δ-catenin與Cdc42在非小細胞肺癌中表達的相關性
張 迪, 王恩華
1.中國醫科大學基礎醫學院病理教研室,遼寧 沈陽110122;2.中國醫科大學附屬第一醫院病理科,遼寧 沈陽110001
?
δ-catenin與Cdc42在非小細胞肺癌中表達的相關性
張 迪1,2, 王恩華1,2
1.中國醫科大學基礎醫學院病理教研室,遼寧 沈陽110122;2.中國醫科大學附屬第一醫院病理科,遼寧 沈陽110001
[摘要]背景與目的:δ-catenin是p120 catenin 亞家族中的成員,可與細胞膜上的E-cadherin直接結合,形成E-cadherin/catenin復合體。δ-catenin還可以通過調節Cdc42(Small GTP酶)活性以影響細胞骨架裝配。該研究檢測非小細胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)中δ-catenin及Cdc42的表達情況并探討了二者表達的相關性。方法:采用免疫組織化學方法檢測122例NSCLC標本中δ-catenin與Cdc42的表達。采用蛋白[質]印跡法(Western blot)及逆轉錄聚合酶鏈反應(reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction,RT-PCR)法檢測肺癌組織中δ-catenin及Cdc42的蛋白及mRNA表達情況。在肺癌細胞系中,分別上調或干擾δ-catenin的表達后,利用G-LISA及Transwell小室法檢測Cdc42活性以及肺癌細胞侵襲能力的改變。結果:δ-catenin和Cdc42在肺癌組織中其蛋白及mRNA表達明顯高于正常肺組織。而在122例NSCLC病例中,δ-catenin陽性表達率為65.57%(80/122),Cdc42過表達率為68.03%(83/122)。δ-catenin陽性表達和Cdc42的過表達具有較好的相關性(P<0.001)。δ-catenin和Cdc42的協同表達與肺癌的高臨床分期、低分化、病理類型為腺癌和淋巴結轉移相關(P<0.05),并且與肺癌患者的不良預后明顯相關。在肺癌細胞系中通過調節δ-catenin表達,改變Cdc42的表達及活性,影響肺癌細胞的侵襲能力。結論:在肺癌組織中δ-catenin和Cdc42的表達具有相關性,而二者協同表達與患者不良預后相關。
[關鍵詞]δ-catenin; Cdc42; Small GTP酶;非小細胞肺癌;預后
Correspondence to: WANG Enhua E-mail: wangeh@hotmail.com
δ-catenin作為p120catenin(p120ctn)亞家族中的重要成員(包括p120ctn、δ-catenin、ARVCF、p0071和plakophilins 1/2/3)[1]。最早發現中樞神經系統表達δ-catenin,并具有促進突觸生長的功能[2]。δ-catenin與同家族的p120的結構及作用相似[1],具有9個Arm重復序列[3-4],與p120共同在細胞膜上的E-cadherin(E-cad)擁有相同的近膜結構域(juxtamembrane domain,JMD)結合位點[5],可以通過與E-cad直接結合形成E-cadherin/catenin復合體,調節細胞間的粘附。
據報道,δ-catenin還可以通過對Small GTP酶活性的調節來影響細胞骨架生長[6-7]。Cdc42 是Small GTP 的核心成員,它們在代謝中存在與GTP結合的活化型和與GDP結合的失活型,兩種形式好像分子開關般動態調節actin細胞骨架的裝配,并引發各種生物學反應,例如細胞的形態、趨化和細胞運動等[8-9]。
因此,推測在肺癌組織中,δ-catenin與Cdc42之間很可能存在著聯系。本研究檢測了122例非小細胞肺癌(non-small cell lung cancer,NSCLC)樣本中δ-catenin及Cdc42的表達情況并探討了它們的表達與臨床病理因素的關系。同時,在肺癌細胞系中分別過表達或干擾δ-catenin進而影響肺癌細胞的侵襲和轉移。
1 材料和方法
1.1標本來源與患者資料
122例具有隨訪資料的原發性肺鱗癌、腺癌來自1998—2005年在中國醫科大學第一附屬醫院行外科手術切除的標本存檔蠟塊。其中男性62例,女性60例,年齡33~80歲,中位年齡為59歲。按2004年WHO肺腫瘤組織學分類標準,其中鱗癌55例,腺癌67例。高分化30例,中分化58例,低分化34例。按照國際抗癌聯盟(Union for International Cancer Control,UICC)于2002年修訂的腫瘤pTNM分期標準,Ⅰ期18例,Ⅱ期40例,Ⅲ期57例,Ⅳ期7例。所有患者術前均未接受放化療,術后常規化療。標本均經4%中性甲醛溶液固定,石蠟包埋。此外,切除35例新鮮肺癌及癌旁正常肺組織,立即放入-70 ℃環境下保存,以備將來提取蛋白及RNA。
另外,對122例中的60例進行了詳實的術后隨訪,生存時間的計算是從手術日期到由于復發或轉移而死亡的日期或末次隨訪日期為止。
1.2免疫組織化學染色與結果判定
標本組織制成4 μm連續切片,二甲苯脫蠟和梯度酒精水化后,經檸檬酸鹽緩沖液(pH 為6.0)高壓抗原修復,再經3%H2O2滅活內源性過氧化物酶活性,非免疫血清封閉非特異性位點,之后切片與單克隆抗體δ-catenin (l∶50,美國Santa公司)和Cdc42 (1∶100,美國Santa公司)在4 ℃條件下溫育過夜。再加生物素標記的山羊抗小鼠二抗(1∶500),采用DAB顯色。PBS代替一抗做陰性對照。
對122例NSCLC標本采用免疫組織化學SP方法檢測δ-catenin與Cdc42的表達以及與各臨床病理因素之間的關系,此外還檢測60例隨訪標本中δ-catenin與Cdc42的表達與患者預后的關系。觀察δ-catenin在腫瘤組織的表達,計數400個腫瘤細胞并計算其中陽性染色細胞的百分數。δ-catenin的評分標準[10]:免疫染色的強度(0為陰性,1為弱陽性,2為中等陽性,3為強陽性);免疫染色的陽性腫瘤細胞數(陰性記0分,1%~25%記1分,26%~50%記2分,51%~75%記3分,大于等于76%記4分)。最終分數即為兩項評分的乘積。為了便于統計,將評分結果分為兩組:小于2為陰性表達;大于等于2為陽性表達。對Cdc42進行免疫組織化學檢測,每張切片隨機選取5個高倍視野,每個視野計數100個瘤細胞,無著色為-,陽性細胞數小于等于25%為+,26%~75%為++,大于等于76%為+++。Cdc42細胞質表達-~+定義為表達正常,將++~+++定義為過度表達[11]。將δ-catenin陽性表達和Cdc42的過表達同時出現的情況,稱為協同表達。
1.3細胞培養與質粒構建轉染
人肺腺癌細胞系H460、LK2(美國Manassas公司),分別培養于含10%滅活胎牛血清、2.3 g/L NaHCO3、100 U/mL青鏈霉素的RPMI-1640和高糖DMEM(美國Gibco公司)培養液中,于37 ℃、CO2體積分數為5%的濕潤空氣培養箱中培養。每2 d用0.25%胰酶消化傳代。
利用脂質體LipofectamineTM2000(美國Invitrogen公司)將含人源性全長δ-catenin cDNA的質粒(pCMV5-FLAG/δ-catenin),導入δ-catenin表達較低的LK2細胞系,并以空載體作為陰性對照。另將設計的δ-catenin siRNA (5’-CUACGUUGACUUCUACUCAUU-3’,5’-UGAGUAGAAGUCAACGUAGUU-3’),利用脂質體L i p o f e c t a m i n eT M2 0 0 0導入δ-catenin表達較高的H460細胞系,同時以非特異性的亂序s i R N A作為陰性對照(5’-UUCUCCGAACUUGUCACAUUU-3’,5’-AUGUGACAAGUUCGGAGAAUU -3’)。
1.4蛋白[質]印跡法(Western blot)檢測
取適量肺癌組織和細胞加入裂解液,在冰浴下超聲處理,低溫高速離心(4 ℃,21 400×g,30 min),收集上清液。將總蛋白的裂解產物進行SDS-PAGE電泳后,轉印至PVDF膜。加入單克隆抗體δ-catenin (1∶200)、Cdc42(l∶300),4 ℃溫育過夜,用山羊抗小鼠二抗37 ℃溫育2 h,ECL發光并曝光膠片,經BioImaging System測定蛋白條帶灰度值。以GAPDH為內對照,并取其與δ-catenin的比值做為相對表達量。
1.5逆轉錄聚合酶鏈反應(reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction,RT-PCR)檢測
采用TRIzol試劑(美國Invitrogen公司)提取肺癌組織和細胞總RNA,利用RNA PCR Kit(AMV)Ver. 3.0試劑盒[寶生物工程(大連)有限公司]進行RT-PCR檢測,引物序列和反應條件見表1。RT-PCR產物于1.5%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳,用自動電泳凝膠成像分析系統(Bio-imaging Systems),測定擴增帶灰度值,以GAPDH為內參照,得到mRNA的相對表達量。
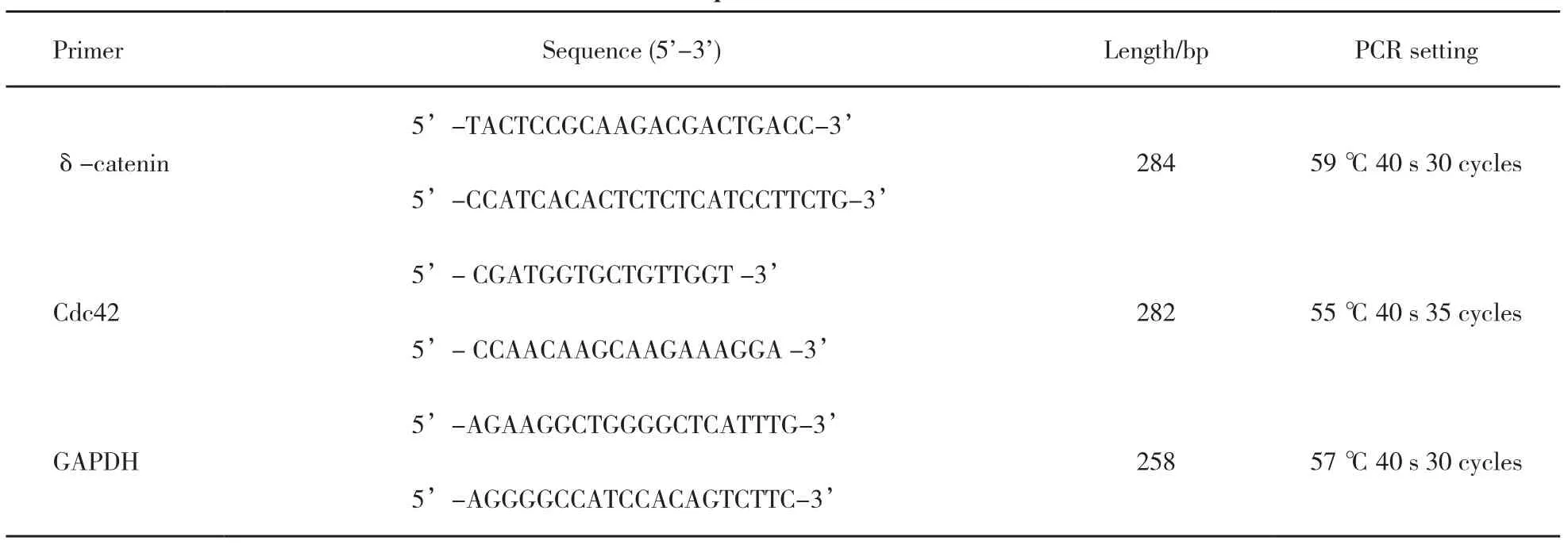
表 1 引物序列和反應條件Tab. 1 Primer sequences and reaction conditions
1.6Cdc42活性的檢測
采用Cdc42 G-LISATM比色法試劑盒(美國Cytoskeleton公司)分析Cdc42活性。將預備好的各細胞系裂解液加入可特異結合活性Cdc42(綁定GTP)的孔板小室中,緩沖液清洗其他成分后,利用分光光度計(BD轉導實驗室)檢測活性Cdc42在490 nm波長處的吸收度。
1.7基質膠侵襲實驗(Transwell小室法)
按照BD公司說明操作,上室內加入100 μL 1∶4稀釋的Matrigel基質膠(美國BD Biosciences公司),在37 ℃、CO2體積分數為5%的條件下放置2 h。取100 μL細胞懸液滴入上室內(3×105個/mL),下室加入含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培養液,上、下室之間用孔徑為8 μm孔徑的Transwell微孔濾膜(美國Corning公司)分開,轉染后24 h,瘤細胞被接種到基質膠,將小室置37 ℃、CO2體積分數為5%的條件下分別放置24 h。棄去上室內液體,擦盡膜上Matrigel基質膠,用100%甲醇固定30 min,常規蘇木精染色,顯微鏡下隨機計數5個視野(×400)的侵襲到微孔膜下表面的細胞。
1.8統計學處理
應用SPSS for Windows 13.0 (SPSS Inc.,Chicago, IL, USA)軟件進行數據分析。免疫組織化學結果采用Pearson’s Chi-Square檢驗。Western blot和RT-PCR檢測結果采用Student’s t檢驗。患者生存分析采用Kaplan-Meier法,logrank檢驗患者生存率的差別。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
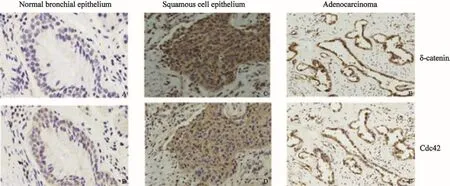
圖 1 δ-catenin和Cdc42在正常肺組織和肺鱗癌、腺癌中的表達Fig. 1 δ-catenin and Cdc42 expression in normal lung tissue, squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma (SP, ×200)δ-catenin (A) and Cdc42 (B) were expressed at low levels in the bronchial epithelial cells of the adjacent normal lung tissues. The expression of δ-catenin was positive in the cytoplasm of lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma (C and E). Cdc42 was over expressed in the cytoplasm of lung squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma cells (D and F)
2 結 果
2.1δ-catenin的陽性表達與Cdc42的過表達一致性和相關性檢測結果
本研究采用免疫組織化學方法檢測發現,δ-catenin和Rac1在正常支氣管上皮細胞的細胞質中呈弱表達或不表達,而在肺癌組織中,二者表達均明顯增高。在122例NSCLC病例中,δ-catenin陰性表達為42例,陽性表達為80例,陽性表達率為65.57% (80/122);Cdc42在肺癌組織中的表達明顯強于支氣管黏膜上皮細胞,其過表達率為68.03%(83/122)(圖1)。Cdc42的過表達與δ-catenin的陽性表達具有較好的相關性(表2,P<0.001)。本研究又分析了在肺癌組織中,δ-catenin陽性表達而同時Cdc42過表達(協同表達)的病例與臨床病理因素的關系(表3)。結果發現,肺腺癌中的協同表達率為64.18%(43/67),明顯高于鱗癌的45.45%(25/55,P<0.05);低分化中的協同表達率為70.59%(24/34),明顯高于高中分化的50.00%(44/88,P<0.05);Ⅲ~Ⅳ期的協同表達率為65.63%(42/64),顯著高于Ⅰ~Ⅱ期的44.83%(26/58,P<0.05);有LN轉移的病例協同表達率是62.35%(53/85),也明顯高于無LN轉移病例的40.54%(15/37,P<0.05)。但協同表達與患者年齡和性別均未見關聯性(P>0.05)。
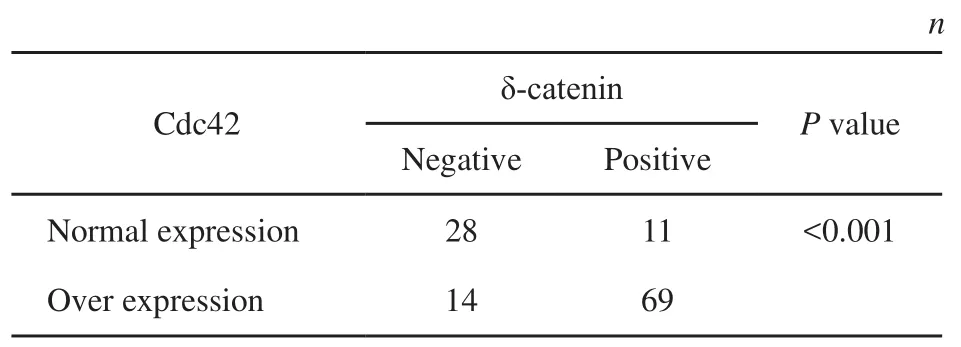
表 2 δ-catenin與Cdc42在肺癌中表達的相關性Tab. 2 Correlation between δ-catenin and Cdc42 in lung cancer
2.2δ-catenin和Cdc42的協同表達與患者的臨床病理因素及不良預后的關系
當δ-catenin和Cdc42協同表達時,患者的平均生存時間和生存率明顯低于其在陰性表達時患者 (圖2,P<0.05)。因而,δ-catenin和Cdc42協同表達與患者的不良預后明顯相關。
2.3肺癌組織中δ-catenin和Cdc42的表達情況
本研究利用Western blot法檢測δ-catenin和Cdc42的蛋白表達情況。結果顯示,在癌旁正常肺組織中可見δ-catenin蛋白表達量較低,而在肺癌組織中其表達明顯增強。Cdc42在肺癌組織中的表達也明顯高于正常肺組織(圖3 A,B)。RT-PCR檢測進一步證實了我們在Western blot中觀察到的結果,在肺癌組織中δ-catenin和Cdc42的表達增均明顯增強(圖3 C,D)。
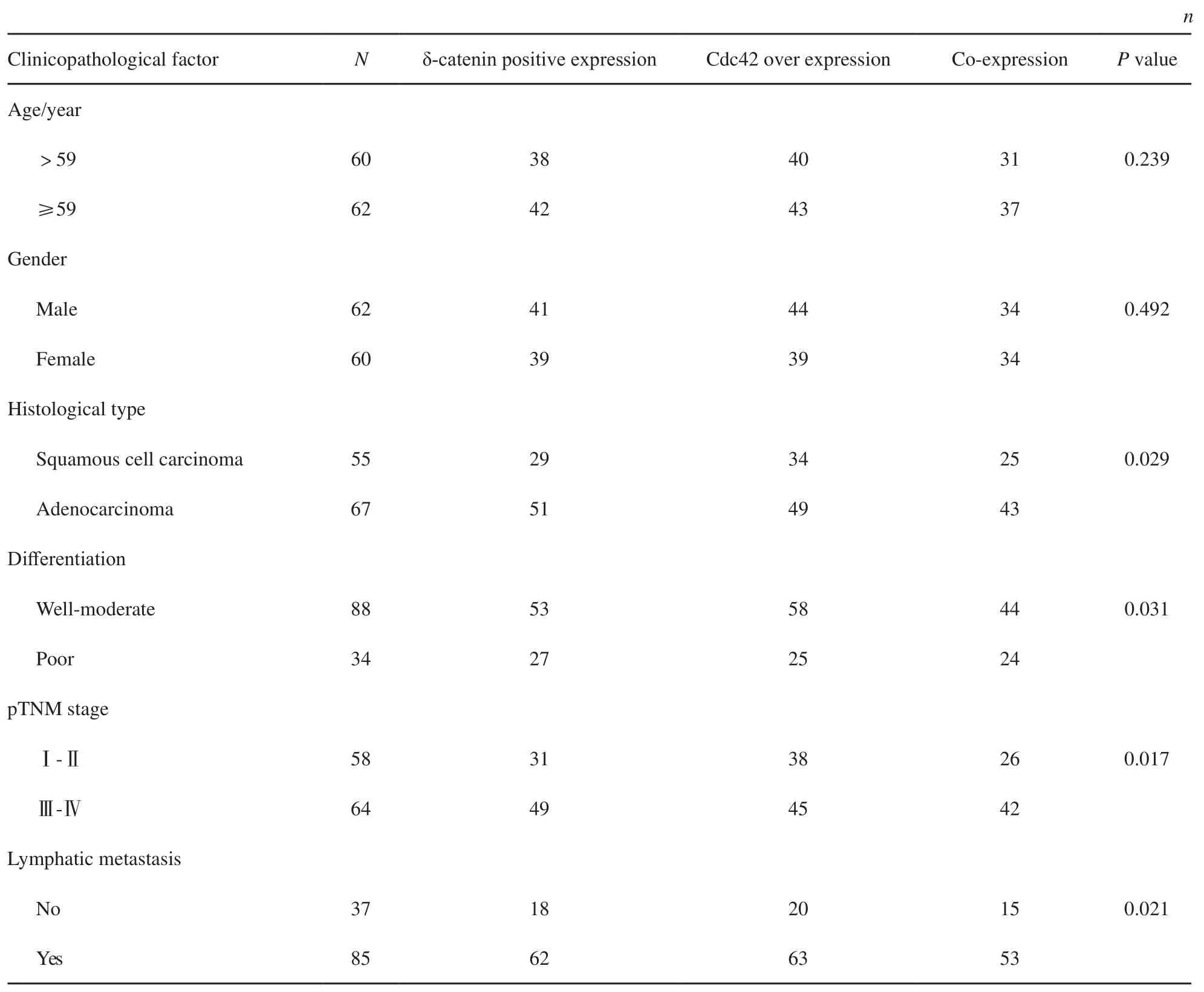
表 3 δ-catenin陽性表達和Cdc42過表達(協同表達)與臨床病理因素的關系Tab. 3 The relationship between δ-catenin and Cdc42 expression and clinicopathological factors
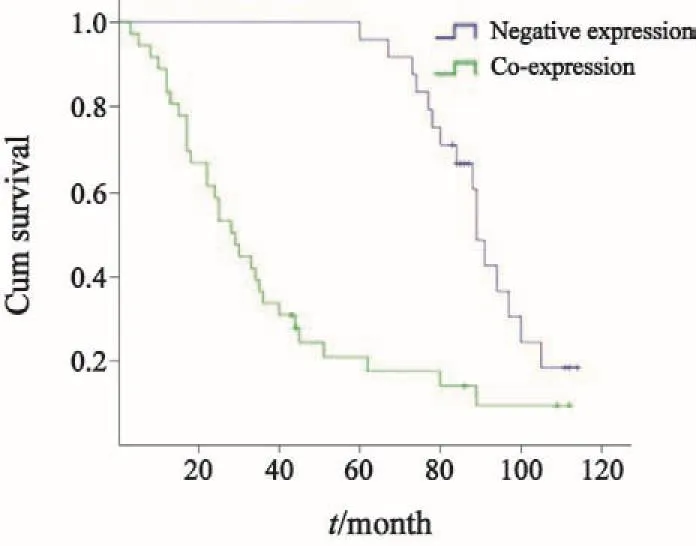
圖 2 Kaplan-Meier生存分析法檢驗δ-catenin和Cdc42協同表達與患者的不良預后的相關性Fig. 2 Kaplan-Meier was used for examining the relationship between co-expression of δ-catenin and Cdc42 and poor prognosis of patients
2.4過表達及沉默δ-catenin對Cdc42表達及活性的影響
為了探討δ-catenin對Rac1的影響,本研究分別檢測了過表達與沉默δ-catenin后Cdc42的表達及活性變化。分析顯示,在H460細胞系中沉默δ-catenin后, Cdc42表達及活性下降(圖4,P<0.05);而在LK2細胞系過表達δ-catenin后,Cdc42表達及活性明顯增加(圖5,P<0.05)。
2.5δ-catenin過表達和表達下調對肺癌細胞侵襲的影響
利用基質膠侵襲實驗檢測δ-catenin過表達或干擾其表達后肺癌細胞侵襲能力的變化(圖6)。δ-catenin過表達后48 h,平均侵襲的細胞數為48.38個,明顯高于對照組的20.55個(P<0.05);而在干擾δ-catenin后48 h,平均侵襲的細胞數為27.70個,顯著低于相應對照組的47.13個(P<0.05)。以上結果表明,上調δ-catenin表達可以促進肺癌細胞的增殖與侵襲能力,而下調δ-catenin表達則抑制腫瘤細胞的增殖與侵襲能力。
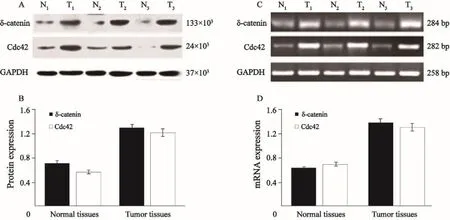
圖 3 在肺癌組織中(T1~T3)中δ-catenin和Cdc42的蛋白及mRNA表達明顯高于癌旁正常肺組織(N1~N3)Fig. 3 The protein and mRNA expressions of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in lung cancer tissues (T1-T3) were significantly higher than those in normal lung tissues (N1-N3)
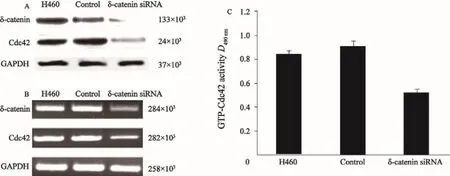
圖 4 Western blot、RT-PCR及G-LISATM檢測H460細胞系中沉默δ-catenin后Cdc42的蛋白及mRNA的表達情況及GTP-Cdc42活性Fig. 4 The protein and mRNA expressions of Cdc42 after knocking down δ-catenin in H460 cell line, and the GTP-Cdc42 activity detected by Western blot, RT-PCR and G-LISATM
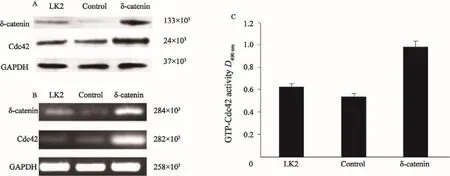
圖 5 Western blot、RT-PCR及G-LISATM檢測LK2細胞系中過表達δ-catenin后Cdc42的蛋白及mRNA的表達情況及GTP-Cdc42活性Fig. 5 The protein and mRNA expressions of Cdc42 after δ-catenin up-regulation in LK2 cell line, and the GTP-Cdc42 activity detected by Western blot, RT-PCR and G-LISATM
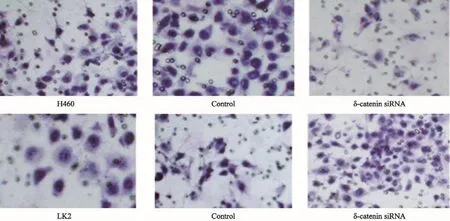
圖 6 Transwell檢測δ-catenin過表達及表達下調對肺癌細胞的侵襲的影響Fig. 6 The effect of δ-catenin up-regulation and down-regulation on the invasion of lung cancer cells detected by Transwell test
3 討 論
δ-catenin和Cdc42在惡性腫瘤組織中的表達情況已有報道[12-19]。但是二者在肺癌組織中的表達是否具有相關性,以及這種相關性與臨床病理因素和患者預后的關系等還未見報道,因而,本研究對122例NSCLC病例進行了檢測分析。結果發現,在肺癌組織中,δ-catenin在細胞質中的表達增強,其蛋白及mRNA表達水平明顯高于正常肺組織,而我們檢測到Cdc42在肺鱗癌和腺癌中也存在過表達。同時δ-catenin陽性表達和Cdc42的過表達具有較好的相關性和一致性,其協同表達與肺癌的高臨床分期、低分化、腺癌和淋巴結轉移相關,并且與腫瘤的不良預后明顯相關。
本研究檢測到δ-catenin陽性表達與Cdc42過表達存在明顯的相關性,同時δ-catenin表達增高時,Cdc42的表達及活性也明顯增強。已知Cdc42是Small GTP酶家族中的核心成員[20],它們存在著與GTP結合的活化狀態和與GDP結合的失活狀態的可能。Cdc42的激活可以影響腫瘤細胞間的粘附功能[5,11],導致細胞偽足的延展,這必將導致腫瘤細胞具有更強的移動能力,有利于細胞向遠處的游走[21-22]。這提示δ-catenin可通過調節Cdc42的表達與活性,促進腫瘤的侵襲轉移。
總之,本研究在肺癌組織中發現δ-catenin 與Cdc42存在協同表達,而這種協同表達也與NSCLC患者的臨床病理因素及預后不良密切相關。此外,δ-catenin可以調節Cdc42的表達與活性,影響肺癌細胞侵襲能力。
[參 考 文 獻]
[1] HATZFELD M. The p120 family of cell adhesion molecules [J]. Eur J Cell Biol, 2005, 84(2-3): 205-214.
[2] KOUTRAS C, LESSARD C B, LéVESQUE G. A nuclear function for the presenilin 1 neuronal partner NPRAP/ δ-catenin[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2011, 27(2): 307-316.
[3] KOSIK K S, DONAHUE C P, ISRAELY I, et al. Delta-catenin at the synaptic-adherens junction[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2005, 15(3): 172-178.
[4] KAWAMURA Y, FAN Q W, HAYASHI H, et al. Expression of the mRNA for two isoforms of neural plakophilin-related arm-repeat protein/delta-catenin in rodent neurons and glial cells[J]. Neurosci Lett, 1999, 277(3): 185-188.
[5] LU Q, PAREDES M, MEDINA M, et al. Delta-catenin, an adhesive junction-associated protein which promotes cell scattering[J]. J Cell Biol, 1999, 144(3): 519-532.
[6] KIM K, SIROTA A, CHEN YH Y H, et al. Dendrite-like process formation and cytoskeletal remodeling regulated by delta-catenin expression[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2002, 275(2):171-184.
[7] ABU-ELNEEL K, OCHIISHI T, MEDINA M, et al. A deltacatenin signaling pathway leading to dendritic protrusions [J]. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(47): 32781-32791.
[8] VEGA F M, RIDLEY A J. Snap shot: Rho family GTPases [J]. Cell, 2007, 129(7): 1430.
[9] SAHAI E, MARSHALL C J. RHO-GTPases and cancer [J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002, 2(2): 133-142.
[10] ZHANG J Y, WANG Y, ZHANG D, et al. Delta-catenin promotes malignant phenotype of non-small cell lung cancer by non-competitive binding to E-cadherin with p120ctn in cytoplasm[J]. J Pathol, 2010, 222(1): 76-88.
[11] ZHANG J Y, ZHANG D, WANG E H. Overexpression of small GTPases directly correlates with expression of δ-catenin and their coexpression predicts a poor clinical outcome in nonsmall cell lung cancer[J].Mol Carcinog, 2013, 52(5):338-347.
[12] BURGER M J, TEBAY M A, KEITH P A, et al. Expression analysis of delta-catenin and prostate-specific membrane antigen: their potential as diagnostic markers for prostate cancer[J]. Int J Cancer, 2002, 100(2): 228-237.
[13] LU Q, DOBBS L J, GREGORY C W, et al. Increased expression of delta-catenin/neural plakophilin-related armadillo protein is associated with the down-regulation and redistribution of E-cadherin and p120ctn in human prostate cancer[J]. Hum Pathol, 2005, 36(10): 1037-1048.
[14] LU Q, ZHANG J, ALLISON R, et al. Identification of extracellular delta-catenin accumulation for prostate cancer detection[J]. Prostate, 2009, 69(4): 411-418.
[15] FANG Y, LI Z, WANG X, et al. Expression and biological role of δ-catenin in human ovarian cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2012, 138(10): 1769-1776.
[16] LI X Y, LIU S L, CHA N, et al. Transcription expression and clinical significance of dishevelled-3 mRNA and δ-catenin mRNA in pleural effusions from patients with lung cancer[J]. Clin Dev Immunol, 2012, 2012: 904946[Epub 2012 Feb 23].
[17] DAI S D, WANG Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Upregulation ofδ-catenin is associated with poor prognosis and enhances transcriptional activity through Kaiso in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Sci, 2011, 102(1): 95-103.
[18] WANG M, DONG Q, ZHANG D, et al. Expression of delta catenin is associated with progression of human astrocytoma [J]. BMC Cancer, 2011, 11: 514. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-514.
[19] GAO M, LIU L, LI S, et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma by miR-137 is regulated by CDC42[J]. Oncol Rep, 2015, 34(5): 2523-2532.
[20] NOBES C D, HALL A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia[J]. Cell, 1995, 81(1): 53-62.
[21] LANE J, MARTIN T, WEEKS H P, et al. Structure and role of WASP and WAVE in Rho GTPase signalling in cancer[J]. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 2014, 11(3): 155-165.
[22] ZINS K, LUCAS T, REICHL P, et al. A Rac1/Cdc42 GTPasespecific small molecule inhibitor suppresses growth of primary human prostate cancer xenografts and prolongs survival in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e74924.
Correlation between δ-catenin and Cdc42 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
ZHANG Di1,2,WANG Enhua1,2(1.Department of Pathology, the College of Basic Medical Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China; 2. Department of Pathology, the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China)
[Key words]δ-catenin; Cdc42; Small GTPase; Non-small cell lung cancer; Prognosis
[Abstract]Background and purpose: δ-catenin is a member of the p120 catenin subfamily, which can directly bind to E-cadherin on the cell membrane, forming E-cadherin/catenin complex. δ-catenin can also affect the cytoskeleton assembly by regulating the activity of Cdc42 (Small GTPase). Therefore, this study detected the expression of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and investigated the relationship between them. Methods: The expressions of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in 122 cases of NSCLC were detected by immunohistochemistry. This study also used Western blot and real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RTFQ-PCR)to detect the protein and mRNA expressions of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in lung cancer tissues. After up-regulating or downregulating δ-catenin in lung cancer cell line, the activity of Cdc42 and invasion ability of lung cancer cells were detected by G-LISA and Transwell. Results: The mRNA and protein expression of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in lung cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in normal lung tissues. In 122 NSCLC cases, the δ-catenin positive expression rate was 65.57% (80/122), and the Cdc42 overexpression rate was 68.03% (83/122). There was a good correlation between δ-catenin positive expression and Cdc42 overexpression (P<0.001). The co-expression of δ-catenin and Cdc42 was related to the high clinical stage, poor differentiation, adenocarcinoma and lymph node metastasis of lung cancer(P<0.05), and was significantly associated with poor prognosis in patients with lung cancer. In the lung cancer cell line,the expression and the activity of Cdc42 were changed by regulating the δ-catenin expression, which affected invasion ability of the lung cancer cells. Conclusion: The δ-catenin expression was significantly correlated with the Cdc42 expression. The co-expression of δ-catenin and Cdc42 in lung cancer was correlated with the poor prognosis of lung cancer.
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3969.2016.03.004
中圖分類號:R734.2
文獻標志碼:A
文章編號:1007-3639(2016)03-0221-09
基金項目:國家自然科學基金(81101779)。
通信作者:王恩華 E-mail:wangeh@hotmail.com
收稿日期:(2015-10-03 修回日期:2016-02-20)

