Wnt/β-catenin通路對大鼠腦出血的保護作用*
李治華,陳 曦,臧衛東,郭付有#
1)鄭州大學基礎醫學院人體解剖學教研室 鄭州 450001 2)鄭州大學第一附屬醫院神經外科 鄭州 450052
?
Wnt/β-catenin通路對大鼠腦出血的保護作用*
李治華1),陳曦2),臧衛東1),郭付有2)#
1)鄭州大學基礎醫學院人體解剖學教研室 鄭州 4500012)鄭州大學第一附屬醫院神經外科 鄭州 450052
關鍵詞腦出血;Wnt/β-catenin通路;RNA干擾;腦保護;大鼠
摘要目的:探討Wnt/β-連環蛋白(β-catenin)通路對大鼠腦出血的保護作用機制。方法:96只成年SD雄性大鼠隨機分為假手術組、腦出血組、腦出血假干預組、siDkk-1干預組4組,采用Real-time PCR方法檢測各組大鼠腦出血后24、72 h腦組織中Wnt-1和糖原合成酶激酶3β(GSK-3β) mRNA表達的變化,采用Western blot法檢測各組大鼠腦出血后24、72 h腦組織中β-catenin表達的變化,各組大鼠處死前均進行行為學檢測。結果:大鼠腦出血后24和72 h,Wnt-1 mRNA水平與假手術組相比均降低,經siDkk-1干預后,Wnt-1 mRNA 水平較腦出血假干預組升高(F=9.040和26.400, P均<0.05)。大鼠腦出血后24 和72 h,GSK-3β mRNA 水平與假手術組相比均升高,經siDkk-1干預后,GSK-3β mRNA水平較腦出血假干預組下降(F=41.100和17.800, P均<0.001)。大鼠腦出血后24和72 h,β-catenin蛋白的表達較假手術組均升高,經siDkk-1干預后,其表達較腦出血假干預組進一步升高(F=15.100和14.000, P均<0.05)。大鼠腦出血后24和72 h,刺激觸須前肢上抬比例較假手術組降低,經siDkk-1干預后,前肢上抬比例較腦出血假干預組升高(F=2 450.000和2 230.000,P均<0.001)。結論:Wnt/β-catenin通路對腦出血大鼠有保護作用,可能是通過活化Wnt-1、抑制 GSK-3β,進而導致β-catenin 在胞漿中聚集、移位入核后啟動Wnt下游靶基因的轉錄所致。
AbstractAim: To investigate the neuroprotective effect of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on intracranial hemor rhage(ICH) in rats.Methods: A total of 96 adult SD rats were allocated into sham-operation group,ICH group,ICH+vehicle-treated group,and ICH+siDkk-1 group.The mRNA expressions of Wnt-1 and GSK-3β were assessed by Real-time PCR at 24 and 72 h after ICH respectively. The expression of β-catenin was evaluated by Western blot analysis. Behavioral test was performed by the vibrissae-elicited forelimb-placing test in different groups.Results: There were remarkably down-regulated expression of Wnt-1 mRNA following ICH at 24 and 72 h, and the mRNA level of Wnt-1 was elevated after siDkk-1 administration(F=9.040 and 26.400, P<0.05). Increased GSK-3β mRNA expression was observed at 24 and 72 h after ICH, and the mRNA level of GSK-3β were reversed after siDkk-1 administration(F=41.100 and 17.800, P<0.001). Western blot analysis showed that β-catenin protein was increased at 24 h and 72 h after ICH respectively, and the level of β-catenin was further up-regulated after being treated by siDkk-1 compared with ICH+vehicle-treated group(F=15.100 and 14.000, P<0.05). Meanwhile, decreased behavior scores regarding forelimb use asymmetry was found in the ICH group. However, the behavior scores regarding forelimb use asymmetry was improved after siDkk-1 administration than those in the ICH+vehicle-treated group at 24 and 72 h after ICH(F=2 450.000 and 2 230.000, P<0.001).Conclusion: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has neuroprotective effects against secondary brain injury following ICH, which may be associated with activation of Wnt-1, inhibition of GSK-3β resulting in β-catenin aggregation in the cytoplasm,subsequent nuclear translocation and the downstream neuroprotective gene transcription.
腦出血是臨床上嚴重威脅人類生命的最常見的腦血管疾病之一。研究[1-2]發現:Wnt信號轉導通路在蛛網膜下腔出血和脊髓損傷后均能發揮重要的神經保護作用。Dickkopf-1(Dkk-1)是調控Wnt通路的關鍵負性因子[3-5],在正常腦組織中很少表達,但在缺血性腦卒中被強烈誘導表達。應用 Dkk-1的拮抗劑或中和抗體誘導Wnt經典通路激活,在缺血性腦卒中發揮了腦保護作用[6]。此外,有研究[7]報道,視網膜神經細胞可以通過Wnt/β-連環蛋白(β-catenin)通路的激活對光所致的感受器損害具有神經保護作用;相反玻璃體內注射Dkk-1能夠使視網膜Wnt/β-catenin通路的保護作用消失。研究[8]發現,Wnt/β-catenin通路不僅可誘導腦源性神經營養因子(brain derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)的表達,而且在調控血腦屏障(blood brain barrier,BBB)的發育及促進BBB的腦內皮細胞完整性方面發揮重要作用[9-10];而誘導BDNF表達可促進神經功能恢復和維持BBB穩定性,進而減輕血管源性腦水腫,對神經有顯著的保護作用。目前有關Wnt通路在大鼠腦出血中的表達及能否對腦出血產生神經保護作用均未見文獻報道。因此,該研究擬通過構建表達Dkk-1靶向小干擾RNA(siDkk-1)的慢病毒載體對腦出血大鼠進行干預,探討激活Wnt通路能否發揮神經保護作用,從而為臨床治療腦出血提供新途徑。
1材料與方法
1.1實驗動物及模型制作選用河南省實驗動物中心提供的體重275~300 g、成年SD雄性大鼠,共96只,經腹腔注射戊巴比妥鈉(45 mg/kg)麻醉后固定在腦立體定位儀上,于前囟前0.2 mm、中線向右旁開3.5 mm處鉆一直徑1 mm的骨孔,用26號針頭經骨孔垂直進針,深度5.5 mm,到達基底節區,用微量注射泵將提前抽取的大鼠股動脈血(100 μL)緩慢注入右側基底節區,留針10 min以防血液沿針孔溢出,無菌骨蠟封閉骨孔,縫合切口。具體方法參見文獻[11]。
1.2表達Dkk-1 siRNA慢病毒載體的構建按照Elbashir等[12]提出的RNAi序列設計原則,結合慢病毒載體的特征,由上海銳勁生物技術有限公司合成針對Dkk-1的慢病毒包裹的特異siRNA片段,實驗用量為2×107個傳導單元(transducing units,Tu)。
1.3動物分組及處理實驗共分為假手術組、腦出血組、腦出血假干預組、siDkk-1干預組4組,每組24只;其中每個時間點(24、72 h) 取6只大鼠采用Real-time PCR檢測Wnt-1、糖原合成酶激酶3β(glycogen synthase kinase 3β,GSK-3β)基因表達的變化,其余動物用Western blot檢測腦組織中β-catenin蛋白表達的變化;不同組別大鼠處死前均進行行為學檢測。假手術組留置注射針而不注射血液。siDkk-1干預組于制作腦出血模型前2 d,術側腦室(腦室立體定位坐標參考前囟后1.5 mm、中線旁開1.0 mm、腦表面下3.2 mm[13])給予體外成功構建且穩定表達的siDkk-1的慢病毒載體10 μL。腦出血假干預組給予轉染試劑包裹的無關序列10 μL。
1.4大鼠腦組織中Wnt-1、GSK-3β mRNA水平檢測Trizol法提取腦組織總RNA,檢測濃度后取1 μg,根據逆轉錄試劑盒(TaKaRa公司)說明進行逆轉錄反應,得到cDNA,再進行Real-time PCR反應,PCR反應體系為:SYBR Premix EX Taq(2×)10 μL,cDNA 2 μL,上、下游引物各0.5 μL(表1),ddH2O 7 μL,總體積20 μL。Real-time PCR反應條件:94 ℃ 2 min;94 ℃ 30 s,60 ℃ 40 s,72 ℃ 30 s,共35個循環;然后72 ℃延伸10 min。根據各個樣本PCR反應的Ct值進行相對定量。腦出血組和siDkk-1干預組目的基因的表達水平分別用其相對于假手術組和腦出血假干預組相應基因表達水平的倍數來表示(2-ΔΔCt),具體操作方法參照文獻[14]。
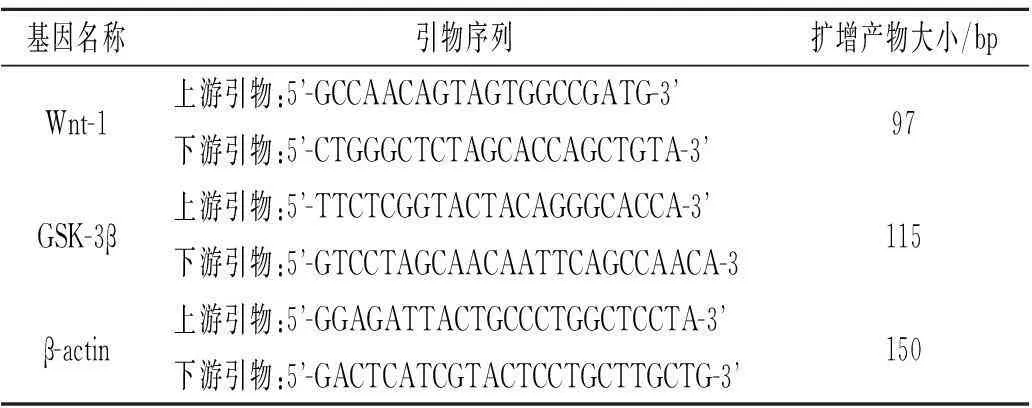
表1 引物序列和擴增產物大小
1.5大鼠腦組織中β-catenin蛋白表達的Western blot檢測大鼠麻醉后灌注處死,取出大腦,在額極后方4 mm處切取3 mm厚的冠狀切片,取血腫周圍1 mm外腦組織(以防血液污染),然后將取得的理想標本置入0.5 mL蛋白裂解緩沖液內并超聲打碎,持續30 s,離心15 min,取10 μL上清液用于蛋白質濃度分析,其余上清液加蛋白上樣緩沖液混勻煮沸,取50 μg的蛋白樣品加入到聚丙烯酰胺電泳槽內電泳,然后轉移到硝酸纖維素膜(PVDF)膜上,脫脂牛奶封閉2 h后,依次加入β-catenin一抗(按11 000稀釋,Cell Signaling Technology公司)和β-actin一抗(按13 000稀釋,北京銳抗生物科技有限公司)、二抗(按12 000稀釋,均為上海威奧生物科技有限公司產品),TBST徹底清洗PVDF膜,加ECL超敏化學發光試劑后立刻在FluorChem E機器上進行曝光,依據條帶的相對灰度值判斷蛋白的表達水平。
1.6行為學檢測采用刺激觸須前肢上抬實驗進行大鼠行為學評估:觀察大鼠在輕觸患側觸須時,對側前肢上抬并成功觸及桌面的情況,重復10次。當右側基底節受損時,大鼠左側前肢出現無力癥狀,計算左側上肢成功上抬的比例。
1.7統計學處理采用SPSS 17.0進行分析,應用單因素方差分析和LSD-t檢驗比較各組大鼠不同時間點腦組織中Wnt-1和GSK-3β mRNA、β-catenin蛋白表達的變化以及行為學的變化,檢驗水準α=0.05。
2結果
2.1各組大鼠不同時間點腦組織中Wnt-1 mRNA表達水平的變化見表2。
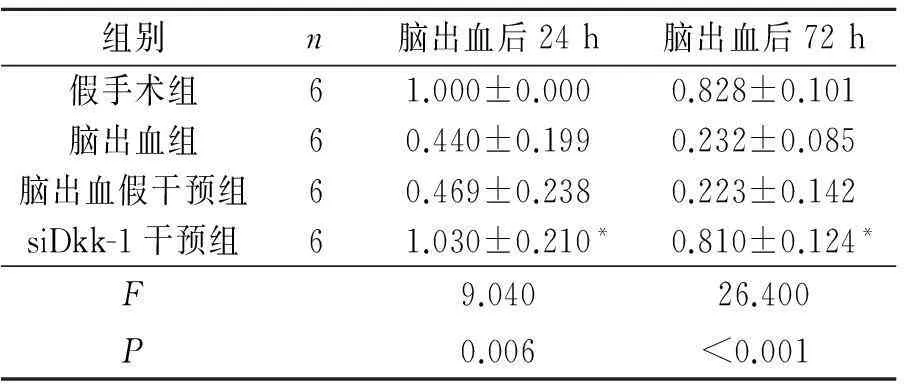
表2 各組大鼠不同時間點
*:與腦出血假干預組相比,P<0.05。
2.2各組大鼠不同時間點腦組織中GSK-3β mRNA表達水平的變化見表3。
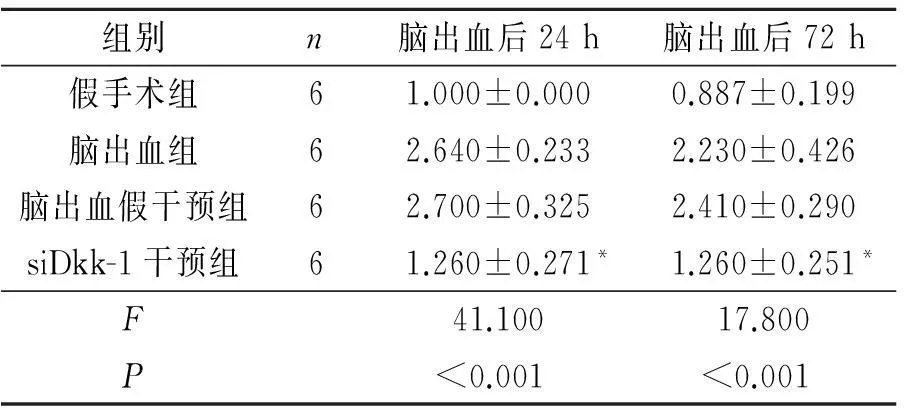
表3 各組大鼠不同時間點
*:與腦出血假干預組相比,P<0.05。
2.3各組大鼠不同時間點腦組織中β-catenin蛋白表達水平的變化見表4。
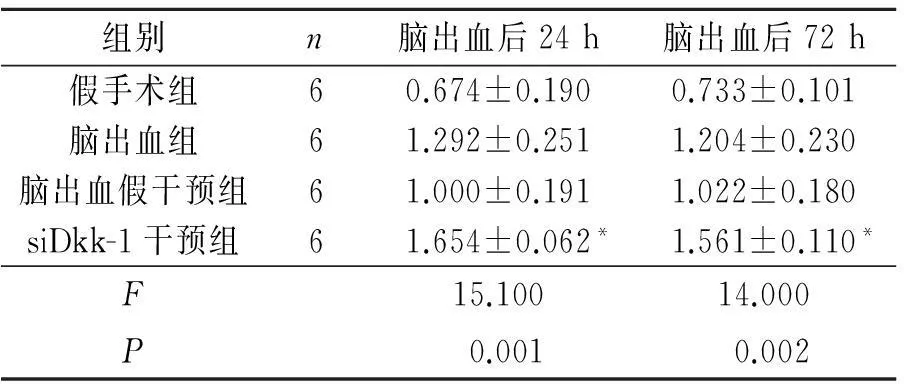
表4 各組大鼠不同時間點
*:與腦出血假干預組相比,P<0.05。
2.4各組大鼠不同時間點行為學檢測結果見表5。
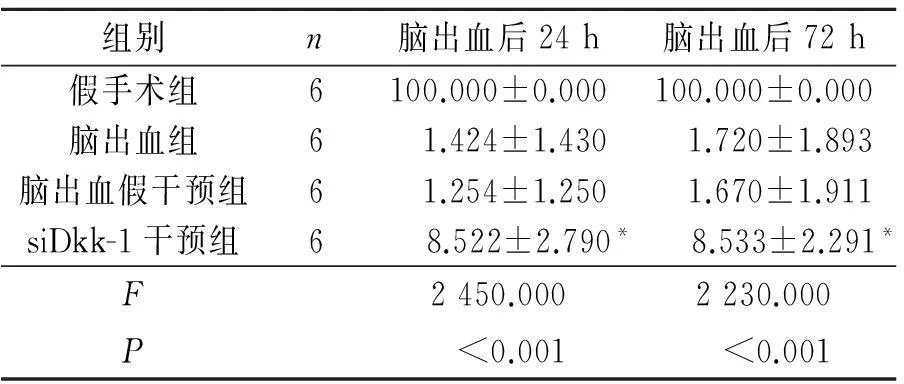
表5 各組大鼠不同時間點行為學檢測結果 %
*:與腦出血假干預組相比,P<0.05。
3討論
經典Wnt通路又稱Wnt/β-catenin通路,在存在Wnt配體的情況下,抑制GSK-3β,導致β-catenin在胞漿中聚集,隨后移位至胞核。在細胞核內,β-catenin與TCF/LEF轉錄激活因子結合,激活Wnt下游靶基因的轉錄,進而參與多種疾病的病理生理變化。該研究結果顯示:大鼠腦出血后Wnt-1 mRNA水平降低,GSK-3β mRNA水平升高,β-catenin蛋白表達升高;經siDkk-1干預后,Wnt-1激活,GSK-3β被抑制,β-catenin進一步升高,同時改善了腦出血大鼠的行為學表現。行為學表現的改善表明激活的Wnt通路在腦出血早期具有腦保護作用;此外,作者前期的動物實驗(待發表)發現siDkk-1通過激活Wnt通路,能夠減輕伊文藍外滲和腦組織含水量,說明Wnt通路的激活可能通過誘導β-catenin的大量表達,進而啟動Wnt下游靶基因的轉錄,促進受損BBB一定程度的修復,發揮了腦保護的作用。
作者在研究中還發現,大鼠腦出血后Wnt-1 mRNA和β-catenin蛋白表達趨勢不完全一致:大鼠腦出血后Wnt-1被抑制,但是與假手術組相比,β-catenin蛋白升高,推測原因可能是除了Wnt-1 以外,還存在其他上調胞質β-catenin蛋白表達的信號通路,例如Wnt 蛋白家族的其他成員,如Wnt-3a、Wnt-8a、Wnt-8b等[15]亦通過穩定胞質β-catenin 水平來介導下游事件;此外PTEN、EGFR通路[16]或β-catenin 降解機制的異常也可導致β-catenin 在胞質濃度的升高,因此,胞質β-catenin受調節的因素很多,它的表達可不完全與Wnt-1一致。
Wnt/β-catenin 通路在腦出血中的表達目前文獻報道極少。2014年Zhou等[17]發現腦出血后Wnt-3a和β-catenin分別在第3和7天達峰值,而且Wnt-3a/β-catenin表達與細胞凋亡呈顯著正相關。但Wnt-1/β-catenin在腦出血中的表達及阻斷Dkk-1表達是否對腦出血具有腦保護作用尚未見文獻報道。鑒于Dkk-1是調控Wnt通路的關鍵負性因子,作者通過體外構建穩定表達Dkk-1 siRNA的慢病毒載體,對大鼠腦出血進行干預,結果發現:大鼠腦出血后腦組織內Wnt-1 mRNA表達下調,而經 siDkk-1干預后不僅能夠激活Wnt-1 mRNA,使其表達上調,而且能夠改善腦出血大鼠的行為學表現。該實驗充分表明:通過應用靶向小干擾技術獲得的siRNA治療腦出血可能是未來腦出血治療的新方向。
綜上所述,Wnt通路活化能抑制GSK-3β的活性,從而使胞漿內β-catenin蛋白的水平升高,進而移位至胞核,激活Wnt下游靶基因的轉錄,發揮腦保護作用,改善行為學表現,但Wnt下游靶基因轉錄的具體機制還有待進一步研究。
參考文獻
[1]Yin ZS,Zu B,Chang J,et al.Repair effect of Wnt3α protein on the contused adult rat spinal cord[J].Neurol Res,2008,30(5):480
[2]李卓,姜惠麗,劉殿瑋,等.Wnt3α在蛛網膜下腔出血后早期腦損傷中對神經發生的作用[J].山東大學學報:醫學版,2014,52(5):15
[3]Cappuccio I,Calderone A,Busceti CL,et al.Induction of Dickkopf-1, a negative modulator of the Wnt pathway, is required for the development of ischemic neuronal death[J].J Neurosci,2005,25(10):2647
[4]Scott EL,Brann DW.Estrogen regulation of Dkk1 and Wnt/β-Catenin signaling in neurodegenerative disease[J].Brain Res,2013,1514:63
[5]Glinka A,Wu W,Delius H,et al.Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction[J].Nature,1998,391(6665):357
[6]Mastroiacovo F,Busceti CL,Biagioni F,et al.Induction of the Wnt antagonist, Dickkopf-1, contributes to the development of neuronal death in models of brain focal ischemia[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2009,29(2):264
[7]Braunger BM,Ohlmann A,Koch M,et al.Constitutive overexpression of Norrin activates Wnt/β-catenin and endothelin-2 signaling to protect photoreceptors from light damage[J].Neurobiol Dis,2013,50(1):1
[8]Yi H,Hu J,Qian J,et al.Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is regulated by the Wnt signaling pathway[J].Neuroreport,2012,23(3):189
[9]Liebner S,Corada M,Bangsow T,et al.Wnt/beta-catenin signaling controls development of the blood-brain barrier[J].J Cell Biol,2008,183(3):409
[10]Artus C,Glacial F,Ganeshamoorthy K,et al.The Wnt/planar cell polarity signaling pathway contributes to the integrity of tight junctions in brain endothelial cells[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2014,34(3):433
[11]Guo F,Hua Y,Wang J,et al.Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage[J].Transl Stroke Res,2012,3(1):130
[12]Elbashir SM,Lendeckel W,Tuschl T.RNA interference is mediated by 21- and 22-nucleotide RNAs[J].Genes Dev,2001,15(2):188
[13]He Z,Ostrowski RP,Sun X,et al.CHOP silencing reduces acute brain injury in the rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage[J].Stroke,2012,43(2):484
[14]郭付有,宋來君,孫紅衛,等.破裂顱內動脈瘤組織中Caspase-3 mRNA的表達與血管平滑肌細胞的凋亡測定[J].鄭州大學學報:醫學版,2007,42(5):877

[15]Peifer M,Polakis P.Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis:a look outside the nucleus[J].Science,2000,287(5458):1606
[16]Brennan KR,Brown AM.Wnt proteins in mammary development and cancer[J].J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia,2004,9(2):119
[17]Zhou L,Deng L,Chang NB,et al.Cell apoptosis and proliferation in rat brains after intracerebral hemorrhage: role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J].Turk J Med Sci,2014,44(6):920
*國家自然科學基金資助項目30801133
Neuroprotective effects of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on intracranial hemorrhage in rats
LIZhihua1),CHENXi2),ZANGWeidong1),GUOFuyou2)
1)DepartmentofHumanAnatomy,SchoolofBasicMedicalSciences,ZhengzhouUniversity,Zhengzhou450001
2)DepartmentofNeurosurgery,theFirstAffiliatedHospital,ZhengzhouUniversity,Zhengzhou450052
Key wordsintracranial hemorrhage;Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway;RNA interference;neuroprotection;rat
doi:10.13705/j.issn.1671-6825.2015.06.006
中圖分類號R743
通信作者#,男,1973年10月生,博士,主任醫師,研究方向:腦血管病,E-mail:chyou666@hotmail.com

