PRC1高表達與前列腺癌生化復發的相關性研究
韓兆冬 羅宏偉 林卓遠 梁應科 陳果 吳永定 何慧嬋
?
PRC1高表達與前列腺癌生化復發的相關性研究
韓兆冬羅宏偉林卓遠梁應科陳果吳永定何慧嬋
510180 廣州,廣州市第一人民醫院泌尿外科(韓兆冬),中心實驗室(韓兆冬,羅宏偉,林卓遠,梁應科,陳果,吳永定);510230 廣州,廣州醫科大學附屬第一醫院 廣東省泌尿外科重點實驗室(何慧嬋)
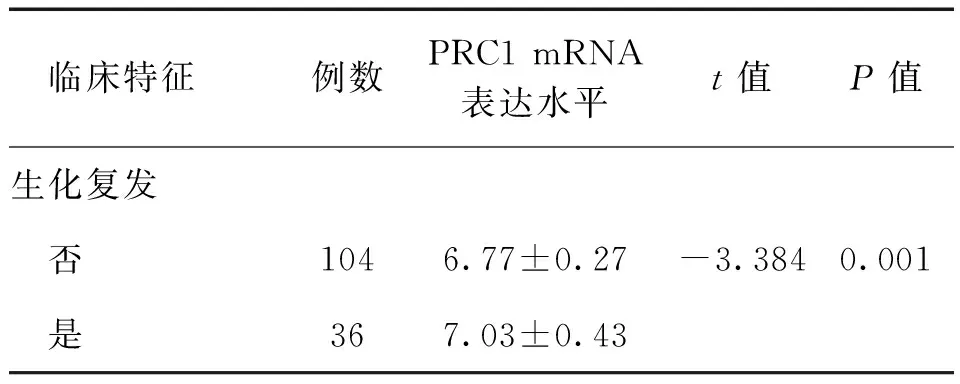
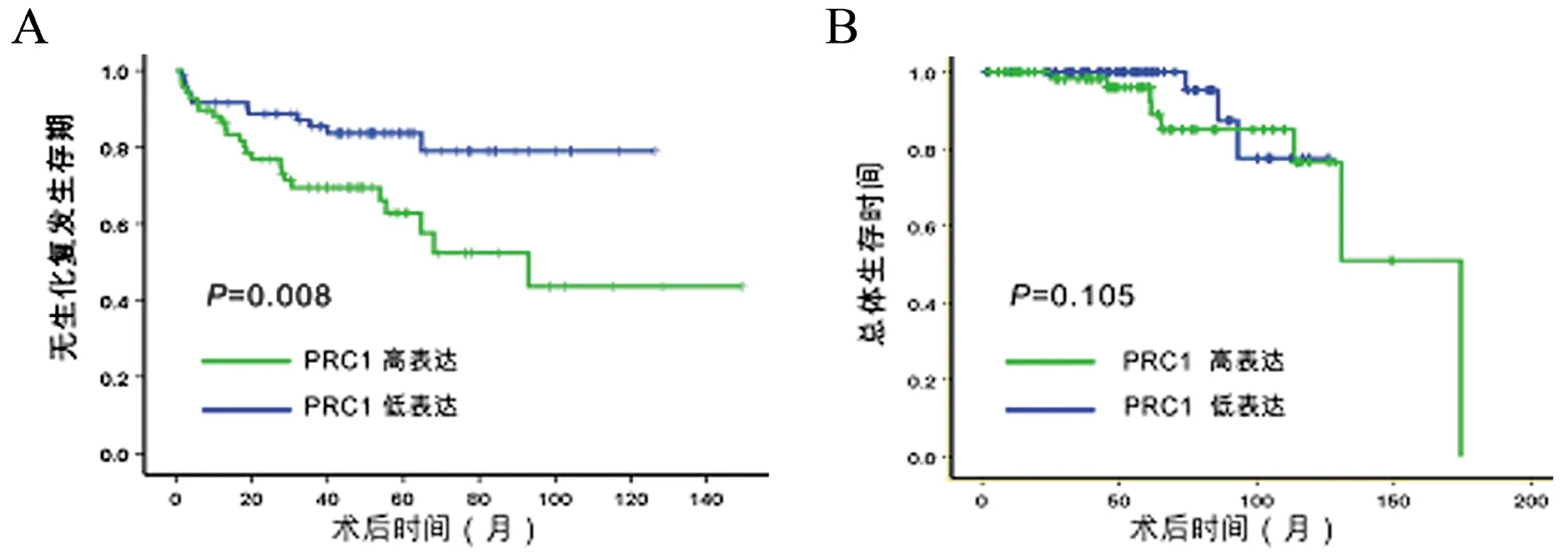
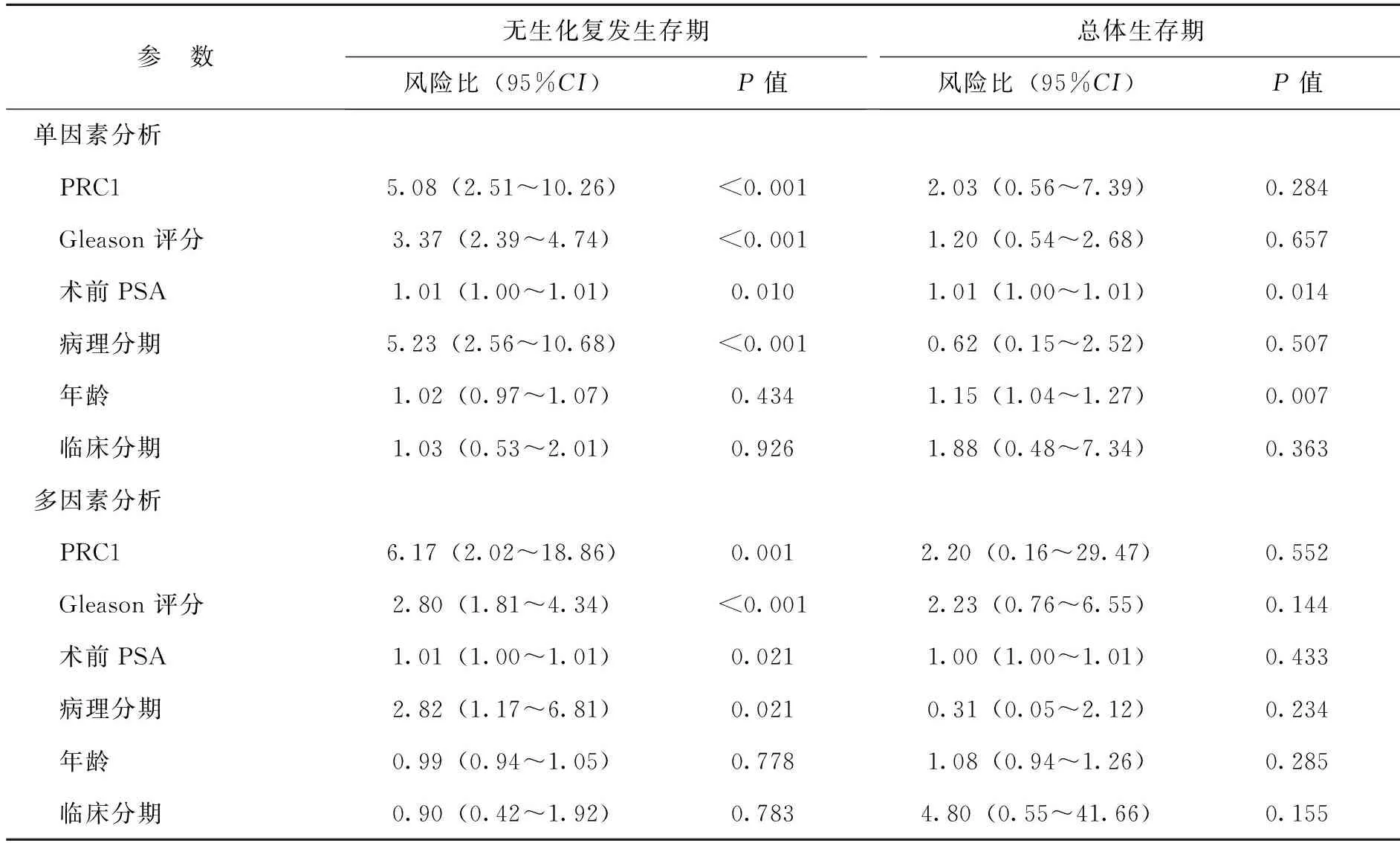
【摘要】目的研究細胞質分裂調控蛋白1(PRC1)在前列腺癌中的表達情況及其與生化復發的相關性。方法采用實時定量PCR及蛋白免疫印跡法檢測PRC1在前列腺癌與癌旁前列腺組織的表達水平,并利用Taylor基因芯片數據庫對PRC1基因mRNA水平進行驗證。Kaplan-Meier法分析前列腺癌患者總體生存率及生化復發時間與PRC1 mRNA表達水平之間的關系。Cox回歸分析臨床病理特征與生化復發的相關性。結果12對前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織中,前列腺癌的PRC1 mRNA及蛋白表達均高于癌旁前列腺組織(P均<0.01)。Taylor基因芯片數據庫分析顯示,PRC1在前列腺癌組織中的表達水平高于非癌組織(P<0.001),且出現生化復發或轉移、Gleason評分高、臨床分期≥T3A期者的PRC1 mRNA表達水平高于無出現生化復化或轉移、Gleason評分低、臨床分期 【關鍵詞】細胞質分裂調控蛋白1;前列腺癌;生化復發;預后 材料與方法 一、材料 12對前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織來源于廣州市第一人民醫院,所有病例均為首次確診并行前列腺癌根治術,術前均未行放射治療或化學治療。前列腺癌患者年齡(65.7±3.5)歲,按TNM分期T1 3例,T2 9例;Gleason評分<7分10例,≥7分2例;術前PSA<4 μg/L 2例,PSA≥4 μg/L 10例。 二、主要試劑及儀器 RNApure 高純總RNA快速抽提試劑盒(離心柱型)購自北京百泰克生物技術有限公司,Trizol總RNA抽提試劑為美國Invitrogene公司產品,RNA逆轉錄試劑為日本Takara寶生物產品;PRC1兔抗人單克隆抗體為美國Abcam公司產品,β-actin抗體為美國Santa Cruz公司產品,SuperSignal?系列Western化學發光底物系統為美國Thermo Scientific公司產品;RotorGene 2000 system實時熒光定量PCR分析系統為澳大利亞Corbett Research產品。 三、方法 1. PRC1 mRNA表達水平的檢測 采用實時定量PCR(RT-PCR)檢測。提取前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織總RNA,取2 μg總RNA進行逆轉錄。PCR總體系20 μl,根據儀器提供的實驗方案配制SYBR Green PCR Master Mix,β-actin作為內參,按PCR儀附帶的實驗方案操作。引物序列:PRC1上游 5’-CCTGTGCCTACTTTGCCTGA-3’,下游5’-CGTGGCTAACACCAAGTCCA-3’,產物長度304 bp;β-actin上游 5’-AGCGAGCATCCCCCAAAGTT-3’,下游5’-GGGCACGAAGGCTC ATCATT-3’,產物長度285 bp。PCR反應步驟:94℃預熱10 min, 94℃ 15 s、56℃退火15 s,循環37次,72℃延伸45 s。根據標準曲線設定閾值,使用Rotor-Gene 5.0軟件分析數據。 2. PRC1蛋白表達水平的檢測 出現高溫災害4年,極端高溫達到37.2℃,影響冬小麥灌漿和干物質積累,千粒重下降,造成逼熟空秕子多,因而減產。 采用蛋白免疫印跡法檢測。從前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織中提取蛋白,取40 μg蛋白在十二烷基硫酸鈉聚丙烯酰胺凝膠電泳(SDS-PAGE)并轉移至雜交硝酸纖維素膜上,然后以脫脂奶粉溶于Tris-HCl緩沖鹽溶液,調節濃度至5%,封閉1 h,隨后洗凈膜并孵育PRC1抗體(1∶2 000)及β-actin抗體(1∶2 000),使用SuperSignal West PICO化學發光檢測系統觀察結果,β-actin作為內參蛋白。 3. Taylor數據庫分析 由于納入本研究的樣本量較少,所以利用Taylor基因芯片數據庫資料進行驗證,并分析PRC1表達水平與前列腺癌臨床病理特征關系。Taylor數據庫[美國國立生物技術信息中心(NCBI)高通量基因數據表達平臺(GEO),檔案編號 GSE21032]是一個公用的數據平臺,其中mRNA表達譜芯片包含帶有臨床隨訪數據的150例原發性前列腺癌及29例非癌組織。 四、統計學處理 結果 一、PRC1在前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織的mRNA及蛋白表達情況 12例前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織中,PRC1 mRNA在前列腺癌組織表達水平為9.22±2.28,比癌旁前列腺組織(1.04±0.29)上調(t=10.781,P<0.001),見圖1; PRC1蛋白在前列腺癌組織的表達水平為3.89±2.55,比癌旁前列腺組織(1.00±0.39)增加(t=4.653,P<0.001),見圖2。 圖1 PRC1 mRNA在前列腺癌及 **P<0.01 二、PRC1與前列腺癌臨床病理特征的關系 為進一步驗證PRC1在前列腺癌中的表達情況,通過Taylor數據庫檢索發現PRC1在前列腺癌組織中的表達(6.87±0.38)高于非癌組織(6.61±0.12)(P<0.001),且出現生化復發或轉移、Gleason評分高、臨床分期≥T3A期者的PRC1 mRNA表達水平高于無出現生化復化或轉移、Gleason評分低、臨床分期 三、 PRC1與前列腺癌生化復發的相關性 以PRC1表達水平量的中位數為分割點,分成高表達組和低表達組。通過Kaplan-Meier 曲線分析Taylor數據庫中前列腺癌患者總體生存率及生化復發時間與PRC1表達量之間的聯系,高表達組的無生化復發率低于低表達組(P=0.008),而2組的總體生存率比較差異無統計學意義(P=0.105),見圖3。此外,在單因素分析中,高表達組與低表達組在生化復發時間上比較差異有統計學意義(HR=5.08, 95%CI2.51~10.26,P<0.001)。在多因素分析中,高表達PRC1(HR=6.17, 95%CI2.02~18.86,P=0.001)、高Gleason評分(HR=2.80, 95%CI1.81~4.34,P<0.001)、術前高PSA水平(HR=1.01, 95%CI1.00~1.01,P=0.021)及高病理分期(HR=2.82, 95%CI1.17~6.81,P=0.021)均為生化復發的危險因素,見表2。 圖2 PRC1蛋白在前列腺癌及癌旁前列腺組織的表達情況 A:蛋白免疫印跡法結果;B:定量分析結果,**P<0.01 表1 PRC1表達與前列腺癌臨床特征的關系 續表 臨床特征例數PRC1mRNA表達水平t值P值生化復發 否1046.77±0.27-3.3840.001 是367.03±0.43 注:因為數據庫中有部分原始數據缺失,所以某些統計項目的納入病例數不相同 圖3 前列腺癌中PRC1表達相關的Kaplan-Meier曲線 A:生化復發時間比較;B:總體生存體率比較 表2 Cox風險預測模型中PRC1表達量對生化復發的診斷價值 討論 前列腺癌是嚴重影響男性健康的惡性腫瘤,我國前列腺癌的發病率呈上升的趨勢。前列腺癌的發生、發展是一個多階段的過程,而且有不同的機制參與腫瘤的進展及預后。生化復發是前列腺癌根治術后疾病復發的早期表現,約17%~64%根治術后患者出現生化復發,其中約1/3發展為轉移性前列腺癌[5]。Punnen等[6]提出生化復發與前列腺癌的進展及轉移密切相關。因此,對生化復發的早期預測有助于觀察前列腺癌的病情變化及指導進一步的治療。 PRC1蛋白由620個氨基酸組成,主要在G2/M期表達,是細胞周期蛋白依賴性激酶的基質,參與紡錘體平行微絲及縮復環的形成,與細胞的有絲分裂密切相關[7-8]。PRC1基因被證實直接受抑癌基因p53的負性調控,在p53缺失的腫瘤細胞中,PRC1表達量明顯增加[9]。Kanehira 等[10]在膀胱癌細胞株內發現PRC1表達量升高,沉默后可導致膀胱癌細胞的死亡。Espinosa等[11]發現PRC1在宮頸癌中高表達。臨床研究發現,PRC1不僅可以作為預測腫瘤發生的因子,也是評估腫瘤預后及療效的參考指標之一。有研究分析448例非小細胞肺癌化學治療后基因變化,發現化學治療后PRC1表達下調,提示PRC1 mRNA表達水平可預測患者預后[12]。Mustacchi等[13]發現,PRC1與早期乳腺癌的發生及患者的預后相關,檢測PRC1有助于治療方案的設計。但PRC1在前列腺癌中的表達情況,筆者尚未見相關報道。 本研究發現,前列腺癌中的PRC1在mRNA及蛋白表達水平均較癌旁前列腺組織明顯升高,出現生化復發或轉移、Gleason評分高、臨床分期≥T3A期者的PRC1 mRNA表達水平高于無出現生化復化或轉移、Gleason評分低、臨床分期 綜上所述,PRC1的表達增高與前列腺癌的惡性程度及生化復發密切相關,與現有的臨床指標聯合應用能更有效預測前列腺癌的預后。雖然PRC1的作用機制仍有待進一步研究,但我們的結果仍然有望為前列腺癌治療提供新的研究方向。 參考文獻 [1]Arsov C, Jankowiak F, Hiester A, Rabenalt R, Quentin M, Schimm?ller L, Blondin D, Antoch G, Albers P. Prognostic value of a cell-cycle progression score in men with prostate cancer managed with activesurveillance after MRI-guided prostate biopsy——a pilot study.Anticancer Res,2014,34(5):2459-2466. [2]Sommariva S, Tarricone R, Lazzeri M, Ricciardi W, Montorsi F.prognostic value of the cell cycle progression score in patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Urol,2016,69(1):107-115. [3]Planas J, Morote J. Biochemical recurrence criteria after radical prostatectomy. Natural history of the disease.Arch Esp Urol,2012,65(1):4-11. [4]張增強,葉永康,黃亞強,吳永定,李牧,何慧嬋. 人肌球蛋白輕鏈9在前列腺癌的表達水平及其對生化復發的預測價值.新醫學,2015,46(11):732-736. [5]魯欣,任善成,孫穎浩.前列腺癌根治術后生化復發的診斷和治療.中華泌尿外科雜志, 2007, 28(12): 861-863. [6]Punnen S, Cooperberg MR, D’Amico AV, Karakiewicz PI, Moul JW, Scher HI, Schlomm T, Freedland SJ. Management of biochemical recurrence after primary treatment of prostate cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Urol,2013,64(6):905-915. [7]Freedland SJ, Gerber L, Reid J, Welbourn W, Tikishvili E, Park J, Younus A, Gutin A, Sangale Z, Lanchbury JS, Salama JK, Stone S. Prognostic utility of cell cycle progression score in men with prostate cancer after primary external beamradiation therapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2013,86(5):848-853. [8]Shrestha S, Wilmeth LJ, Eyer J, Shuster CB.PRC1 controls spindle polarization and recruitment of cytokinetic factors during monopolar cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell,2012,23(7):1196-1207. [9]Li C, Lin M, Liu J. Identification of PRC1 as the p53 target gene uncovers a novel function of p53 in the regulation ofcytokinesis. Oncogene, 2004,23(58):9336-9347. [10]Kanehira M, Katagiri T, Shimo A, Takata R, Shuin T, Miki T, Fujioka T, Nakamura Y.Oncogenic role of MPHOSPH1, a cancer-testis antigen specific to human bladder cancer.Cancer Res,2007,67(7):3276-3285. [11]Espinosa AM, Alfaro A, Roman-Basaure E, Guardado-Estrada M, Palma, Serralde C, Medina I, Juárez E, Bermúdez M, Márquez E, Borges-Ibáez M, Muoz-Cortez S, Alcántara-Vázquez A, Alonso P, Curiel-Valdez J, Kofman S, Villegas N, Berumen J.Mitosis is a source of potential markers for screening and survival and therapeutic targets in cervicalcancer.PLoS One, 2013;8(2):e55975. [12]Tang H, Xiao G, Behrens C, Schiller J, Allen J, Chow CW, Suraokar M, Corvalan A, Mao J, White MA, Wistuba II, Minna JD, Xie Y.A 12-gene set predicts survival benefits from adjuvant chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancerpatients.Clin Cancer Res,2013,19(6):1577-1586. [13]Mustacchi G, Sormani MP, Bruzzi P, Gennari A, Zanconati F, Bonifacio D, Monzoni A, Morandi L.Identification and validation of a new set of five genes for prediction of risk in early breast cancer.Int J Mol Sci,2013,14(5):9686-9702. (本文編輯:林燕薇) DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2016.07.005 基金項目:廣東省自然科學基金(2014A030310066);廣州市衛生局一般引導項目(20141A010013);廣東省科技計劃項目(2013B021800055);廣州市科技計劃項目(2014J4100072) 通訊作者,何慧嬋, E-mail:xiaohejian@21cn.com (收稿日期:2016-02-25) Correlation analysis between overexpression of protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer HanZhaodong,LuoHongwei,LinZhuoyuan,LiangYingke,ChenGuo,WuYongding,HeHuichan. DepartmentofUrology,GuangzhouFirstPeople’sHospital,GuangzhouMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou510180,ChinaCorrespondingauthor,HeHuichan,E-mail:xiaohejian@21cn.com 【Abstract】ObjectiveTo investigate the correlation between the expression level of protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 (PRC1) and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. MethodsThe expression levels of PRC1 protein and mRNA between the prostate cancer and adjacent benign tissues were statistically compared using Western blot and RT-PCR. The expression of PRC1 mRNA was validated by microarray-based Taylor database. Kaplan-Meier plot was performed to evaluate the overall survival and analyze the correlation between PRC1 expression and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. Cox proportional hazards regression model was utilized to assess the correlation between clinicopathological characteristics and biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. ResultsAmong 12 pairs of prostate cancer and adjacent benign tissues, the expression levels of PRC1 protein and mRNA in the prostate cancer tissues were significantly higher than those in the adjacent benign prostate tissues (both P<0.01). Microarray-based Taylor database revealed that the expression of PRC1 in the cancer tissues was significantly up-regulated compared with that in the non-cancerous tissues (P<0.001). In addition, the expression of PRC1 mRNA in patients with biochemical recurrence or metastasis of prostate cancer, high Gleason score and clinical staging ≥T3A was significantly up-regulated compared with their counterparts with no biochemical recurrence or metastasis of prostate cancer, low Gleason score and clinical staging 【Key words】Protein regulator of cytokinesis 1; Prostate cancer; Biochemical recurrence; Prognosis