罕見胰腺腫瘤:來自良性平滑肌瘤轉(zhuǎn)移1例及文獻(xiàn)復(fù)習(xí)
姜翀弋+王巍+袁祖榮
摘 要 通過罕見胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤1例及相關(guān)文獻(xiàn)復(fù)習(xí),對胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤的鑒別診斷和治療方法進(jìn)行闡述,為社區(qū)醫(yī)生拓寬思路,減少誤診提供幫助。
關(guān)鍵詞 胰腺 轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤 鑒別診斷
中圖分類號:R734.2 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識碼:A 文章編號:1006-1533(2014)04-0012-03
Rare pancreatic tumor: one case with pancreatic
benign metastasiging leiomyoma and review of literature
JIANG Chongyi, WANG Wei, YUAN Zurong
(Biliary and Pancreatic Diseases Diagnosis and Treatment Center of General
Surgical Department of Huadong Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200040, China)
ABSTRACT Through a case of rare pancreatic metastatic tumor and the related literature review, this article elaborates the differential diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic metastatic tumors to help broaden the idea of community physicians to reduce misdiagnosis.
KEY WORDS pancreas; metastatic tumor; differential diagnosis
胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤在臨床上少見,其發(fā)生率約占胰腺腫瘤的2.0%~5.0%[1-2]。從原發(fā)腫瘤出現(xiàn)到發(fā)生腫瘤胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移的平均間隔期約為9年[2-3]。最常見的胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移腫瘤來自腎癌、肺癌、乳腺癌或結(jié)腸癌[1,4]。黑色素瘤、甲狀腺癌與間質(zhì)腫瘤的胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移也有報道[5]。由于胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤的臨床癥狀與胰腺原發(fā)腫瘤相似,因此在診斷上常難以進(jìn)行鑒別[6]。子宮來源的胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤更為罕見,僅有少量病例報道,且均為惡性腫瘤[7-9]。我們報道1例子宮肌瘤來源的胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤。
1 病例介紹
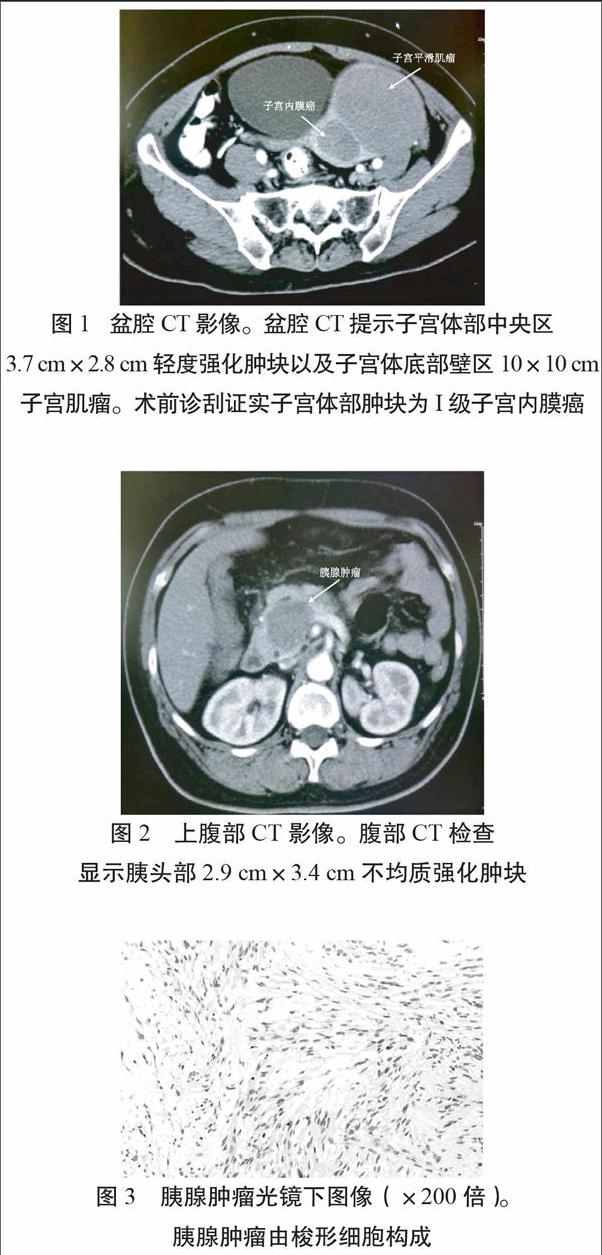
52歲女性患者,因為絕經(jīng)后陰道出血1月來我院就診。無腹痛、黃疸、發(fā)熱、體重減輕或其他伴隨癥狀。體檢捫及下腹部約10 cm腫塊,質(zhì)硬,固定,邊界清楚。術(shù)前常規(guī)實驗室檢查以及腫瘤標(biāo)志物(包括CA19-9、CA-125)均正常。盆腔CT檢查提示子宮體部中央?yún)^(qū)3.7 cm×2.8 cm輕度強(qiáng)化腫塊,以及子宮體底部壁區(qū)10×10 cm子宮肌瘤(圖1)。此外,上腹部CT檢查時偶然發(fā)現(xiàn)胰頭部存在2.9 cm×3.4 cm不均質(zhì)強(qiáng)化腫塊(圖2)。術(shù)前經(jīng)診刮證實子宮體部腫塊為I級子宮內(nèi)膜癌。患者遂接受手術(shù),術(shù)中發(fā)現(xiàn)胰頭部腫瘤直接侵犯腸系膜上靜脈,無法切除,通過前列腺穿刺針行胰腺腫瘤穿刺活檢,并行子宮加雙側(cè)附件切除術(shù)。術(shù)后病理學(xué)檢查證實子宮腫瘤為子宮內(nèi)膜癌,侵犯子宮肌層。子宮壁的巨大腫塊為子宮肌瘤。在顯微鏡下見胰腺腫瘤組織的梭形細(xì)胞,無壞死與有絲分裂象(圖3)。胰腺腫瘤的免疫組化顯示SMA、desmin與vimentin強(qiáng)陽性,CD117與S-100陰性,雌激素與孕激素受體陽性。根據(jù)上述病理學(xué)檢查結(jié)果與免疫組化特征,我們考慮該胰腺腫瘤為良性轉(zhuǎn)移性平滑肌瘤(benign metastasizing leiomyoma, BML)。該患者術(shù)后拒絕接受任何后續(xù)治療。在一年的隨訪期間,沒有發(fā)現(xiàn)胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移腫瘤增大或其他復(fù)發(fā)跡象。
2 討論
臨床上胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤極少見。Faure等[10]分析269例手術(shù)切除的胰腺腫瘤病例中轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤僅有8例(3.0%)。Minni等[11]總結(jié)708例胰腺腫瘤病例僅發(fā)現(xiàn)3例轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤(0.4%)。Adsay等[5]回顧分析了973例胰腺腫瘤切除標(biāo)本,其中胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤38例(3.8%),以肺癌轉(zhuǎn)移最為多見,其次為消化道腫瘤與淋巴瘤。由于胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤無特異臨床癥狀,約有1/3的病例在術(shù)前會被誤認(rèn)為胰腺原發(fā)性腫瘤。Lee等[12]回顧文獻(xiàn)發(fā)現(xiàn),胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤有5.0%患者存在體重降低,腹痛占20.0%,黃疸30.0%,而超過45.0%的患者無任何癥狀。有報道認(rèn)為影像學(xué)檢查對于胰腺原發(fā)和轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤的鑒別沒有幫助[13]。細(xì)針穿刺活檢可能有助于術(shù)前診斷[14-16]。
術(shù)前我們曾考慮本病例胰腺腫瘤為子宮內(nèi)膜癌轉(zhuǎn)移可能,但缺乏影像學(xué)依據(jù)支持。由于擔(dān)心穿刺活檢可能導(dǎo)致出血、胰瘺等相關(guān)并發(fā)癥,因而選擇了直接行剖腹探查。術(shù)后胰腺標(biāo)本的病理學(xué)檢查提示該腫瘤由梭形細(xì)胞構(gòu)成,結(jié)合病理檢查與免疫組化檢測結(jié)果提示為BML。BML為來源于子宮平滑肌瘤的轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤,發(fā)生率較低,迄今臨床報道的病例數(shù)僅百余例[17-18]。最常見的轉(zhuǎn)移部位為肺或淋巴結(jié)[17],胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移為首次報道。該腫瘤雖發(fā)生轉(zhuǎn)移,但生長緩慢,常無臨床表現(xiàn),具有激素依賴性特點,預(yù)后較好[17-18]。
對于腫瘤的孤立性轉(zhuǎn)移病灶,目前均認(rèn)為手術(shù)切除有助于改善患者的預(yù)后[19]。但胰腺手術(shù)相關(guān)的巨大手術(shù)創(chuàng)傷,使臨床醫(yī)生對胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤患者是否能夠從手術(shù)治療中獲益存在疑問。目前相關(guān)的臨床研究較少。最大宗的報道來自美國麻省總院的Konstantinidis[20],其回顧了15年內(nèi)接受胰腺手術(shù)的2 224例患者,其中40例(1.8%)為胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤。這部分患者的圍手術(shù)期并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率為37.5%,死亡率為2.5%,中位生存時間4.4年,5年生存率42.0%。德國Niess等對26例胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤患者的回顧分析也得到類似的結(jié)論[21],73.0%的患者能達(dá)到R0切除,圍手術(shù)期并發(fā)癥發(fā)生率35.0%,無圍手術(shù)期死亡病例,患者3年生存率73.2%,5年生存率52.3%,中位生存時間63個月。此外,胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤的手術(shù)切除率可達(dá)64.0%,遠(yuǎn)高于胰腺導(dǎo)管腺癌15.0%~20.0%的手術(shù)切除率[11]。上述研究結(jié)果提示對于全身狀況較好的胰腺孤立轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤患者采取積極的手術(shù)治療可有效改善患者預(yù)后[20-21]。
3 結(jié)論
胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移性腫瘤的臨床發(fā)生率低,術(shù)前鑒別診斷較困難。細(xì)致的病史采集結(jié)合影像學(xué)檢查與穿刺活檢可能有助于診斷。手術(shù)切除胰腺轉(zhuǎn)移病灶是可以考慮的治療方案,尤其對于經(jīng)過充分評估的病例,手術(shù)有助于改善患者預(yù)后。
參考文獻(xiàn)
[1] Ballarin R, Spaggiari M, Cautero N, et al. Pancreatic metastases from renal cell carcinoma: the state of the art[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17(43): 4747-4756.
[2] Reddy S, Edil BH, Cameron JL, et al. Pancreatic resection of isolated metastases from nonpancreatic primary cancers[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2008, 15(11): 3199-3206.
[3] Eidt S, Jergas M, Schmidt R, et al. Metastasis to the pancreas—an indication for pancreatic resection?[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2007, 392(5): 539-542.
[4] Tsitouridis I, Diamantopoulou A, Michaelides M, et al. Pancreatic metastases: CT and MRI findings[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2010, 16(1): 45-51.
[5] Adsay NV, Andea A, Basturk O, et al. Secondary tumors of the pancreas: an analysis of a surgical and autopsy database and review of the literature[J]. Virchows Arch, 2004, 444(6): 527-535.
[6] Sparks DA, Chase DM, Forsyth M, et al. Late presentation of a mucinous ovarian adenocarcinoma which was initially diagnosed as a primary pancreatic carcinoma: a case report and review of the literature[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2010, 4: 90. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-90.
[7] Nishimura C, Naoe H, Hashigo S, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterine cervix: a case report[J]. Case Rep Oncol, 2013, 6(2): 256-262.
[8] Kuwatani M, Kawakami H, Asaka M, et al. Pancreatic metastasis from small cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix demonstrated by endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration[J]. Diagn Cytopathol, 2008, 36(11): 840-842.
[9] Garcia-Calvo M, Lisnock J, Bull HG, et al. The target of ezetimibe is Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1)[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(23): 8132-8137.
[10] Faure JP, Tuech JJ, Richer JP, et al. Pancreatic metastasis of renal cell carcinoma: presentation, treatment and survival[J]. J Urol, 2001, 165(1): 20-22.
[11] Minni F, Casadei R, Perenze B, et al. Pancreatic metastases: observations of three cases and review of the literature[J]. Pancreatology, 2004, 4(6): 509-520.
[12] Lee CW, Wu RC, Hsu JT, et al. Isolated pancreatic metastasis from rectal cancer: a case report and review of literature[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2010, 8: 26. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-8-26.
[13] Charnsangavej C, Whitley NO. Metastases to the pancreas and peripancreatic lymph nodes from carcinoma of the right side of the colon: CT findings in 12 patients[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1993, 160(1): 49-52.
[14] Larghi A, Lugli F, Sharma V, et al. Pancreatic metastases from a bronchopulmonary carcinoid diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle tissue acquisition[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(3): 502-504.
[15] Gagovic V, Spier BJ, DeLee RJ, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound fine-needle aspiration characteristics of primary adenocarcinoma versus other malignant neoplasms of the pancreas[J]. Can J Gastroenterol, 2012, 26(10): 691-696.
[16] Gilani SM, Tashjian R, Danforth R, et al. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the pancreas: diagnostic significance of fine-needle aspiration cytology[J]. Acta Cytol, 2013, 57(4): 418-422.
[17] Lim SY, Park JC, Bae JG, et al. Pulmonary and retroperitoneal benign metastasizing leiomyoma[J]. Clin Exp Reprod Med, 2011, 38(3): 174-177.
[18] Xiao H, Li B, Li W, et al. A rare case of benign abdominal wall and pelvic metastasizing leiomyomas following hysterectomy[J]. J Obstet Gynaecol, 2012, 32(2): 198-199.
[19] Poston GJ. Surgical strategies for colorectal liver metastases[J]. Surg Oncol, 2004, 13(2-3): 125-136.
[20] Konstantinidis IT, Dursun A, Zheng H, et al. Metastatic tumors in the pancreas in the modern era[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2010, 211(6): 749-753.
[21] Niess H, Conrad C, Kleespies A, et al. Surgery for metastasis to the pancreas: is it safe and effective?[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2013, 107(8): 859-864.
(收稿日期:2013-09-16)

