響應面法優化樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C
夏永軍,張賢芳,許贛榮*
(江南大學生物工程學院,工業生物技術教育部重點實驗室,江蘇 無錫 214122)
響應面法優化樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C
夏永軍,張賢芳,許贛榮*
(江南大學生物工程學院,工業生物技術教育部重點實驗室,江蘇 無錫 214122)
分析樟芝液態發酵菌絲體中的活性代謝產物Antrodin C,并以此化合物為目標,采用Plackett-Burman設計和Box-Behnken中心組合響應面分析,對樟芝液態發酵產Antrotin C培養基進行統計學篩選和優化。結果表明:葡萄糖、黃豆粉和MgSO4對Antrodin C的合成影響最為顯著。在葡萄糖 72.0g/L、黃豆粉 5.91g/L、MgSO4 0.614g/L時,樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C最大預測值為178.59mg/L。驗證實驗Antrodin C實際產量達到(177.83±0.32)mg/L,表明實驗建立的模型能較好地預測實際發酵產Antrodin C情況。通過對培養基的優化,樟芝液態發酵Antrodin C產量比優化前(95.72mg/L)提高了85.8%。
樟芝;液態發酵;Antrodin C;鑒定;Plackett-Burman;響應面
樟芝(Antrodia camphorata)是臺灣特有的珍稀藥用真菌,子實體僅附著于臺灣特有的牛樟樹中空腐朽內壁生長。長期以來一直被用于解毒、解酒、治療癌癥、止痛等方面,被稱為靈芝之王。近年來,研究發現樟芝子實體中含有豐富的三萜、甾醇、多糖、腺苷類化合物,具有抑制癌細胞增生、增加免疫力、抗氧化、抗炎等生理活性[1-6]。但是由于其寄生條件苛刻,且生長極為緩慢,在市場上供給嚴重短缺,其價格高升至15000美元/kg。
目前,許多學者以人工培養的方式培養牛樟芝,以緩解市場短缺的壓力,其中深層液態發酵已經發展成為工業化培養模式。2004年,Nakamura等[7]從樟芝液態發酵菌體中分離得到5種新的馬來酸和琥珀酸衍生物(Antrodin A~E),是液態發酵樟芝菌體中的主要活性成分,其中Antrodin B和Antrodin C對LLC癌癥細胞具有良好的抑制效果。Phuong等[8]研究顯示樟芝菌絲體中含有的Antrodin A~E對HCV病毒都具有很好的抑制活性,其中Antrodin A抑制能力最高;研究同時發現在體內Antrodin C可以轉化為Antrodin A,從而展現良好的保肝活性,Antrodin A結構式見圖1。Wu等[9]研究發現樟芝菌絲體中一種新的馬來酸衍生物Antrocinnamomins A能顯著的抑制NO的產生。
目前,樟芝液態樟芝液態發酵的研究多注重于菌體多糖[10-13]、抗氧化性[14]等方面的研究,而三萜類化合物由于檢測方法和目標化合物不明確,研究很少。對于Antrodins類化合物的研究主要集中于其藥理活性,而發酵條件和調控方面未見相關報道。這類化合物是樟芝菌絲體的特征活性產物,與樟芝的保肝等藥理活性密切相關。因此,本實驗對樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C的培養基進行統計學篩選和進一步的響應面優化。
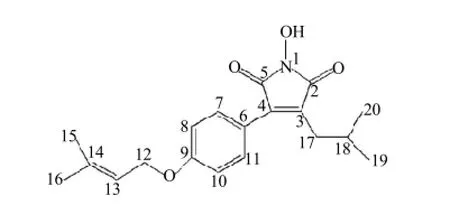
圖1 化合物Antrodin C結構式Fig.1 Structural formula of antrodin C
1 材料與方法
1.1 材料與試劑
1.1.1 菌種
樟芝菌A.camphorata 上海福茂食用菌有限公司。
1.1.2 試劑
葡萄糖、麥芽糖、蔗糖、MgSO4、KH2PO4、正己烷、乙酸乙酯、無水乙醇均為國產分析純試劑;乙腈(色譜純)、甲醇(色譜純) 德國Meker公司;黃豆粉、豆粕、玉米漿粉 市售。
1.2 儀器與設備
Agilent 1200高效液相色譜系統 美國Agilent公司;液相色譜-質譜儀 美國Waters公司;核磁共振譜儀 瑞士Bruker公司;恒溫搖床 太倉市實驗設備廠。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 培養基與培養條件
樟芝菌A.camphorata接種于PDA斜面,28℃避光培養9 d,于4℃保藏。
孢子懸浮液制備:取PDA斜面,利用含有吐溫-80 (體積分數0.1% )的無菌水25mL洗下茄子瓶斜面的孢子,鏡檢孢子數達到1×106個/mL。
種子培養基:葡萄糖 20g/L、黃豆粉4g/L、MgSO40.5g/L、KH2PO40.5g/L,pH 5.5。液體種子在28℃、110r/min條件下培養4d。
液態發酵基礎培養基:葡萄糖50g/L、黃豆粉4g/L、MgSO40.5g/L、KH2PO40.5g/L,pH 5.5。接種量為15%,在28℃、110r/min條件下培養7d。
所有培養基均在115℃滅菌20min。
1.3.2 Antrodin C和菌體量分析
1.3.2.1 Antrodin C的確定
取樟芝液態發酵菌體粉末30g,無水乙醇50℃振蕩萃取1h,重復萃取兩次。將萃取液真空濃縮后用乙酸乙酯-水進行分配萃取,然后濃縮乙酸乙酯層得到樟芝菌體粗提物,4℃放置備用。將樟芝菌體粗提物進行硅膠柱層析,洗脫液為正己烷-乙酸乙酯(體積比為19:1~1:5),得到10個洗脫組分。將組分6反復進行硅膠柱層析和制備液相,得到化合物AC-2。制備液相色譜條件為:色譜柱:Sepax Sapphire C18(10.0mm×250mm);流動相:體積比85:15甲醇-水;檢測波長254nm。將制備得到的化合物AC-2進行質譜和核磁分析,確認其結構。
1.3.2.2 Antrodin C含量測定
采用HPLC法測定Antrodin C含量。取樟芝菌發酵液100mL,抽濾得到較干菌體,加入少量無水乙醇研磨5min,然后用無水乙醇定容至100mL,50℃振蕩萃取1.5h,靜置后0.22μm濾膜過濾,進行HPLC分析,分析條件如下:色譜柱:Sepax Amethyst C18(4.6mm×150mm);流速:1mL/min;檢測波長:254nm;流動相A:水-乙酸體積比200:1:流動相B:乙腈;洗脫梯度如下:0~15min,流動相B 50%~100%;15~15.5min,流動相B 100%~50%;15.5~25min,流動相B 50%。
Antrodin C標樣由本實驗室自行制備,經過UV、MS、NMR、HPLC分析,其純度≥96%。
1.3.2.3 菌體生物量測定
將發酵液抽濾后,收集菌體,50℃烘干至恒質量,稱質量并測定水分。
1.3.3 試驗設計
1.3.3.1 Plackett-Burman設計
Plackett-Burman設計是一種篩選關鍵影響因素的有效方法,特別是針對多變量的試驗體系。試驗采用12個Plackett-Burman設計,評估11個因素(包括3個虛擬項)對樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C的影響。每個因素設定兩個水平:-1代表低水平,1代表高水平。試驗設計的因素和水平如表1所示。不同因素的水平取值是根據前期實驗結果而設定的。利用Design Expert 7.0軟件對結果進行分析,篩選出顯著影響樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C的因素。

表1 Plackett-Burman試驗因素及水平Table 1 Factors and levels of Plackett-Burman design g/L
1.3.3 響應面試驗設計
響應面試驗分析同樣采用Design Expert 7.0軟件。根據Box-Behnken模型的中心組合試驗設計原理,設計三因素三水平共15個響應面試驗,低中高3個水平分別用-1、0、1代表,試驗設計見表2。

表3 Plackett-Burman試驗設計及結果Table 3 Plackett-Burman design arrangement and results
2 結果與分析
2.1 Antrodin C的確定和初步測定
分離純化得到的化合物AC-2為黃色油狀液體,UV (乙醇)最大吸收波長為235.2nm,EIMS m/z:330[M+1]+、262、264、173,與文獻報道一致[15]。1H NMR和13C NMR的數據與文獻報道的Antrodin C一致[7]。確認HPLC圖譜中的化合物AC-2就是Antrodin C。前期對碳氮源進行預篩選,測得Antrodin C產量為95.72mg/L。
2.2 Plackett-Burman設計法篩選重要因子
實驗過程中每組發酵設定3個平行樣,2 8℃、110r/min培養7d,以發酵終期Antrodin C產量為響應值,結果如表3所示,Antrodin C產量變化幅度30.79~141.33mg/L較大,表明實驗優化過程對樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C非常重要。利用Design Expert 7.0軟件對實驗結果進行分析。
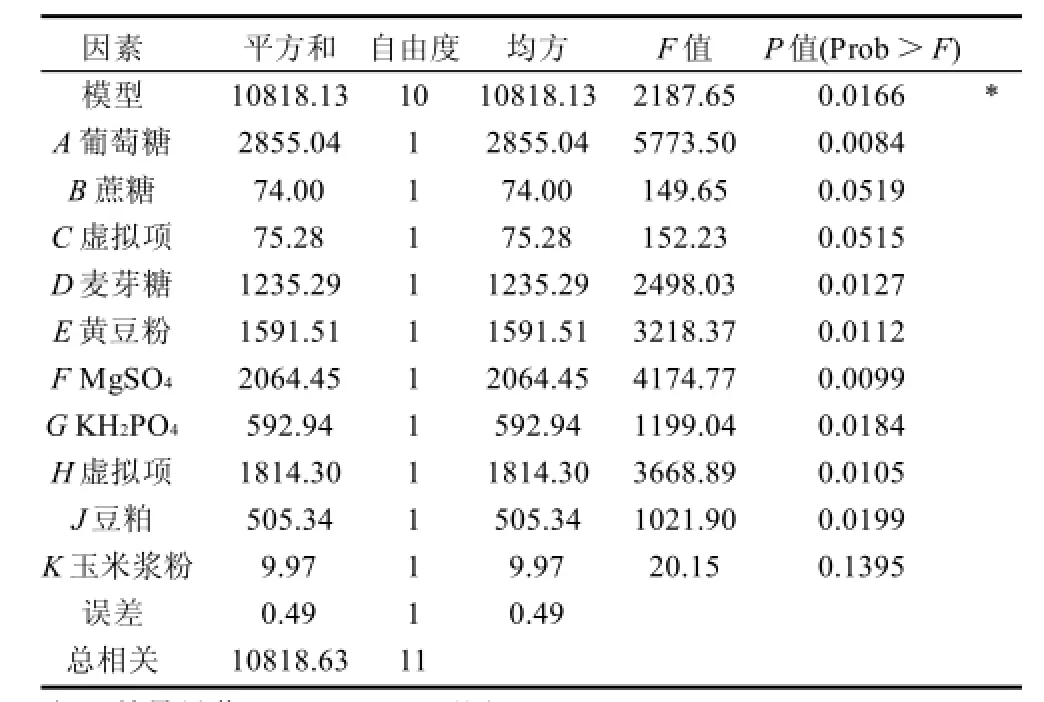
表4 Plackett-Burman試驗分析結果Table 4 Analysis of variance for the regression model established based on Plackett-Burman design
由表4可知,回歸模型的P值為0.0166(P<0.05),說明該模型顯著。即該模型在被研究的整個回歸區域擬合良好。培養基中各因素對樟芝液態發酵Antrodin C產量(R)的影響效應大小順序依次為:葡萄糖> MgSO4>黃豆粉>麥芽糖>KH2PO4>豆粕>蔗糖>玉米漿粉,其中葡萄糖(P=0.0084 )、MgSO4(P=0.0099)、黃豆粉(P=0.0112)是主要的影響因素。其他因素玉米漿粉、麥芽糖、KH2PO4、豆粕、蔗糖雖有影響,但是小于上述3個因素。因此,確定葡萄糖、MgSO4、黃豆粉為影響Antrodin C產量(R)的3個顯著性因素,利用響應面分析法對培養基的這3個組分進行更深入的研究。
通過Design Expert軟件對數據進行分析,獲得多元一次回歸方程:
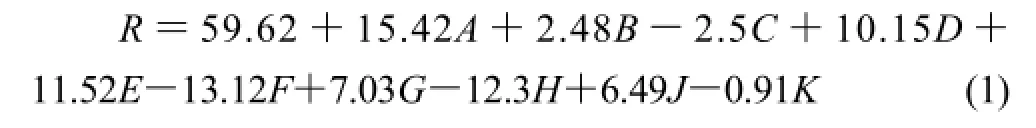
2.3 響應面分析
2.3.1 響應面回歸模型的建立和分析

表5 Box-Behnken試驗設計下Antrodin C產量分析Table 5 Box-Behnken experimental design and results for response surface analysis
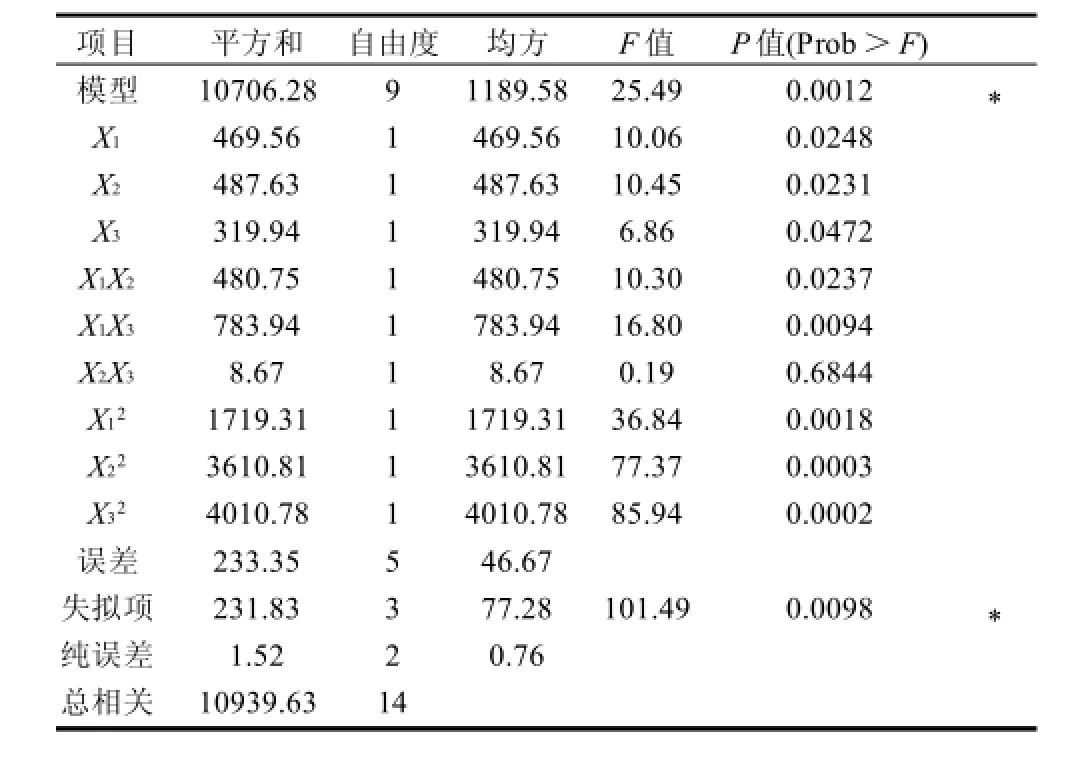
表6 Box-Behnken試驗設計下影響Antrodin C產量回歸方程的顯著性檢驗Table 6 Significance analysis for the regression model established based on Box-Behnken design
選取葡萄糖、MgSO4、黃豆粉為自變量,實驗設計及結果如表5所示。通過Design Expert軟件對實驗數據進行二次多項式回歸擬合,獲得樟芝液態發酵Antrodin C產量(Y)對葡萄糖、黃豆粉、MgSO4的二次多項式回歸方程為:
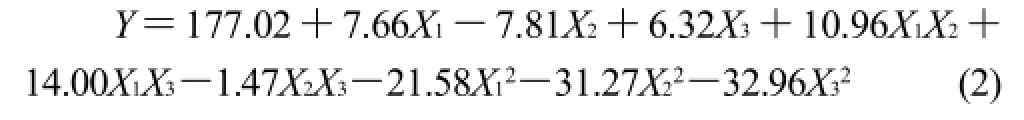
該二次項方程及各項方差分析如表6所示。模型F值為25.49,P值為0.0012,說明模型高度顯著。方差分析表明,葡萄糖、黃豆粉、MgSO4的二次項對Antrodin C合成有顯著影響。此模型相關系數R2=0.9787,表明回歸方程的擬合程度較好,預測值和實測值之間具有高度的相關性,可以應用于樟芝Antrodin C產量的理論預測。模型中失擬項P值為0.0098,說明由噪音引起模型偏差的概率為0.98%,模型失擬項顯著。
2.3.2 顯著影響因素的交互作用分析
經Design Expert軟件分析可得到3個顯著影響因子之間的響應面分析圖和等高圖,如圖2~4所示。響應面分析圖譜表示兩組獨立變量對樟芝液太發酵產Antrodin C的影響,而另外一個因素取0水平值。等高線圖譜表示兩組獨立變量的交互作用是否顯著,形狀越橢圓說明交互作用影響越顯著。由圖2~4可知,每組響應面圖譜都有明顯的頂峰,即影響因素的最佳值落在試驗設計的取值范圍內。葡萄糖和黃豆粉以及葡萄糖和MgSO4這兩組影響因素兩兩之間的交互作用對Antrodin C的合成均有顯著影響。
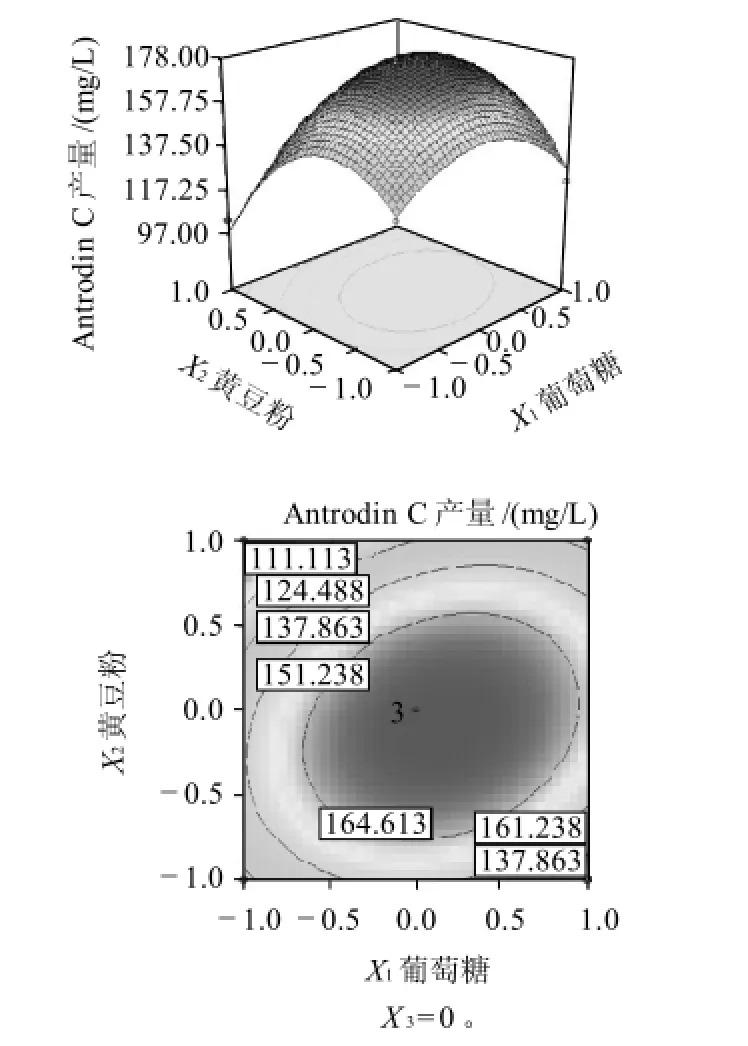
圖2 葡萄糖和黃豆粉交互作用對Antrodin C產量影響Fig.2 Effects of glucose and soybean flour on antrodin C production
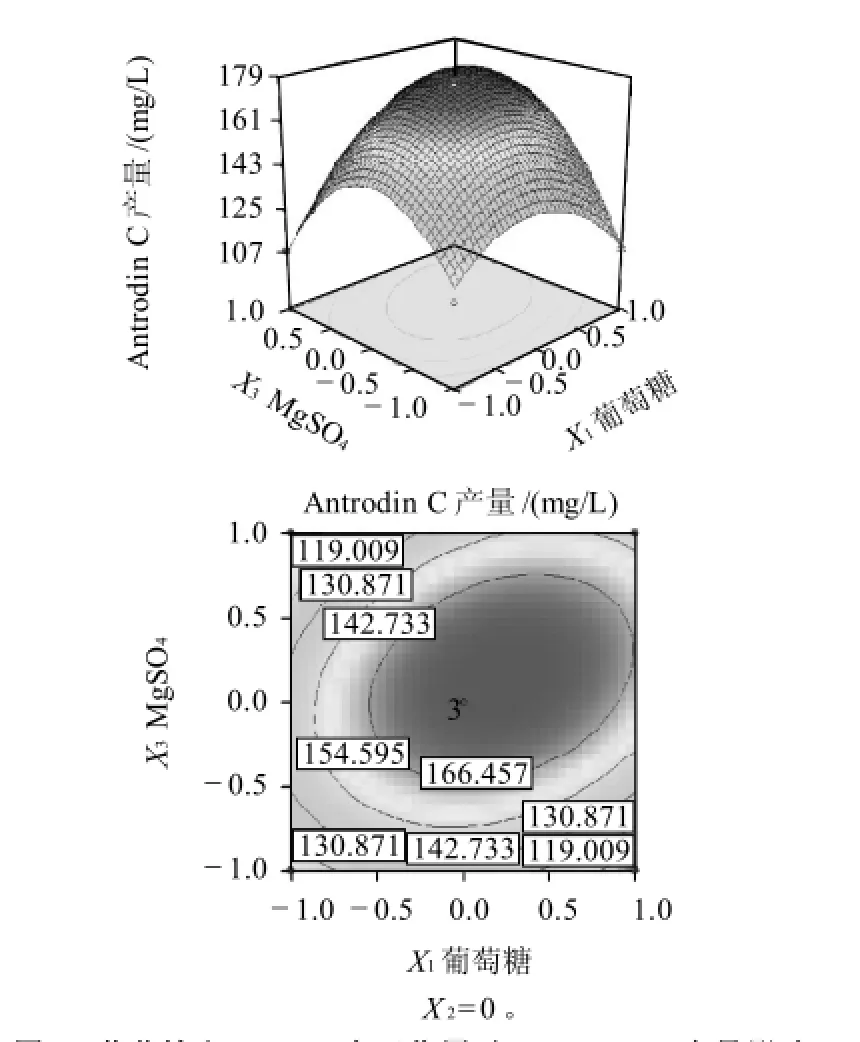
圖3 葡萄糖和MgSO4交互作用對Antrodin C產量影響Fig.3 Effects of glucose and MgSO4 on antrodin C production
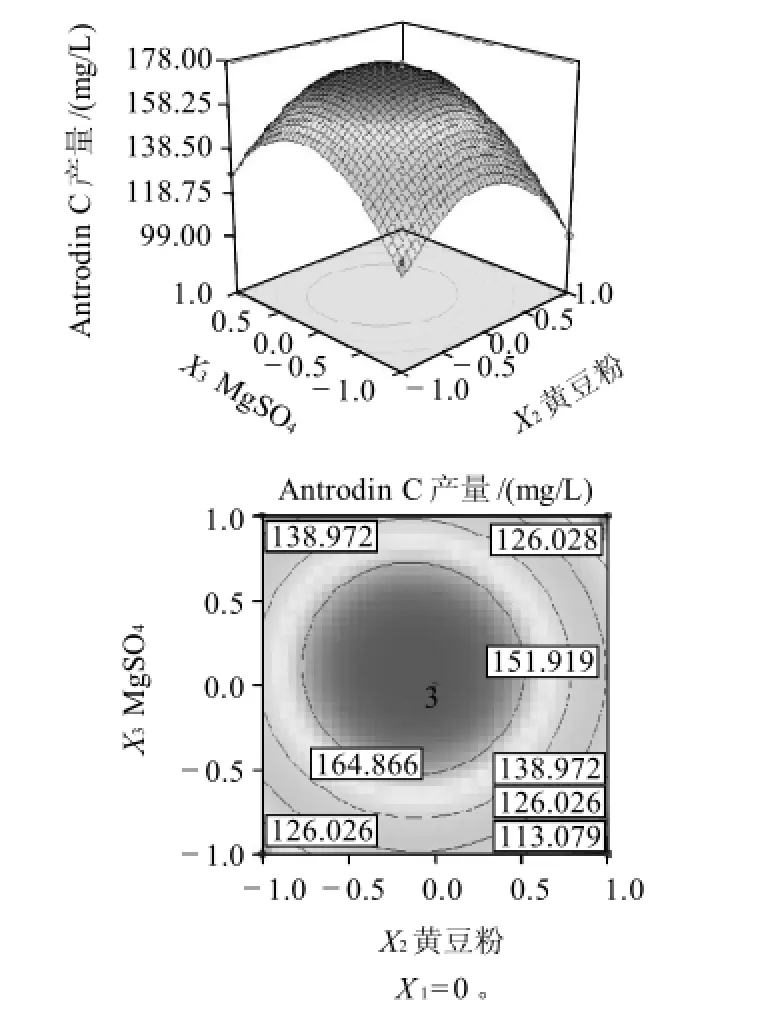
圖4 黃豆粉和MgSO4交互作用對Antrodin C產量影響Fig.4 Effects of soybean powder and MgSO4 on antrodin C production
2.4 樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C最優培養基配方的獲取與驗證
對模型回歸方程進行進一步分析,回歸模型存在穩點,穩點為樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C量最大值,即得到的最優培養基組成為葡萄糖72.0g/L、黃豆粉5.91g/L、MgSO40.614g/L時,理論上樟芝液態發酵培養基Antrodin C產量的最大值為178.59mg/L。
根據上述回歸分析結果和響應面試驗特點,在實驗水平內進行驗證,發酵7d后實際Antrodin C產量為(177.83±0.32)mg/L,菌體生物量達到13.4g/L,可見該模型能較好地預測實際產Antrodin C情況。
3 結 論
本實驗首次對樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C的培養基進行統計學篩選和響應面優化。結果顯示,統計學優化策略能非常有效的優化調控樟芝液態發酵過程中活性代謝產物。葡萄糖、黃豆粉和MgSO4對Antrodin C的產量影響最為顯著。在葡萄糖72.0g/L、黃豆粉5.91g/L、MgSO40.614g/L時Antrodin C產量最大預測值為178.59mg/L。通過實驗驗證,樟芝液態發酵產Antrodin C產量達到(177.83±0.32)mg/L,比優化前(95.72mg/L)提高了85.8%。實驗中發現,麥芽糖對樟芝液態發酵的影響也較大,能夠較快的促進樟芝的生長,因此在后續實驗中可以考慮利用葡萄糖和麥芽糖的混合碳源進行發酵。
[1]SHAO Y Y, CHEN C C, WANG H Y. Chemical constituents of Antrodia camphorata submerged whole broth[J]. Natural Product Research, 2008, 22(13): 1151-1157.
[2]HSU Y L, KUO Y C, KUO P L, et al. Apoptotic effects of extract from Antrodia camphorata fruiting bodies in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines[J]. Cancer Lett, 2005, 221(1): 77-89.
[3]TZENG Y M, GEETHANGILI M, LING S T. Purification of bioactive compounds from Antrodia camphorata and their pharmacological activities [J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2009, 108(1): 21-28.
[4]SONG T Y, YEN G C. Antioxidant properties of Antrodia camphorata in submerged culture[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2002, 50(11): 3322-3327.
[5]LIU J J, HUANG T S, HSU M L, et al. Antitumor effects of the partially purified polysaccharides from Antrodia camphorata and the mechanism of its action[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2004, 201(2): 186-193.
[6]CHEN J J, LIN W J, LIAO C H, et al. Anti-inflammatory benzenoids from Antrodia camphorata[J]. J Nat Prod, 2007, 70(6): 989-992.
[7]NAKAMURA N, HIRAKAWA A, GAO J J, et al. Five new maleic and succinic acid derivatives from the mycelium of Antrodia camphorata and their cytotoxic effects on LLC tumor cell line[J]. Journal of Nature Product, 2004, 67(1): 46-48.
[8]PHUONG T, MA C M, HATTORI M, et al. Inhibitory effects of antrodins A-E from Antrodia camphorata and their metabolites on hepatitis C virus protease[J]. Phytother Res, 2009, 23(4): 582-584.
[9]WU M D, CHENG M J, WANG B C, et al. Maleimide and maleic anhydride derivatives from the mycelia of Antrodia cinnamomea and their nitric oxide inhibitory activities in macrophages[J]. J Nat Prod, 2008, 71(7): 1258-1261.
[10]SHU C H, LUNG M Y. Effect of pH on the production and molecular weight distribution of exopolysaccharide by Antrodia camphorata in batch cultures[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2004, 39(8): 931-937.
[11]SHIH I L, PAN K, HSIEH C. Influence of nutritional components and oxygen supply on the mycelial growth and bioactive metabolites production in submerged culture of Antrodia cinnamomea[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2006, 41(5): 1129-1135.
[12]賈薇, 劉艷芳, 張勁松, 等. 樟芝深層發酵培養條件的優化[J]. 食品科學, 2004, 25(5): 52-55.
[13]凌慶枝, 劉國慶, 袁懷波, 等. pH和無機鹽對樟芝液體發酵的影響[J]. 食品科學, 2007, 28(11): 365-369.
[14]SHU C H, LUNG M Y. Effect of culture pH on the antioxidant properties of Antrodia camphorata in submerged culture[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2008, 39(1): 1-8.
[15]LIU Yongli, DI Xin, LIU Xingchao, et al. Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the determination of antrodin B and antrodin C from Antrodia camphorata extract in rat plasma for pharmacokinetic study[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2010, 53(3): 781-784.
Optimization of Medium Components for Antrodin C Production by Antrodia camphorata Using Response Surface Methodology
XIA Yong-jun,ZHANG Xian-fang,XU Gan-rong*
(Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, China)
The bioactive compound antrodin C was analyzed in the mycelia of A. camphorata in submerged fermentation. The fermentation medium for antrodin C production was optimized using Plackett-Burman design and response surface methodology. The results showed that glucose, soybean powder flour and MgSO4were the major factors that influence the production of antrodin C. Box-Behnken design and response surface analysis were used to determine the optimal response value of the major factors. A quadratic regression model was established. Based on response surface analysis of the mathematical model, the optimal culture medium composition was determined as glucose 72.0 g/L, soybean flour 5.91 g/L and MgSO4 0.614 g/L. The predicted yield of antrodin C was 178.59 mg/L. After cultivation under the optimal conditions for 7 days, the content of antrodin C reached up to (177.83 ± 0.32) mg/L, which was 85.8% higher than before the optimization (95.72 mg/L).
Antrodia camphorata;submerged fermentation;antrodin C;identification;Plackett-Burman;response surface methodology
Q815
A
1002-6630(2012)11-0185-05
2011-06-08
夏永軍(1981—),男,博士研究生,研究方向為藥用真菌人工培養及其活性產物。E-mail:dreamup@126.com
*通信作者:許贛榮(1954—),男,教授,博士,研究方向為藥用真菌培養、生物技術在煙草加工中的應用、粗甘油的高附加值轉化。E-mail:grxu123@126.com

