社會支持對老年類風濕關節炎患者生活質量的影響
包淑貞 (西寧市第一人民醫院風濕血液科,青海 西寧 810000)
類風濕關節炎(RA)是以多關節炎癥為主要表現的慢性疾病。關節疼痛是RA患者常見的癥狀,由于長期疼痛,嚴重影響了患者的生活質量(QOL)〔1〕,同時可伴有抑郁〔2〕,本文擬調查老年RA患者的生活質量,旨在為改善患者的疼痛癥狀,給患者更多的社會支持,提高其QOL提供依據。
1 資料與方法
1.1 研究對象 2010年1月至2010年12月我院住院或門診老年RA患者82例,符合1987年美國風濕病學會制訂的RA診斷標準,知情自愿接受本研究的問卷調查,并且能夠理解問卷調查的內容。其中男30例,女52例;年齡60~86〔平均(66.73 ±15.56)〕歲;病程0.25 ~15年。
1.2 方法及內容 采用問卷調查方法,包括:①一般情況包括患者的性別、年齡、學歷和病程;②采用WHOQOL-BREFQOL量表問卷調查。該量表由軀體健康(PHD)、心理功能(PSD)、社會關系(SRD)、環境(ED)4個領域24個條目,領域得分按正向計分(即得分越高,QOL越好),領域得分再通過公式:領域轉換后得分 =(所屬條目的平均分 ×4-4)×(100÷16)轉換成百分制。③社會支持評定量表(SSRS)應用肖水源編制的社會
支持評定量表。該量表用于測量個體社會關系的3個維度共10個條目,每個條目從無支持由低到高分為4個等級,總分40分。分為客觀支持,主觀支持和對支持的利用度3個維度,總得分和各分量表得分越高,說明社會支持程度越好。
1.3 統計學處理 采用SPSS13.0軟件,數據以x ±s表示;進行多組間均數方差分析和多組間兩兩SNK-q檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結 果
2.1 患者QOL及社會支持評分情況 男性與女性患者的QOL總評分及各領域得分比較差異不顯著(P>0.05);男性與女性患者社會支持總分及各維度得分比較差異不顯著(P>0.05);病程 >1年的患者的軀體健康、心理功能、環境以及QOL總評分明顯低于病程≤1年的(P<0.05);病程 >1年的患者的主觀支持、支持利用及社會支持總評分明顯低于病程≤1年的(P <0.05);見表1。
2.2 社會支持各維度與QOL各領域相關線性分析 社會支持項目中的主觀支持與QOL領域中的環境和心理功能呈正相關(r=2.661、1.780;P<0.05);支持利用與心理功能和軀體健康呈正相關(r=1.647、3.235;P<0.05);見表2。
表1 患者QOL及社會支持評分情況比較( ±s)
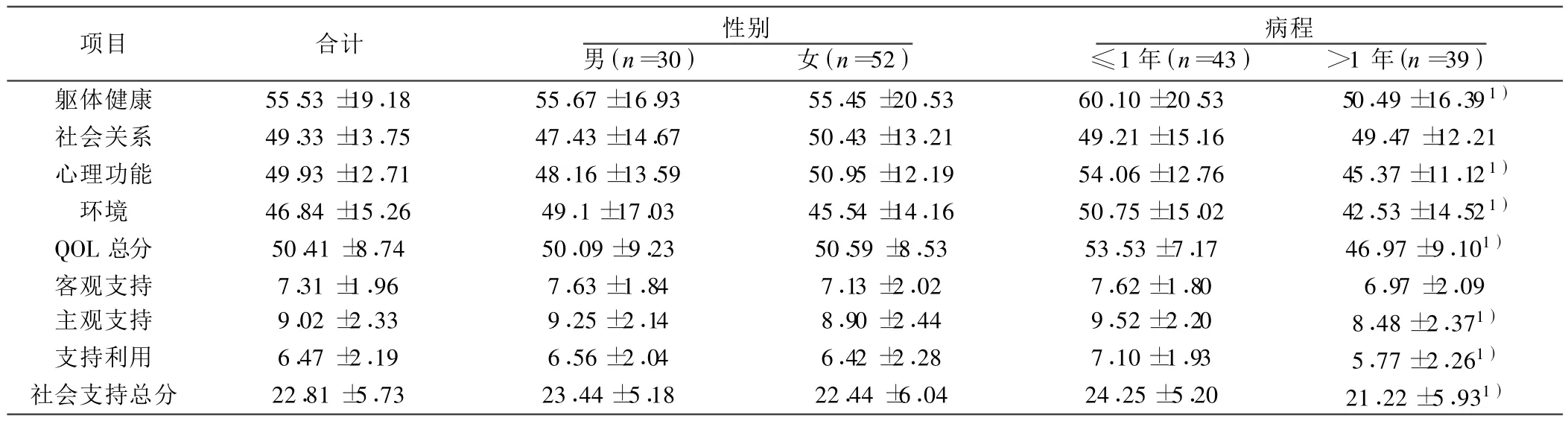
表1 患者QOL及社會支持評分情況比較( ±s)
與病程≤1年比較:1)P<0.05
項目 合計 性別男(n=30) 女(n=52)病程≤1年(n=43) >1年(n=39)軀體健康 55.53 ±19.18 55.67±16.93 55.45 ±20.53 60.10±20.53 50.49±16.39 1)社會關系 49.33 ±13.75 47.43 ±14.67 50.43 ±13.21 49.21 ±15.16 49.47 ±12.21心理功能 49.93 ±12.71 48.16±13.59 50.95 ±12.19 54.06±12.76 45.37±11.12 1)環境 46.84 ±15.26 49.1±17.03 45.54 ±14.16 50.75±15.02 42.53±14.52 1)QOL總分 50.41 ±8.74 50.09±9.23 50.59 ±8.53 53.53±7.17 46.97±9.101)客觀支持 7.31 ±1.96 7.63 ±1.84 7.13 ±2.02 7.62 ±1.80 6.97 ±2.09主觀支持 9.02 ±2.33 9.25±2.14 8.90 ±2.44 9.52±2.20 8.48±2.371)支持利用 6.47 ±2.19 6.56±2.04 6.42 ±2.28 7.10±1.93 5.77±2.261)社會支持總分 22.81±5.73 23.44±5.18 22.44±6.04 24.25±5.20 21.22±5.931)
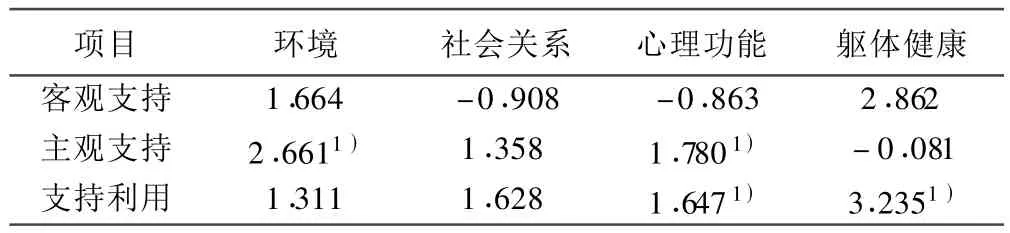
表2 社會支持各維度與QOL各領域多元線性回歸分析結果〔r(相關系數)〕
3 討 論
國外 RA被描述為“5D”,即死亡(Death),殘疾(Disability),痛苦(Discomfort),經濟損失(Dollar cost),藥物中毒(Drug toxicity)。國外有調查研究顯示,按照1987年美國風濕學會制定的RA患者診斷標準,RA在成人的發病率在2.0/1 000~10.7/1 000〔3〕,其死亡率可達到正常人群的 3倍〔4〕。 以往關于RA疾病的傳統研究都主要關注措施的制訂和疾病的治療方法上,不能全面反映患者的實際情況,而患者健康相關QOL已經成為如何更好治療患者,改善生活的主要決定性因素〔5~7〕。
RA患者長期以來忍受著疼痛、殘疾、喪失勞動、巨大的經濟負擔、心理壓力以及長期服藥帶來的不良反應等,這些都嚴重影響著病人的QOL。本研究發現,RA患者WHOQOL-BREF的各維度評分均低于60分,尤其表現在病程在1年以上的患者,可見RA患者生理和心理健康都低于正常人,與其軀體功能(包括活動、自理、疼痛)、心理功能、社會功能和環境各方面都是密切相關的。疼痛、殘疾和壓力對以上4個方面有不同程度的影響。尤其是關節畸形患者嚴重影響了軀體活動,擾亂了病人的正常活動,甚至生活不能自理,QOL高度惡化。大部分病人不愿外出,與社會失去聯系,人際關系惡化,社交能力降低或喪失,導致情感職能、精神健康嚴重受損〔8〕。老年RA患者病程長,臨床癥狀只能緩解,疾病無法根治,嚴重者可以臥床不起,生活不能自理,伴有各種疼痛癥狀,QOL評分下降更明顯。本研究顯示社會支持對于老年RA患者QOL的改善有著重大意義,尤其表現在主觀支持和支持的利用度上,可以很好地改善患者的心理和軀體健康狀況。為有效控制RA的發病,應開展病例報告制度。其內容包括患者的一般健康狀況、疼痛、傷殘、藥物副作用、醫療費用等項目〔9〕,對報告數據進行綜合分析〔10,11〕,以預防或減緩患者的關節永久性結構損壞和長期殘疾〔12〕。而健康QOL量表是目前為止,評價患者心理和身體健康的最常用量表〔13,14〕。綜上,開展疾病監測,對患者進行 QOL調查,合理提供社會支持,可以在很大程度上改善患者的QOL。
1 黎 琴,黃如嬌,韋燕萍,等 .類風濕性關節炎患者生活質量研究進展〔J〕.解放軍護理雜志,2009;26(19):41-2.
2 楊 紅,何素梅 .疼痛對類風濕性關節炎住院婦女抑郁癥狀的影響〔J〕.中國中醫急癥,2008;17(3):413-4.
3 Alamanos Y,Voulgari P,Drosos A.Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis,based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria:a systematic review〔J〕.Semin Arthritis Rheum,2006;36(3):182-8.
4 Sokka T,Krishnan E,Hakkinen A,et al.Functional disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients compared with a community population in Finland〔J〕.Arthritis Rheum,2003;48(1):59-63.
5 Davis JC,Heijde D,van der Dougados M,et al.Reductions in health-related quality of life in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and improvements with etanercept therapy〔J〕.Arthritis Rheum,2005;53(4):494-501.
6 Emery P,Kosinski M,Li T,et al.Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis patients with abatacept and methotrexate significantly improved health-related quality of life〔J〕.J Rheumatol,2006;33(4):681-9.
7 Gladman DD,Mease PJ,Cifaldi MA,et al.Adalimumab improves joint-related and skin-related functional impairment in patients with psoriatic arthritis:patient-reported outcomes of the adalimumab effectiveness in psoriatic arthritis trial〔J〕.Ann Rheum Dis,2007;66(2):163-8.
8 楊 帆,蘭光華.類風濕性關節炎患者病情與生活質量的相關研究〔J〕.中國民康醫學,2006;18(13):536-8.
9 Greenhalgh J,Long AF,Flynn R.The use of patient reported outcome measures in routine clinical practice:lack of impact or lack of theory〔J〕?Soc Sci Med,2005;60(4):833-43.
10 Pincus T,Bergman MJ,Yazici Y,et al.An index of only patient-reported outcome measures,routine assessment of patient index data 3(RAPID3),in two abatacept clinical trials:similar results to disease activity score(DAS28)and other RAPID indices that include physicianreported measures〔J〕.Rheumatology(Oxford),2008;47(3):345-9.
11 Pincus T,Yazici Y,Bergman M,et al.A proposed continuous quality improvement approach to assessment and management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis without formal joint counts based on quantitative routine assessment of patient index data(RAPID)scores on a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire(MDHAQ) 〔J〕.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol,2007;21(4):789-804.
12 Pincus T,Chung C,Segurado OG,et al.An index of patient reported outcomes(PRO-index)discriminates effectively between active and control treatment in 4 clinical trials of adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.J Rheumatol,2006;33(11):2146-52.
13 Salaffi F,De Angelis R,Stancati A,et al.MArche pain prevalence investigation group(MAPPING)study health-related quality of life in multiple musculoskeletal conditions:a cross-sectional population based epidemiological study.Ⅱ.The MAPPING study〔J〕.Clin Exp Rheumatol,2005;23(6):829-39.
14 Veehof MM,ten Klooster PM,Taal E,et al.Comparison of internal and external responsiveness of the generic Medical Outcome Study Short Form-36(SF-36)with disease-specific measures in rheumatoid arthritis〔J〕.J Rheumatol,2008;35(4):610-7.

