運動降低冠心病發病率與血漿氧化低密度脂蛋白低水平相關
張寶瑋龔 惠張 潔
(1上海立信會計學院體育教學部 上海 200235;2上海市第一人民醫院影像科 上海 200013;3復旦大學生物醫學研究院 上海 200032)
運動降低冠心病發病率與血漿氧化低密度脂蛋白低水平相關
張寶瑋1龔 惠3張 潔2△
(1上海立信會計學院體育教學部 上海 200235;2上海市第一人民醫院影像科 上海 200013;
3復旦大學生物醫學研究院 上海 200032)
目的 探討運動降低冠心病發病率與血漿氧化低密度脂蛋白(oxidized low density lipoprotein,Ox-LDL)低水平相關。方法健康體檢者和急性心梗(acute myocardial infarction,AMI)患者根據有無高血脂分為常脂組和高脂組,再根據有無運動習慣進一步分為運動組和對照組,觀察血脂參數總膽固醇、三酰甘油、高密度脂蛋白、低密度脂蛋白及Ox-LDL的水平,并分析AMI患者的血管病變程度。結果與健康體檢者相比,無論是高脂還是常脂的AMI患者血漿Ox-LDL水平均明顯升高。運動組的血漿Ox-LDL水平比相應對照組低,但其他血脂參數的差異不大。在AMI患者中,運動組多支冠狀動脈損害較對照組輕微。結論運動抑制冠心病的發生發展與血漿Ox-LDL低水平可能相關,培養運動習慣可在一定程度上抑制冠心病的發生發展。
運動; 冠心病; 氧化低密度脂蛋白; 血脂
【Abstraet】 Objcetivc To explore whether the occurrence of coronary heart disease prevented by sport has relationship to the low level of plasma oxidized low density lipoprotein(Ox-LDL). Mcthods
Healthy subjects and patients with acute myocardial infarction(AMI)were recruited in the trial and were devided into hyperlipidemia group and ortholiposis group,respectively,which were re-devided into sport group and control group.The plasma lipids parameters,such as TC,TG,HDL,LDL and Ox-LDL,were evaluated,and the vascular damage was analyzed in AMI patients. Rcsults Plasma Ox-LDL level was significantly increased in AMI patients compared to healthy subjects.Sport greatly decreased plasma Ox-LDL level either in healthy subjects with hyperlipidemia or in AMI patients with or without hyperlipidemia,although it had little effect on other plasma lipids level.In AMI patients,multi-vessel damage in sport group was better than that in control group. Conelusions The high level of Ox-LDL may be one of critical factors for the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease.Sport couldprevent the occurrence and development of coronary heart disease in subjects with or without hyperlipemia,which is associated with low Ox-LDL level in plasma.
【Kcy words】 sport; coronary heart disease; oxidized low density lipoprotein; plasma lipid
*This work was supportcd by thc National Natural Seicnec Foundation of China(81370258).
血脂代謝異常是引起冠心病的重要原因。運動對血脂具有調控作用,提示運動調控血脂可防治冠心病。目前臨床上檢測的血脂參數主要有總膽固醇(total cholesterol,TC),三酰甘油(triacylglycerol,TG),高密度脂蛋白(high-density lipoprotein,HDL),低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL),其中LDL被認為是導致冠脈粥樣硬化的主要脂蛋白[1]。有研究認為運動可降低血清LDL水平,尤其可降低高脂患者的LDL水平,但也有研究認為運動對LDL無明顯影響[2]。傳統觀念認為血漿LDL高水平導致LDL氧化生成氧化LDL (oxidized LDL,Ox-LDL)[3],而Ox-LDL可導致冠狀血管內皮炎癥、凋亡等損傷,進而發展為冠心病[4]。即使血漿LDL水平正常,體內炎癥等因素也會引起LDL氧化,從而導致血漿Ox-LDL水平急劇升高,引發冠心病[5]。
本研究在健康體檢者和急性心梗(acute myocardial infarction,AMI)患者中分別篩選出有運動習慣和無運動習慣的人群,觀察運動對血脂參數TC、TG、HDL、LDL及血漿Ox-LDL水平的作用,并比較有無運動習慣的AMI患者心梗發展的嚴重程度,從而研究運動是否與血漿Ox-LDL低水平相關,以期為防治冠心病提供參考。
資料和方法
研究對象健康體檢者來自上海市第一人民醫院門診體檢者,年齡40~70歲,男女不限,無代謝性疾病,無高血壓[收縮壓<140 mmHg(1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa,下同),舒張壓<90 mmHg],包括部分高血脂但無器質性病變的體檢者。AMI患者為上海市第一人民醫院心內科收治的初發AMI患者,年齡40~70歲,ST段明顯抬高,診斷明確且病程在3個月以內,糖尿病、高血壓、肝、腎、肺、腦病及其他心臟病和近2周內服用抗氧化劑及調脂劑者除外。健康體檢者和AMI患者在性別及年齡方面無差異。在上述兩組內篩選出入院前有運動習慣者作為運動組,即每天參加快走、慢跑、游泳、打乒乓球等運動40 min以上或每周運動時間>5 h且持續2年以上者。在上述兩組內篩選出2年內基本無運動習慣或每周運動時間<2 h者作為對照組。常脂組:TC<5.2 mmol/L,TG為0.6~1.7 mmol/L,HDL>1.04 mmol/L,LDL<3.12 mmol/L;高脂組:TC、TG或LDL超出上述范圍。除Ox-LDL外,以上血脂參數由我院檢驗科測定。
血漿Ox-LDL檢測所有受試者取靜脈血,離心分離血漿,經LDL沉淀化處理后,用ELISA試劑盒(美國Cell Bio Labs公司)檢測血漿Ox-LDL水平。最終樣品用酶標儀(Infinite M200,瑞士Tecan公司)在波長450 nm處讀取吸光度(D)值,根據標準曲線計算各樣本的Ox-LDL水平。
細胞凋亡檢測培養的冠脈內皮細胞用不同濃度的Ox-LDL和LDL處理48 h后,4%多聚甲醛固定后用TUNEL染色試劑盒(德國默克公司)進行染色,在Leica顯微鏡下觀察拍照,TUNEL陽性核呈棕色(表示細胞凋亡),TUNEL陰性核呈藍色,細胞凋亡率用TUNEL陽性細胞占總細胞的百分數來表示。
統計學分析數據分析和圖標制作使用Prism 5.0軟件,數據結果以±s表示。兩組間比較采用獨立樣本t檢驗,血管病變采用χ2檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義,P<0.01為差異有顯著統計學意義。
結 果
高脂組運動人群的血漿Ox-LDL水平健康體檢者及AMI患者的基本指標見表1,已排除高血壓及器質性病變的患者。在健康體檢者中,有運動習慣的占33.4%,高于AMI組的19.0%。血漿Ox-LDL水平受高脂的影響較大,將健康體檢者分為高脂組和常脂組,分別觀察運動組和對照組的血脂參數TC、TG、LDL、HDL及Ox-LDL水平,以明確運動與血脂的關系(表2)。結果提示,常脂運動組健康體檢者血漿中TC、LDL及Ox-LDL水平較對照組低,差異無統計學意義。高脂組的 TC、TG、LDL、HDL及Ox-LDL均明顯高于常脂組,與對照組相比,運動組的TC、TG、LDL及HDL相應降低,差異無統計學意義,但Ox-LDL顯著降低(P<0.05)。Ox-LDL水平升高是心梗的重要誘發因素,由此推測在高脂狀態下,運動與血漿Ox-LDL低水平相關,可能對于預防心梗有重要作用。
AMI患者運動組的血漿Ox-LDL水平及血管病變程度AMI患者的血脂水平見表3,高脂組的TC、TG和LDL均高于常脂組。無論是高脂還是常脂的AMI患者血漿中Ox-LDL水平均明顯高于健康體檢者的相應各組,但差異無統計學意義。無論在高脂組還是常脂組,運動組的血漿Ox-LDL水平均明顯低于相應對照組,但其他血脂參數變化不大。為了進一步說明運動抑制心梗的發生發展是否與Ox-LDL低水平有關,本研究觀察了AMI患者對照組和運動組的單支血管病變和多支血管病變患者的比例(表4)。結果顯示,運動組的多支病變血管比例為23.4%,明顯低于對照組的42.7%。提示運動與血漿Ox-LDL低水平有關,可能在一定程度上抑制對血管的損傷作用,這可能是運動抑制冠心病發生發展的原因之一。
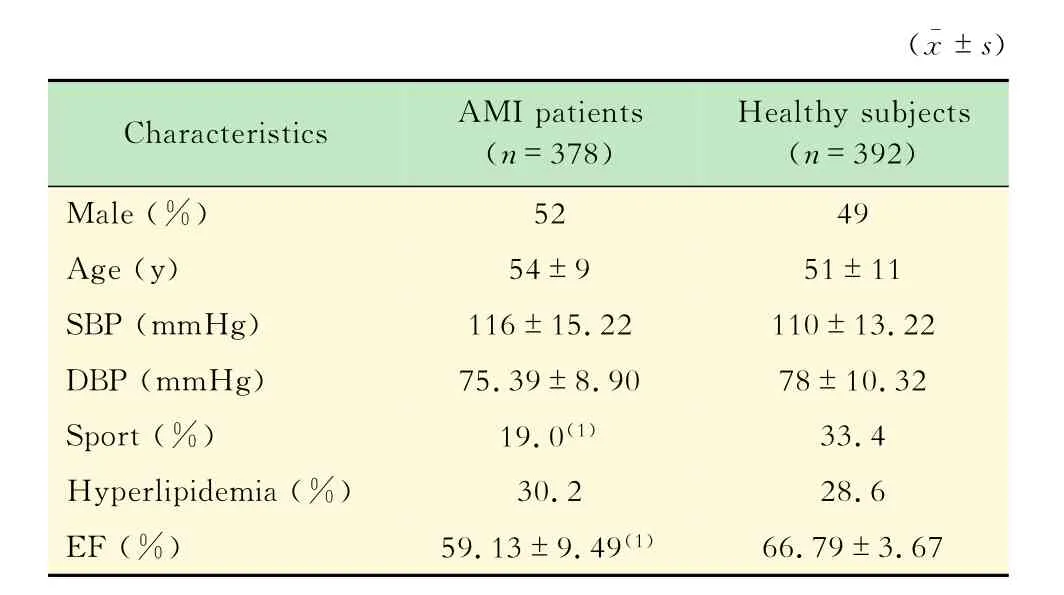
表1 健康體檢者和 AMI患者的基本指標Tab 1 Charaetcristies of hcalthy subjcets and AMI paticnts
表2 運動對健康體檢者血脂的影響Tab 2 Thc cffcet of sport on blood lipids in hcalthy subjcets(±s)
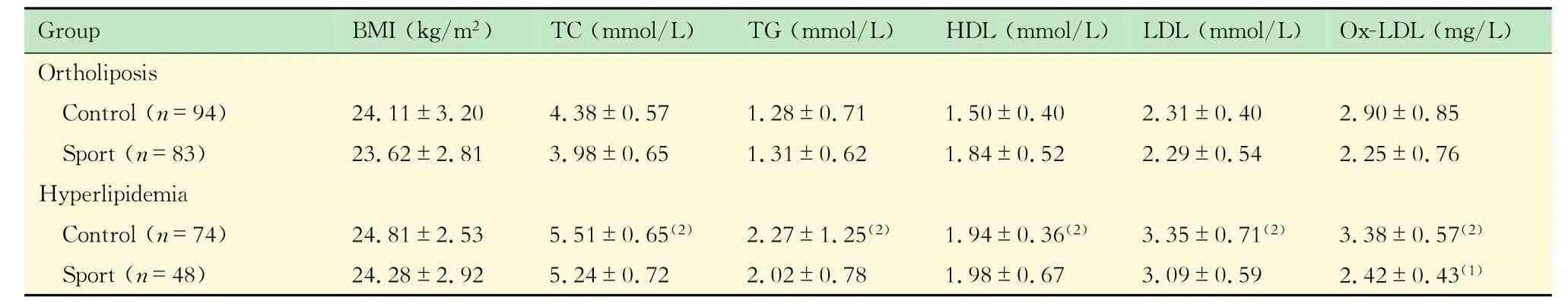
表2 運動對健康體檢者血脂的影響Tab 2 Thc cffcet of sport on blood lipids in hcalthy subjcets(±s)
BMI:Body mass index;TC:Total cholesterol;TG:Triglyceride;HDL:High density lipid;LDL:Low density lipid;Ox-LDL:Oxidized low density lipid.(1)Sport vs.Control,P<0.05;(2)Hyperlipidemia vs.Ortholiposis,P<0.05.
GroupBMI(kg/m2)TC(mmol/L)TG(mmol/L)HDL(mmol/L)LDL(mmol/L)Ox-LDL(mg/L)OrtholiposisControl(n=94)24.11±3.204.38±0.571.28±0.711.50±0.402.31±0.402.90±0.85Sport(n=83)23.62±2.813.98±0.651.31±0.621.84±0.522.29±0.542.25±0.76HyperlipidemiaControl(n=74)24.81±2.535.51±0.65(2)2.27±1.25(2)1.94±0.36(2)3.35±0.71(2)3.38±0.57(2)Sport(n=48)24.28±2.925.24±0.722.02±0.781.98±0.673.09±0.592.42±0.43(1)
表3 運動對AMI患者血脂的影響Tab 3 Thc cffcet of sport on blood lipids of AMI paticnts(±s)
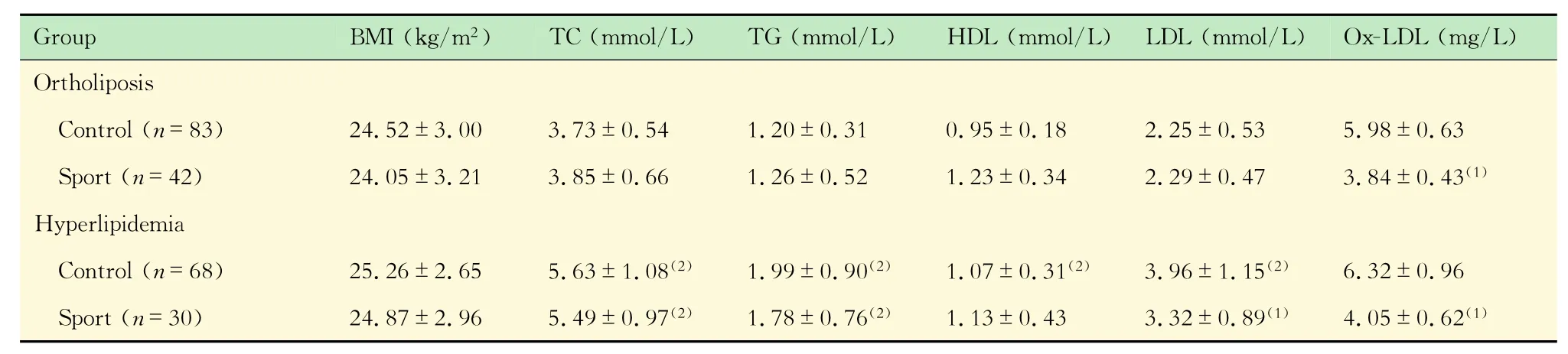
表3 運動對AMI患者血脂的影響Tab 3 Thc cffcet of sport on blood lipids of AMI paticnts(±s)
BMI:Body mass index;TC:Total cholesterol;TG:Triglyceride;HDL:High density lipid;LDL:Low density lipid;Ox-LDL:Oxidized low density lipid.(1)Sport vs.Control,P<0.05;(2)Hyperlipoidemia vs.Ortholiposis,P<0.05.
GroupBMI(kg/m2)TC(mmol/L)TG(mmol/L)HDL(mmol/L)LDL(mmol/L)Ox-LDL(mg/L)OrtholiposisControl(n=83)24.52±3.003.73±0.541.20±0.310.95±0.182.25±0.535.98±0.63Sport(n=42)24.05±3.213.85±0.661.26±0.521.23±0.342.29±0.473.84±0.43(1)HyperlipidemiaControl(n=68)25.26±2.655.63±1.08(2)1.99±0.90(2)1.07±0.31(2)3.96±1.15(2)6.32±0.96Sport(n=30)24.87±2.965.49±0.97(2)1.78±0.76(2)1.13±0.433.32±0.89(1)4.05±0.62(1)
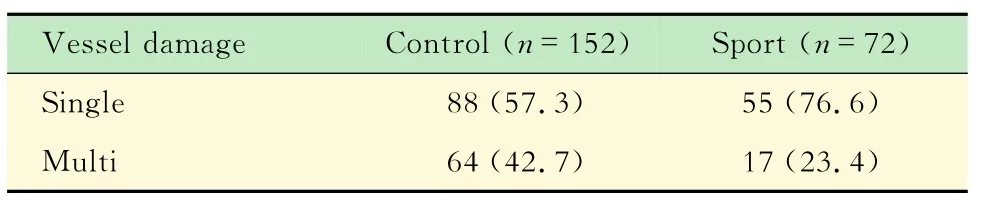
表4 AMI患者運動組和對照組的血管病變Tab 4 Comparison of vcsscl damagc bctwccn sport group and eontrol group in AMI paticnts[n(%)]
討 論
冠心病是由于脂質沉積在冠狀動脈壁,使管腔變窄或完全阻塞導致心肌漸進性或突發性缺血缺氧而引起血管腔狹窄或阻塞,進而造成心肌缺血、缺氧或壞死而引起的心臟病[6],死亡率高。Ox-LDL參與動脈粥樣硬化斑塊(包括冠狀血管內斑塊)形成的多個進程,包括脂質沉積、局部免疫、細胞凋亡等,可導致斑塊破裂等嚴重后果[7]。因此血漿Ox-LDL水平升高被認為是引起動脈粥樣硬化或者動脈粥樣斑塊惡化進而導致冠心病的重要原因之一。
生理情況下,體內氧化系統和抗氧化系統處于相對平衡狀態,體內的LDL不易被氧化或氧化后迅速被清除,因此Ox-LDL在血漿及組織中的含量極低[1,4]。既往研究認為,在高血脂情況下,血漿中增多的脂質以LDL的形式經完整的內膜侵入內皮下發生氧化,從而引起Ox-LDL升高,進一步損傷血管。越來越多的證據表明,即使LDL水平正常,在體內氧化應激水平較高的情況下(如高血壓、感染),LDL也易發生氧化,導致Ox-LDL水平明顯升高,從而導致血管損傷,引起冠心病的發生發展[4]。這可以解釋為何臨床上急性冠心病患者血漿Ox-LDL急劇升高[9],但僅有部分患者伴有高血脂[10]。
有關運動如何降低冠心病發病率的相關報道較多。運動能提高神經系統內分泌系統的功能,產生大量兒茶酚胺,后者一方面促進肝臟脂肪組織中脂肪分解成游離脂肪酸入血,被肌肉等組織攝取并分解產能,另一方面使心臟收縮加強、加快,提高吸氧量,為脂肪的徹底氧化提供足夠的氧氣[11]。既往研究認為,運動對血脂的調控作用是抑制冠心病發生發展的重要原因。有研究顯示運動可明顯降低TC 及LDL,但也有不同觀點認為運動對LDL等影響不大,這可能與入選人群的年齡、運動量及持續時間等多種因素相關[2]。
運動是否與血漿低Ox-LDL水平相關從而抑制冠心病的發生發展,相關研究較少。本研究觀察到,高脂體檢者血漿Ox-LDL水平升高,而運動組血漿Ox-LDL水平相對較低,這可能是運動降低冠心病發病率的原因之一。AMI患者無論是常脂組還是高脂組,血漿Ox-LDL水平均明顯升高,升高程度與冠心病嚴重程度密切相關[12]。AMI患者運動組血漿Ox-LDL水平相應降低,血管損傷程度較對照組輕微。綜上所述,運動與血漿Ox-LDL低水平有關,從而可能抑制血管病變。另外,在健康體檢者和AMI患者中,運動組和對照組相比,LDL和TC的差異無統計學意義,可能與本文研究對象的年齡較大、相對以及運動量相對較小有關。
目前有關運動降低血漿Ox-LDL水平的具體機制研究甚少。Ox-LDL主要由LDL在一些氧化酶的作用下氧化修飾而成,氧自由基等在其生成過程中發揮了重要作用[1]。有氧運動可有效清除氧自由基,抑制過氧化反應[13]。由此推測,運動抑制LDL的氧化修飾,從而降低血漿Ox-LDL水平。因此,培養運動習慣可在一定程度上預防血漿Ox-LDL水平升高,而低水平Ox-LDL對于抑制冠心病的發生發展有一定的作用。
[1] Steinbrecher UP,Parthasarathy S,Leake DS,et al. Modification of low-density lipoprotein by endothelial-cells involves lipid-peroxidation and degradation of low-density lipoprotein phospholipids[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1984,81(12):3883-3887.
[2] Durstine JL,Haskell WL.Effects of exercise training on plasma lipids and lipoproteins[J].Exerc Sport Sci Rev,1994,22:477-521.
[3] Nenseter MS,Gudmundsen O,Malterud KE,et al.Effect of cholesterol feeding on the susceptibility of lipoproteins to oxidative modification[J].Biochim Biophys Acta,1994,1213(2):207-214.
[4] Tsimikas S,Miller YI.Oxidative modification of lipoproteins:mechanisms,role in inflammation and potential clinical applications in cardiovascular disease[J]. Curr Pharm Des,2011,17(1):27-37.
[5] Srimahachota S,Wunsuwan R,Siritantikorn A,et al. Effects of lifestyle modification on oxidized LDL,reactive oxygen species production and endothelial cell viability in patients with coronary artery disease[J].Clin Biochem,2010,43(10-11):858-862.
[6] 葛均波,方唯一,沈偉峰.現代心臟病學進展[M].上海:復旦大學出版社,2012:27.
[7] Colles SM,Maxson JM,Carlson SG,et al.Oxidized LDL-induced injury and apoptosis in atherosclerosis.Potential roles for oxysterols[J].Trends Cardiovasc Med,2001,11 (3-4):131-138.
[8] Hong D,Bai YP,Gao HC,et al.Ox-LDL induces endothelial cell apoptosis via the LOX-1-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway[J].Atherosclerosis,2014,24,235(2):310-317.
[9] Huang H,Ma R,Liu D,et al.Oxidized low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the ratio in the diagnosis and evaluation of therapeutic effect in patients with coronary artery disease[J].Dis Markers,2012,33(6):295-302.
[10] Ekmekcioglu C,Mehrabi MR,Glogar HD,et al.Oxidized low-density lipoprotein is localized in the ventricles of hearts from patients with coronary heart disease[J].Int J Clin Lab Res,2000,30(3):133-140.
[11] Sofi F,Capalbo A,Cesari F,et al.Physical activity during leisure time and primary prevention of coronary heart disease:an updated meta-analysis of cohort studies[J]. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil,2008,15(3):247-257.
[12] Ehara S,Ueda M,Naruko T,et al.Elevated levels of oxidized low density lipoprotein show a positive relationship with the severity of acute coronary syndromes [J].Circulation,2001,103(15):1955-1960.
[13] Maleki BH,Tartibian B,Vaamonde D.The effects of 16 weeks of intensivecycling training on seminal oxidants and antioxidants in male road cyclists[J].Clin J Sport Med,2014,24(4):302-307.
Sport prcvcnts thc oeeurrcnec and dcvclopmcnt of eoronary hcart discasc aeeoeiatcd with low plasma Ox-LDL lcvcl
ZHANG Bao-wei1,GONG Hui3,ZHANG Jie2△
(1Department of Physical Education,Shanghai Lixin University of Commerce,Shanghai 200235,China;2Departemnt of Radiology,Shanghai General Hospital,Shanghai 200013,China;3Institutes of Biomedical Sciences,Fudan University,Shanghai 200032,China)
R 543.3
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2015.06.007
2015-04-20;編輯:段佳)
國家自然科學基金(81370258)
△Corresponding author E-mail:zhangjie1975@163.com

