算法不會重復陷入局部最優,加快收斂速度。這使得TWBWO算法在收斂速度和尋優精度上都具有明顯的優越性。
穩定性是評價算法優劣的一個重要因素,為了驗證TWBWO算法的穩定性,對TWBWO算法和五個對比算法在F3測試函數上進行30次獨立實驗,收集實驗結果并繪制箱型圖,結果如圖9所示。從箱型圖可以看出,TWBWO算法30次獨立實驗所得到的最優值分布基本在一條直線上,相比于BWO算法分布波動更小、更均勻,對比另外四個算法更是有著巨大的優勢,證明TWBWO算法具有更為優越的穩定性。
4 結束語
針對原始白鯨算法在某些情況下,中后期的探索和開發能力不足、多樣性和求解精度降低、容易陷入局部最優等問題,提出一種基于混沌反向學習和水波算法改進的白鯨優化算法(TWBWO)來提高計算精度和收斂速度,增強全局搜索和跳出局部最優的能力。算法初期通過混沌映射和反向學習策略初始化種群,提高種群的質量和多樣性,提高初始解的質量。引入水波算法(WWO)的折射操作對每次迭代得到的最優解進行折射,增強算法跳出局部最優的能力,提高算法的計算精度,進一步提升算法的尋優性能。
實驗結果表明,即使在高維情況下,TWBWO算法在收斂速度和求解精度以及穩定性方面都更為優秀,尋優性能更強。相較于提高初始種群質量和折射當前最優解來提高算法性能,如何改進算法的勘探階段和開發階段進一步提升算法性能,是下一步工作研究的重點。
圖9 F3最優解分布箱型圖
Fig.9 Box plot of F3 optimal solution distribution
參考文獻:
[1]Ouyang Weimin, Ramachandran V. Classroom education effect evaluation model based on MFO intelligent optimization algorithm[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2021,40(4) : 6791-6802.
[2]Zhong Changting, Li Gang, Meng Zeng. Beluga whale optimization: a novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022,251: article No.109215.
[3]黃欣, 趙敏彤, 郇嘉嘉, 等. 基于BWO-DBSCAN和CSA-OCRKELM的變電站數據流異常檢測方法[J]. 廣東電力, 2023,36(5): 39-48. (Huang Xin, Zhao Mintong, Jun Jiajia, et al. A substation data flow anomaly detection method based on BWO-DBSCAN and CSA-OCRKELM[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2023,36(5): 39-48.)
[4]Houssein E H. Sayed A. Dynamic candidate solution boosted beluga whale optimization algorithm for biomedical classification[J]. Mathematics, 2023,11(3): article No.707.
[5]蔡海良, 胡凱, 李軍, 等. 基于BWO-ELM算法與VR-GIS技術的電力光纜故障診斷及定位研究[J]. 計算機測量與制, 2022, 30(12): 98-104,111. (Cai Hailiang, Hu Kai, Li Jun, et al. Research on power fiber optic cable fault diagnosis and localization based on BWO-ELM algorithm and VR-GIS technology[J]. Computer Measurement and System, 2022,30(12): 98-104,111.
[6]Ma Denglong, Tan Wei, Wang Qingsheng, et al. Application and improvement of swarm intelligence optimization algorithm in gas emission source identification in atmosphere[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2018,56: 262-271.
[7]Zhang Jinghua, Dong Ze. A general intelligent optimization algorithm combination framework with application in economic load dispatch problems[J]. Energies, 2019,12(11): article No.2175.
[8]Gurses D, Pholdee N, Bureerat S, et al. A novel hybrid water wave optimization algorithm for solving complex constrained engineering problems[J]. Materials Testing, 2021,63(6):560-564.
[9]Yin Qiang, Cao Ben, Li Xue,et al. An intelligent optimization algorithm for constructing a DNA storage code: NOL-HHO[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020,21(6) : article No.2191.
[10]Cui Fan, Ni Jianyu, Du Yunfei, et al. Soil water content estimation using ground penetrating radar data via group intelligence optimization algorithms: an application in the northern shaanxi coal mining area[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2021,39(1): 318-335.
[11]Nie Xin, Luo Jian. The hybrid intelligent optimization algorithm and multi-objective optimization based on big data[J]. Journal of Phy-sics: Conference Series, 2021,1757(1) : article No.012132.
[12]Hu Shanshan, Liu Hui, Feng Yufei, et al. Tool wear prediction in glass fiber reinforced polymer small-hole drilling based on an improved circle chaotic mapping grey wolf algorithm for BP neural network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023,13(5): article No.2811.
[13]Huang Yujie, Li Yibing, Zhang Zitang, et al. A novel path planning approach for AUV based on improved whale optimization algorithm using segment learning and adaptive operator selection[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023,280: article No.114591.
[14]付接遞. 鯨魚優化算法改進與應用研究[D]. 銀川:寧夏大學, 2022. (Fu Jiedi. Research on the improvement and application of whale optimization algorithm[D]. Yinchuan:Ningxia University, 2022.)
[15]Sun Yulong, Li Hongjuan, Shabaz M,et al. Research on building truss design based on particle swarm intelligence optimization algorithm[J]. International Journal of System Assurance Enginee-ring and Management, 2021,13: 38-48.
[16]Azam A, Bardhan A, Kaloop M R, et al. Modeling resilient modulus of subgrade soils using LSSVM optimized with swarm intelligence algorithms[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022,12: article No.14454.
[17]Ozbay F A. A modified seahorse optimization algorithm based on chao-tic maps for solving global optimization and engineering problems[J]. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal, 2023,41: 1-26.
[18]Zhang Danfeng, Han Congai, Zhang Haiyan, et al. The simulation design of microwave absorption performance for the multi-layered carbon-based nanocomposites using intelligent optimization algorithm[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021,11(8): article No.1951.
[19]Li Yuzhou, Sun Chuanxia, Hu Yinglei. Whale optimization algorithm-based deep learning model for driver identification in intelligent transport systems[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2023,75(2):3497-3515.
[20]Lambrinidis G, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A. Multi-objective optimization methods in novel drug design[J]. Expert Opinion on Drug Disco-very, 2021,16(6): 647-658.
[21]Zhang Meilun, Zhang Jin, Xu Maoda, et al. Improved SFLA algorithm with hybrid SA strategy for multi-objective reactive power planning optimization of distribution network[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021,1865(4) : article No.042056.
[22]Yonghua Bai, Minzhou Luo, Pang Fenglin. An algorithm for solving robot inverse kinematics based on FOA optimized BP neural network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021,11(15): article No.7129.
[23]Jiang Wenjun, Zhang Ning. Research on characteristics of paper-plastic composite film based on intelligent optimization algorithm[J]. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 2021,25(S1): article No.27.
[24]Zhang Junrong, Tang Huiming, Tannant D D, et al. A novel model for landslide displacement prediction based on EDR selection and multi-swarm intelligence optimization algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2021,21(24): article No.8352.
[25]Shokouhandeh H, Kamarposhti M, Holderbaum W, et al. Optimal operation of distributed generations considering demand response in a microgrid using GWO algorithm[J]. Computer Systems Science and Engineering, 2023,47(1):809-822.

