口腔鱗癌患者LevelⅣ淋巴結轉移風險因素研究
李傳真郭傳瑸
·臨床研究與應用·
口腔鱗癌患者LevelⅣ淋巴結轉移風險因素研究
李傳真①②郭傳瑸①
目的:探討口腔癌同側頸部LevelⅣ淋巴結轉移的影響因素。方法:收集北京大學口腔醫院頜面外科2000年1月至2011年12月同期行頸淋巴清掃術及原發灶手術治療的口腔癌患者624例(644側),采用χ2檢驗及Logistic回歸分析LevelⅣ轉移風險因素。結果:頸淋巴結轉移患者334例(345側),LevelⅣ轉移35側(5.43%,35/644),跳躍性轉移4側(0.62%,4/644)。pNLevelsⅠ~Ⅲ頸部的LevelⅣ轉移率1.31%(4/303),pN+LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ頸部的LevelⅣ轉移率為9.14%(31/341),χ2檢驗表明pN+LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ與LevelⅣ轉移有關聯。pN+LevelⅢ、前三區的pN+Level數3枚、前三區的陽性淋巴結數≥3枚的患者,pN+LevelⅣ發生率分別為22.47%(20/89)、28.57%(10/35)、14.60%(20/137)。進一步應用Logistic回歸分析前三區淋巴結轉移狀態與LevelⅣ轉移關系,結果證實前三區的pN+Level數為3枚(pN+LevelⅠ+pN+LevelⅡ+pN+LevelⅢ)與LevelⅣ轉移有關聯。結論:對于口腔癌患者,LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移將增加LevelⅣ轉移風險。
口腔癌 轉移 頸淋巴結
口腔癌是口腔頜面部常見的惡性腫瘤之一,目前對于早期口腔癌的頸部處理主要采用手術治療[1]。近年來,口腔癌個體化治療已被多數學者接受,個體化頸淋巴結清掃術主要體現在手術時機、組織器官功能保存、淋巴結清掃區域的選擇等。口腔癌頸淋巴結轉移主要發生于LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ,LevelsⅣ~Ⅴ少見[2],從個體化、精細化手術治療方面考慮,早期口腔癌患者是否清掃LevelsⅣ~Ⅴ值得探討。因此研究LevelⅣ轉移的風險因素對于早期口腔癌患者的LevelⅣ手術治療有指導意義,本研究對口腔癌LevelsⅣ轉移影響因素進行分析。
1 材料與方法
1.1臨床資料
收集北京大學口腔醫院頜面外科2000年1月至2011年12月口腔鱗狀細胞癌患者的資料;口腔癌定義及范圍參考國際抗癌聯盟(UICC)2002分期。病例入選標準:1)原發灶為口腔癌,排除唇癌、舌根癌、軟腭癌、口咽癌、頜骨癌、上頜竇癌,且無其他頭頸癌治
療史;2)初次手術治療,非復發癌;3)術前無化療、放療;4)同期行原發灶切除及全頸清掃術或擇區性頸清術;5)有完整的病歷資料。符合納入標準共624例(644側),中位年齡57(20~86)歲,其中全頸清掃術(comprehensive neck dissection,CND)544例(560側),擴展型肩胛舌骨肌上頸淋巴清掃術(extended supraomohyoid neck dissection,SND)80例(84側)。
1.2手術方法
頸部淋巴結分區:LevelⅠ為頦下群及頜下群,LevelⅡ為頸深上群,LevelⅢ為頸深中群,LevelⅣ為頸深下群,LevelⅤ為頸后三角區的副神經群、頸橫動脈及鎖骨上群[3]。頸清手術方式:全頸淋巴清掃術(清掃LevelsⅠ~Ⅴ)、擴展肩胛舌骨肌上頸淋巴清掃術(清掃LevelsⅠ~Ⅳ)。頸清淋巴結標本由參與手術人員按LevelsⅠ~Ⅴ分離處理。
1.3統計學方法
采用SPSS 16.0軟件統計分析,單因素分析采用χ2檢驗,多因素分析采用Logistic回歸分析,檢驗水準α=0.05。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。分析變量包括年齡、性別、原發灶部位、生長方式、T分期、病理分級、LevelⅢ轉移、前三區(LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ)轉移淋巴結枚數、前三區的pN+Levels(Level with pathologically positive node)枚數。
2 結果
2.1頸部轉移淋巴結分布情況
本組624例(644側)頸清患者中,轉移334例(345側),轉移率53.53%(334/624)。淋巴結共17 847枚,平均數27.71枚;轉移淋巴結共1 058枚,轉移淋巴結均數3.07枚/側,轉移淋巴結分布情況見表1~3。
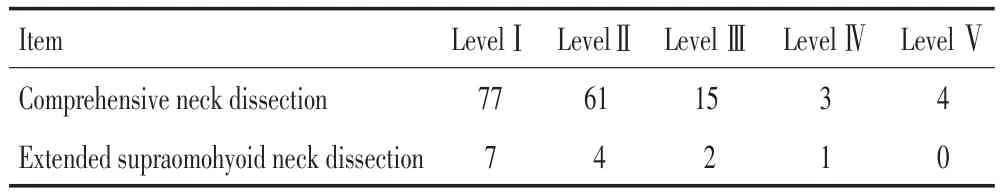
表1 單個淋巴結分區發生轉移的頸清側側Table 1Number of the sick sides for single pN+Level(necks)
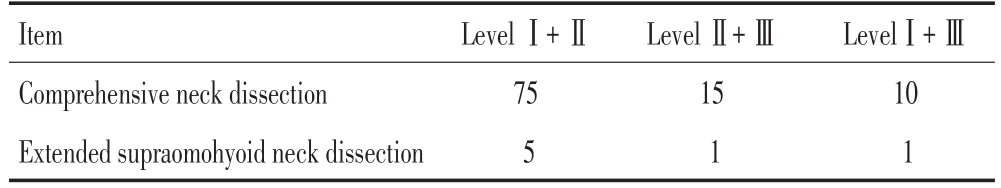
表22 個淋巴結分區發生轉移的頸清側側Table 2Number of the sick sides for two pN+Levels(necks)
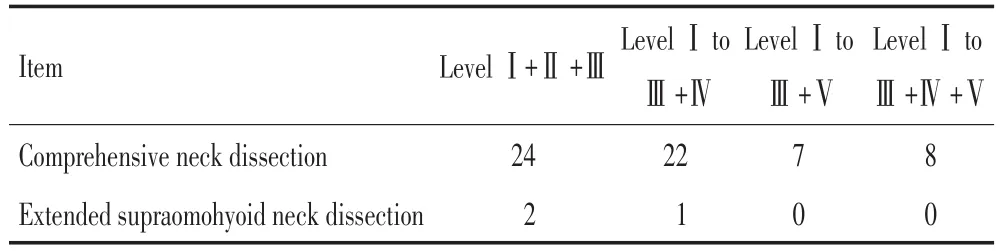
表33 枚或3枚以上淋巴結分區發生轉移的頸清側側Table 3Number of the sick sides for pN+Levels≥3(necks)
2.2單因素分析
LevelⅣ轉移35側(5.43%,35/644),其中LevelⅣ跳躍性轉移4側(0.62%,4/644);在LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移情況下,LevelⅣ轉移比例明顯增大,占88.57%(31/ 35)。LevelⅣ轉移患者中,原發灶為舌癌21側(21/ 255側),口底癌8側(8/84側),其他部位6側(下牙齦癌、磨牙后區癌、頰癌、上牙齦癌、上腭癌,6/305側)。2.2.1臨床病理因素與LevelⅣ轉移關系的單因素分析臨床病理因素與LevelⅣ轉移的單因素分析結果(表4),提示原發灶部位、生長方式、病理分級等因素的P值分別為<0.001、0.050、0.016,年齡、性別、T分期等因素的P值分別為0.251、0.485、0.242,說明原發灶部位、生長方式、病理分級與LevelⅣ轉移有關。
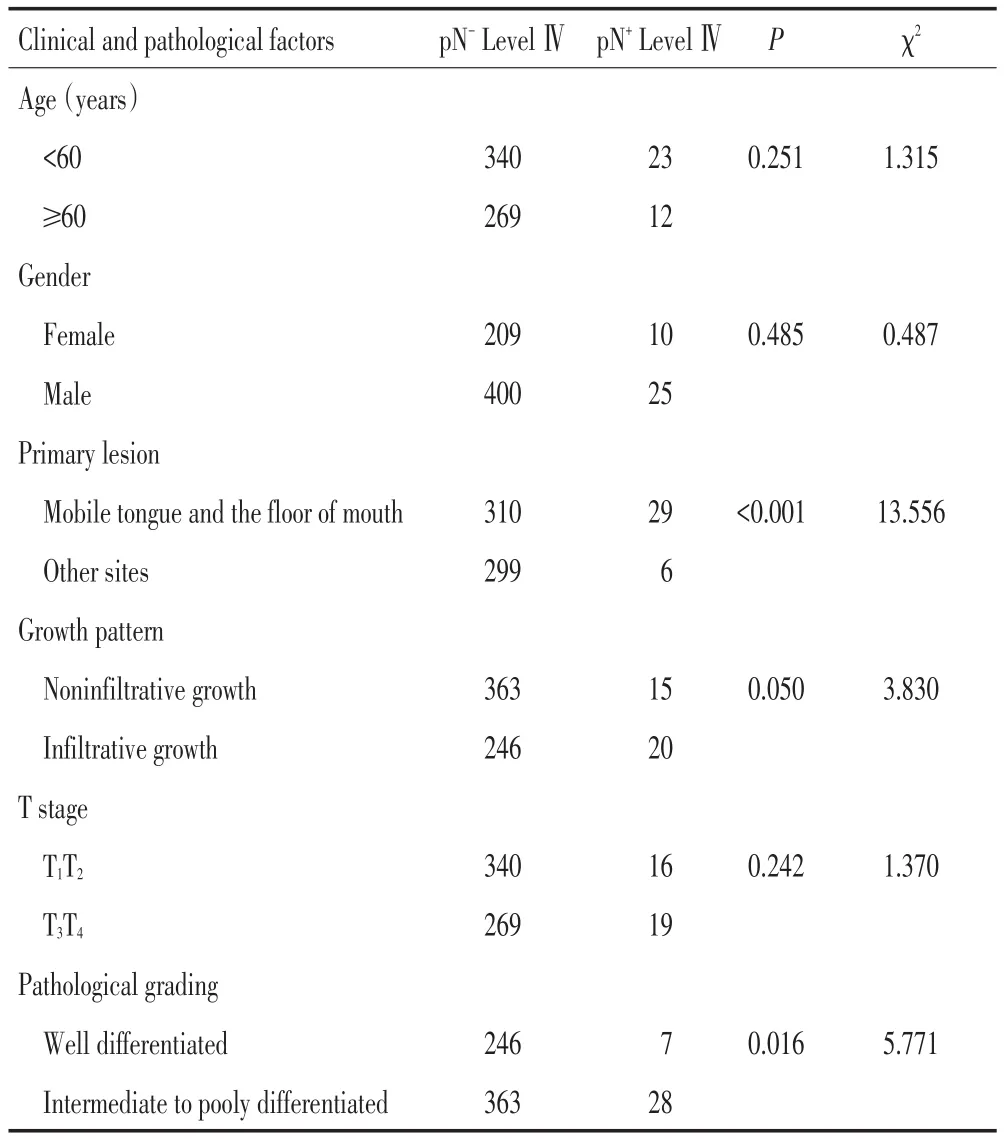
表4 LevelⅣ轉移風險因素的單因素分析結果側Table 4Chi-square test results for risk factor of LevelⅣmetastases(necks)
2.2.2LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移狀態與LevelⅣ轉移關系單因素分析1)pN-LevelⅠ~Ⅲ(LevelⅠ~Ⅲwith pathologically negative node)頸部LevelⅣ轉移率1.31%(4/303),pN+LevelⅠ~Ⅲ(LevelⅠ~Ⅲwith pathologically positive node)頸部LevelⅣ轉移率為9.14%(31/341),Fisher's精確檢驗法檢驗結果P<0.001。2)pN+LevelⅠ、pN+LevelⅡ、pN+LevelⅢ、pN+LevelⅣ發生率分別為8.81%(20/227)、7.73%(16/ 207)、22.47%(20/89)。3)前三區的pN+Level枚數分別1、2、3枚時,pN+LevelⅣ發生率分別為7.14%(13/ 182)、6.67%(8/120)、28.57%(10/35)。4)前三區的陽
性淋巴結枚數分別1、2、≥3枚時,pN+LevelⅣ轉移率分別為4.20%(5/119)、7.41%(6/81)、14.60%(20/ 137)。
從以上數據可知,當LevelⅢ發生轉移、前三區pN+Level為3枚,即pN+LevelⅠ+pN+LevelⅡ+pN+LevelⅢ、前三區轉移淋巴結枚數≥3枚時,LevelⅣ轉移率明顯增高,因此本研究以其作為分割點進行統計學分析。
χ2檢驗結果(表5),pN-LeveⅢ組、前三區pN-Level轉移淋巴結為3枚組和前三區陽性淋巴結≥3枚組,三組間數據比較的P<0.001,說明LevelⅣ轉移與pN+LevelⅢ、前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚、前三區的陽性淋巴結≥3枚相關聯。
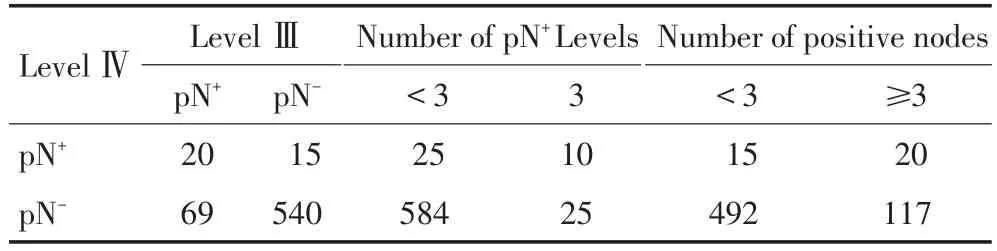
表5 LevelⅣ轉移風險因素的χ2檢驗結果側Table 5Chi-square test results for risk factor of LevelⅣmetastases(necks)
2.3多因素分析
Logistic回歸分析結果(表6),變量包括年齡、性別、原發灶部位、生長方式、T分期、病理分級、前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚、LevelsⅢ轉移、轉移淋巴結≥3枚等,結果顯示僅原發灶部位組及前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚組間比較的P<0.050,說明原發灶部位、前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚與LevelⅣ轉移有關。
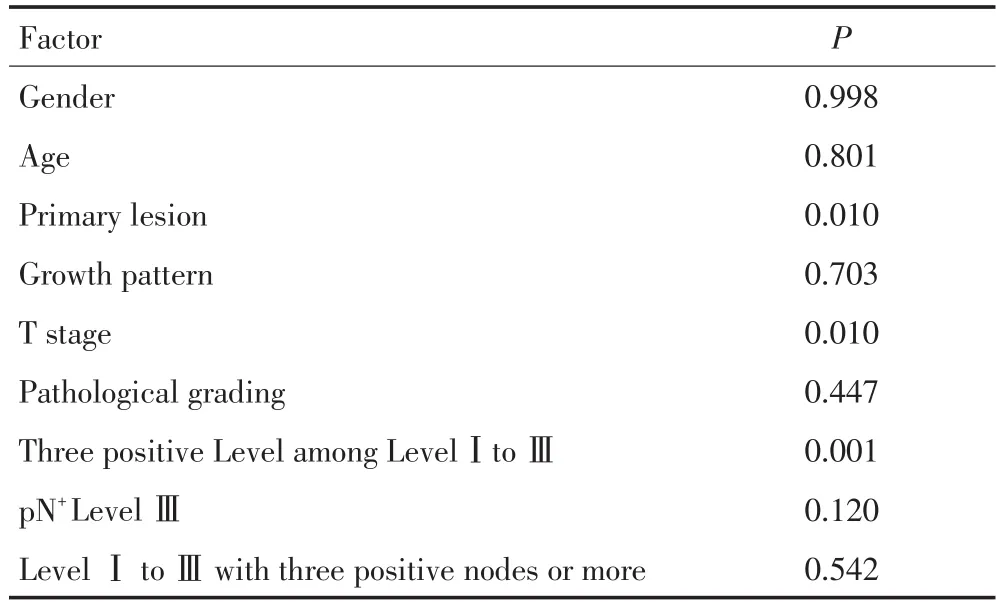
表6 LevelⅣ轉移風險因素的Logistic回歸分析結果Table 6Results of logistic regression analysis for risk factor of LevelⅣmetastases
3 討論
LevelⅣ為頸深下群淋巴結,位于肩胛舌骨肌以下沿頸內靜脈排列,一般情況下LevelⅣ主要接納頦下LevelⅢ淋巴液回流,LevelⅠ淋巴液也可以直接回流注入LevelⅣ[4]。由于LevelⅣ位于下頸部,口腔癌癌栓從原發灶脫離后,隨淋巴液逐級回流,層層過濾才到達LevelⅣ。因此,相對于LevelⅠ、LevelⅡ、LevelⅢ,LevelⅣ轉移率較低。本組病例中LevelⅣ轉移率5.43%,LevelⅣ跳躍性轉移4側,發生率為0.62%。
LevelⅣ跳躍性轉移可能與前哨淋巴結位于LevelⅣ有關。研究表明少數頭頸癌患者的頸部前哨淋巴結可能位于LevelⅣ[5],特別是舌癌前哨淋巴結位于LevelⅣ相對常見,23側舌癌頸清標本中前哨淋巴結位于LevelⅣ4例[6]。本研究中,4側LevelⅣ跳躍性轉移的患者中,原發灶位于舌癌的2側。
口腔癌一旦發生LevelⅣ轉移后,患者預后較差[7],生存率明顯下降。有研究LevelsⅣ~Ⅴ淋巴結轉移患者5年的無病生存率(DFS)、疾病特異生存率(DSS)、總生存率(OS)分別為14%、12%、10%;LevelsⅣ~Ⅴ無淋巴結轉移患者5年的DFS、DSS、OS分別為48%、52%、38%,兩者間差異有統計學意義[8]。有研究對795例患者單因素分析表明,下頸部轉移與遠處轉移有關[9],Level V轉移增加遠處轉移的風險。有研究表明LevelsⅠ~V頸清術患者的5年生存率較LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ頸清術患者差,兩者間的頸部控制率(68%vs.81%)、遠處轉移(36%vs.21%)、無病生存率(43%vs.59%)、疾病特異生存率(46%vs.66%)、總生存率(37%vs.49%)差異均有統計學意義[10]。由于LevelsⅣ轉移患者預后較差,因此對于LevelⅣ轉移風險較大的患者應積極進行頸部處理。
本組病例中,35側LevelⅣ轉移患者中,29側原發灶位于舌及口底部,單因素及多因素分析均證實LevelⅣ轉移可能與原發灶部位有關,提示舌癌及口底癌患者的LevelⅣ轉移風險增加。以往研究認為50%的LevelⅣ轉移患者伴有其他頸淋巴結分區轉移[11],這提示pN+LevelⅣ與LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移有關。本研究中,pN-LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ患者LevelⅣ轉移率1.31%,pN+LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ患者LevelⅣ轉移率(9.14%)明顯高于pN-LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ患者,證實兩者間差異有統計學意義。進一步分析前三區(LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ)轉移狀態與LevelⅣ轉移關系,單因素檢驗結果表明LevelⅢ轉移、前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚、前三區的陽性淋巴結≥3枚與LevelⅣ轉移有統計學相關性。但
是,多因素分析結果顯示僅前三區的pN+Level枚數為3枚,即pN+Level+pN+LevelⅡ+pN+LevelⅢ與LevelⅣ密切相關。雖然多因素分析未能證實LevelⅢ轉移、前三區的陽性淋巴結≥3枚與LevelⅣ密切相關,但是由于頸部出現LevelⅢ轉移、前三區的陽性淋巴結≥3枚時,LevelⅣ轉移率明顯增加,分別為22.47%、14.60%,因此本研究認為若出現LevelⅢ轉移、前三區的陽性淋巴結≥3枚情況,LevelⅣ轉移的風險增加。
綜上所述,本研究認為LevelⅣ轉移有以下特點:1)LevelⅣ轉移率較低(5.43%),跳躍性轉移少見(0.62%);2)LevelⅣ轉移多見于舌癌、口底癌病例;3)LevelⅣ轉移常伴有LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移,這提示LevelⅣ轉移可能與LevelsⅠ~Ⅲ轉移有關。LevelⅢ發生轉移的情況下,LevelⅣ轉移可能性高達22.47%。因此,本研究認為若出現LevelⅢ轉移,應對LevelⅣ淋巴結積極處理。
1Division of Oral and Maxillofacial Oncology.Chinese Society of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.The protocol of treatment guideline of oral and maxillofacial malignant noeplasms[J].China J Oral Maxillofacial Surgery,2010,8(2):98-106.[中華口腔醫學會口腔頜面外科專業委員會腫瘤學組.口腔頜面部惡性腫瘤治療指南[J].中國口腔頜面外科雜志,2010,8(2):98-106.]
2Li CZ,Guo CB.Effect of primary site for oral and maxillary squamous cell carcinoma on location of neck node metastasis.[J].J Peking University(Health Sciences),2014,46(3):469-473.[李傳真,郭傳瑸.口腔頜面部鱗癌原發灶部位對頸淋巴結轉移區域的影響[J].北京大學學報(醫學版),2014,46(3):469-473.]
3Robbins KT,ClaymanG,Levine PA,et al.Neck dissection classifi cation update:revisions proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery[J].Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg,2002,128(7):751-758.
4Lengelé B,Hamoir M,Scalliet P,et al.Anatomical bases for the radiological delineation of lymph node areas.Major collecting trunks,head and neck[J].Radiother Oncol,2007,85(1):146-155.
5Flach GB,Broglie MA,van Schie A,et al.Sentinel node biopsy for oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in the previously treated neck[J].Oral Oncology,2012,48(1):85-89.
6Shoaib T,Soutar DS,Macdonal DG.The nodal neck Level of sentinel lymph nodes in mucosal head and neck cancer[J].Br J Plastic Surg,2005,58(6):790-794.
7Shibuya Y,Ohtsuki Y,Hirai C,et al.Oral squamous cell carcinoma with microscopic extracapsular spread in the cervical lymphnodes[J].Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg,2014,43(4):387-392.
8Liao CT,Lee LY,Huang SF,et al.Outcome analysis of patients with oral cavity cancer and extracapsular spread in neck lymphnodes[J].Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys,2011,81(4):930-937.
9Lim JY,Lim YC,Kim SH,et al.Predictive factors of isolated distant metastasis after primary definitive surgery without systemic treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J].Oral Oncology,2010,46(7):504-508.
10 Liao CT,Hsueh C,Lee LY,et al.Neck dissection field and lymph node density predict prognosis in patients with oral cavity cancer and pathological node metastases treated with adjuvant therapy[J]. Oncology,2012,48(4):329-336.
11 Shah JP,Candela FC,Poddar AK.The patterns of cervical lymph node metastases from squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity[J].Cancer,1990,66(1):109-113.
(2014-11-05收稿)
(2015-01-29修回)
(編輯:邢穎)
Study on LevelⅣmetastasis risk factor of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients
Chuanzhen LI1,Chuanbin GUO2
Chuanbin GUO;E-mail:guodazuo@sina.com
Objective:To investigate the LevelⅣmetastasis risk factor of oral cancer patient's ipsilateral neck.Methods:The medical records of 624 cases(644 sides of the neck)that underwent neck dissection at the time of primary surgery for oral carcinoma were included.Chi-square test and logistic regression analysis were performed to determine the factors associated with LevelⅣmetastasis.Results:Out of 334 cases(345 neck sides)with positive lymph nodes,only 35 sides(5.43%,35/644)showed LevelⅢinvolvement and only 4 sides(0.62%,4/644)developed skip metastasis(LevelⅢ).The metastatic rate of LevelⅣwas 1.31%(4/303)for pNLevelsⅠ-Ⅲnecks and 9.14%(31/341)for pN+LevelsⅠ-Ⅲnecks.Using Chi-square test,pN+LevelsⅠ-Ⅲlymph node metastases were associated with the LevelⅣnodal metastases.For necks with pN+LevelⅢ,with three positive Levels among LevelsⅠ-Ⅲ,and with positive lymph node≥3 among LevelsⅠ-Ⅲ,the LevelⅣmetastasis rates were 22.47%(20/89),28.57%(10/35),and 14.60%(20/ 137),respectively.Furthermore,logistic regression was applied to identify the relationship between the metastasis situation of the aforementioned three Levels and LevelⅣ.Three positive Levels among LevelsⅠ-Ⅲ(pN+LevelⅠ+pN+LevelⅡ+pN+LevelⅢ)were confirmed to correlate with the presence of the positive lymph nodes in LevelⅣ.Conclusion:In oral cancer patients,LevelsⅠ-Ⅲmetastaces will increase the risk of LevelⅣmetastasis.
oral carcinoma,metastasis,neck node

10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.20141758
①北京大學口腔醫學院口腔頜面外科(北京市100081);②海口市人民醫院口腔頜面外科
郭傳瑸guodazuo@sina.com
1Department of Oral and Maxillary Surgery,Peking University School of Stomatology,Beijing 100081,and Haikou People's Hospital,Haikou 570208,China;2Department of Oral and Maxillary Surgery,Peking University School of Stomatology,Beijing 100081,China
李傳真專業方向為口腔腫瘤外科治療。
E-mail:faxli@126.com

