右美托咪定麻醉對開腹手術患者手術情況、RAAS活性及腎功能的影響
何清泉,瞿玉蓮
(臺州市腫瘤醫院 麻醉科,浙江 臺州 317502)
右美托咪定麻醉對開腹手術患者手術情況、RAAS活性及腎功能的影響
何清泉Δ,瞿玉蓮
(臺州市腫瘤醫院 麻醉科,浙江 臺州 317502)
目的 研究右美托咪定麻醉對開腹手術患者手術情況、腎素-血管緊張素-醛固酮系統(renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system,RAAS)活性及腎功能的影響。方法 選擇2012年5月~2015年10月期間在臺州市腫瘤醫院接受開腹手術的96例患者進行研究,采用隨機數表法分為右美托咪定組(D組)和對照組(C組)并接受不同的麻醉方案,比較2組患者的手術情況、腎功能指標以及血漿腎素及血管緊張素Ⅱ含量。結果 D組和C組患者的手術時間、術中出血量、術中輸液量以及蘇醒時間均無顯著性差異;開腹后10 min和關腹前10 min,D組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素II、胱抑素C(cystatin C,Cys-C)、α1-微球蛋白(α1-microglobulin,α1-MG)含量顯著低于C組(P<0.05)。結論 右美托咪定麻醉用于開腹手術能夠抑制RAAS系統的激活、保護腎功能,麻醉效果更為確切。
右美托咪定;開腹手術;腎素-血管緊張素-醛固酮系統;腎功能
開腹手術是普外科常規的手術入路,能夠獲得清晰的手術視野以及充分的操作空間,但同時也會對機體造成較大創傷并引起血流動力學改變、腎素-血管緊張素-醛固酮系統(renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system,RAAS)激活,同時也會造成腎功能發生輕微損傷。在臨床實踐中,制定合理且有效的全身麻醉方案能夠保證手術的順利進行并減輕手術操作所造成的創傷[1-2]。右美托咪定是一類新型的麻醉藥物,能夠高選擇性地激動α2腎上腺素能受體并起到鎮靜、穩定血流動力學、減輕應激反應的作用[3-5]。在下列研究中,本研究分析了右美托咪定麻醉對開腹手術患者手術情況、RAAS活性及腎功能的影響。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選擇2012年5月~2015年10月期間在臺州市腫瘤醫院接受開腹手術的96例患者進行研究,所有患者均完善術前檢查、明確手術指征,包括胃大部切除術28例、膽囊切除術31例、腸段切除術22例、肝切除術15例。取得知情同意后,采用隨機數表法將入組患者分為右美托咪定組(D組)和對照組(C組),每組48例,接受不同的全身麻醉。D組患者中男性31例、女性17例,年齡28~65歲、平均(42.9±7.2)歲,體重指數(23.2±4.9)kg/m2,胃大部切除術13例、膽囊切除術16例、腸段切除術12例、肝切除術7例;C組患者中男性29例、女性19例,年齡25~66歲、平均(44.2±6.5)歲,體重指數(23.7±4.3)kg/m2,胃大部切除術15例、膽囊切除術15例、腸段切除術10例、肝切除術8例。2組患者一般資料的比較差異無統計學意義。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 麻醉方法:2組患者進入手術室后均連接心電監護、建立靜脈通路,常規檢測血壓、心率、血氧飽和度、腦電雙頻指數以及心電圖。麻醉誘導方案如下:咪達唑侖(江蘇恩華藥業股份有限公司,國藥準字H20143222)0.05 mg/kg、芬太尼(江蘇恩華藥業股份有限公司,國藥準字H20143314)3 μg/kg、羅庫溴銨(浙江仙琚制藥股份有限公司,國藥準字H20093186)0.8 mg/kg、丙泊酚(浙江九旭藥業有限公司,國藥準字H20084531)1.5 mg/kg靜脈推注,七氟醚吸入;氣管插管后按照下列方案進行麻醉維持:丙泊酚4~6 mg/(kg·h)微泵注入、七氟醚吸入,維持腦電雙頻指數(bispectral index,BIS)在40~60,必要時追加羅庫溴銨和芬太尼。D組患者在麻醉誘導前給予0.4 μg/kg右美托咪定(江蘇恒瑞醫藥股份有限公司,國藥準字H20090248)靜脈注射,C組患者給予等劑量0.9% NaCl注射液靜脈注射。
1.2.2 觀察指標:手術過程中,觀察2組患者的術中情況,具體包括手術時間、術中出血量、術中輸液量以及蘇醒時間。手術前(T0)、開腹后10 min(T1)和關腹前10 min(T2)時,分別采集2組患者的外周靜脈血,離心得到血漿標本后采用酶標儀及配套的酶聯免疫吸附試劑盒測定腎素、血管緊張素II以及胱抑素C(cystatin C,Cys-C)、α1-微球蛋白(α1-microglobulin,α1-MG)的含量。

2 結果
2.1 手術情況 D組和C組患者的手術時間、術中出血量、術中輸液量以及蘇醒時間均差異無統計學意義。見表1。
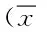
表1 2組患者的手術情況±s)
2.2 血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量 手術前(T0),D組和C組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量差異無統計學意義;開腹后10 min(T1)和關腹前10 min(T2)時,D組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量與T0時比較差異無統計學意義,C組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量與T0時比較顯著升高(P<0.05);D組患者T1和T2時的血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量顯著低于C組(P<0.05)。見表2。
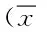
表2 2組患者的術中血漿腎素、血管緊張素Ⅱ含量±s)
#P<0.05,與C組比較,compared with C group;*P<0.05,與同組T0時比較,compared with the same group at T0
2.3 血漿Cys-C、α1-MG含量 手術前(T0),D組和C組患者的血漿Cys-C、α1-MG含量差異無統計學意義;開腹后10 min(T1)和關腹前10 min(T2)時,D組和C組患者的血漿Cys-C、α1-MG含量與T0時比較顯著升高(P<0.05);D組患者T1和T2時的血漿Cys-C、α1-MG含量顯著低于C組(P<0.05)。見表3。

表3 2組患者的術中血漿Cys-C、α1-MG含量
#P<0.05,與C組比較,compared with C group;*P<0.05,與同組T0時比較,compared with the same group at T0
3 討論
開腹手術是普外科應用最廣泛的手術入路,術中操作不可避免會造成創傷,制定合理的麻醉方案能夠減輕開腹手術操作所引起的創傷。右美托咪定是一類高選擇性的α2腎上腺素能受體激動劑,能夠激動中樞神經系統藍斑核的α2受體并產生鎮靜效果,激動突觸前膜的α2受體并產生抗應激效果[6-7]。近年來,右美托咪定被越來越多地用于外科手術的靜吸復合麻醉。已有研究報道,右美托咪定具有穩定術中生命體征、血流動力學特征、減輕蘇醒期躁動的效果[8-10]。本研究在開腹手術中聯合使用右美托咪定和常規靜吸復合麻醉,旨在發揮右美托咪定的鎮靜、穩定血流動力學、減輕應激反應的作用。本研究首先對2組患者的術中情況進行比較和分析,結果顯示:D組和C組患者的手術時間、術中出血量、術中輸液量以及蘇醒時間均差異無統計學意義。這就說明聯合使用右美托咪定不會影響開腹手術的操作情況以及術后蘇醒過程。
應激反應的激活是機體遭受手術創傷時的防御性反應,腎素-血管緊張素-醛固酮(RAAS)系統是介導機體應激反應的重要機制之一[11]。RAAS系統的激活表現為腎素大量合成和分泌,進而作用于血管緊張素原并產生血管緊張素I,后者在血管緊張素轉化酶的作用下合成有活性的血管緊張素II[12-14]。已有研究證實,右美托咪定對甲狀腺手術、后腹腔鏡手術患者的RAAS系統活性具有抑制效應[15-16]。本研究對開腹手術患者麻醉后RAAS系統激活程度的分析顯示,D組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素II含量與T0時比較差異無統計學意義,而C組患者的血漿腎素、血管緊張素II含量與T0時比較顯著升高(P<0.05)。這就說明在常規麻醉條件下,開腹手術會激活RAAS系統,引起腎素、血管緊張素II含量升高;聯合使用右美托咪定麻醉能夠避免RAAS系統的激活,腎素、血管緊張素II含量無顯著改變。
開腹手術操作對機體造成的創傷除了表現為RAAS系統的激活外,還會對腎功能造成影響。術中循環血容量的丟失、血流動力學的改變以及血管活性物質的大量分泌會造成腎臟入球小動脈收縮、腎小球灌注量減少,進而出現腎小球濾過率降低[17-18]。血肌酐和血尿素氮是臨床上反應腎功能的常用指標,但是受到腎臟自身代償機制的影響,上述2項指標盡在腎功能損傷較為嚴重時才發生改變,無法反映術中腎小球灌注減少所造成的輕微腎損傷。Cys-C、α1-MG是近年來發現的反應早期腎損傷的敏感指標,2種分子均為能夠自由通過腎小球濾過膜的小分子蛋白,前者不會被重吸收、后者在近曲小管被分解代謝,均能反映腎功能是否發生損傷[19-20]。本研究對2組患者血清中Cys-C和α1-MG含量的分析證實:2組患者術中的血清Cys-C和α1-MG含量均高于術前且D組患者術中的血清Cys-C和α1-MG含量顯著低于C組(P<0.05)。由此說明右美托咪定對開腹手術所引起的輕微腎損傷具有保護效應。
右美托咪定麻醉用于開腹手術能夠抑制RAAS系統的激活、保護腎功能,麻醉效果更為確切。
[1] Hotta K, Inoue S, Taira K, et al.Comparison of the analgesic effect between continuous wound infiltration and single-injection transversus abdominis plane block after gynecologic laparotomy[J].J Anesth, 2016, 30(1): 31-38.
[2] Yang XL, Dai SH, Zhang J, et al.Anesthesia management of surgery for sigmoid perforation and acute peritonitis patient following heart transplantation: case report[J].Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(7):11632-11635.
[3] 衣選龍,劉素麗,初春芹,等.右美托咪定對后腹腔鏡手術患者血漿腎素、血管 緊張素II和腎功能的影響[J].臨床麻醉學雜志,2012,28(12):1167-1169.
[4] 施正元.右美托咪定對老年患者全麻手術應激反應的影響[J].江蘇醫藥,2011,37(23):2815-2816.
[5] Ge YL, Li X, Gao JU, et al.Beneficial effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on cognitive function and cerebral injury following a carotid endarterectomy[J].Exp Ther Med, 2016, 11(3):1128-1134.
[6] Li Y, Wang B, Zhang LL, et al.Dexmedetomidine combined with general anesthesia provides similar intraoperative stress response reduction when compared with a combined general and epidural anesthetic technique[J].Anesth Analg, 2016, 122(4):1202-1210.
[7] Si Y, Bao H, Han L, et al.Dexmedetomidine protects against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling activation[J].J Transl Med, 2013, 9(11): 141.
[8] Kaur S, Gupta KK, Singh A, Sunita, et al.Arousal from sedation in lower abdominal surgeries under spinal anesthesia: Comparison between dexmedetomidine and clonidine[J].Anesth Essays Res, 2016, 10(1):98-103.
[9] 余潔,邵雪泉,鄭麗花,等.右美托咪啶對腹腔鏡膽囊切除術患者七氟烷麻醉復蘇期躁動的影響[J].中國內鏡雜志,2015,21(2):159-161.
[10] Shi ZY.Efect of dexmedetomidine on stres response to anesthesia and surgery in the elderly[J].Jiangsu Med J, 2011, 37(23): 2815-2816.
[11] Boegehold MA, Drenjancevic I, Lombard JH.Salt, Angiotensin II, Superoxide, and Endothelial Function[J].Compr Physiol, 2015, 6(1):215-254.
[12] Tang YJ, Zhang ZZ, Chen SQ, et al.Effect of topical propranolol gel on plasma renin, angiotensin II and vascular endothelial growth factor in superficial infantile hemangiomas[J].J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2015, 35(5):759-762.
[13] Afroze SH, Munshi MK, Martínez AK, et al.Activation of the renin-angiotensin system stimulates biliary hyperplasia during cholestasis induced by extrahepatic bile duct ligation[J].Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2015, 308(8): 691-701.
[14] Li Y, Hu J, Qian H, et al.Novel findings: Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in thoracic aortic dissection and aneurysm[J].J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, 2015, 16(4):1130-1134.
[15] Yi XL, Liu SL, Chu CQ, et al.Efects of dexmedetomidine on plasma rennin and angiotensin I and renal function in patients undergoing retroperiton eoscopic surgery[J].J Clin Anesthesiol, 2012, 28(12): 1167-1169.
[16] He QX, Lu Y, Gu XX, et al.Effects of pre-injection of dexmedetomidine on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system during recovery period of general anesthesia in thyroid surgery[J].The Journal of Practical Medicin, 2015,31(1): 125-127.
[17] Pan Z, Feng L, Long H, et al.Effects of local pancreatic renin-angiotensin system on the microcirculation of rat with severe acute pancreatitis[J].Korean J Physiol Pharmacol, 2015,19(4):299-307.
[18] Li C, Lin Y, Luo R, et al.Intrarenal renin-angiotensin system mediates fatty acid-induced ER stress in the kidney[J].Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2016, 310(5): 351-363.
[19] Colantonio LD, Tanner RM, Warnock DG, et al.The role of cystatin-C in the confirmation of reduced glomerular filtration rate among the oldest old[J].Arch Med Sci, 2016, 12(1):55-67.
[20] Terzi I, Papaioannou V, Papanas N, et al.Alpha1-microglobulin as an early biomarker of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury: a prospective cohort study[J].Hippokratia, 2014, 18(3):262-268.
(編校:王儼儼)
Effects of dexmedetomidine anesthesia on surgery condition,RAAS activity and renal function in laparotomy
HE Qing-quanΔ, QU Yu-lian
(Department of Anesthesiology, Taizhou Tumor Hospital, Taizhou 317502, China)
ObjectiveTo study the effect of dexmedetomidine anesthesia on surgery condition, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activity and renal function of laparotomy patients.Methods96 patients
laparotomy in our hospital during May 2012 to October 2015 were studied, which were divided into dexmedetomidine group (D group) and control group (C Group) by random number table method and received different anesthetic regimes.Then surgery condition, renal function indexes and plasma renin, angiotensin II levels of two groups were compared.ResultsThe operation time, intraoperative blood loss, intraoperative transfusion volume and awakening time of D group and C group had no significant difference.10 min after opening abdomen and 10 min before closing abdomen, the plasma renin, angiotensin II, cystatin C (Cys-C),α1-microglobulin (α1-MG) contents were significantly lower than those of C group(P<0.05).ConclusionDexmedetomidine anesthesia applicated in laparotomy could inhibit the RAAS activity, protect renal function, and its anesthesia effect is more precise.
dexmedetomidine; laparotomy; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; renal function
10.3969/j.issn.1005-1678.2016.06.29
何清泉,通信作者,男,本科,主治醫生,研究方向:麻醉,E-mail:heqingquanzj@163.com。
R614.2
A

