面內平動功能梯度斜板的主動振動控制
王忠民, 鄒德志
(西安理工大學 土木建筑工程學院,西安 710048)
?
面內平動功能梯度斜板的主動振動控制
王忠民, 鄒德志
(西安理工大學 土木建筑工程學院,西安710048)
對新型功能梯度材料制成的面內平動斜板,通過直角坐標系和斜角坐標系的坐標變換,建立了在斜角坐標系下受多個集中控制力作用的橫向振動控制微分方程。采用微分求積法,將微分方程和邊界條件對空間坐標進行離散化處理,得到了時域內振動控制系統的狀態方程。應用最優控制法,對面內平動功能梯度斜板的無量綱運動速度小于一階無量綱臨界速度時的等幅振動和大于一階無量綱臨界速度時的發散失穩兩種情況進行了數值仿真,得到控制前后若干個節點撓度隨時間的變化曲線。結果表明,該方法能夠有效地控制面內平動功能梯度斜板的橫向振動,特別是對于發散失穩的抑制。
面內平動斜板;功能梯度材料;最優振動控制;微分求積法
在造船工業和橋梁工程等領域,斜板、加肋斜板的應用越來越廣泛。目前,許多學者在面內平動(或軸向運動)矩形板或薄膜的線性振動、非線性振動、穩定性以及振動控制方面做了大量的研究。Gorman[1]用解析法研究了矩形板的自由振動特性。Lin[2]以對邊簡支對邊自由的軸向運動板為對象,分析了軸向運動速度、長寬比和剛度對板的穩定性的影響。Shin等[3]分析了軸向運動矩形薄膜的振動特性。周銀鋒等[4]研究了軸向運動Kelvin-Voigt黏彈性矩形板的橫向振動特性。阮苗等[5]分析了受切向均布隨從力的功能梯度(Functionally Graded Materials,FGM)斜板的穩定性。Hossain Nezhad Shirazi等[6]利用模糊控制策略對功能梯度矩形板進行了控制,其中沒有考慮板的軸向運動。賀容波等[7]提出了基于光電層合簡支板的最優模糊多模態主動振動控制算法。浦玉學等[8]提出基于次級通道在線辨識的變步長振動主動控制算法,以某實時控制器進行了簡支梁振動主動控制試驗。在斜板結構的彎曲、屈曲及后屈曲研究方面,李國豪[9]提出了各向異性斜板彎曲的平衡微分方程及其實用的近似解法。紀冬梅等[10]采用Galerkin法,以小波作為試函數,得出了斜板在不同邊長比與不同斜角下的后屈曲四級漸近解。黎振源等[11]分析了兩對邊簡支、另兩對邊自由簡支斜板橋振動頻率特性,以及單輛標準車靠邊行駛、靠中行駛和兩輛標準車并排行駛時的車橋振動特性。阮苗等[12]研究了功能梯度斜板在兩對邊受有均布壓力作用下的屈曲問題,討論了斜板的幾何外形尺寸、夾角、梯度指標以及中面變形等因素對臨界屈曲荷載的影響。
在上述研究的基礎上,對新型功能梯度材料制成的面內平動斜板,采用二元Diracδ函數,建立了在集中控制力作用下的橫向振動控制微分方程;采用微分求積法,將微分方程和邊界條件進行離散化處理,得到了振動控制系統的狀態方程;應用最優控制法,確定了最優控制率,對系統進行數值仿真,得到了控制前后所求點的撓度隨時間的變化曲線。
1 運動功能梯度斜板的控制微分方程
1.1受控系統的力學模型
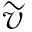
X=XcVc+XmVm=XcVc+Xm(1-Vc)
(1)
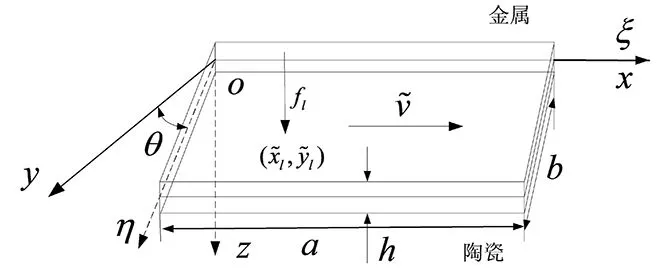
圖1 面內平動的FGM斜板Fig.1 In-plane translating skew plate made of functionally graded materials
1. 2控制微分方程
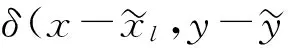
(2)
式中:w(x,y,t)是板的撓度函數;μ是泊松比,Em、ρm和Ec、ρc分別是金屬、陶瓷的楊氏模量和密度,Ecm=Ec-Em,ρcm=ρc-ρm;4為重調和算子,即
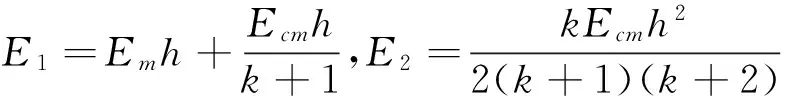
由圖2知,直角坐標和斜角坐標的關系為
x=ξ+ηcosθ,y=ηsinθ
(3)
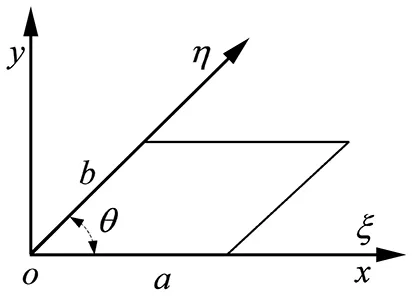
圖2 直角坐標與斜角坐標Fig.2 Rectangular coordinates and skew coordinates
對控制微分方程(2),應用式(3),可得到斜角坐標系下的控制微分方程,即
(4)
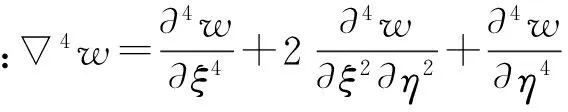
引入無量綱量
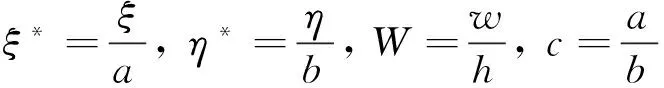
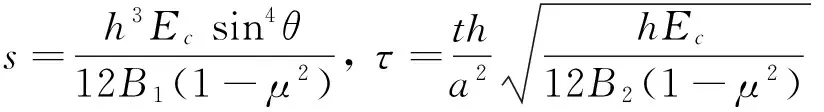
(5)
得到斜角坐標系下無量綱量表示的控制微分方程
(6)
1. 3微分方程的離散
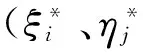
(7)
四邊簡支斜板的邊界條件為
W1j=WNj=Wi1=WiN=0
(i,j=1,2,…,N)
(8a)
(i=2,N-1;j=2,3,…,N-1)
(8b)
(j=2,N-1;i=2,3,…,N-1)
(8c)
(9)
二元Diracδ(ξ*,η*)函數的展開式
(10)
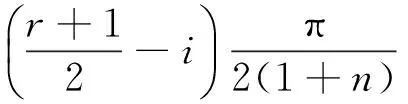
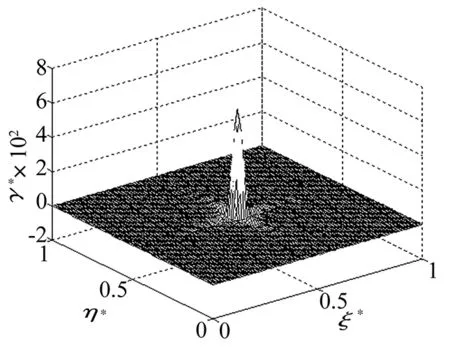
圖3 二元Diracδ(ξ*-0.5,η*-0.5)函數的部分和隨坐標變量的變化曲面Fig.3 Curved surface of partial sum for Dirac function δ(ξ*-0.5,η*-0.5) versus two variables
本文采用不均勻分布節點方式,即
(12)
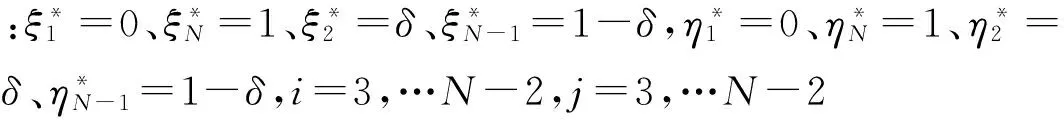
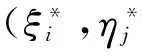
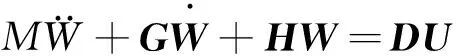
(13)
式中:U(τ)=[u1(τ),u2(τ),u3(τ),u4(τ),u5(τ)]T為無量綱控制力列陣。
2 最優控制器設計
將方程(13)寫成狀態方程
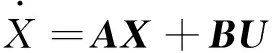
(14a)
Y=CX
(14b)
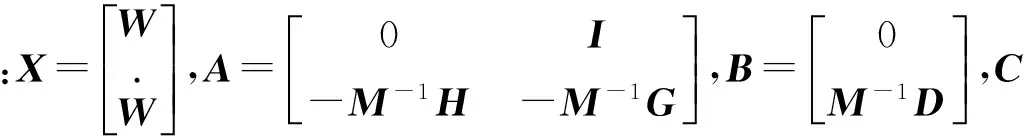
對于無限時間輸出調節器,二次型指標為
(15)
用極小值原理[17],得到唯一最優控制率
U*(τ)=-R-1BTPX(τ)
(16)
式中:P是正定對稱常值矩陣,是下列Riccati代數方程的唯一解
PA+ATP-PBR-1BTP+Q=0
(17)
最優狀態X*(τ)是下列微分方程和初始條件的解
X(τ0)=X0
(18)
在式(16)中,令K=-R-1BTP,有最優指標
(19)
受控系統閉環控制框圖如圖4所示。
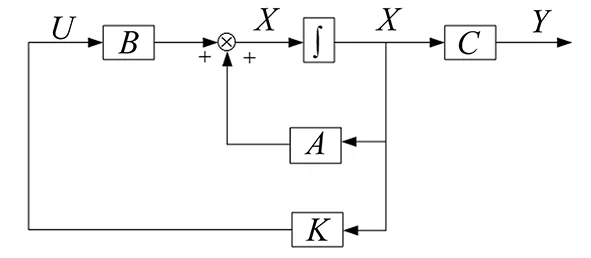
圖4 受控系統閉環結構圖Fig.4 Closed-loop structurediagram of the controlled system
3 數值算例
取板的邊長a=b=1,即長寬比c=a/b=1;采用的FGM 板由 金屬Aluminum 和陶瓷Zirconia兩種材料構成,其彈性模量分別為Em=70 GPa和Ec=151 GPa,密度分別為ρm=2 707 kg/m3和ρc=3 000 kg/m3,泊松比μ=μm=μc=0.3;梯度指標k=1,斜板的夾角θ=75°,N=9。
對于無控制力作用的運動功能梯度斜板,前三階復頻率ω1、ω2、ω3的實部和虛部隨無量綱速度v的變化曲線如圖5所示。可以看出,當無量綱速度小于一階無量綱臨界速度5.49時,第一階復頻率的虛部是0,板是穩定的;當無量綱速度大于5.49小于6.9時,第一階復頻率虛部不為0,實部為0,斜板發生發散失穩。
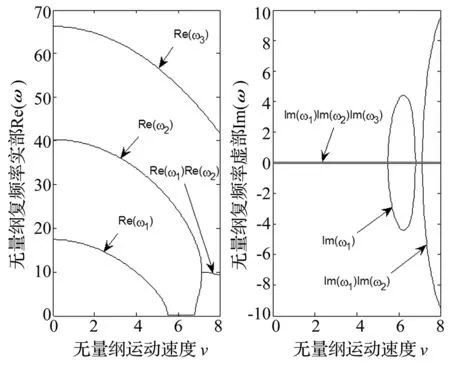
圖5 前三階無量綱復頻率的實部與虛部隨無量綱速度的變化曲線Fig.5 Curve of real part and imaginary part of the first three dimensionless complex frequency versus velocity
在以下分析中,取斜板上A1、A2、A3點為控制對象。為了清晰地表示這三個點的位置,將板畫成矩形,如圖6所示。在方程(14a)中,將B取成0矩陣,即無控制狀態,取初始條件為
[000000000000000000
00000000000.10000000
-0.10000000000000]T
對無量綱運動速度v=3,用Runge-Kutta法計算了A1、A2、A3點處的無量綱撓度隨無量綱時間的變化情況,如圖7-圖9(圖中均為無量綱量)。由圖可以看出,其變化規律是等幅穩態振動。
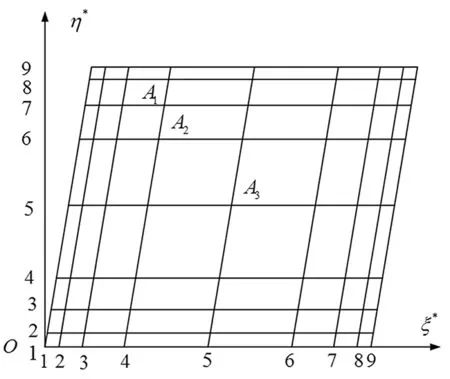
圖6 A1、A2、A3點所在位置Fig.6 Location of point A1、A2、A3
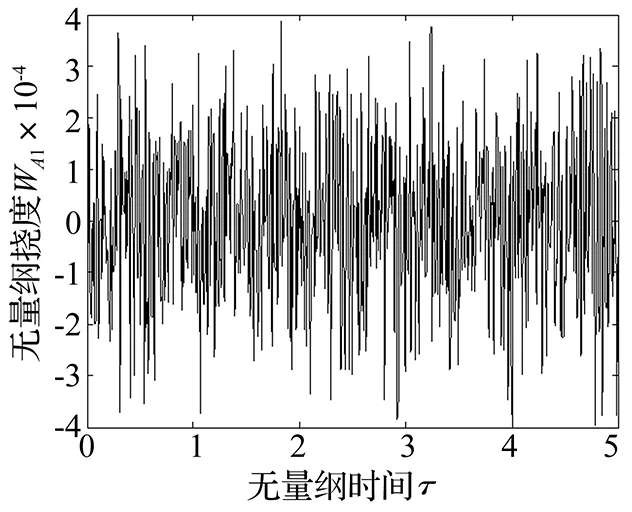
圖7 控制前A1點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=3)Fig.7 Curve for deflection of point A1 versus time under uncontrolled state(v=3)
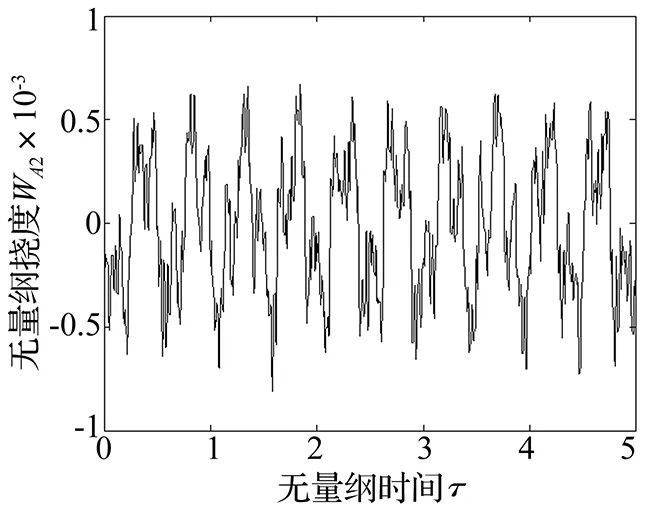
圖8 控制前A2點撓度隨時間的變化曲線圖(v=3)Fig.8 Curve for deflection of point A2 versus time under uncontrolled state(v=3)
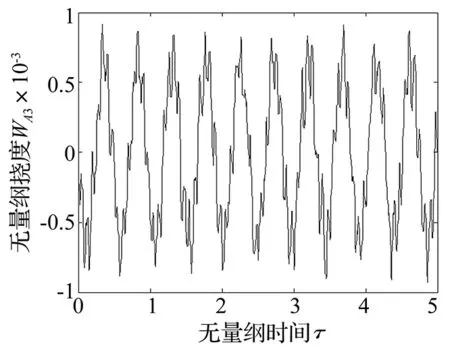
圖9 控制前A3點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=3)Fig.9 Curve for deflection of point A3 versus time under uncontrolled state(v=3)
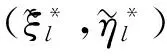
D3=[0.000 028 109 162 15,0.000 083 491 291 43,
-0.013 192 615 874 43,0.000 083 491 291 43,
0.000 028 109 162 15,0.000 083 491 291 43,
0.000 247 990 164 49,-0.039 185 391 967 64,
0.000 247 990 164 49,0.000 083 491 291 43,
-0.013 192 615 874 43,-0.039 185 391 967 64,
6.191 757 430 466 36,-0.039 185 391 967 64,
-0.013 192 615 874 43,0.000 083 491 291 43,
0.000 247 990 164 49,-0.039 185 391 967 64,
0.000 247 990 164 49,0.000 083 491 291 43,
0.000 028 109 162 15,0.000 083 491 291 43,
-0.013 192 615 874 43,0.000 083 491 291 43,
0.000 028 109 162 15]T
對方程式(14a)和式(16)~(18)進行數值計算,得到控制后的無量綱撓度隨無量綱時間的變化曲線如圖10~圖12所示(圖中均為無量綱量)。從這些響應曲線可以看出,控制后板的無量綱撓度隨無量綱時間的響應曲線呈現為顯著的衰減,斜板的振動受明顯的抑制,在無量綱時間大于2 s后,無量綱撓度幾乎趨于0。
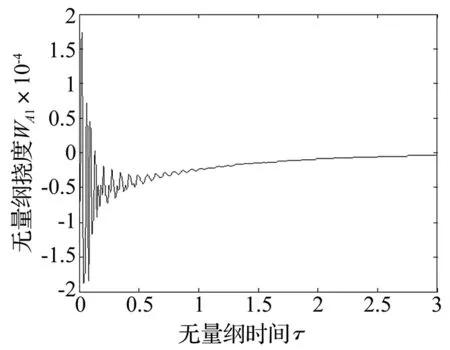
圖10 控制后A1點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=3)Fig.10 Curve for deflection of point A1versus time under controlled state(v=3)
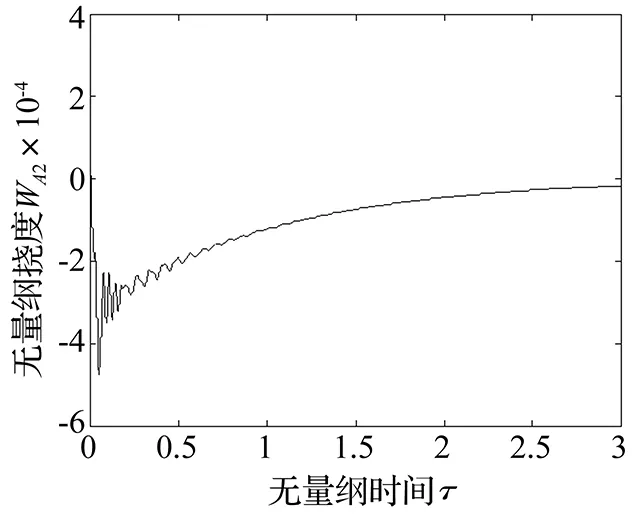
圖11 控制后A2點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=3)Fig.11 Curve for deflection of point A2versus time under controlled state(v=3)
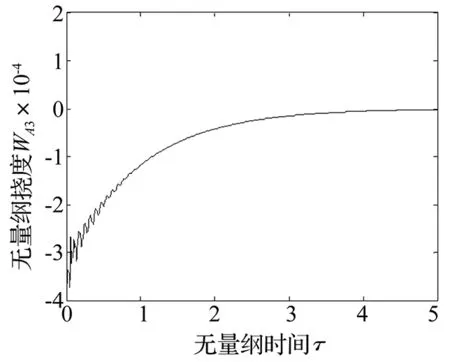
圖12 控制后A3點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=3)Fig.12 Curve for deflection of point A3 versus time under controlled state(v=3)
在圖5中,當斜板的無量綱速度v=6時,斜板呈現為發散失穩狀態,導致產生發散失穩的主要原因是第一階復頻率的虛部Im(ω1)=-4.136, 實部是0。v=6時的響應曲線如圖13~圖15,文中只畫出前兩秒的變化曲線,可以看出各點的撓度絕對值隨時間的增加越來越大。實施控制后響應曲線如圖16-圖18所示,顯然斜板的無量綱撓度絕對值的增大現象得到明顯的抑制,使其在短時間內趨近于0,最優控制效果非常明顯。在最優控制中,合理選擇加權矩陣Q和R更利于確定最優控制律。
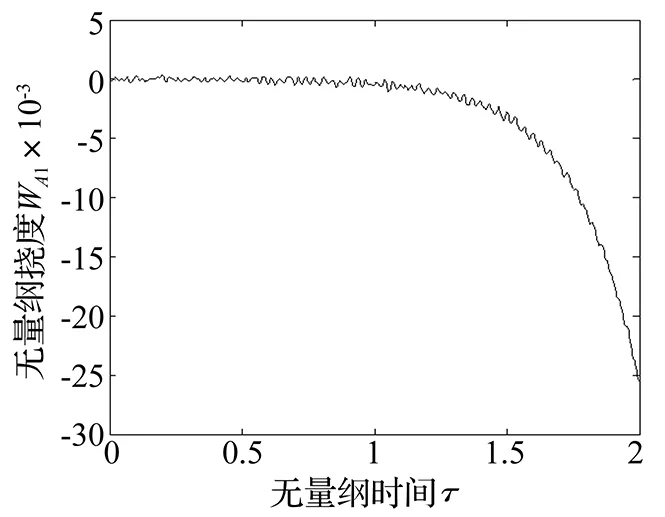
圖13 控制前A1點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.13 Curve for deflection of point A1 versus time under uncontrolled state(v=6)
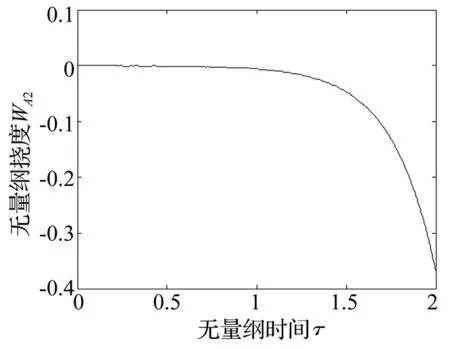
圖14 控制前A2點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.14 Curve for deflection of point A2 versus time under uncontrolled state(v=6)
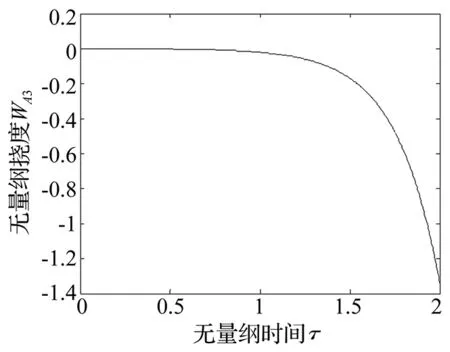
圖15 控制前A3點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.15 Curve for deflection of point A3versus time under uncontrolled state(v=6)
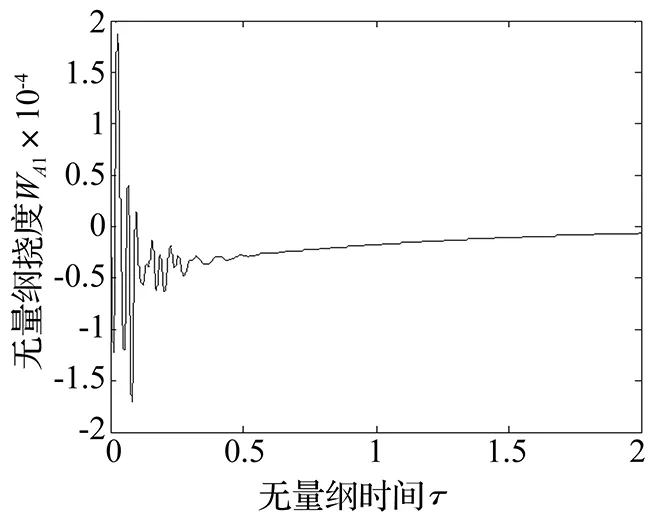
圖16 控制后A1點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.16 Curve for deflection of point A1 versus time under controlled state(v=6)
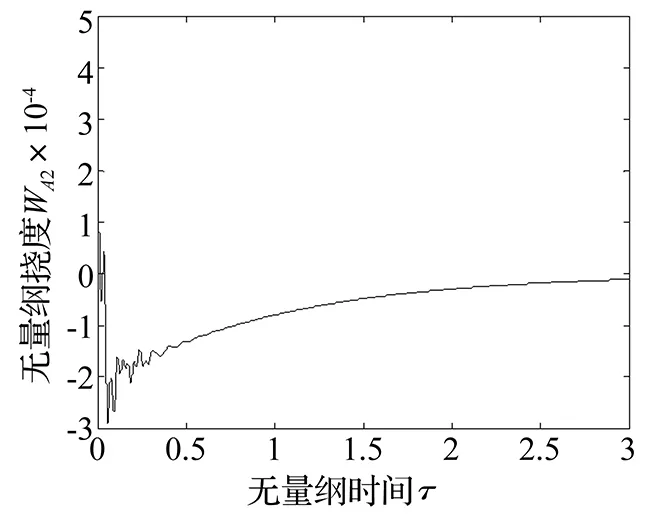
圖17 控制后A2點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.17 Curve for deflection of point A2versus time under controlled state(v=6)
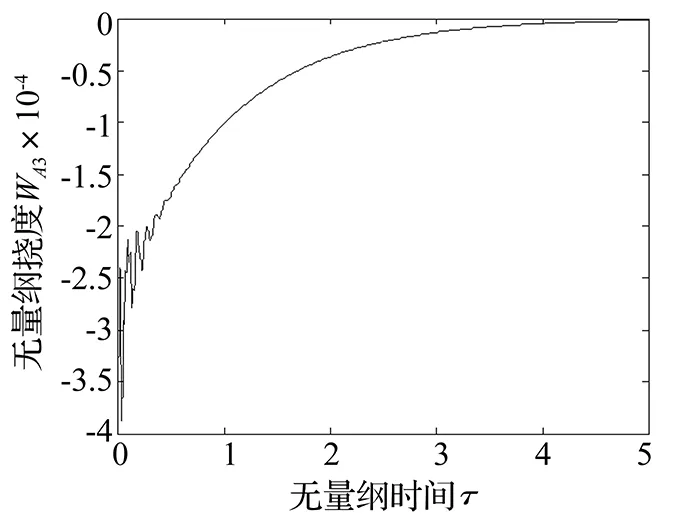
圖18 控制后A3點撓度隨時間的變化曲線(v=6)Fig.18 Curve for deflection of point A3versus time under controlled state(v=6)
4 結 論
利用微分求積法,對面內平動功能梯度斜板的控制微分方程進行了空間離散,建立了時域內的狀態方程。應用Runge-Kutta法,對無控制的斜板,計算了面內平動速度小于一階無量綱臨界速度(v=3,等幅振動)和大于一階臨界速度(v=6,發散失穩)兩種情況的斜板撓度隨時間的變化情況。再用最優控制理論,求得了最優控制率,并對斜板在這兩種情況下穩態振動和發散失穩分別進行了主動控制。仿真結果表明了該法的可行性和有效性。
[1] Gorman D J. Free vibration analysis of rectangular plates[M]. New York: Elsevier North Holland, 1982.
[2] Lin C C. Stability and vibration characteristics of axially moving plates[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1997, 34(24): 3179-3190.
[3] Changho S, Jintai C, Wonsuk K. Dynamic characteristics of the out-of-plane vibration for an axially moving membrane [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 286(4/5): 1019-1031.
[4] Zhou Yin-feng, Wang Zhong-min. Transverse vibration characteristics of axially moving viscoelastic plate[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2007, 28(2): 209-218.
[5] Ruan Miao, Wang Zhong-min, Wang Yan. Dynamic stability of functionally graded materials skew plates subjected to uniformly distributed tangential follower forces[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2012, 18(7): 913-923.
[6] Hossain Nezhad Shirazi A, Qwji H R, Rafeeyan M. Active vibration control of an FGM rectangular plate using fuzzy logic controllers[C]//Procedia Engineering,2011,14:3019-3026.
[7] 賀容波, 鄭世杰. 光電層合簡支板的多模態最優模糊主動振動控制[J]. 振動與沖擊,2015, 34(10): 77-81.
HE Rong-bo,ZHENG Shi-jie. Multi-modal optimal fuzzy active vibration control of a photo-electric laminated simplysupported plate[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(10): 77-81.
[8] 浦玉學,張方,姜金輝. 變步長自適應結構振動主動控制算法[J]. 振動與沖擊,2015, 34(8):199-205.
PU Yu-xue,ZHANG Fang,JIANG Jin-hui. A varying step adaptive algorithm for structural vibration active control[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(10): 199-205.
[9] 李國豪. 關于斜交異性斜板的彎曲理論[J]. 同濟大學學報, 1997, 25(2): 121-126.
LI Guo-hao. On the bending theory of skew anisotropic skew plate[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 1997, 25(2): 121-126.
[10] 紀冬梅, 胡毓仁. 小波加權殘值法在斜板后屈曲上的應用[J]. 應用力學學報, 2008, 25(4): 673-677.
JI Dong-mei, HU Yu-ren. Wavelet weighted residuals with application to post-buckling analysis of skew plates[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2008, 25(4): 673-677.
[11] 黎振源, 夏桂云, 李傳習. 簡支斜板的車-橋耦合振動分析[J]. 交通科學與工程, 2010, 26(1): 59-65.
LI Zhen-yuan, XIA Gui-yun, LI Chuan-xi. Vibrating frequencies and vehicle-bridge vibration of simply- supported skewed slab[J]. Journal of Transport Science and Engineering, 2010, 26(1): 59-65.
[12] 阮苗, 王忠民. 功能梯度斜板的屈曲分析[J]. 機械工程學報, 2011, 47(6):57-61.
RUAN Miao, WANG Zhong-min. Buckling analysis of functionally graded skew thin plate[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(6):57-61.
[13] Ruan Miao,Wang Zhong-min. Transverse vibrations of moving skew plates made of functionally graded material[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, first published on December,2014,17:1-14.
[14] 王永亮. 微分求積法和微分求積單元法的原理與應用[D]. 南京: 南京航天航空大學, 2001.
[15] 何甲興, 王淑云, 楊明. Fourier級數的求和理論與方法—求和因子法求和[J]. 數學的實踐與認識, 2003, 33(12): 112-118.
HE Jia-xing, WANG Shu-yun, YANG Ming. On summation theory and method of Fourier series-summing by summation factor[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory,2003,33(12):112-118.
[16] 金鈺. 二元傅里葉級數的收斂階[J]. 寧夏師范學院學報:自然科學版, 2008, 29(6): 80-82.
JIN Yu. The convergent order of a double Fourier series[J]. Journal of Ningxia Teaches University:Natural Science, 2008, 29(6): 80-82.
[17] 關新平, 吳忠強. 現代控制理論[M]. 北京: 電子工業出版社, 2012.
Active vibration control for an in-plane translating skew plate made of functionally graded materials
WANG Zhongmin, ZOU Dezhi
(School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an 710048, China)
Through the coordinate transformation between an orthogonal coordinate system and a skew angle coordinate system, the transverse vibration control differential equation for an in-plane translating skew plate made of a new kind of functionally graded materials subjected to multiple concentrated control forces was derived in the skew angle coordinate system. The differential quadrature method was used to discretize the differential equation and boundary conditions, and the state equations of the vibration control system in time domain were built. Using the optimal control method, the optimal control law was obtained. For the cases that the axially dimensionless moving velocity of an in-plane translating skew plate was less than the first order dimensionless critical speed(equal amplitude vibration) and it was greater than the first order dimensionless critical speed(divergence and instability), some numerical simulations for the system were implemented, and varying curves of deflections of some certain nodes versus time under uncontrolled and controlled conditions were plotted. The numerical results showed that the optimal control method can effectively control the vibration of the in-plane translating skew plate made of functionally graded materials, particularly, suppress the divergence and instability of the plate.
in-plane translating skew plate; functionally graded materials; optimal vibration control; differential quadrature method
國家自然科學基金項目(11272254);陜西省自然科學基礎研究計劃項目(2015JM1029)
2015-03-12修改稿收到日期:2015-08-05
王忠民 男,博士, 教授, 博士生導師,1957年生
O326
A
10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.15.014

