環境激勵下結構模態辨識的識別概率直方圖方法研究
陳太聰 李盈盈 蘇成 馬海濤

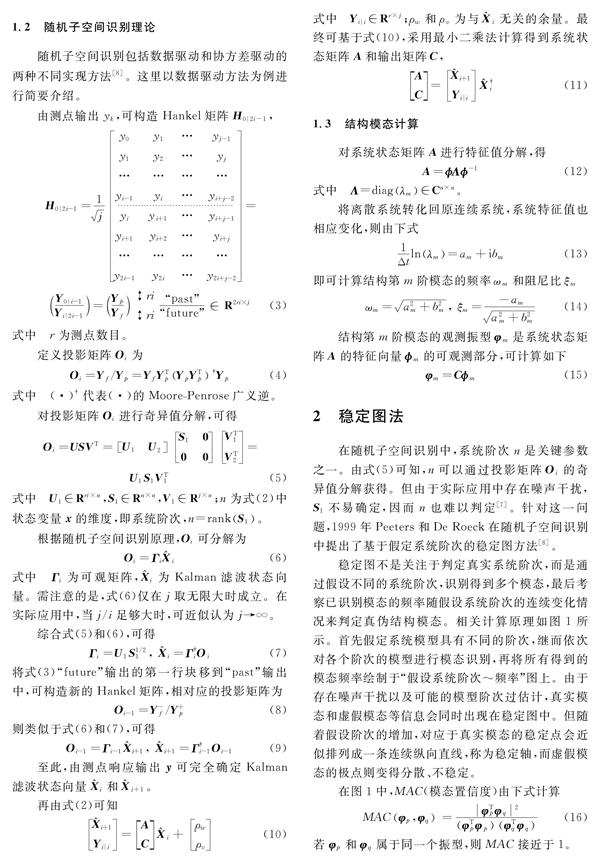
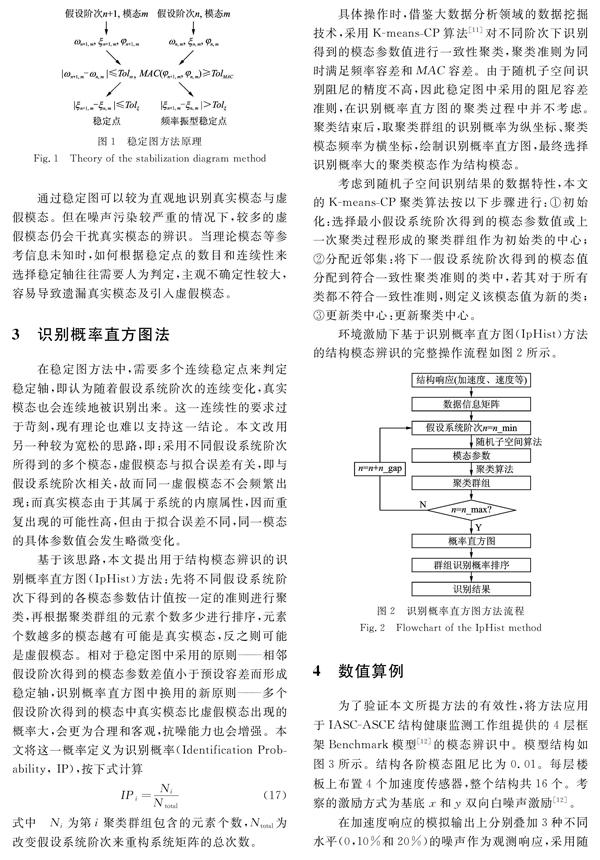
摘要: 在環境激勵下辨識結構模態時,系統階次作為關鍵計算參數不易準確判定,通常采用基于假設系統階次的穩定圖方法來輔助進行,但其中穩定軸的判定較為主觀,容易遺漏真實模態及引入虛假模態。基于數據挖掘技術,提出識別概率直方圖(Identificationprobability Histogram,IpHist)的新方法,對不同假設系統階次下通過隨機子空間識別得到的多組備選模態,根據頻率容差和模態置信度容差準則進行一致性聚類,繼而計算群組聚類結果的識別概率,并繪制相應的識別概率直方圖,最后選取識別概率大的結果作為結構模態結果。通過IASCASCE結構健康監測工作組提供的4層框架Benchmark模型算例,闡述了所提IpHist方法在環境激勵下辨識結構模態的有效性,顯示了方法較強的抗噪能力。
關鍵詞: 模態辨識; 隨機子空間; 穩定圖; 識別概率直方圖
中圖分類號: O327; TU317+.1文獻標志碼: A文章編號: 10044523(2016)04056107
DOI:10.16385/j.cnki.issn.10044523.2016.04.001
引言
近年來,針對環境激勵進行結構模態識別的多種方法在結構檢測領域得到了廣泛的應用[12],其中的隨機子空間法[3]直接在時域內進行數據分析,避免了傳統頻域方法——峰值拾取法[4]中頻率分辨率誤差的問題,不僅能識別結構系統的模態頻率,也能識別結構系統的模態振型和阻尼比,在實際結構檢測中逐漸受到重視[5]。在該方法的應用中,系統的階次是關鍵的計算參數,常用的辦法是對觀測矩陣進行奇異值分解,繼而根據奇異值的突變情況來確定系統的階次[6]。但在工程實踐中,由于受到多種噪聲的影響,奇異值的突變狀態不易辨別,難以準確判定系統的階次[7]。Peeters和De Roeck提出了基于假設系統階次的穩定圖方法[8],可實現噪聲情況下的模態識別[9],但其中穩定軸的判定較為主觀,識別結果容易遺漏真實模態及引入虛假模態。針對這些問題,作者先期探討了應用直方圖取代穩定圖的可能性,獲得了較好的辨識效果[10]。在此基礎上,本文將明確提出識別概率的概念,并引入一致性聚類算法,給出識別概率直方圖(Identificationprobability Histogram,簡稱IpHist)方法的完整操作流程,應用于隨機子空間識別過程中,實現環境激勵下真實結構模態的有效辨識。
Abstract: During the modal identification of a structure subjected to ambient excitations, the system order as a crucial computation parameter is not easy to be determined, and the stabilization diagram method based on assumed system orders is often adopted to help the identification. But how to distinguish the stabilization axes is in fact subjective, which may lead to possible inclusion of pseudo vibration modes instead of real modes into the final results. To avoid these problems, an identificationprobability histogram (IpHist) method in use of the data mining technique is proposed in the present paper. Firstly, the stochastic subspace method is applied to identify the alternative modes with different assumed system orders. Then, all the alternative modes are clustered into several categories by using the criteria of frequency tolerance and MAC tolerance, and the identification probability of each category is obtained along with the corresponding identificationprobability histogram. Finally, the clustered modes with large identification probability are chosen to be the structural modes. By taking a fourstory Benchmark model provided by the IASCASCE structural health monitoring workgroup as example, numerical results are presented to illustrate the effectiveness and antinoise capacity of the proposed IpHist method for modal identification of structures subjected to ambient excitations.
Key words: modal identification; stochastic subspace; stabilization diagram; identificationprobability histogram

