Akt抑制劑與利妥昔單抗聯合應用對伯基特淋巴瘤細胞株Daudi增殖及凋亡的影響
楊玉婷,譚曉虹,岑洪 (廣西醫科大學附屬腫瘤醫院,南寧 530021)
?
Akt抑制劑與利妥昔單抗聯合應用對伯基特淋巴瘤細胞株Daudi增殖及凋亡的影響
楊玉婷,譚曉虹,岑洪 (廣西醫科大學附屬腫瘤醫院,南寧 530021)
摘要:目的探討Akt抑制劑(AZD5363)與利妥昔單抗聯合應用對伯基特淋巴瘤(BL)細胞株Daudi增殖和凋亡的影響,并探討其相關機制。方法培養人BL細胞株Daudi,將其分為對照組(只含等量溶媒)、AZD5363組(加入40 μmol/L AZD5363)、利妥昔單抗組(加入50 μg/mL利妥昔單抗)、聯合用藥組(加入40 μmol/L AZD5363+50 μg/mL利妥昔單抗),置于培養箱中培養24~72 h。分別采用CCK8法、流式細胞術測算AZD5363、利妥昔單抗及兩者聯合對Daudi細胞的增殖抑制和凋亡率,采用Western blotting法檢測細胞磷酸化Akt(p-Akt)和總Akt(T-Akt)蛋白。結果與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,聯合用藥組在24、48、72 h時Daudi細胞增殖抑制率高(P均<0.05)。AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組與對照組相比,聯合用藥組與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,干預Daudi細胞48、72 h后細胞凋亡率高(P均<0.05)。對照組、AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組細胞p-Akt相對表達量分別為0.59±0.06、0.33±0.03、0.45±0.04、0.18±0.04,AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組與對照組相比,聯合用藥組與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,P均<0.05。結論AZD5363與利妥昔單抗聯合應用可增強對BL細胞株Daudi的增殖抑制作用,促使細胞凋亡,其作用機制可能是通過抑制Akt磷酸化,阻斷PI3k/Akt信號轉導通路,從而發揮抗腫瘤效應。
關鍵詞:伯基特淋巴瘤;Daudi細胞;利妥昔單抗;磷酸化Akt
近年來,靶向治療成為繼手術、放療、化療后腫瘤治療最有效的手段。分子靶向治療藥物血液學毒性低、患者耐受性好。已有證據表明,伯基特淋巴瘤(BL)的病理機制與PI3K/Akt信號通路異常密切相關,該通路持續活化及MYC基因過表達協同促進人BL的發生、發展。Akt是P13K/Akt信號轉導通路的樞紐基因,通過Akt抑制劑AZD5363干擾該靶點,阻斷PI3K/Akt通路,能否抑制Daudi細胞增殖、促進細胞凋亡目前研究較少。利妥昔單抗聯合化療的療效優于單純化療,目前廣泛應用于BL的治療。本研究觀察了Akt抑制劑AZD5363與利妥昔單抗聯合應用對BL細胞株Daudi增殖和凋亡的影響,并探討其機制。
1材料與方法
1.1主要試劑與儀器利妥昔單抗(10 mg/mL)為羅氏公司產品。AZD5363購自Selleck中國分公司。細胞增殖與毒性檢測試劑盒(CCK8)購自上海七海復泰公司。RPMI1640細胞培養液及胎牛血清購自美國Gibco公司。Annexin V-PE凋亡試劑盒購自BD Biosciences公司。抗磷酸化抗體[磷酸化Akt(p-Akt)]、總Akt(T-Akt,均為抗兔多克隆抗體)、內參照GAPDH及其相對應的二抗均購自Abcam公司。流式細胞儀購自美國BIO RAD公司。
1.2細胞來源及培養BL細胞株Daudi購自中國科學院上海細胞庫。細胞在含10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素及100 μg/mL鏈霉素的RMPI1640培養液中懸浮生長,置于37 ℃、5% CO2飽和濕度培養箱中培養。收集對數生長期的細胞用于實驗。
1.3AZD5363聯合利妥昔單抗對Daudi細胞增殖影響的觀察采用CCK8法。取對數生長期的Daudi細胞懸液,調整細胞密度為5×104/mL,以每孔100 μL接種于96孔板,細胞分為空白調零組(不接種細胞)、對照組(只含等量溶媒)、AZD5363組(分別加入5、10、20、40、80 μmol/L AZD5363)、利妥昔單抗組(分別加入25、50、75、100 μg/mL利妥昔單抗),置于含有5% CO2的37 ℃孵箱內進行孵育24 h。25、50、75、100 μg/mL的利妥昔單抗作用24 h對Daudi細胞的抑制率分別為16.35%、18.15%、21.89%、24.36%,可見利妥昔單抗在體外對Daudi細胞表現出較弱的增殖抑制作用,50 μg/mL的利妥昔單抗對Daudi細胞的抑制率已基本達效應平臺,因此本研究選用50 μg/mL作為聯合用藥的利妥昔單抗最終藥物濃度。濃度為5、10、20、40、80 μmol/L的AZD5363作用24 h對Daudi細胞對應的抑制率分別為5.61%、13.42%、18.02%、21.32%、45.23%,隨著AZD5363濃度的增加,其抑制率增加,選用中間抑制濃度40 μmol/L作為與利妥昔單抗(50 μg/mL)聯合的干預濃度。取對數生長期的Daudi細胞懸液,調整細胞密度為5×104/mL,以每孔100 μL接種于96孔板,設置對照組(只含等量溶媒)、AZD5363組(加入40 μmol/L AZD5363)、利妥昔單抗組(加入50 μg/mL利妥昔單抗)、聯合用藥組(加入40 μmol/L AZD5363+50 μg/mL利妥昔單抗),每組設6個復孔,孵育24~72 h。孵育結束加入10 μL CCK8試劑,孵育2 h,測定樣品在450 nm的吸光度值。每個實驗完成3次,計算細胞的增殖抑制率。
1.4 AZD5363聯合利妥昔單抗對Daudi細胞凋亡影響的觀察 取對數生長期的Daudi細胞懸液接種于25 mL培養瓶,按1.3設置對照組、AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組,培養48~72 h后收集細胞,按照Becton Dieainson公司AnnexinV-PE雙染試劑盒說明書處理后,采用流式細胞術檢測各組Daudi細胞的凋亡情況。
1.5細胞p-Akt、Akt蛋白檢測采用Western blotting法。取Daudi細胞懸液,按1.3設置對照組、AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組,培養24 h后收集細胞,提取各組細胞的總蛋白,取40~60 μg蛋白上樣,SDS-PAGE電泳50 min,4 ℃ 150 V轉膜約1.5 h,封閉,洗膜,分別加入p-Akt、T-Akt、GAPDH的一抗,4 ℃孵育過夜,洗膜,加入二抗室溫孵育,用顯色劑顯色成像,分析各條帶灰度值,以GAPDH為內參校正相對蛋白表達量。
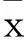
2結果
AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組在24 h時Daudi細胞增殖抑制率分別為21.32%、18.15%、35.13%,48 h時分別為35.64%、20.44%、44.73%,72 h時分別為47.31%、22.19%、71.33%,聯合用藥組與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,P均<0.05。對照組、AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組干預Daudi細胞48 h后細胞凋亡率分別為12.53%、29.17%、19.96%、47.21%,72 h時分別為14.01%、40.70%、22.61%、65.23%,AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組與對照組相比,聯合用藥組與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,P均<0.05。各組p-Akt、T-Akt蛋白表達情況見表1。
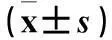
表1 各組p-Akt、T-Akt蛋白表達比較
注:與對照組相比,*P<0.05;與AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組相比,△P<0.05。
3討論
BL是一種高侵襲性的非霍奇金淋巴瘤(NHL),占全部NHL的3%~5%,占兒童全部淋巴瘤的30%~50%。通過高劑量強度的多藥化療、中樞神經系統侵犯的預防治療、不斷改善的支持治療,BL患者的預后顯著改善[1]。老年患者常常難以完成大劑量的多藥化療,這有可能是導致療效不佳的重要原因。利妥昔單抗是針對CD20的單克隆抗體,在一些惰性淋巴瘤和侵襲性淋巴瘤的治療中取得了非常好的效果,利妥昔單抗聯合化療已成為這些淋巴瘤的標準治療方案[2,3]。
對于難以完成大劑量多藥化療的BL患者,能否通過分子靶向治療來改善預后目前研究較少。小分子靶向治療在一些血液系統惡性腫瘤和實體瘤中取得了非常好的療效,而MYC基因異常是導致BL發生的病理生理學基礎[4],PI3K信號能夠阻止MYC降解,維持其活性[5]。最近在BL中發現一些突變能夠激活PI3K信號通路[6],PI3K激活能在質膜上產生第二信使PIP3,導致Akt活化。活化的Akt通過磷酸化多種酶、激酶和轉錄因子等下游因子,進而調節細胞的功能(包括凋亡、DNA修復、細胞周期的停滯及葡萄糖代謝等)。研究證實PI3K/Akt通路在多種實體瘤、血液惡性腫瘤細胞系及體內的腫瘤持續活化[7,8]。應用PI3K/Akt通路抑制劑可以下調Akt的磷酸化,因而PI3K/Akt通路可作為治療BL的靶點。PI3K抑制劑或Akt抑制劑對BL都具有抗腫瘤療效,PI3K抑制劑如idelalisib、duvelisib等治療BL的研究已較多,而Akt抑制劑治療BL的研究則較少[9]。此外,亦有研究證實,Akt抑制劑AZD5363可以抑制41~182種實體及血液腫瘤細胞,單藥或聯合用藥治療多種惡性腫瘤具有潛在療效[10]。因而,本實驗對Akt抑制劑AZD5363、利妥昔單抗及兩者聯合作用于BL細胞株Daudi的化療效果進行探討。研究結果顯示,AZD5363能夠抑制Daudi細胞的增殖及促進細胞凋亡,而聯合利妥昔單抗對Daudi細胞的生長抑制及促凋亡作用明顯增強,單藥利妥昔單抗對Daudi細胞作用不明顯,僅有輕微的生長抑制及促凋亡作用。本研究結果顯示,AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組、聯合用藥組較對照組細胞p-Akt表達量低,聯合用藥組較AZD5363組、利妥昔單抗組細胞p-Akt表達量低,提示AZD5363、利妥昔單抗可能是通過抑制Akt蛋白磷酸化來抑制細胞增殖,促進細胞凋亡。
可見,AZD5363與利妥昔單抗聯合應用可增強對BL細胞株Daudi的增殖抑制作用并促使細胞凋亡,其作用機制可能是通過抑制Akt磷酸化,阻斷PI3k/Akt信號轉導通路,從而發揮抗腫瘤效應。
參考文獻:
[1] Costa LJ, Xavier AC, Wahlquist AE, et al. Trends in survival of patients with Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia in the USA: an analysis of 3691 cases[J]. Blood, 2013,121(24):4861-4866.
[2] Thomas DA, Faderl S, O′Brien S, et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with hyper-CVAD plus rituximab for the treatment of adult Burkitt and Burkitt-type lymphoma or acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J]. Cancer, 2006,106(7):1569-1580.
[3] Barnes JA, Lacasce AS, Feng Y, et al. Evaluation of the addition of rituximab to CODOX-M/IVAC for Burkitt′s lymphoma: a retrospective analysis[J]. Ann Oncol, 2011,22(8):1859-1864.
[4] Park SS, Kim JS, Tessarollo L, et al. Insertion of c-Myc into Igh induces B-cell and plasma-cell neoplasms in mice[J]. Cancer Res, 2005,65(4):1306-1315.
[5] Kumar A, Marques M, Carrera AC. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation in late G1is required for c-Myc stabilization and S phase entry[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2006,26(23):9116-9125.
[6] Schmitz R, Young RM, Ceribelli M, et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics[J]. Nature, 2012,490(7418):116-120.
[7] Bauer TM, Patel MR, Infante JR. Targeting PI3 kinase in cancer[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2015,146:53-60.
[8] Engelman JA. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2009,9(8):550-562.
[9] Oki Y, Fanale M, Romaguera J, et al. Phase Ⅱ study of an Akt inhibitor MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma[J]. Br J Haematol, 2015,171(4):463-470.
[10] Davies BR, Greenwood H, Dudley P, et al. Preclinical pharmacology of AZD5363, an inhibitor of akt: pharmacodynamics, antitumor activity, and correlation of monotherapy activity with genetic background[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2012,11(4):873-887.
Effects of Akt inhibitor combined with rituximab on proliferation and apoptosis of Burkitt′s lymphoma cell line Daudi
YANGYuting,TANXiaohong,CENHong
(TumorHospitalofGuangxiMedicalUniversity,Nanning530021,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of Akt inhibitor (AZD5363) combined with rituximab on cell proliferation and apoptosis of Burkitt′s lymphoma (BL) Daudi cells in vitro, and to explore its mechanism. MethodsHuman BL Daudi cells were cultured and then were divided into four groups: the control group (treated by 1640 culture medium with fetal bovine serum), AZD5363 group (treated by 40 μmol/L AZD5363), rituximab group (treated by 50 μg/mL rituximab) and the combination group (treated by 40 μmol/L AZD5363 + 50 μg/mL rituximab). They were all put into the incubator for 24-72 h. The growth inhibition and apoptosis rate of Daudi cells were detected by CCK-8 colorimetry and flow cytometer respectively. In addition, the expression of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and total Akt (T-Akt) was detected by Western blotting.ResultsThe growth inhibition rate of the combination group after 24, 48 and 72 h was significantly increased as compared with that of the AZD5363 and rituximab groups (all P<0.05). The difference of apoptosis rate among the control group and AZD5363 group, rituximab group and the combination group was statistically significant after 48 and 72 h, and the apoptosis rate in the combination group was higher than those of the AZD5363 and rituximab group after 48 and 72 h (all P<0.05). The expression of p-Akt in the control group, AZD5363 group, rituximab group and the combination group were respectively 0.59±0.06, 0.33±0.03, 0.45±0.04 and 0.18±0.04 after 24 h, and the difference of expression of p-Akt was statistically significant among the control group and experimental groups, between AZD5363 group and the combination group, between the combination group and AZD5363 group, rituximab group (all P<0.05). ConclusionsAZD5363 in combination with rituximab can significantly inhibit cell proliferation and promote the apoptosis of BL Daudi cells. Inhibition of Akt phosphorylation and blocking of PI3k/Akt signal transduction pathway may be the mechanism of its antitumor effect.
Key words:Burkitt′s lymphoma; Daudi cells; rituximab; phosphorylated Akt
(收稿日期:2015-12-07)
中圖分類號:R733
文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:1002-266X(2016)11-0008-03
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2016.11.003
通信作者簡介:岑洪(1971-),男,碩士研究生導師,主任醫師,主要研究方向為血液腫瘤的基礎與靶向治療。E-mail: cenhong02@163.com
第一作者簡介:楊玉婷(1990-),女,碩士研究生,主要研究方向為血液腫瘤的基礎與靶向治療。E-mail: 2403124794@qq.com
基金項目:國家自然科學基金資助項目(81160298);廣西醫療衛生適宜技術研究與開發課題(S201301-02) 。

