胃癌組織MGMT蛋白的表達及臨床意義
夏旻明 陸國文 章懿欣
胃癌組織MGMT蛋白的表達及臨床意義
夏旻明 陸國文 章懿欣
目的 檢測胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況,分析其與胃癌生物學行為及長期預后的相關性。方法 收集262例胃癌組織及癌旁正常組織,采用免疫組織化學法測定組織內MGMT蛋白的表達情況,統計分析胃癌組織及癌旁正常組織MGMT蛋白表達的差異、胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌臨床病理參數的關系及胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌患者5年死亡及生存時間的關系。結果 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達陽性率顯著低于癌旁正常組織,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌腫瘤大小、浸潤深度分級、淋巴結轉移分級、遠處轉移分級、腹膜擴散情況和TNM分期相關,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陰性表達是胃癌5年死亡及5年生存時間的獨立危險因素。結論 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達顯著降低,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白低表達與胃癌惡性生物學行為密切相關,與胃癌長期不良預后獨立相關。
胃癌 MGMT蛋白 預后 生物學行為
胃癌是世界范圍內最常見的惡性腫瘤之一,幾乎2/3的胃癌發生在欠發達地區[1]。DNA甲基化出現在多種惡性腫瘤中,可引起致癌基因過表達,也可導致抑癌基因沉默,參與腫瘤的發生發展過程[2,3]。分子標記物DNA修復蛋白06-甲基鳥嘌呤 -DNA-甲基轉移酶(MGMT)編碼基因屬于抑癌基因[4]。MGMT基因啟動子甲基化可導致腫瘤組織MGMT蛋白低表達[5]。MGMT蛋白低表達與肺癌﹑乳腺癌和子宮內膜癌等惡性腫瘤預后不良密切相關[6,7]。本文探討MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌臨床特征和預后的相關性。
1 臨床資料
1.1一般資料 2006年2月至2008年5月本院腫瘤外科經手術病理確診胃癌患者262例。其中男156例,女106例;年齡≥60歲121例,<60歲141例。病理診斷:腺癌214例,印戒細胞癌22例,其他26例。腫瘤大小:<5cm 182例﹑≥5cm 80例。浸潤深度分級:T1 25例﹑T2 42例﹑T3 67例﹑T4 128例。淋巴結轉移分級:N0 82例﹑N1 38例﹑N2 47例﹑N3a 60例﹑N3b 35例。遠處轉移分級:M0 186例﹑M1 76例。腹膜擴散50例﹑腹膜未擴散212例。TNM分期:Ⅰ期47例﹑Ⅱ期60例﹑Ⅲ期78例﹑Ⅳ期77例。患者均排除既往惡性腫瘤病史和并存其他惡性腫瘤。
1.2免疫組織化學檢測 術中獲取的胃癌組織及癌旁正常組織經10%甲醛固定﹑石蠟包埋和常規切片后保存。采用鏈霉素親生物素-過氧化物酶法(試劑盒由福州邁新生物技術開發公司提供)檢測胃癌組織及癌旁正常組織MGMT蛋白表達。陽性細胞為細胞核和/或細胞漿呈棕色顆粒。陽性細胞數<10%為MGMT蛋白表達陰性,>10%為MGMT蛋白表達陽性。
1.3隨訪觀察 胃癌患者手術后隨訪5年,前3年,隨訪1次/3個月;后2年,隨訪1次/6個月。總生存期為術后至最后隨訪或死亡時間。
1.4統計學方法 采用SPSS 19.0.統計軟件。單因素分析采用卡方檢驗﹑log-rank檢驗和單因素Cox回歸分析,多因素分析采用二分類Logistic回歸分析和多因素Cox回歸分析。P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
作者單位:315040 浙江省寧波市鄞州人民醫院腫瘤外科
2 結果
2.1胃癌組織及癌旁正常組織MGMT蛋白的表達 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陽性表達150例(57.3%),癌旁正常組織MGMT蛋白陽性表達236例(90.1%),差異有統計學意義(χ2=72.755,P<0.001)。
2.2胃癌組織MGMT基因啟動子甲基化狀態與胃癌臨床特征的相關性 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況與腫瘤大小﹑浸潤深度分級﹑淋巴結轉移分級﹑遠處轉移分級﹑腹膜擴散情況和TNM分期相關(均P<0.05),而性別﹑年齡和病理診斷與胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達無顯著相關(均P>0.05)。見表1。
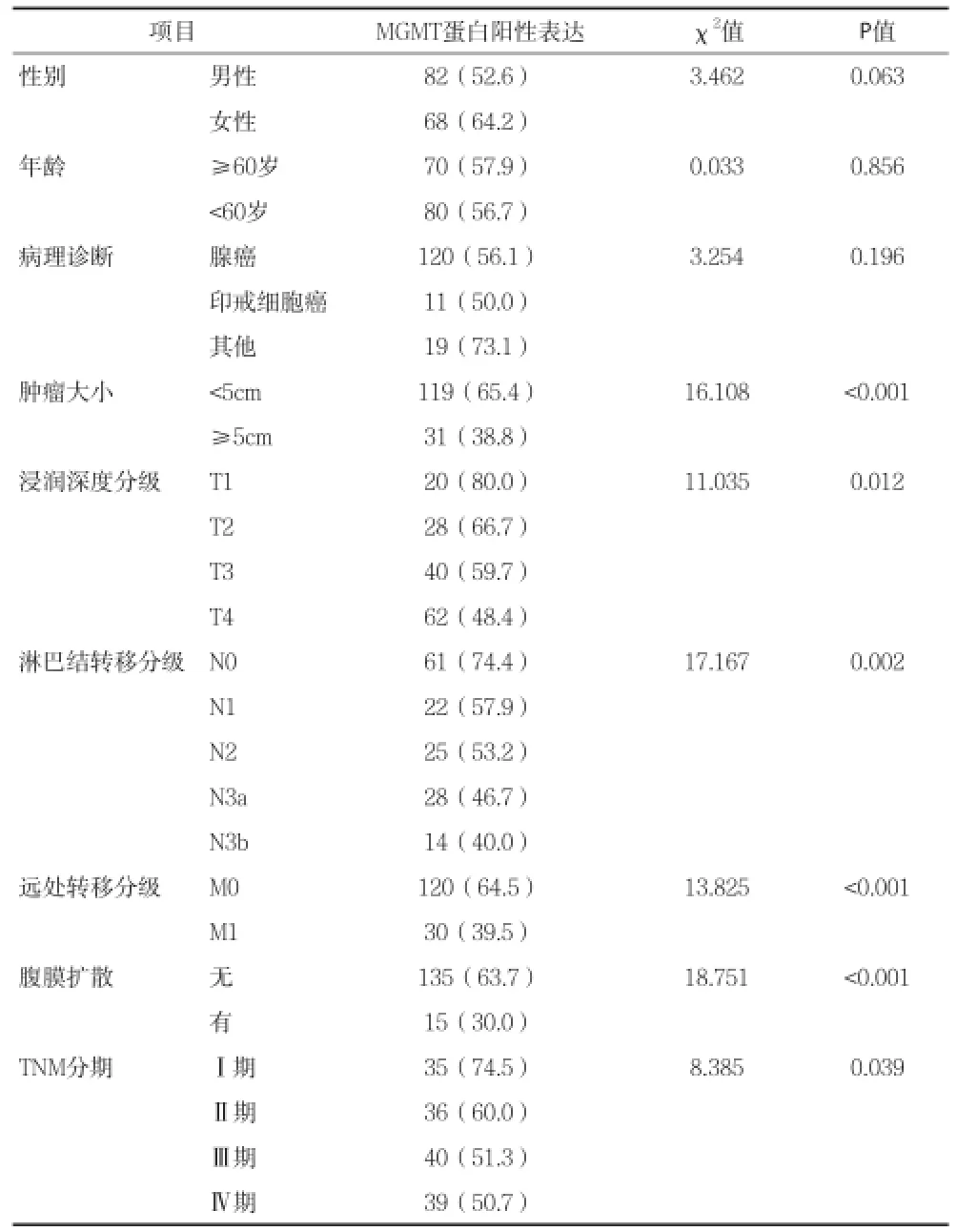
表1 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況與胃癌臨床特征的相關性[n(%)]
2.3胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況與胃癌患者5年死亡的相關分析 腫瘤大小﹑浸潤深度分級﹑淋巴結轉移分級﹑遠處轉移分級﹑腹膜擴散情況﹑TNM分期和胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌患者5年死亡相關(均P<0.05),而性別﹑年齡和病理診斷與胃癌患者5年死亡無顯著相關(均P>0.05)。經二分類Logistic回歸分析,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陰性表達(OR=5.716,95%CI=2.218-9.301,P<0.001)﹑腫瘤大小(OR=4.213;95%CI=1.982~8.887;P<0.001)﹑腹膜擴散(OR=4.879;95% CI=1.761~9.235;P<0.001)和遠處轉移(OR=3.911;95%CI=1.995~8.204;P<0.001)是胃癌5年死亡的獨立危險因素。見表2。
2.4胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況與胃癌患者5年生存時間的相關分析 腫瘤大小﹑浸潤深度分級﹑淋巴結轉移分級﹑遠處轉移分級﹑腹膜擴散情況﹑TNM分期和胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌患者5年生存時間相關(均P<0.05),而性別﹑年齡和病理診斷與胃癌患者5年生存時間無顯著相關(均P>0.05)。經多因素Cox回歸分析,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陰性表達(HR=4.287,95%CI=2.091~6.411,P<0.001)﹑腫瘤大小(HR=3.102;95%CI=1.912~6.219;P<0.001)﹑腹膜擴散(HR=3.563;95% CI=1.988~7.520;P<0.001)和遠處轉移(HR=4.273;95%CI=2.518~8.005;P<0.001)是胃癌5年生存時間的獨立危險因素。(見表3)。胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陰性表達患者5年生存時間明顯短于胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陽性表達患者(P<0.001)(見圖1)。
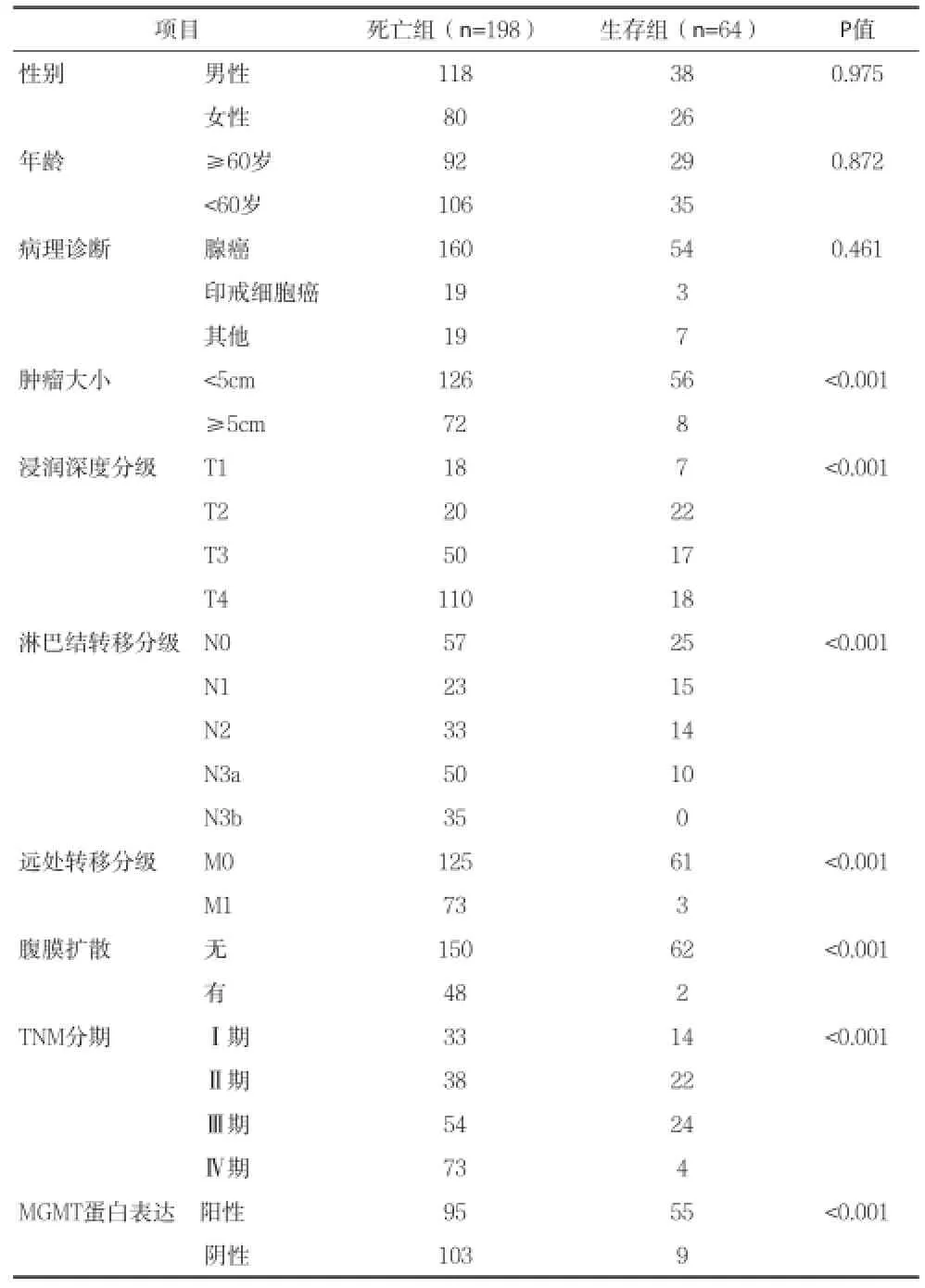
表2 影響胃癌患者5年死亡的相關因素分析(n)
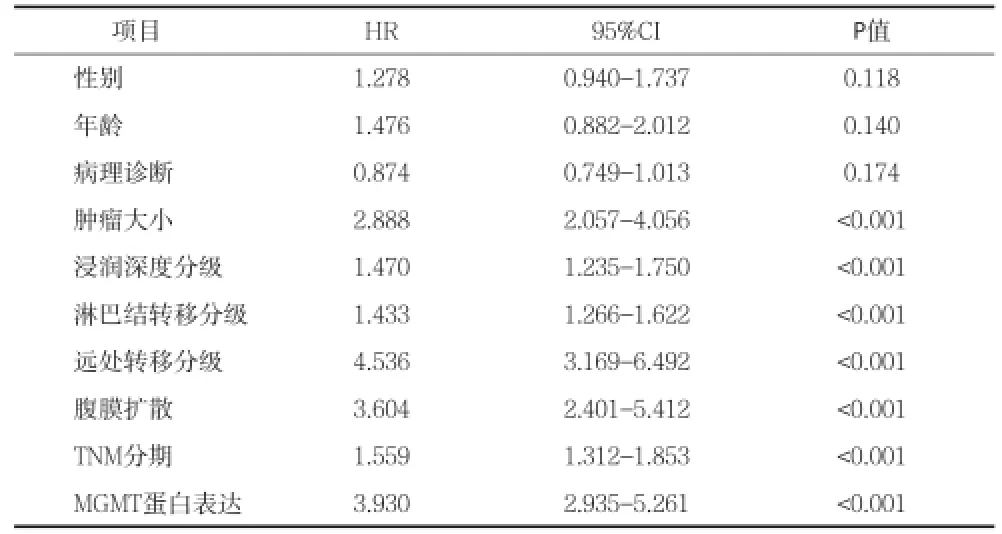
表3 影響胃癌患者5年生存時間的相關因素分析
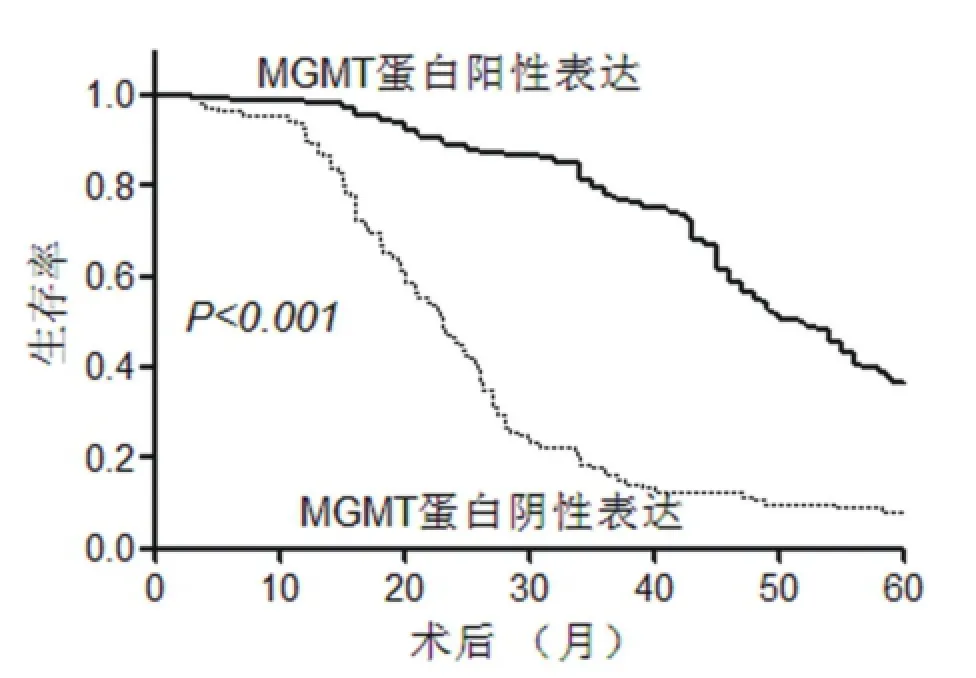
圖1 胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達情況與胃癌患者5年生存時間的相關分析
3 討論
胃癌的發生發展是一個多因素相互作用的過程,DNA修復基因的缺失與胃癌的易感性﹑惡性程度及腫瘤相關的臨床癥狀有關[8]。MGMT是一種高效的DNA直接修復酶,可將6-氧-甲基鳥嘌呤分子上的甲基轉移到自身的半胱氨酸殘基上,從而修復DNA分子的損傷。人類MGMT的編碼基因是一種常見的腫瘤抑制基因。MGMT基因啟動子甲基化可使MGMT蛋白表達減少。MGMT蛋白低表達可以促進肺癌﹑腦膠質瘤及乳癌等發生,也與癌癥的惡性程度及不良預后相關。
最近,有研究提示,45.1%的胃癌組織MGMT蛋白表達缺失或下降[9]。本資料顯示,42.7%的胃癌組織MGMT蛋白低表達,基本與之相符合。本資料也顯示,與癌旁正常組織比較,胃癌組織的MGMT蛋白表達顯著下降,提示MGMT蛋白表達缺失與胃癌的發生可能相關。究其原因可能與MGMT蛋白表達減少從而DNA修復能力缺失相關[10~12]。目前,少有研究揭示MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌臨床病理特征之間的關系。本資料顯示,MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌的腫瘤大小﹑浸潤深度﹑淋巴結轉移﹑遠處轉移﹑腹膜擴散和TNM分期密切相關,即腫瘤的惡性程度越高,MGMT蛋白陽性表達率越低,提示MGMT蛋白在腫瘤的發展過程中可能起重要作用,表明MGMT蛋白可能成為評價胃癌預后的一個生物學指標。
MGMT蛋白低表達與諸多癌癥的高度惡性生物學行為顯著相關,也與膠質瘤﹑肺癌等不良臨床預后相關。MGMT蛋白表達與胃癌預后的關系缺乏研究。本資料中胃癌患者經過5年隨訪,觀察其5年的病死率和生存時間,采用多因素分析發現,除腫瘤大小﹑腹膜擴散和遠處轉移外,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白陰性表達也成為胃癌患者5年死亡和生存時間的獨立危險因素。這也提示,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白的檢測可能成為胃癌預后預測的重要手段。
綜述所示,MGMT蛋白低表達可能參與胃癌的發生發展過程,胃癌組織MGMT蛋白的檢測可較好的評價胃癌的惡性生物學行為,同時也可能成為胃癌預后預測的重要手段。
1Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011,61(2):69~90.
2Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Goel A. DNA methylation and microRNA biomarkers for noninvasive detection of gastric and colorectal cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014,455(1):43~57.
3Masri S, Kinouchi K, Sassone-Corsi P. Circadian clocks, epigenetics,and cancer. Curr Opin Oncol, 2015,27(1):50~56.
4Chen Y, Hu F, Zhou Y, et al. MGMT promoter methylation and glioblastoma prognosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Med Res, 2013,44(4):281~290.
5Camara-Quintana JQ, Nitta RT, Li G. Pathology: commonly monitored glioblastoma markers: EFGR, EGFRvIII, PTEN, and MGMT. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2012,23(2):237~246.
6Inno A, Fanetti G, Di Bartolomeo M, et al. Role of MGMT as biomarker in colorectal cancer. World J Clin Cases, 2014,2(12):835~839.
7Cankovic M, Nikiforova MN, Snuderl M, et al. The role of MGMT testing in clinical practice: a report of the association for molecular pathology. J Mol Diagn, 2013,15(5):539~555.
8Matsusaka K, Funata S, Fukayama M, et al. DNA methylation in gastric cancer, related to Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus. World J Gastroenterol, 2014,20(14):3916~3926.
9Yousuf A, Bhat MY, Pandith AA, et al. MGMT gene silencing by promoter hypermethylation in gastric cancer in a high incidence area. Cell Oncol, 2014,37(4):245~252.
10Jin J, Xie L, Xie CH, et al. Aberrant DNA methylation of MGMT and hMLH1 genes in prediction of gastric cancer. Genet Mol Res,2014,13(2):4140~4145.
11Song B, Ai J, Kong X, et al. Aberrant DNA Methylation of P16, MGMT,and hMLH1 Genes in Combination with MTHFR C677T Genetic Polymorphism in gastric cancer. Pak J Med Sci, 2013,29(6):1338~1343. 12 Kup?inskait?-Noreikien? R, Skiecevi?ien? J, Jonaitis L, et al. CpG island methylation of the MLH1, MGMT, DAPK, and CASP8 genes in cancerous and adjacent noncancerous stomach tissues. Medicina,2013,49(8):361~366.
Objective This study aimed to investigate and to assess the relationship between the expression of MGMT protein in gastric cancer tissues,biological behavior of gastric cancer and long-term prognosis. Methods A total of 262 cases of gastric cancer tissues and normal tissues adjacent to carcinomas were collected. The expressions of intra-tissue MGMT proteins were measured using immunohistochemistry. The difference of expression of MGMT proteins between gastric cancer tissues and normal tissues adjacent to carcinomas,the relationship between expression of MGMT proteins in gastric cancer tissues and clinicopathological parameter of gastric cancer,and the relationship between expression of MGMT proteins in gastric cancer tissues and 5-year mortality and overall survival of patients with gastric cancers were analyzed statistically. Results Positive rate of expression of MGMT proteins was markedly lower in gastric cancer tissues than in normal tissues adjacent to carcinomas. The expression of MGMT protein in gastric cancer tissues was obviously associated with tumor size,invasion depth,lymph node metastasis,distant metastasis,peritoneal dissemination,and TNM stage. The negative expression of MGMT protein in gastric cancer tissues was identifi ed as an independent risk factor for 5-year mortality and overall survival of gastric cancers. Conclusion The expression of MGMT protein in gastric cancer tissues is decreased markedly. Low expression of MGMT protein in gastric cancer tissues is highly associated with malignant biological behavior of gastric cancer,and independently related to long-term poor prognosis of gastric cancer.
Gastric cancer MGMT protein Prognosis Biological behavior
浙江省寧波市科技計劃項目(2013C50026)

