網絡安全
網絡安全
·編者按·
2016年國家網絡安全宣傳周于9月19日至25日舉行。2016年4月19日,習近平主持召開網絡安全和信息化工作座談會并發表重要講話時強調:“要樹立正確的網絡安全觀,全天候全方位感知網絡安全態勢,增強網絡安全防御能力和威懾能力。”
信息安全、網絡安全、網絡空間安全是近年來國內外網絡空間領域出現頻度較高的詞匯。隨著全球社會信息化的深入發展和持續推進,相比物理的現實社會,網絡空間中的虛擬社會在各個領域所占的比重越來越大,有的已經超過了半數。數量的增長帶來了質量的變化,以數字化、網絡化、智能化、互聯化、泛在化為特征的網絡社會,為信息安全帶來了新技術、新環境和新形態,信息安全開始更多地體現在網絡安全領域,反映在跨越時空的網絡系統和網絡空間之中,反映在全球化的互聯互通之中。
網絡安全和信息化是事關國家經濟社會可持續發展、事關國家長治久安、事關人民群眾福祉的重大戰略問題,習近平總書記作出了重要論斷:“沒有網絡安全就沒有國家安全,沒有信息化就沒有現代化”。深刻闡述了網絡安全信息化發展的辯證關系,指出“網絡安全和信息化是一體之兩翼,驅動之雙輪,必須統一謀劃,統一部署,統一推進,統一實施。”自十八大以來,以習近平為總書記的新一屆黨中央高度重視網絡安全與信息化建設事業的發展,習近平總書記在重大會議以及演講中多次提及網絡安全問題,體現了習近平總書記網絡強國戰略思想。
本專題得到連一峰教授(中國科學院軟件研究所)、王世偉研究員(上海社會科學院信息研究所)、張志斌研究員(中國科學院計算技術研究所)、朱洪亮博士(北京郵電大學信息安全中心)的大力支持。
·熱點數據排行·
截至 2016年 9月 20日,中國知網(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的數據報告顯示,以“網絡安全(network security)”“網絡空間安全(cyberspace security)”為詞條可以檢索到的期刊文獻分別為7186條與16464條,本專題將相關數據按照:研究機構發文數、作者發文數、期刊發文數、被引用頻次進行排行,結果如下。
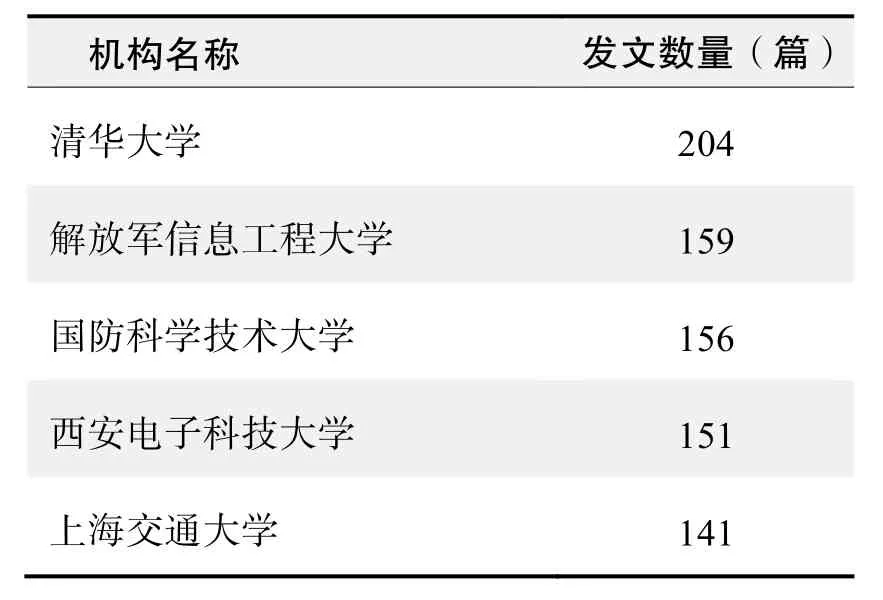
研究機構發文數量排名(CNKI)
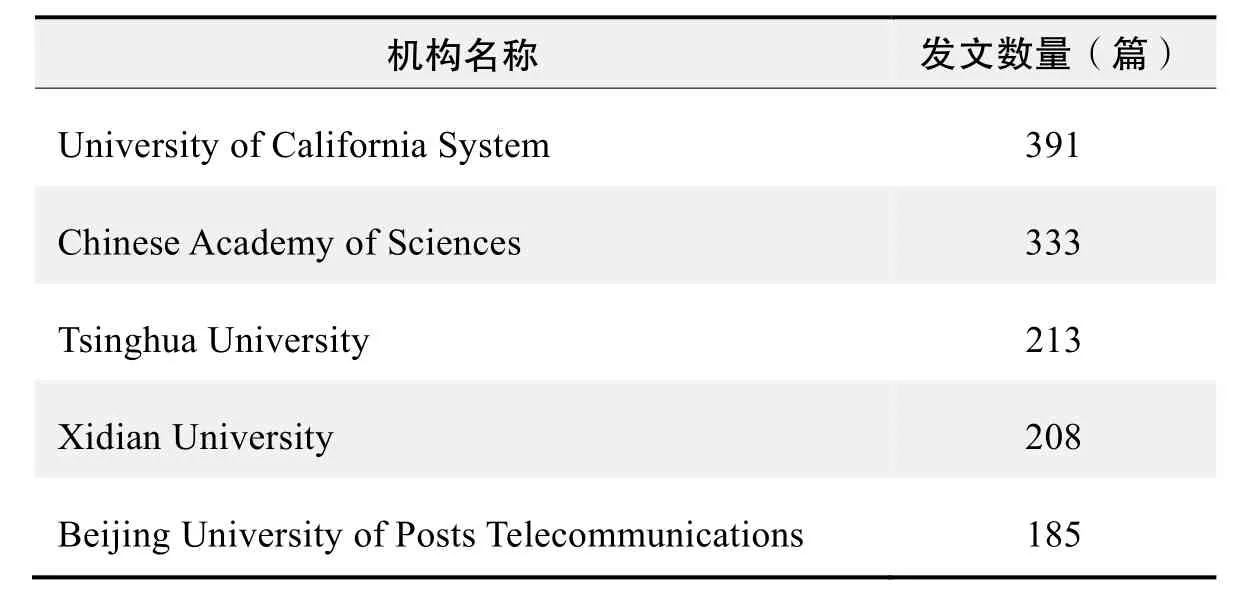
研究機構發文數量排名(WOS)
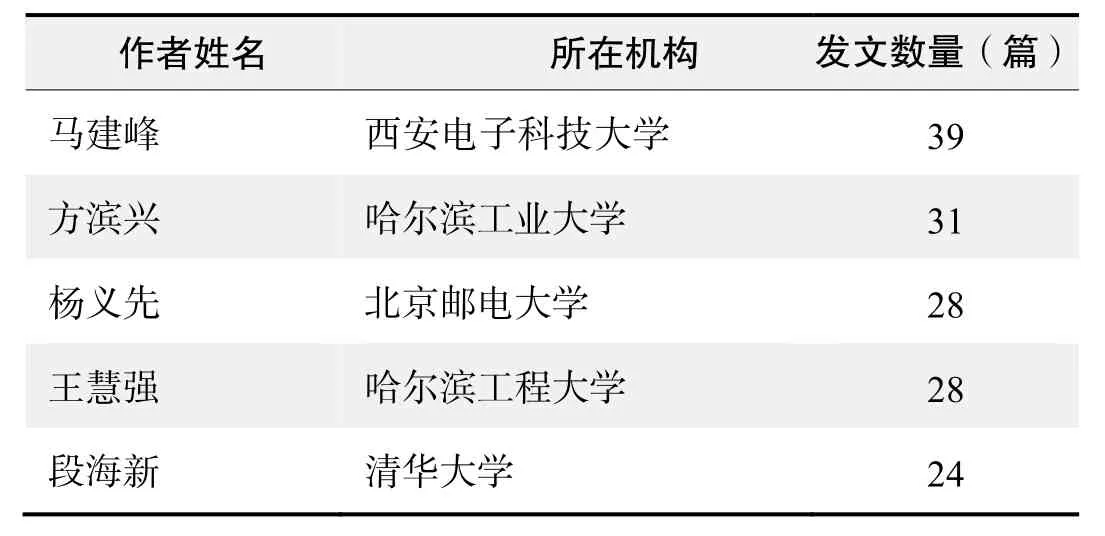
作者發文數量排名(CNKI)
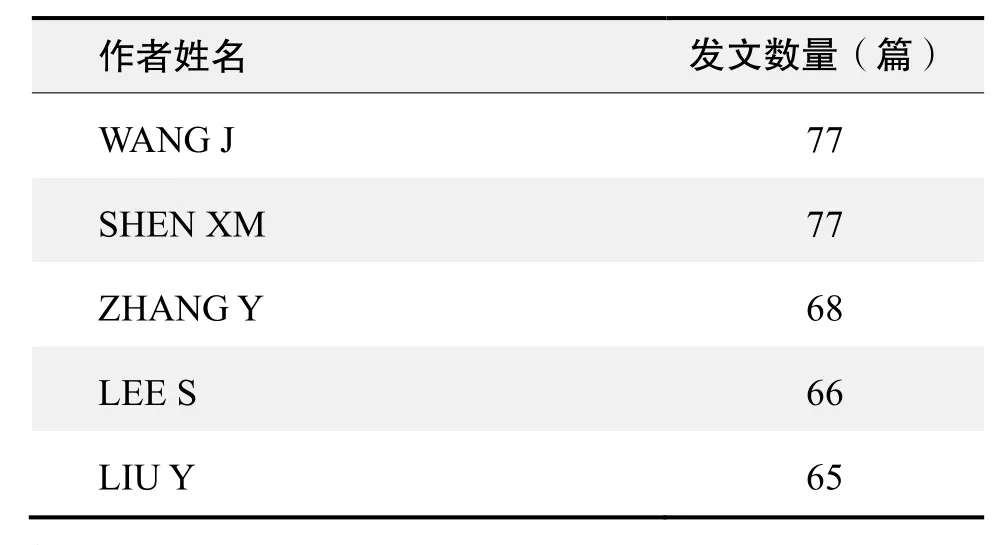
作者發文數量排名(WOS)
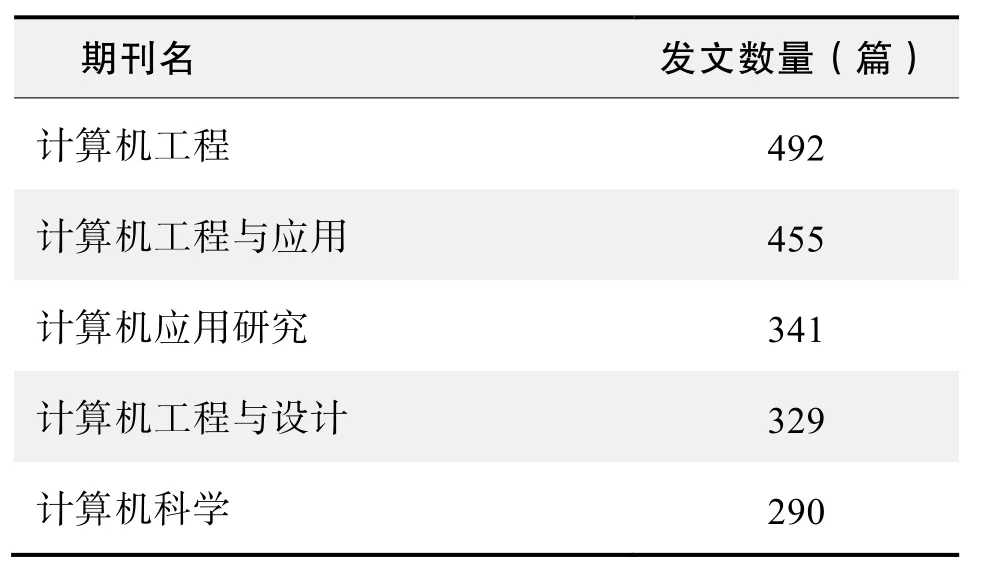
期刊發文數量排名(CNKI)
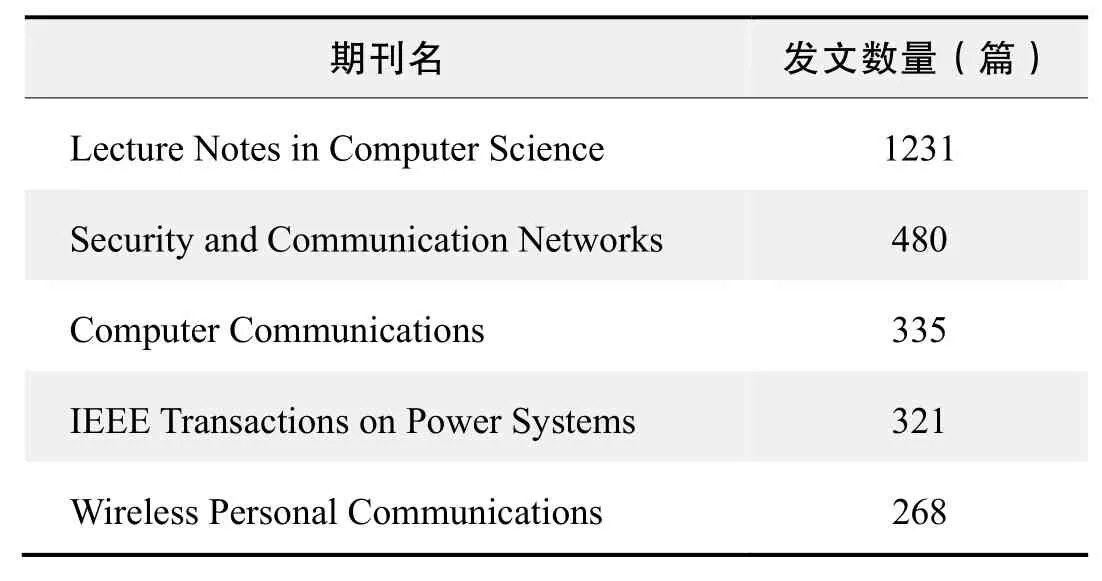
期刊發文數量排名(WOS)
根據中國知網(CNKI)數據報告,以“網絡安全(network security)”“網絡空間安全(cyberspace security)”為詞條可以檢索到的高被引論文排行結果如下。
根據Web of Science統計數據,以“網絡安全(network security)”“網絡空間安全(cyberspace security)”為詞條可以檢索到的高被引論文排行結果如下。

國外數據庫高被引論文排行
·經典文獻推薦·
基于Web of Science檢索結果,利用Histcite軟件選取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次數)TOP50文獻作為節點進行分析,得到本領域推薦的經典文獻如下。
SPINS: Security protocols for sensor networks
Perrig A; Szewczyk R; Tygar JD; et al.
來源出版物:Wireless Networks, 2002, 8(5): 521-534
Security in wireless sensor networks
Perrig A; Stankovic J; Wagner D
來源出版物:Communications of the ACM, 2004, 47(6): 53-57
A survey of security issues in mobile ad hoc and sensor networks
Djenouri, Djamel; Khelladi, Lyes; Badache, Nadjib
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2005, 7(4): 2-28
Sensor network security: A survey
Chen, Xiangqian; Makki, Kia; Yen, Kang; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2009, 11(2): 52-73
The relay-eavesdropper channel: Cooperation for secrecy
Lai, Lifeng; El Gamal, Hesham
來源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,2008, 54(9): 4005-4019
·推薦綜述·
從層次角度看網絡空間安全技術的覆蓋領域
方濱興
1引言
為實施國家安全戰略,加快網絡空間安全人才培養,國務院學位委員會、教育部于2015年6月決定增設“網絡空間安全”一級學科,于2015年10月決定增列“網絡空間安全”一級學科博士學位授權點,這對于我國加快網絡空間安全人才隊伍建設和核心技術的自主創新具有重要意義。
美國國家安全54號總統令和國家安全23號總統令中對網絡空間(cyberspace)的定義是:“網絡空間是連接各種信息技術基礎設施的網絡,包括互聯網、各種電信網、各種計算機系統、各類關鍵工業設施中的嵌入式處理器和控制器。還涉及人與人之間相互影響的虛擬信息環境。”該定義強調網絡空間是大范圍連接的網絡,這種說法有一定的局限性,導致物理隔離的網絡、ad hoc網絡等局域連接的網絡不包含在網絡空間中。
本文對網絡空間的定義是:“網絡空間就是所有由可對外交換信息的電磁設備作為載體,通過與人互動而形成的虛擬空間,包括互聯網、通信網、廣電網、物聯網、社交網絡、計算系統、通信系統、控制系統等。”首先,定義強調的“信息交換”不僅包括全局范圍連接,也包括局域連接。因此,網絡空間包括了局域連接的網絡。其次,定義強調的“由電磁設備作為載體”明確了信息交換的途徑,即通過電磁設備交換信息。因此,聲音、化學、生物交換信息不屬于網絡空間的范疇。最后,定義強調的“與人互動而形成的虛擬空間”說明網絡空間區別于陸、海、空、天的物理空間,是一個用于解決人的問題的虛擬空間。
在此基礎上,本文首先提出了四橫八縱的網絡空間安全技術的覆蓋領域,該體系縱向上分為設備層、系統層、數據層和應用層4個層次,橫向上覆蓋了信息安全、信息保密、信息對抗、云的安全、大數據、物聯網安全、移動安全和可信計算8個主要領域;然后,分別介紹了在每個領域在不同層次所面臨的安全問題及對應的安全技術;最后給出了結論。
2網絡空間安全的層次模型
網絡空間中的任一信息系統或系統體系自底向上可分為設備層、系統層、數據層和應用層4個層次,每個層次都面臨著不同的安全問題,相應地形成了網絡空間安全的4層次模型。設備層的安全應對在網絡空間中信息系統設備所面對的安全問題;系統層的安全應對在網絡空間中信息系統自身所面對的安全問題;數據層的安全應對在網絡空間中處理數據的同時所帶來的安全問題;應用層的安全應對在信息應用的過程中所形成的安全問題。
網絡空間安全的研究領域主要包括信息安全、信息保密、信息對抗、云的安全、大數據、物聯網安全、移動安全、可信計算領域。其中,信息安全是核心和根本,其他領域是信息安全向外的延伸。圍繞這8個領域,本文歸納總結了網絡空間安全的4層次模型面臨著的安全問題及相應的安全技術。
3設備層的安全
信息安全領域在設備層主要面臨物理設備損毀的安全問題,例如“911恐怖襲擊導致IT公司消失”事件。針對設備損毀問題,應當關注物理安全,物理安全是對網絡與信息系統物理裝備的保護,例如生存性技術、容錯技術、容災技術、冗余備份技術等。
信息保密領域在設備層主要面臨輻射泄密的安全問題,例如側信道攻擊。電磁輻射是指計算機電子線路在運行中所出現的電平翻轉形成了交變電磁場,其能量形成了電磁波在空間進行傳播。應該關注干擾屏蔽技術以防止輻射泄密。信息對抗領域在設備層主要面臨電磁破壞的安全問題,例如激光槍、高能炸彈、電磁炸彈。事實上,信息對抗是能量的對抗,具體包括維持我方使用與控制的能力,抵擋敵人阻礙我方使用的手段以及妨礙敵人達到相同目的的方式。針對電磁破壞,應該關注電子對抗技術,例如電子防護技術、電子攻擊技術以及電子作戰支援技術等。
云安全領域在設備層主要面臨平臺崩潰的安全問題,即云的不可靠性,例如大規模平臺宕機、服務中斷等。在設備層面實現可靠的云是物理安全災備問題的一個實例化,可采用多副本冗余的方法保證云平臺的容災性,例如,復云的概念——云服務商之間建立接口互相備份,按照實際使用的情況結算。
大數據領域在設備層主要面臨設備失效的安全問題。大數據的數據量大和傳統意義上的數據量大是有區別的,后者要求每條數據是精準的、不可缺失的;而前者關注的是非線性的數據,數據是可缺失的。針對大數據的設備失效問題,要重點關注數據保障技術,它解決的問題不是傳統意義上嚴格的災備,數據不需要完全恢復,允許在不影響大數據計算的前提下,缺失某些數據。
物聯網安全領域在設備層主要面臨電子干擾的安全問題。物聯網的物理支撐是傳感器,電子電磁波干擾會造成傳感器網絡以及其他傳輸通道的安全問題。針對上述問題,應該關注物聯網的探針安全技術,例如干擾控制技術、安全路由技術、入侵檢測技術等。
移動安全領域在設備層主要面臨終端被攻擊的安全問題。移動終端是移動互聯網的重要載體,移動終端逐漸由通信工具向個人的信息處理中心轉變,這使得移動終端成為新的安全熱點。移動終端的智能化,帶來了非法篡改信息、非法訪問、病毒和惡意代碼等新的安全問題。因此,需要關注移動終端安全技術,涵蓋終端自身安全性、終端防泄密和終端運行維護管理等。
可信計算領域在設備層主要面臨底層設備故障引起的安全問題。為解決此問題,提高提供可信計算服務的硬件實體可靠性,包括元器件可靠性、設備可靠性和系統可靠性。以可信賴平臺模塊(TPM,trusted plateform module)為核心提供可信硬件平臺,并作為可信計算平臺的信任根,建立一級信任一級的信任鏈。
4系統層的安全
信息安全領域在系統層面主要面臨針對系統的黑客攻擊,例如安全漏洞的惡意利用、非法控制系統、系統資源消耗等。黑客攻擊導致運行環境出現安全問題,則需要研究運行安全。運行安全是指對網絡與信息系統的運行過程和運行狀態的保護,主要涉及對網絡與信息系統的可控性、可用性等信息安全屬性的保護,主要的保護方式有風險分析、安全策略、入侵防護、入侵檢測、應急響應、系統恢復等。
信息保密領域在系統層面主要面臨遠程木馬攻擊造成的網絡竊密問題。網絡竊密是指未經信息持有人授權,通過網絡攻擊手段竊取秘密信息,以達到個人目的、經濟利益、政治或軍事優勢等。秘密信息包括個人信息、敏感信息、專有信息等。遠程木馬通過網絡從代碼的角度去竊密信息,因此,在系統層應關注網絡防竊技術。
信息對抗領域在系統層面主要面臨僵尸網絡攻擊問題。黑客利用蠕蟲等手段在互聯網中數百到數十萬臺計算機上植入僵尸程序以便達到暗中操控的目的,這些被操控的計算機構成的網絡被稱作僵尸網絡。針對僵尸網絡,應該關注網絡對抗技術,例如基于蜜罐密網對僵尸網絡的監測技術、計算機網絡防衛技術等。
云安全領域在系統層主要面臨針對平臺的攻擊問題。應對云平臺攻擊,需要構建安全的云,保證不讓用戶受到外來的攻擊、保證用戶的信息不被外界所竊取或篡改、保證用戶的程序不被外界所劫持,主要防護技術包括云身份認證與訪問控制、云風險評估、虛擬運行環境安全等。
大數據領域在系統層面主要面臨運行干擾引發的安全問題。由于計算量大、數據量大,當某個計算節點中斷服務時,就需要通過擺動、浮動等方式轉移計算任務,此時計算的可靠性就成為了關鍵問題。相對應地,應該關注系統確保技術,以保證大數據計算的可靠性。
物聯網安全在系統層主要面臨傳輸干擾引發的安全問題。物聯網多元化、異構化的網絡環境加劇了數據傳輸環節的脆弱性,例如,針對傳播環節的中間人攻擊,攻擊者攔截通信雙方的通話,使通信的兩端認為他們正在通過一個私密的連接與對方直接對話。針對傳輸干擾,應該關注物聯網的傳輸安全技術防御干擾和欺騙,例如安全認證技術、安全數據融合技術等。
移動安全領域在系統層主要面臨傳輸阻塞所引發的安全問題。移動終端的通信依靠運營商的基站,攻擊者可以通過攻擊基站,使其阻塞,進而中斷基站服務,例如,運營商之間的拒絕服務攻擊,就是向某基站大量地發送數據,將其資源占滿,使其提供正常服務。針對上述問題,應該關注移動互聯網的信道安全技術,例如終端與基站之間的安全通信協議和標準等。
可信計算領域在系統層主要面臨軟件故障所造成的安全問題。軟件故障會導致系統崩潰,為此,需要關注可信計算的軟件確保技術,軟件確保是使軟件在收到惡意攻擊的情形下依然能夠繼續正確運行及確保軟件在授權范圍內被合法使用的思想,主要技術包括軟件可信建模、程序安全性分析以及軟件運行監控等。軟件確保由信息確保發展而來,未來將進一步發展為系統確保、服務確保,最終成為實體確保。
5數據層的安全
信息安全領域在數據層主要面臨數據冒充、數據篡改、數據劫持等信息篡改的安全問題。相應地,應該關注數據安全技術。數據安全是指對信息在數據收集、處理、存儲、檢索、傳輸、交換、顯示、擴散等過程中的保護,使得在數據處理層面保障信息依據授權使用,不被非法冒充、竊取、篡改、抵賴。數據安全主要涉及對機密性、真實性、完整性、不可否認性、可用性等信息安全屬性的保護。主要技術包括針對信息丟失的數據備份技術、針對信息竊取的加密保護技術、針對信息篡改的完整性檢查技術、針對信息抵賴的數字簽名技術、針對信息冒充的身份認證技術以及針對數據丟失的數據備份技術等。
信息保密領域在數據層主要面臨通過暴力破解密碼來非法侵入系統并獲取私密信息等安全問題。暴力破解本質上是算法層面的對抗,常用的辦法有字典攻擊和彩虹表,前者通過逐一嘗試字典中的各種明文字符串進行密碼破解,后者利用彩虹表進行散列值反查明文。針對上述安全問題,應該關注新型密碼的設計和實現。
信息對抗領域在數據層面主要面臨情報竊取的安全問題。攻擊者往往通過密碼破解、繞過認證以及加密機制破解等方式達到信息竊取的目的,并最終演化為沒有硝煙的情報戰爭。贏得情報戰爭的勝利,需要關注情報對抗技術。情報對抗是指敵我雙方為獲取對方情報和破壞對方搜集己方情報,向對方宣傳虛假信息、以掩飾己方軍事意圖而進行的各種對抗活動,主要包括信息竊取、軍事謀略、行動保密。
云安全領域在數據層面主要面臨操作抵賴的安全問題。為防止操作抵賴需要建立可信的云,保證租戶在云中的程序不被其他租戶或云服務商所篡改和分析,保證租戶在云中的數據不被其他租戶或云服務商所篡改和竊取。可信的云的研究可從可信云框架、數據安全、審計和權限分割等幾方面展開。
大數據領域在數據層面主要面臨數據混亂所造成的安全問題。大數據在數據層面存在著海量的混亂數據,有價值的數據與噪聲數據混雜在一起,導致數據無法被有效利用,例如網絡水軍散布的虛假言論。針對數據混亂問題,應該主要關注大數據的數據確保技術,建立數據的甄選機制,將有價值的數據從混亂的數據中區分出來,進而解決大數據的可信問題。
物聯網領域在數據層面主要面臨隱私泄露的安全問題。相應地,應該關注物聯網的信息確保技術,主要包括數據的隱私保護和訪問控制技術。隱私保護是使個人或物體等實體不愿被其他人獲取的隱私信息得到應有的保護,隱私信息主要包括數據信息、位置信息。訪問控制是按用戶身份來限制用戶對某些信息的訪問或限制對某些控制功能的使用。
移動安全領域在數據層面主要面臨電話竊聽的安全問題。電話竊聽內容包括移動終端之間的音視頻數據和文本數據,其本質是數據傳輸過程中出現的數據篡改問題。針對此問題,應該關注通信安全技術,建立端對端的安全通信。這類技術仍屬于傳統的信息安全技術范疇,但要考慮終端移動所帶來的特殊需求,例如端對端加密、身份替換等。
可信計算領域在數據層面主要面臨非法程序所帶來的數據不可信問題。數據可信是一種觀念性的概念,涉及到數據來源可信、數據傳輸途徑可信、數據處理過程可信等多個方面。要解決非法程序造成的數據不可信問題,需要關注可信證明技術,建立程序的鑒別體系,確定程序的可信性,涉及的主要技術包括加密簽名技術、數據溯源技術、數據訪問控制技術、數據使用控制技術等。
6應用層的安全
信息安全領域在應用層主要面臨有害信息傳播的安全問題。有害信息包括謠言、暴力渲染、欺詐、色情誘惑等。有害信息的傳播本質上是內容安全問題,由此,應該關注內容安全的相關技術。內容安全是對信息在網絡內流動中的選擇性阻斷,以保證信息流動的可控能力,主要涉及信息的可控性、可用性等。相關技術包括文本特征抽取、字符串匹配、信息過濾與封堵等。
信息保密領域在應用層主要面臨信息匯聚所引發的信息泄露問題。攻擊者通過匯聚公開發布內容,利用大數據手段從中挖掘用戶隱私。針對此問題,應該關注脫密驗證技術,通過歸納學習、機器學習、統計分析等方法得到數據對象間的內在特性,據此分別在數據發布層面和數據查詢層面建立脫密驗證體系信息對抗領域在應用層主要面臨制造輿論的安全問題。信息對抗在應用層關注的是輿情、心理,美國稱之為傳播對抗。中國最早稱之為心理戰,目前包括心理戰、法律戰和輿論戰。為全面掌控輿情,應對新媒體引發的新問題,應該關注傳播對抗技術,主要包括輿情的發現與獲取、輿情的分析與引導、輿情的預警與處置等。
云安全領域在應用層主要面臨云平臺惡意濫用所造成的安全問題。攻擊者能夠利用云平臺進行拒絕服務攻擊,利用云平臺進行僵尸網絡攻擊等。針對云的惡意濫用,需要在應用層實現可控的云,即云平臺不會被利用作為攻擊工具,保證在云平臺中的程序不是惡意程序,保證在云平臺中的用戶可以被追溯責任,保證在云平臺中的用戶沒有害人的能力。可控的云涉及的主要技術包括檢測和預防云上木馬傳播、防御云做DDoS攻擊、防御云做有害信息傳播等。
大數據領域在應用層主要面臨隱私挖掘所造成的信息泄露問題。隱私泄露是大數據特性引發的特有的安全問題,大數據在應用層其他安全問題都能夠在其他領域找到。沒有大數據之前,信息呈現碎片化,且相對安全。大數據的出現導致攻擊者能夠從海量的數據中挖掘出用戶感興趣的信息,獲得更高層次的知識和規律,進而獲取用戶的隱私信息。針對隱私挖掘,需要關注大數據的服務確保技術,必須建立隱私保護體系,否則,大數據就是一把雙刃劍。
物聯網安全領域在應用層主要面臨惡意滲透所造成的失控問題。物聯網的核心應用是控制,物理信息系統將信息和物理環境相結合的目的就是以遠程的、可靠的、實時的、安全的、協作的方式控制物理實體。工業控制系統產品越來越多地采用通用協議、通用硬件和通用軟件,通過各種方式與互聯網等公共網絡連接,病毒、木馬等威脅正在向工業控制系統擴散。由此,應該關注物聯網的控制安全技術,主要技術包括控制安全保障體系、控制安全框架模型、控制安全異常發現等。
移動安全在應用層主要面臨支付冒充的安全問題。伴隨網購消費的快速發展,網上支付日益普及,隨之而來的網上支付冒充的安全問題也備受關注。移動終端病毒或木馬的侵襲、支付軟件自身存在的漏洞,很可能會造成支付隱患。同時,移動支付追求便捷的用戶體驗,
可信計算在應用層主要面臨信譽不實所引發的安全問題。可信計算在設備層實現硬件可靠,在系統層實現軟件確保,在數據層證明程序可信。那么,在應用層要解決的就是信任缺失的問題,要做到信任可控,其中,應用的信任度是應用的行為表現符合主體(使用者)預期的程度,應用的可控度是主體對應用行為表現的限制能力。由此,應該關注信任可控技術,主要包括應用級完整性保障技術、應用異常檢測技術和應用信任協商技術等。
7結束語
本文基于網絡空間安全層次模型,系統地梳理了目前的網絡空間安全技術體系。從層次的角度來看,物理層的安全主要研究能量對抗,系統層的安全主要研究代碼對抗,數據層的安全主要研究算法對抗,應用層的安全則根據不同應用研究不用的內容。從領域的角度來看,信息安全包括物理安全、運行安全、數據安全、內容安全;信息保密包括干擾屏蔽、網絡防竊、新型密碼、脫密驗證;信息對抗包括電子對抗、網絡對抗、情報對抗、傳播對抗;云的安全包括可靠的云、安全的云、可信的云、可控的云;大數據包括穩定確保、系統確保、數據確保、隱私確保;物聯網安全包括探針安全、傳輸安全、信息確保、控制安全;移動安全包括終端安全、信道安全、通信安全、應用安全;可信計算包括硬件可靠、軟件確保、可信證明、信任可控。
【作者單位:哈爾濱工業大學】
(摘自《網絡與信息安全學報》2015年1期)
大數據安全與隱私保護
馮登國,張敏,李昊
1引言
當今,社會信息化和網絡化的發展導致數據爆炸式增長。據統計,平均每秒有200萬用戶在使用谷歌搜索,Facebook用戶每天共享的東西超過40億,Twitter每天處理的推特數量超過3.4億。同時,科學計算、醫療衛生、金融、零售業等各行業也有大量數據在不斷產生。2012年全球信息總量已經達到2.7 ZB,而到2015年這一數值預計會達到8 ZB。
這一現象引發了人們的廣泛關注。在學術界,圖靈獎獲得者Jim Gray提出了科學研究的第四范式,即以大數據為基礎的數據密集型科學研究;2008年《Nature》推出了大數據專刊對其展開探討;2011年《Science》也推出類似的數據處理專刊。IT產業界行動更為積極,持續關注數據再利用,挖掘大數據的潛在價值。目前,大數據已成為繼云計算之后信息技術領域的另一個信息產業增長點。據Gartner預測,2013年大數據將帶動全球IT支出340億美元,到2016年全球在大數據方面的總花費將達到2320億美元。Gartner將“大數據”技術列入 2012年對眾多公司和組織機構具有戰略意義的十大技術與趨勢之一不僅如此,作為國家和社會的主要管理者,各國政府也是大數據技術推廣的主要推動者。2009年3月美國政府上線了data. gov網站,向公眾開放政府所擁有的公共數據。隨后,英國、澳大利亞等政府也開始了大數據開放的進程,截至目前,全世界已經正式有35個國家和地區構建了自己的數據開放門戶網站。美國政府聯合6個部門宣布了2億美元的“大數據研究與發展計劃”。在我國,2012年中國通信學會、中國計算機學會等重要學術組織先后成立了大數據專家委員會,為我國大數據應用和發展提供學術咨詢。
目前大數據的發展仍然面臨著許多問題,安全與隱私問題是人們公認的關鍵問題之一。當前,人們在互聯網上的一言一行都掌握在互聯網商家手中,包括購物習慣、好友聯絡情況、閱讀習慣、檢索習慣等等。多項實際案例說明,即使無害的數據被大量收集后,也會暴露個人隱私。事實上,大數據安全含義更為廣泛,人們面臨的威脅并不僅限于個人隱私泄漏。與其它信息一樣,大數據在存儲、處理、傳輸等過程中面臨諸多安全風險,具有數據安全與隱私保護需求。而實現大數據安全與隱私保護,較以往其它安全問題(如云計算中的數據安全等)更為棘手。這是因為在云計算中,雖然服務提供商控制了數據的存儲與運行環境,但是用戶仍然有些辦法保護自己的數據,例如通過密碼學的技術手段實現數據安全存儲與安全計算,或者通過可信計算方式實現運行環境安全等。而在大數據的背景下,Facebook等商家既是數據的生產者,又是數據的存儲、管理者和使用者,因此,單純通過技術手段限制商家對用戶信息的使用,實現用戶隱私保護是極其困難的事。
當前很多組織都認識到大數據的安全問題,并積極行動起來關注大數據安全問題。2012年云安全聯盟CSA組建了大數據工作組,旨在尋找針對數據中心安全和隱私問題的解決方案。本文在梳理大數據研究現狀的基礎上,重點分析了當前大數據所帶來的安全挑戰,詳細闡述了當前大數據安全與隱私保護的關鍵技術。需要指出的是,大數據在引入新的安全問題和挑戰的同時,也為信息安全領域帶來了新的發展契機,即基于大數據的信息安全相關技術可以反過來用于大數據的安全和隱私保護。
2大數據研究概述
2.1大數據來源與特征
普遍的觀點認為,大數據是指規模大且復雜、以至于很難用現有數據庫管理工具或數據處理應用來處理的數據集。大數據的常見特點包括大規模(volume)、高速性(velocity)和多樣性(variety)。
根據來源的不同,大數據大致可分為如下幾類:
1)來自于人。人們在互聯網活動以及使用移動互聯網過程中所產生的各類數據,包括文字、圖片、視頻等信息;
2)來自于機。各類計算機信息系統產生的數據,以文件、數據庫、多媒體等形式存在,也包括審計、日志等自動生成的信息;
3)來自于物。各類數字設備所采集的數據。如攝像頭產生的數字信號、醫療物聯網中產生的人的各項特征值、天文望遠鏡所產生的大量數據等。
2.2大數據分析目標
目前大數據分析應用于科學、醫藥、商業等各個領域,用途差異巨大。但其目標可以歸納為如下幾類:
1)獲得知識與推測趨勢。
人們進行數據分析由來已久,最初且最重要的目的就是獲得知識、利用知識。由于大數據包含大量原始、真實信息,大數據分析能夠有效地摒棄個體差異,幫助人們透過現象、更準確地把握事物背后的規律。基于挖掘出的知識,可以更準確地對自然或社會現象進行預測。典型的案例是Google公司的Google Flu Trends網站。它通過統計人們對流感信息的搜索,查詢 Google服務器日志的IP地址判定搜索來源,從而發布對世界各地流感情況的預測。又如,人們可以根據Twitter信息預測股票行情等。
2)分析掌握個性化特征。
個體活動在滿足某些群體特征的同時,也具有鮮明的個性化特征。正如“長尾理論”中那條細長的尾巴那樣,這些特征可能千差萬別。企業通過長時間、多維度的數據積累,可以分析用戶行為規律,更準確地描繪其個體輪廓,為用戶提供更好的個性化產品和服務,以及更準確的廣告推薦。例如,Google通過其大數據產品對用戶的習慣和愛好進行分析,幫助廣告商評估廣告活動效率,預估在未來可能存在高達到數千億美元的市場規模。
3)通過分析辨識真相。
錯誤信息不如沒有信息。由于網絡中信息的傳播更加便利,所以網絡虛假信息造成的危害也更大。例如,2013年4月24日,美聯社Twitter帳號被盜,發布虛假消息稱總統奧巴馬遭受恐怖襲擊受傷。雖然虛假消息在幾分鐘內被禁止,但是仍然引發了美國股市短暫跳水。由于大數據來源廣泛及其多樣性,在一定程度上它可以幫助實現信息的去偽存真。目前人們開始嘗試利用大數據進行虛假信息識別。例如,社交點評類網站Yelp利用大數據對虛假評論進行過濾,為用戶提供更為真實的評論信息;Yahoo和 Thinkmail等利用大數據分析技術來過濾垃圾郵件。
2.3大數據技術框架
大數據處理涉及數據的采集、管理、分析與展示等。
1)數據采集與預處理(Data Acquisition & Preparation)。
大數據的數據源多樣化,包括數據庫、文本、圖片、視頻、網頁等各類結構化、非結構化及半結構化數據。因此,大數據處理的第一步是從數據源采集數據并進行預處理操作,為后繼流程提供統一的高質量的數據集。
由于大數據的來源不一,可能存在不同模式的描述,甚至存在矛盾。因此,在數據集成過程中對數據進行清洗,以消除相似、重復或不一致的數據是非常必要的。文獻[4-7]中數據清洗和集成技術針對大數據的特點,提出非結構化或半結構化數據的清洗以及超大規模數據的集成。
數據存儲與大數據應用密切相關。某些實時性要求較高的應用,如狀態監控,更適合采用流處理模式,直接在清洗和集成后的數據源上進行分析。而大多數其它應用則需要存儲,以支持后繼更深度的數據分析流程。為了提高數據吞吐量,降低存儲成本,通常采用分布式架構來存儲大數據。這方面有代表性的研究包括:文件系統 GFS,HDFS和 Haystack等;NoSQL數據庫Mongodb、CouchDB、HBase、Redis、Neo4j等。
2)數據分析(Data Analysis)。
數據分析是大數據應用的核心流程。根據不同層次大致可分為3類:計算架構、查詢與索引以及數據分析和處理。
在計算架構方面,MapReduce是當前廣泛采用的大數據集計算模型和框架。為了適應一些對任務完成時間要求較高的分析需求,文獻[12]對其性能進行了優化;文獻[13]提出了一種基于MapReduce架構的數據流分析解決方案 MARISSA,使其能夠支持實時分析任務;文獻[14]提出了基于時間的大數據分析方案Mastiff;文獻[15]也針對廣告推送等實時性要求較高的應用,提出了基于MapReduce的TiMR框架來進行實時流處理。
在查詢與索引方面,由于大數據中包含了大量的非結構化或半結構化數據,傳統關系型數據庫的查詢和索引技術受到限制,而 NoSQL二類數據庫技術得到更多關注。例如,文獻[16]提出了一個混合的數據訪問架構HyDB以及一種并發數據查詢及優化方法。文獻[17]對key-value類型數據庫的查詢進行了性能優化。
在數據分析與處理方面,主要涉及的技術包括語義分析與數據挖掘等。由于大數據環境下數據呈現多樣化特點,所以對數據進行語義分析時,就較難統一術語進而挖掘信息。文獻[18]針對大數據環境,提出了一種解決術語變異問題的高效術語標準化方法。文獻[19]對語義分析中語義本體的異質性展開了研究。傳統數據挖掘技術主要針對結構化數據,因此迫切需要對非結構化或半結構化的數據挖掘技術展開研究。文獻[20]提出了一種針對圖片文件的挖掘技術,文獻[21]提出了一種大規模TEXT文件的檢索和挖掘技術。
3)數據解釋(Data Interpretation)。
數據解釋旨在更好地支持用戶對數據分析結果的使用,涉及的主要技術為可視化和人機交互。
目前已經有了一些針對大規模數據的可視化研究,通過數據投影、維度降解或顯示墻等方法來解決大規模數據的顯示問題。由于人類的視覺敏感度限制了更大屏幕顯示的有效性,以人為中心的人機交互設計也將是解決大數據分析結果展示的一種重要技術。
4)其他支撐技術(Data Transmission & Virtual Cluster)。
雖然大數據應用強調以數據為中心,將計算推送到數據上執行,但是在整個處理過程中,數據的傳輸仍然是必不可少的,例如一些科學觀測數據從觀測點向數據中心的傳輸等。文獻[24-25]針對大數據特征研究高效傳輸架構和協議。
此外,由于虛擬集群具有成本低、搭建靈活、便于管理等優點,人們在大數據分析時可以選擇更加方便的虛擬集群來完成各項處理任務。因此需要針對大數據應用展開的虛擬機集群優化研究。
3大數據帶來的安全挑戰
科學技術是一把雙刃劍。大數據所引發的安全問題與其帶來的價值同樣引人注目。而最近爆發的“棱鏡門”事件更加劇了人們對大數據安全的擔憂。與傳統的信息安全問題相比,大數據安全面臨的挑戰性問題主要體現在以下幾個方面。
3.1大數據中的用戶隱私保護
大量事實表明,大數據未被妥善處理會對用戶的隱私造成極大的侵害。根據需要保護的內容不同,隱私保護又可以進一步細分為位置隱私保護、標識符匿名保護、連接關系匿名保護等。
人們面臨的威脅并不僅限于個人隱私泄漏,還在于基于大數據對人們狀態和行為的預測。一個典型的例子是某零售商通過歷史記錄分析,比家長更早知道其女兒已經懷孕的事實,并向其郵寄相關廣告信息。而社交網絡分析研究也表明,可以通過其中的群組特性發現用戶的屬性。例如通過分析用戶的Twitter信息,可以發現用戶的政治傾向、消費習慣以及喜好的球隊等。
當前企業常常認為經過匿名處理后,信息不包含用戶的標識符,就可以公開發布了。但事實上,僅通過匿名保護并不能很好地達到隱私保護目標。例如,AOL公司曾公布了匿名處理后的3個月內部分搜索歷史,供人們分析使用。雖然個人相關的標識信息被精心處理過,但其中的某些記錄項還是可以被準確地定位到具體的個人。紐約時報隨即公布了其識別出的1位用戶。編號為4417749的用戶是1位62歲的寡居婦人,家里養了3條狗,患有某種疾病,等等。另一個相似的例子是,著名的DVD租賃商Netflix曾公布了約50萬用戶的租賃信息,懸賞100萬美元征集算法,以期提高電影推薦系統的準確度。但是當上述信息與其它數據源結合時,部分用戶還是被識別出來了。研究者發現,Netflix中的用戶有很大概率對非top 100,top 500,top 1000的影片進行過評分,而根據對非top影片的評分結果進行去匿名化(de-anonymizing)攻擊的效果更好。
目前用戶數據的收集、存儲、管理與使用等均缺乏規范,更缺乏監管,主要依靠企業的自律。用戶無法確定自己隱私信息的用途。而在商業化場景中,用戶應有權決定自己的信息如何被利用,實現用戶可控的隱私保護。例如,用戶可以決定自己的信息何時以何種形式披露,何時被銷毀。包括:1)數據采集時的隱私保護,如數據精度處理;2)數據共享、發布時的隱私保護,如數據的匿名處理、人工加擾等;3)數據分析時的隱私保護;4)數據生命周期的隱私保護;5)隱私數據可信銷毀等。
3.2大數據的可信性
關于大數據的一個普遍的觀點是,數據自己可以說明一切,數據自身就是事實。但實際情況是,如果不仔細甄別,數據也會欺騙,就像人們有時會被自己的雙眼欺騙一樣。
大數據可信性的威脅之一是偽造或刻意制造的數據,而錯誤的數據往往會導致錯誤的結論。若數據應用場景明確,就可能有人刻意制造數據、營造某種“假象”,誘導分析者得出對其有利的結論。由于虛假信息往往隱藏于大量信息中,使得人們無法鑒別真偽,從而做出錯誤判斷。例如,一些點評網站上的虛假評論,混雜在真實評論中使得用戶無法分辨,可能誤導用戶去選擇某些劣質商品或服務。由于當前網絡社區中虛假信息的產生和傳播變得越來越容易,其所產生的影響不可低估。用信息安全技術手段鑒別所有來源的真實性是不可能的。
大數據可信性的威脅之二是數據在傳播中的逐步失真。原因之一是人工干預的數據采集過程可能引入誤差,由于失誤導致數據失真與偏差,最終影響數據分析結果的準確性。此外,數據失真還有數據的版本變更的因素。在傳播過程中,現實情況發生了變化,早期采集的數據已經不能反映真實情況。例如,餐館電話號碼已經變更,但早期的信息已經被其它搜索引擎或應用收錄,所以用戶可能看到矛盾的信息而影響其判斷。
因此,大數據的使用者應該有能力基于數據來源的真實性、數據傳播途徑、數據加工處理過程等,了解各項數據可信度,防止分析得出無意義或者錯誤的結果。
密碼學中的數字簽名、消息鑒別碼等技術可以用于驗證數據的完整性,但應用于大數據的真實性時面臨很大困難,主要根源在于數據粒度的差異。例如,數據的發源方可以對整個信息簽名,但是當信息分解成若干組成部分時,該簽名無法驗證每個部分的完整性。而數據的發源方無法事先預知哪些部分被利用、如何被利用,難以事先為其生成驗證對象。
3.3如何實現大數據訪問控制
訪問控制是實現數據受控共享的有效手段。由于大數據可能被用于多種不同場景,其訪問控制需求十分突出。
大數據訪問控制的特點與難點在于:
1)難以預設角色,實現角色劃分。由于大數據應用范圍廣泛,它通常要為來自不同組織或部門、不同身份與目的的用戶所訪問,實施訪問控制是基本需求。然而,在大數據的場景下,有大量的用戶需要實施權限管理,且用戶具體的權限要求未知。面對未知的大量數據和用戶,預先設置角色十分困難。
2)難以預知每個角色的實際權限。由于大數據場景中包含海量數據,安全管理員可能缺乏足夠的專業知識,無法準確地為用戶指定其所可以訪問的數據范圍。而且從效率角度講,定義用戶所有授權規則也不是理想的方式。以醫療領域應用為例,醫生為了完成其工作可能需要訪問大量信息,但對于數據能否訪問應該由醫生來決定,不應該需要管理員對每個醫生做特別的配置。但同時又應該能夠提供對醫生訪問行為的檢測與控制,限制醫生對病患數據的過度訪問。
此外,不同類型的大數據中可能存在多樣化的訪問控制需求。例如,在Web 2.0個人用戶數據中,存在基于歷史記錄的訪問控制;在地理地圖數據中,存在基于尺度以及數據精度的訪問控制需求;在流數據處理中,存在數據時間區間的訪問控制需求,等等。如何統一地描述與表達訪問控制需求也是一個挑戰性問題。
4大數據安全與隱私保護關鍵技術
當前函需針對前述大數據面臨的用戶隱私保護、數據內容可信驗證、訪問控制等安全挑戰,展開大數據安全關鍵技術研究。本節選取部分重點相關研究領域予以介紹。
4.1數據發布匿名保護技術
對于大數據中的結構化數據(或稱關系數據)而言,數據發布匿名保護是實現其隱私保護的核心關鍵技術與基本手段,目前仍處于不斷發展與完善階段。
以典型的k匿名方案為例。早期的方案及其優化方案通過元組泛化、抑制等數據處理,將準標識符分組。每個分組中的準標識符相同且至少包含k-1個元組,因而每個元組至少與k-1個其他元組不可區分。由于k匿名模型是針對所有屬性集合而言,對于具體的某個屬性則未加定義,容易出現某個屬性匿名處理不足的情況。若某等價類中某個敏感屬性上取值一致,則攻擊者可以有效地確定該屬性值。針對該問題研究者提出l多樣化(l-diversity)匿名。其特點是在每一個匿名屬性組里敏感數據的多樣性滿足要大于或等于 l。實現方法包括基于裁剪算法的方案以及基于數據置換的方案等。此外,還有一些介于k匿名與Z多樣化之間的方案。進一步的,由于 l-diversity只是能夠盡量使敏感數據出現的頻率平均化。當同一等價類中數據范圍很小時,攻擊者可猜測其值。t貼近性(t-closeness)方案要求等價類中敏感數據的分布與整個數據表中數據的分布保持一致。其它工作包括(k, e)匿名模型(X, Y)匿名模型等。上述研究是針對靜態、一次性發布情況。而現實中,數據發布常面臨數據連續、多次發布的場景。需要防止攻擊者對多次發布的數據聯合進行分析,破壞數據原有的匿名特性。
在大數據場景中,數據發布匿名保護問題較之更為復雜:攻擊者可以從多種渠道獲得數據,而不僅僅是同一發布源。例如,在前所提及的Netflix應用中,人們發現攻擊者可通過將數據與公開可獲得的imdb相對比,從而識別出目標在Netflix的賬號。并據此獲取用戶的政治傾向與宗教信仰等(通過用戶的觀看歷史和對某些電影的評論和打分分析獲得)。此類問題有待更深入的研究。
4.2社交網絡匿名保護技術
社交網絡產生的數據是大數據的重要來源之一,同時這些數據中包含大量用戶隱私數據。截至2012年10月Face book的用戶成員就已達10億。由于社交網絡具有圖結構特征,其匿名保護技術與結構化數據有很大不同。
社交網絡中的典型匿名保護需求為用戶標識匿名與屬性匿名(又稱點匿名),在數據發布時隱藏了用戶的標識與屬性信息;以及用戶間關系匿名(又稱邊匿名),在數據發布時隱藏用戶間的關系。而攻擊者試圖利用節點的各種屬性(度數、標簽、某些具體連接信息等),重新識別出圖中節點的身份信息。
目前的邊匿名方案大多是基于邊的增刪。隨機增刪交換邊的方法可以有效地實現邊匿名。其中文獻[44]在匿名過程中保持鄰接矩陣的特征值和對應的拉普拉斯矩陣第二特征值不變,文獻[45]根據節點的度數分組,從度數相同的節點中選擇符合要求的進行邊的交換,類似的還有文獻[46-47]。這類方法的問題是隨機增加的噪音過于分散稀少,存在匿名邊保護不足問題。
另一個重要思路是基于超級節點對圖結構進行分割和集聚操作。如基于節點聚集的匿名方案、基于基因算法的實現方案、基于模擬退火算法的實現方案以及先填充再分割超級節點的方案。文獻[52]所提出的k-security概念,通過k個同構子圖實現圖匿名保護。基于超級節點的匿名方案雖然能夠實現邊的匿名,但是與原始社交結構圖存在較大區別,以犧牲數據的可用性為代價。
社交網絡匿名方案面臨的重要問題是,攻擊者可能通過其他公開的信息推測出匿名用戶,尤其是用戶之間是否存在連接關系。例如,可以基于弱連接對用戶可能存在的連接進行預測,適用于用戶關系較為稀疏的網絡;根據現有社交結構對人群中的等級關系進行恢復和推測;針對微博型的復合社交網絡進行分析與關系預測;基于限制隨機游走方法,推測不同連接關系存在的概率,等等。研究表明,社交網絡的集聚特性對于關系預測方法的準確性具有重要影響,社交網絡局部連接密度增長,集聚系數增大,則連接預測算法的準確性進一步增強。因此,未來的匿名保護技術應可以有效抵抗此類推測攻擊。
4.3數據水印技術
數字水印是指將標識信息以難以察覺的方式嵌入在數據載體內部且不影響其使用的方法,多見于多媒體數據版權保護。也有部分針對數據庫和文本文件的水印方案。
由數據的無序性、動態性等特點所決定,在數據庫、文檔中添加水印的方法與多媒體載體上有很大不同。其基本前提是上述數據中存在冗余信息或可容忍一定精度誤差。例如,Agrawal等人基于數據庫中數值型數據存在誤差容忍范圍,將少量水印信息嵌入到這些數據中隨機選取的最不重要位上。而Sion等人提出一種基于數據集合統計特征的方案,將一比特水印信息嵌入在一組屬性數據中,防止攻擊者破壞水印.此外,通過將數據庫指紋信息嵌入水印中,可以識別出信息的所有者以及被分發的對象,有利于在分布式環境下追蹤泄密者;通過采用獨立分量分析技術(簡稱 ICA),可以實現無需密鑰的水印公開驗證。其它相關工作包括文獻[64-65],若在數據庫表中嵌入脆弱性水印,可以幫助及時發現數據項的變化。
文本水印的生成方法種類很多,可大致分為基于文檔結構微調的水印,依賴字符間距與行間距等格式上的微小差異;基于文本內容的水印,依賴于修改文檔內容,如增加空格、修改標點等;以及基于自然語言的水印,通過理解語義實現變化,如同義詞替換或句式變化等。
上述水印方案中有些可用于部分數據的驗證。例如在文獻[58-59]中,殘余元組數量達到閡值就可以成功驗證出水印。該特性在大數據應用場景下具有廣闊的發展前景,例如:強健水印類(Robust Watermark)可用于大數據的起源證明,而脆弱水印類(Fragile Watermark)可用于大數據的真實性證明。存在問題之一是當前的方案多基于靜態數據集,針對大數據的高速產生與更新的特性考慮不足,這是未來函待提高的方向。
4.4數據溯源技術
如前所述,數據集成是大數據前期處理的步驟之一由于數據的來源多樣化,所以有必要記錄數據的來源及其傳播、計算過程,為后期的挖掘與決策提供輔助支持。
早在大數據概念出現之前,數據溯源(DataProvenance)技術就在數據庫領域得到廣泛研究。其基本出發點是幫助人們確定數據倉庫中各項數據的來源,例如了解它們是由哪些表中的哪些數據項運算而成,據此可以方便地驗算結果的正確性,或者以極小的代價進行數據更新。數據溯源的基本方法是標記法。后來概念進一步細化為why-和where-兩類,分別側重數據的計算方法以及數據的出處。除數據庫以外,它還包括 XML數據、流數據與不確定數據的溯源技術。數據溯源技術也可用于文件的溯源與恢復。例如文獻[74]通過擴展Linux內核與文件系統,創建了一個數據起源存儲系統原型系統,可以自動搜集起源數據。此外也有其在云存儲場景中的應用。
未來數據溯源技術將在信息安全領域發揮重要作用。在 2009年呈報美國國土安全部的“國家網絡空間安全”的報告中,將其列為未來確保國家關鍵基礎設施安全的3項關鍵技術之一。然而,數據溯源技術應用于大數據安全與隱私保護中還面臨如下挑戰:
1)數據溯源與隱私保護之間的平衡。一方面,基于數據溯源對大數據進行安全保護首先要通過分析技術獲得大數據的來源,然后才能更好地支持安全策略和安全機制的工作;另一方面,數據來源往往本身就是隱私敏感數據。用戶不希望這方面的數據被分析者獲得。因此,如何平衡這兩者的關系是值得研究的問題之一。
2)數據溯源技術自身的安全性保護。當前數據溯源技術并沒有充分考慮安全問題,例如標記自身是否正確、標記信息與數據內容之間是否安全綁定等等。而在大數據環境下,其大規模、高速性、多樣性等特點使該問題更加突出。
4.5角色挖掘
基于角色的訪問控制(RBAC)是當前廣泛使用的一種訪問控制模型。通過為用戶指派角色、將角色關聯至權限集合,實現用戶授權、簡化權限管理。早期的RBAC權限管理多采用“自頂向下”的模式:即根據企業的職位設立角色分工。當其應用于大數據場景時,面臨需大量人工參與角色劃分、授權的問題(又稱為角色工程)。
后來研究者們開始關注“自底向上”模式,即根據現有“用戶-對象”授權情況,設計算法自動實現角色的提取與優化,稱為角色挖掘。簡單來說,就是如何設置合理的角色。典型的工作包括:以可視化的形式,通過用戶權限二維圖的排序歸并的方式實現角色提取;通過子集枚舉以及聚類的方法提取角色等非形式化方法;也有基于形式化語義分析、通過層次化挖掘來更準確提取角色的方法。總體來說,挖掘生成最小角色集合的最優算法時間復雜度高,多屬于NP-完全問題。因而也有研究者關注在多項式時間內完成的啟發式算法。在大數據場景下,采用角色挖掘技術可根據用戶的訪問記錄自動生成角色,高效地為海量用戶提供個性化數據服務。同時也可用于及時發現用戶偏離日常行為所隱藏的潛在危險。但當前角色挖掘技術大都基于精確、封閉的數據集,在應用于大數據場景時還需要解決數據集動態變更以及質量不高等特殊問題。
4.6風險自適應的訪問控制
在大數據場景中,安全管理員可能缺乏足夠的專業知識,無法準確地為用戶指定其可以訪問的數據。風險自適應的訪問控制是針對這種場景討論較多的一種訪問控制方法。Jason的報告描述了風險量化和訪問配額的概念。隨后,Cheng等人提出了一個基于多級別安全模型的風險自適應訪問控制解決方案。Ni等人提出了另一個基于模糊推理的解決方案,將信息的數目和用戶以及信息的安全等級作為進行風險量化的主要參考參數。當用戶訪問的資源的風險數值高于某個預定的門限時,則限制用戶繼續訪問。文獻[90]提出了一種針對醫療數據提供用戶隱私保護的可量化風險自適應訪問控制。通過利用統計學和信息論的方法,定義了量化算法,從而實現基于風險的訪問控制。但同時,在大數據應用環境中,風險的定義和量化都較之以往更加困難。
5大數據服務與信息安全
5.1基于大數據的威脅發現技術
由于大數據分析技術的出現,企業可以超越以往的“保護-檢測-響應-恢復”(PDRR)模式,更主動地發現潛在的安全威脅。例如,IBM推出了名為IBM大數據安全智能的新型安全工具,可以利用大數據來偵測來自企業內外部的安全威脅,包括掃描電子郵件和社交網絡,標示出明顯心存不滿的員工,提醒企業注意,預防其泄露企業機密。
“棱鏡”計劃也可以被理解為應用大數據方法進行安全分析的成功故事。通過收集各個國家各種類型的數據,利用安全威脅數據和安全分析形成系統方法發現潛在危險局勢,在攻擊發生之前識別威脅。
相比于傳統技術方案,基于大數據的威脅發現技術具有以下優點。
1)分析內容的范圍更大。
傳統的威脅分析主要針對的內容為各類安全事件。而一個企業的信息資產則包括數據資產、軟件資產、實物資產、人員資產、服務資產和其它為業務提供支持的無形資產。由于傳統威脅檢測技術的局限性,其并不能覆蓋這六類信息資產,因此所能發現的威脅也是有限的。而通過在威脅檢測方面引入大數據分析技術,可以更全面地發現針對這些信息資產的攻擊。例如,通過分析企業員工的即時通信數據、Email數據等可以及時發現人員資產是否面臨其他企業“挖墻腳”的攻擊威脅。再比如,通過對企業的客戶部訂單數據的分析,也能夠發現一些異常的操作行為,進而判斷是否危害公司利益。可以看出,分析內容范圍的擴大使得基于大數據的威脅檢測更加全面。
2)分析內容的時間跨度更長。
現有的許多威脅分析技術都是內存關聯性的,也就是說實時收集數據,采用分析技術發現攻擊。分析窗口通常受限于內存大小,無法應對持續性和潛伏性攻擊。而引入大數據分析技術后,威脅分析窗口可以橫跨若干年的數據,因此威脅發現能力更強,可以有效應對APT類攻擊。
3)攻擊威脅的預測性。
傳統的安全防護技術或工具大多是在攻擊發生后對攻擊行為進行分析和歸類,并做出響應。而基于大數據的威脅分析,可進行超前的預判。它能夠尋找潛在的安全威脅,對未發生的攻擊行為進行預防。
4)對未知威脅的檢測。
傳統的威脅分析通常是由經驗豐富的專業人員根據企業需求和實際情況展開,然而這種威脅分析的結果很大程度上依賴于個人經驗。同時,分析所發現的威脅也是已知的。而大數據分析的特點是側重于普通的關聯分析,而不側重因果分析,因此通過采用恰當的分析模型,可發現未知威脅。
雖然基于大數據的威脅發現技術具有上述的優點,但是該技術目前也存在一些問題和挑戰,主要集中在分析結果的準確程度上。一方面,大數據的收集很難做到全面,而數據又是分析的基礎,它的片面性往往會導致分析出的結果的偏差。為了分析企業信息資產面臨的威脅,不但要全面收集企業內部的數據,還要對一些企業外的數據進行收集,這些在某種程度上是一個大問題。另一方面,大數據分析能力的不足影響威脅分析的準確性。例如,紐約投資銀行每秒會有 5000次網絡事件,每天會從中捕捉25 TB數據。如果沒有足夠的分析能力,要從如此龐大的數據中準確地發現極少數預示潛在攻擊的事件,進而分析出威脅是幾乎不可能完成的任務。
5.2基于大數據的認證技術
身份認證是信息系統或網絡中確認操作者身份的過程。傳統的認證技術主要通過用戶所知的秘密,例如口令,或者持有的憑證,例如數字證書,來鑒別用戶。這些技術面臨著如下兩個問題。
首先,攻擊者總是能夠找到方法來騙取用戶所知的秘密,或竊取用戶持有的憑證,從而通過認證機制的認證。例如攻擊者利用釣魚網站竊取用戶口令,或者通過社會工程學方式接近用戶,直接騙取用戶所知秘密或持有的憑證。
其次,傳統認證技術中認證方式越安全往往意味著用戶負擔越重。例如,為了加強認證安全,而采用的多因素認證。用戶往往需要同時記憶復雜的口令,還要隨身攜帶硬件USB Key一旦忘記口令或者忘記攜帶USB Key,就無法完成身份認證。為了減輕用戶負擔,一些生物認證方式出現,利用用戶具有的生物特征,例如指紋等,來確認其身份。然而,這些認證技術要求設備必須具有生物特征識別功能,例如,指紋識別。因此很大程度上限制了這些認證技術的廣泛應用。
而在認證技術中引入大數據分析則能夠有效地解決這兩個問題。基于大數據的認證技術指的是收集用戶行為和設備行為數據,并對這些數據進行分析,獲得用戶行為和設備行為的特征,進而通過鑒別操作者行為及其設備行為來確定其身份。這與傳統認證技術利用用戶所知秘密,所持有憑證,或具有的生物特征來確認其身份有很大不同。具體地,這種新的認證技術具有如下優點。
1)攻擊者很難模擬用戶行為特征來通過認證,因此更加安全。利用大數據技術所能收集的用戶行為和設備行為數據是多樣的,可以包括用戶使用系統的時間、經常采用的設備、設備所處物理位置,甚至是用戶的操作習慣數據。通過這些數據的分析能夠為用戶勾畫一個行為特征的輪廓。而攻擊者很難在方方面面都模仿到用戶行為,因此其與真正用戶的行為特征輪廓必然存在一個較大偏差,無法通過認證。
2)減小了用戶負擔。用戶行為和設備行為特征數據的采集、存儲和分析都由認證系統完成。相比于傳統認證技術,極大地減輕了用戶負擔。
3)可以更好地支持各系統認證機制的統一。基于大數據的認證技術可以讓用戶在整個網絡空間采用相同的行為特征進行身份認證,而避免不同系統采用不同認證方式,且用戶所知秘密或所持有憑證也各不相同而帶來了種種不便。
雖然基于大數據的認證技術具有上述優點,但同時也存在一些問題和挑戰函待解決。
1)初始階段的認證問題。基于大數據的認證技術是建立在大量用戶行為和設備行為數據分析的基礎上,而初始階段不具備大量數據。因此,無法分析出用戶行為特征,或者分析的結果不夠準確。
2)用戶隱私問題。基于大數據的認證技術為了能夠獲得用戶的行為習慣,必然要長期持續地收集大量的用戶數據。那么如何在收集和分析這些數據的同時,確保用戶隱私也是函待解決的問題。它是影響這種新的認證技術是否能夠推廣的主要因素。
5.3基于大數據的數據真實性分析
目前,基于大數據的數據真實性分析被廣泛認為是最為有效的方法。許多企業已經開始了這方面的研究工作,例如,Yahoo和 Thinkmail等利用大數據分析技術來過濾垃圾郵件;Yelp等社交點評網絡用大數據分析來識別虛假評論;新浪微博等社交媒體利用大數據分析來鑒別各類垃圾信息等。
基于大數據的數據真實性分析技術能夠提高垃圾信息的鑒別能力。一方面,引入大數據分析可以獲得更高的識別準確率。例如,對于點評網站的虛假評論,可以通過收集評論者的大量位置信息、評論內容、評論時間等進行分析,鑒別其評論的可靠性。如果某評論者為某品牌多個同類產品都發表了惡意評論,則其評論的真實性就值得懷疑;另一方面,在進行大數據分析時,通過機器學習技術,可以發現更多具有新特征的垃圾信息。然而該技術仍然面臨一些困難,主要是虛假信息的定義、分析模型的構建等。
5.4大數據與“安全-即-服務(Security-as-a-Service)”
前面列舉了部分當前基于大數據的信息安全技術,未來必將涌現出更多、更豐富的安全應用和安全服務。由于此類技術以大數據分析為基礎,因此如何收集、存儲和管理大數據就是相關企業或組織所面臨的核心問題。除了極少數企業有能力做到之外,對于絕大多數信息安全企業來說,更為現實的方式是通過某種方式獲得大數據服務,結合自己的技術特色領域,對外提供安全服務。一種未來的發展前景是,以底層大數據服務為基礎,各個企業之間組成相互依賴、相互支撐的信息安全服務體系,總體上形成信息安全產業界的良好生態環境。
6小結
大數據帶來了新的安全問題,但它自身也是解決問題的重要手段。本文從大數據的隱私保護、信任、訪問控制等角度出發,梳理了當前大數據安全與隱私保護相關關鍵技術。但總體上來說,當前國內外針對大數據安全與隱私保護的相關研究還不充分。只有通過技術手段與相關政策法規等相結合,才能更好地解決大數據安全與隱私保護問題。
【作者單位:中國科學院軟件研究所】
(摘自《計算機學報》2014年1期)
·高被引論文摘要·
被引頻次:897
網絡安全入侵檢測:研究綜述
蔣建春,馬恒太,任黨恩,等
入侵檢測是近年來網絡安全研究的熱點。首先說明入侵檢測的必要性,并給出入侵檢測的概念和模型,概述了多種入侵檢測方法及體系結構。最后,討論了該領域當前存在的問題及今后的研究方向。
網絡安全;入侵檢測
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2000, 11(11): 1460-1466
被引頻次:607
信息安全綜述
沈昌祥,張煥國,馮登國,等
21世紀是信息的時代。信息成為一種重要的戰略資源,信息的獲取、處理和安全保障能力成為一個國家綜合國力的重要組成部分。信息安全事關國家安全、事關社會穩定。 因此, 必須采取措施確保我國的信息安全。近年來,信息安全領域的發展十分迅速,取得了許多新的重要成果。信息安全理論與技術的內容十分廣泛,但由于篇幅所限,這里主要介紹密碼學、可信計算、網絡安全和信息隱藏等方面的研究和發展。
信息安全;密碼學;可信計算;網絡安全;信息隱藏
來源出版物:中國科學(E輯:信息科學): 2007, 37(2): 129-150
被引頻次:472
層次化網絡安全威脅態勢量化評估方法
陳秀真,鄭慶華,管曉宏,等
安全評估是貫穿信息系統生命周期的重要管理手段,是制定和調整安全策略的基礎和前提。只有充分識別系統安全風險,才能有針對性地采取有效的安全防范措施。基于IDS(intrusion detection system)海量報警信息和網絡性能指標,結合服務、主機本身的重要性及網絡系統的組織結構,提出采用自下而上、先局部后整體評估策略的層次化安全威脅態勢量化評估模型及其相應的計算方法。該方法在報警發生頻率、報警嚴重性及其網絡帶寬耗用率的統計基礎上,對服務、主機本身的重要性因子進行加權,計算服務、主機以及整個網絡系統的威脅指數,進而評估分析安全威脅態勢。實驗表明,該系統減輕了管理員繁重的報警數據分析任務,能夠提供服務、主機和網絡系統3個層次的直觀安全威脅態勢,使其對系統的安全威脅狀況有宏觀的了解。而且,可以從安全態勢曲線中發現安全規律,以便調整系統安全策略,更好地提高系統安全性能,為指導安全工程實踐、設計相應安全風險評估和管理工具提供了有價值的模型和算法。
網絡安全;威脅評估模型;威脅指數;入侵檢測系統;威脅態勢
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2006, 17(4): 885-897
被引頻次:418
網絡蠕蟲研究與進展
文偉平,卿斯漢,蔣建春,等
隨著網絡系統應用及復雜性的增加,網絡蠕蟲成為網絡系統安全的重要威脅。在網絡環境下,多樣化的傳播途徑和復雜的應用環境使網絡蠕蟲的發生頻率增高、潛伏性變強、覆蓋面更廣,網絡蠕蟲成為惡意代碼研究中的首要課題。首先綜合論述網絡蠕蟲的研究概況,然后剖析網絡蠕蟲的基本定義、功能結構和工作原理,討論網絡蠕蟲的掃描策略和傳播模型,歸納總結目前防范網絡蠕蟲的最新技術。最后給出網絡蠕蟲研究的若干熱點問題與展望。
網絡安全;網絡蠕蟲;功能結構;掃描策略;傳播模型
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2004, 15(8): 1208-1219
被引頻次:342
Internet測量與分析綜述
張宏莉,方濱興,胡銘曾
Internet的測量與分析為加強網絡管理、提高網絡利用率、防范大規模網絡攻擊提供了技術平臺,已成為學術界、企業界和國家政府部門所普遍關心的重要問題之一。介紹了網絡測量與分析的主要研究內容,以及國內外相關領域的研究現狀,并對該領域的關鍵技術和難點問題進行了分析,同時給出了網絡測量與分析的3個典型應用案例。
網絡測量與分析;Internet映射;網絡安全;網絡管理;TCP/IP;BGP
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2003, 14(1): 110-116
被引頻次:298
認證理論與技術的發展
李中獻,詹榜華,楊義先
身份驗證和信息認證是網絡安全技術的兩個重要方面,身份驗證機制限制非法用戶訪問網絡資源;信息認證機制則保證了信息在傳送過程中的完整性和信息來源的可靠性,在某些情況下,信息認證比信息保密更為重要。本文詳細論述了信息安全領域中身份認證和信息認證的理論和技術。主要介紹了網絡安全中的用戶身份認證和信息認證的各種實現方法、技術現狀及發展趨勢,綜合評價了某些認證機制和方案的優劣。
信息安全;身份認證;信息認證
來源出版物:電子學報, 1999, 27(1): 98-102
被引頻次:288
基于OpenFlow的SDN技術研究
左青云,陳鳴,趙廣松,等
軟件定義網絡(software-defined networking,簡稱SDN)技術分離了網絡的控制平面和數據平面,為研發網絡新應用和未來互聯網技術提供了一種新的解決方案。綜述了基于OpenFlow的SDN技術發展現狀,首先總結了邏輯控制和數據轉發分離架構的研究背景,并介紹了其關鍵組件和研究進展,包括OpenFlow交換機、控制器和SDN技術,然后從4個方面分析了基于OpenFlow的 SDN技術目前所面臨的問題和解決思路。結合近年來的發展現狀,歸納了在校園網、數據中心以及面向網絡管理和網絡安全方面的應用,最后探討了未來的研究趨勢。
OpenFlow;未來互聯網;控制器;虛擬化;軟件定義網絡
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2013, 24(5): 1078-1097
被引頻次:287
基于支持向量機的入侵檢測系統
饒鮮,董春曦,楊紹全
目前的入侵檢測系統存在著在先驗知識較少的情況下推廣能力差的問題。在入侵檢測系統中應用支持向量機算法,使得入侵檢測系統在小樣本(先驗知識少)的條件下仍然具有良好的推廣能力。首先介紹入侵檢測研究的發展概況和支持向量機的分類算法,接著提出了基于支持向量機的入侵檢測模型,然后以系統調用執行跡(system call trace)這類常用的入侵檢測數據為例,詳細討論了該模型的工作過程,最后將計算機仿真結果與其他檢測方法進行了比較。通過實驗和比較發現,基于支持向量機的入侵檢測系統不但所需要的先驗知識遠遠小于其他方法,而且當檢測性能相同時,該系統的訓練時間將會縮短。
入侵檢測;網絡安全;支持向量機;統計學習;模式識別
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2003, 14(4): 798-803
被引頻次:268
僵尸網絡研究
諸葛建偉,韓心慧,周勇林,等
僵尸網絡是一種從傳統惡意代碼形態進化而來的新型攻擊方式,為攻擊者提供了隱匿、靈活且高效的一對多命令與控制機制,可以控制大量僵尸主機實現信息竊取、分布式拒絕服務攻擊和垃圾郵件發送等攻擊目的。僵尸網絡正步入快速發展期,對因特網安全已造成嚴重威脅,對中國大陸造成的危害尤為嚴重。介紹了僵尸網絡的演化過程和基本定義,深入剖析了僵尸網絡的功能結構與工作機制,討論了僵尸網絡的命令與控制機制和傳播模型,并歸納總結了目前跟蹤、檢測和防御僵尸網絡的最新研究成果,最后探討了僵尸網絡的發展趨勢和進一步的研究方向。
網絡安全;僵尸網絡;惡意代碼;僵尸程序;傳播模型
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2008, 19(3): 702-715
被引頻次:247
無線傳感器網絡安全技術綜述
裴慶祺,沈玉龍,馬建峰,等
詳細闡述了傳感器網絡安全現狀、面臨的安全挑戰及其需要解決的安全問題。從密鑰管理、安全路由、認證、入侵檢測、DoS攻擊、訪問控制方面討論傳感器網絡的各種安全技術,并進行綜合對比。希望通過這些說明和對比,能夠幫助研究者為特定傳感器網絡應用環境選擇和設計安全解決方案。最后總結和討論傳感器網絡安全技術的研究方向。
傳感器網絡;密鑰管理;安全路由;入侵檢測;DoS攻擊
來源出版物:通信學報, 2007, 28(8): 113-122
被引頻次:1361
Wireless mesh networks: A survey
Akyildiz, IF; Wang, XD; Wang, WL
來源出版物:Computer Networks, 2007, 47(4): 445-487
被引頻次:813
SPINS: Security protocols for sensor networks
Perrig, A; Szewczyk, R; Tygar, JD; et al.
來源出版物:Wireless Networks, 2002, 8(5): 521-534
被引頻次:734
Securing ad hoc networks
Zhou, LD; Zygmunt, JH
來源出版物:IEEE Network, 1999, 13(6): 24-30
被引頻次:451
Bro: A system for detecting network intruders in real-time
Paxson, V
來源出版物:Computer Networks-The International Journal of Computer and Telecommunications Networking, 1999,31(23-24): 2435-2463
被引頻次:186
Security in mobile ad hoc networks: Challenges and solutions
Yang, H; Luo, HY; Ye, F; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Wireless Communications, 2004, 11(1): 38-47
被引頻次:176
Routing security in wireless ad hoc networks
Deng, HM; Li, W; Agrawal, DP
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Magazine, 2002,40(10): 70-75
被引頻次:175
A survey of security issues in mobile ad Hoc and sensor networks
Djenouri, Djamel; Khelladi, Lyes; Badache, Nadjib
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2005, 7(4): 2-28
被引頻次:146
A survey of security issues in wireless sensor networks
Wang, Yong; Attebury, Garhan; Ramamurthy, Byrav
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials Nuclear Technology, 2006, 8(2): 2-22
被引頻次:144
Security technology for smart grid networks
Metke, Anthony R; Ekl, Randy L
來源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2010, 1(1): 99-107
被引頻次:129
Sensor network security: A survey
Chen, Xiangqian; Makki, Kia; Yen, Kang; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2009, 11(2): 52-73
·推薦論文摘要·
基于博弈模型的網絡安全最優攻防決策方法
劉剛,張宏,李千目
為了有效地實施網絡安全風險管理,降低安全風險損失,該文基于博弈理論,通過分析攻擊者和防御者的攻防交互,設計了一種網絡安全最優攻防決策方法。該方法首先根據網絡的拓撲信息、節點的可達關系和脆弱性信息,生成網絡的狀態攻防圖,計算攻防圖中各原子攻擊成功的概率和危害指數,從而得出所有可能攻擊路徑的成功概率和危害指數,進一步計算不同網絡安全狀態下攻防雙方采取不同攻防策略的效用矩陣。根據狀態攻防圖,基于非合作非零和博弈模型,提出了一種最優攻防決策算法,結合脆弱點的防控措施,生成了最優攻防策略。通過一個典型的網絡實例分析了該方法在網絡安全風險管理中的應用。實驗結果表明:該方法能夠有效地生成最優的攻防決策方案。
網絡安全;風險管理;狀態攻防圖;博弈理論;最優決策
來源出版物:南京理工大學學報, 2014, 38(1): 12-21
基于時空維度分析的網絡安全態勢預測方法
劉玉嶺,馮登國,連一峰,等
現有網絡安全態勢預測方法無法準確反映未來安全態勢要素值變化對未來安全態勢的影響,且不能很好地處理各安全要素間的相互影響關系對未來網絡安全態勢的影響,提出了基于時空維度分析的網絡安全態勢預測方法.首先從攻擊方、防護方和網絡環境3方面提取網絡安全態勢評估要素,然后在時間維度上預測分析未來各時段內的安全態勢要素集,最后在空間維度上分析各安全態勢要素集及其相互影響關系對網絡安全態勢的影響,從而得出網絡的安全態勢。通過對公用數據集網絡的測評分析表明,該方法符合實際應用環境,且相比現有方法提高了安全態勢感知的準確性。
網絡安全;安全態勢預測;安全態勢要素;空間數據發掘;時空維度
來源出版物:計算機研究與發展, 2014, 51(8): 1681-1694
一種基于UML的網絡安全體系建模分析方法
布寧,劉玉嶺,連一峰,等
在現有法律法規和標準體系的指導下,提出了一種通用的網絡安全體系框架,闡述了安全目標、安全邊界、安全體系要素與安全服務和安全風險評估之間的關系.在網絡安全體系框架的基礎上,利用統一建模語言(Unified Modeling Language,UML)在建模表述上的強大性和通用性給出了安全目標、安全邊界和安全體系要素的建模方法,以規范化安全體系的表示形式并消除溝通中的歧義性。利用建立的模型,安全管理員使用提出的網絡安全建模分析方法,可以驗證業務流程的目標滿足性并得出可能的安全風險。最后通過一個典型網上銀行網絡的建模分析,驗證了提出的安全體系框架和建模分析方法的有效性和合理性。相比于傳統的方法,該方法建模分析要素更為全面,且推導得出的結果指導性更強。
網絡安全體系;UML建模;安全目標;安全邊界;安全措施
來源出版物:計算機研究與發展, 2014, 51(7): 1578-1593
論信息安全、網絡安全、網絡空間安全
王世偉
本文論述“信息安全”概念的出現和發展,依據近年來全球信息安全領域的文獻資料,并結合與之相關的實踐活動,闡述“信息安全”“網絡安全”“網絡空間安全”三者的聯系與區別。信息安全可泛稱各類信息安全問題,網絡安全指稱網絡所帶來的各類安全問題,網絡空間安全則特指與陸域、海域、空域、太空并列的全球五大空間中的網絡空間安全問題。三者均類屬于非傳統安全領域,都聚焦于信息安全,可以相互使用,但各有側重;三者的概念不同,提出的背景不同,所涉及的內涵與外延不同。厘清三者的關系,有助于在信息安全研究與實踐的邏輯起點上形成清晰的認知,在信息安全的基礎理論研究中形成業界內外公認的學術規范。
信息安全;網絡安全;網絡空間安全;信息安全政策;網絡安全戰略
來源出版物:中國圖書館學報, 2015, 41(216): 72-84
網絡安全分析中的大數據技術應用
王帥,汪來富,金華敏
隨著網絡安全信息規模的增長,應用大數據技術進行網絡安全分析成為業界研究熱點。從網絡安全分析的需求及傳統技術的不足出發,分析了引入大數據分析的必要性,從安全數據存儲、檢索、分析等層面探討了大數據技術在網絡安全分析中的應用,在此基礎上提出一個基于大數據的網絡安全分析平臺。并對典型攻擊場景的關聯分析方法進行了詳細闡述。
大數據;安全分析;攻擊檢測
來源出版物:電信科學, 2015, 7: 1-6
一種改進的網絡安全態勢量化評估方法
席榮榮,云曉春,張永錚
在基于隱馬爾可夫模型的網絡安全態勢評估中,觀測序列的獲取和狀態轉移矩陣的確立是影響評估準確性的關鍵。目前觀測序列多以隨機方式獲取,不能有效表征網絡的安全性;而狀態轉移矩陣往往依據經驗給出,具有很強的主觀性。該文提出改進方法:首先,基于警報的統計特性提出警報質量的概念,依據警報質量獲取的觀測序列,可改進數據源的有效性;其次,基于安全事件和防護措施的博弈過程,提出確定狀態轉移矩陣的方法,并結合攻擊成功的概率對其進行修正,提高狀態轉移矩陣的有效性.對比實驗證明,基于改進算法生成的風險值對網絡安全態勢的量化更加合理。
觀測序列;狀態轉移矩陣;警報質量;博弈矩陣;攻擊成功的概率
來源出版物:計算機學報, 2015, 38(4): 749-758
網絡空間安全綜述
張煥國,韓文報,來學嘉,等
隨著信息技術的發展與廣泛應用,人類社會進入信息化時代。在信息時代,人們生活和工作在網絡空間中。網絡空間是所有信息系統的集合,是人類生存的信息環境。因此,必須確保網絡空間的安全。本文綜合介紹網絡空間的概念、網絡空間安全學科、密碼學、網絡安全、信息系統安全和信息內容安全領域的研究發展、存在的問題和一些研究熱點。
網絡空間安全;信息安全;密碼學;網絡安全;信息系統安全;信息內容安全
來源出版物:中國科學:信息科學, 2016, 46(2): 125-164
網絡信息安全:一局持續變化的恒久棋局
潘柱廷
網絡信息安全是一個持續變化的博弈棋局。本文從南向(技術領域)和北向(觀念和管理)兩個方面,探究這個棋局的本質性結構。仿照醫學的分科模式,將網絡安全領域分解成多個子領域,并探究各子領域的內在規律和關鍵人群。
網絡空間安全;信息安全;黑客
來源出版物:科技導報, 2016, 34(14): 107-112
網絡安全態勢認知融合感控模型
劉效武,王慧強,呂宏武,等
為了分析網絡威脅的演化趨勢,并探討安全態勢的自主感知和調控問題,將跨層結構和認知環融入模型的設計,提出一種基于融合的網絡安全態勢認知感控模型,增強網絡安全系統的層間交互和認知能力。在分析模型組件及其功能的基礎上,利用多源融合算法得到各異質傳感器對網絡安全事件的準確決策,結合對安全事件威脅等級和威脅因子關系的推演,克服威脅因子獲取過程中需處理網絡組件間復雜隸屬關系的不足,從而提出包含服務級、主機級和網絡級的層次化態勢感知方法,提高對網絡威脅的表達能力。而且通過對態勢感知曲線的分析,搭建離散計算和連續控制之間的橋梁,形成閉環反饋控制結構,解決安全態勢自感知和自調控的問題。仿真實驗結果表明:基于融合的網絡安全態勢認知感控模型及方法能夠融合異質安全數據,動態感知威脅的演化趨勢,并具有一定的自主調控能力,達到了認知感控的研究目的,為監控和管理網絡提供了新的方法和手段。
網絡安全態勢感知;認知計算;多源融合;量化感知;認知調控
來源出版物:軟件學報, 2016, 27(8): 2099-2114
Principles of physical layer security in multiuser wireless networks: A survey
Mukherjee, Amitav; Fakoorian, S. Ali A;Huang, Jing; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2014, 16(3): 1550-1573
Understanding security failures of two-factor authentication schemes for real-time applications in hierarchical wireless sensor networks
Wang, Ding; Wang, Ping
來源出版物:AD HOC Networks, 2014, 20: 1-15
Security in wireless ad-hoc networks: A survey
Di Pietro, R; Guarino, S; Verde, N. V; et al.
來源出版物:Computer Communications, 2014, 51:1-20
A Survey on security aspects for LTE and LTE-A networks
Cao, Jin; Ma, Maode; Li, Hui; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials,2014, 16(1): 283-302
Integrated security analysis on cascading failure in complex networks
Yan, Jun; He, Haibo; Sun, Yan
來源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security
A mean field game theoretic approach for security enhancements in mobile ad hoc networks
Wang, Yanwei; Yu, F. Richard; Tang, Helen; et al.
來源出版物: IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(3): 1616-1627
Security and privacy in mobile social networks: Challenges and solutions
Liang, Xiaohui; Zhang, Kuan; Shen, Xuemin; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Wireless Communications, 2014, 21(1): 33-41
k-Zero day safety: A network security metric for measuring the risk of unknown vulnerabilities
Wang, Lingyu; Jajodia, Sushil; Singhal, Anoop; et al.
來源出版物: IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2014, 11(1): 30-44
Safeguarding 5G wireless communication networks using physical layer security
Yang, Nan; Wang, Lifeng; Geraci, Giovanni; et al.
來源出版物: IEEE Communications Magazine, 2015,53(4): 20-27
Relay selection for security enhancement in cognitive relay networks
Liu, Yuanwei; Wang, Lifeng; Tran Trung Duy; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Wireless Communications Letters,2015, 4(1): 46-49
On the security of cognitive radio networks
Elkashlan, Maged; Wang, Lifeng; Duong, Trung Q; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2015, 64(8): 3790-3795
Physical layer network security in the full-duplex relay system
Chen, Gaojie; Gong, Yu; Xiao, Pei; et al.
來源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(3): 6443-6462
Security and trust management in opportunistic networks: A survey
Wu, Yue; Zhao, Yimeng; Riguidel, Michel; et al.
來源出版物:Security and Communication Networks, 2015,8(9): 1812-1827
Security of software defined networks: A survey
Alsmadr, Izzat; Xu, Dianxiang
來源出版物:Computers & Security, 2015, 53: 79-108
Optimizing resource and data security in shared sensor networks
Huygens, Christophe; Matthys, Nelson;Joosen, Wouter; et al.
來源出版物:Security and Communication Networks, 2016,9(2): 149-165
來源出版物:Information Sciences, 2016, 327: 288-299
編輯:衛夏雯
Wireless sensor networks will be widely deployed in the near future. While much research has focused on making these networks feasible and useful,security has
little attention. We present a suite of security protocols optimized for sensor networks: SPINS. SPINS has two secure building blocks: SNEP and muTESLA. SNEP includes: Data confidentiality, two-party data authentication, and evidence of data freshness. muTESLA provides authenticated broadcast for severely resource-constrained environments. We implemented the above protocols, and show that they are practical even on minimal hardware: the performance of the protocol suite easily matches the data rate of our network. Additionally,we demonstrate that the suite can be used for building higher level protocols.
secure communication protocols; sensor networks; mobile ad hoc networks; MANET; authentication of wireless communication; secrecy and confidentiality;cryptography
Wireless sensor network applications include ocean and wildlife monitoring, manufacturing machinery performance monitoring, building safety and earthquake monitoring, and many military applications. A major benefit of these systems is that they perform in-network processing to reduce large streams of raw data into useful aggregated information. Protecting it all is critical. Because sensor networks pose unique challenges, traditional security techniques used in traditional networks cannot be applied directly. To make sensor networks economically viable, sensor devices are limited in their energy,computation, and communication capabilities research. People cover several important security challenges,including key establishment, secrecy, authentication,privacy, robustness to denial-of-service attacks, secure routing, and node capture. Security is sometimes viewed as a standalone component of a system's architecture, where a separate module provides security. To achieve a secure system, security must be integrated into every component,since components designed without security can become a point of attack.
Security in mobile ad hoc networks is difficult to achieve, notably because of the vulnerability of wireless links, the limited physical protection of nodes, the dynamically changing topology, the absence of a certification authority, and the lack of a centralized monitoring or management point. Earlier studies on mobilead hoc networks(MANETs) aimed at proposing protocols for some fundamental problems, such as routing, and tried to cope with the challenges imposed by the new environment. These protocols, however, fully trust all nodes and do not consider the security aspect. They are consequently vulnerable to attacks and misbehavior. More recent studies focused on security problems in MANETs,and proposed mechanisms to secure protocols and applications. This article surveys these studies. It presents and discusses several security problems along with the currently proposed solutions(as of July 2005) at different network layers of MANETs. Security issues involved in this article include routing and data forwarding, medium access, key management and intrusion detection systems(IDSs). This survey also includes an overview of security in a particular type of MANET, namely, wireless sensor networks(WSNs).
Wireless sensor networks(WSNs) use small nodes with constrained capabilities to sense, collect, and disseminate information in many types of applications. As sensor networks become wide-spread, security issues become a central concern, especially in mission-critical tasks. In this paper, we identify the threats and vulnerabilities to WSNs and summarize the defense methods based on the networking protocol layer analysis first. Then we give a holistic overview of security issues. These issues are divided into seven categories: cryptography, key management, attack detections and preventions, secure routing, secure location security, secure data fusion, and other security issues. Along the way we analyze the advantages and disadvantages of current secure schemes in each category. In addition, we also summarize the techniques and methods used in these categories, and point out the open research issues and directions in each area.
sensor networks; security; ad hoc networks;survey; key management; attack detections and preventions;secure routing; secure location; secure data aggregation;node compromise
This paper establishes the utility of user cooperation in facilitating secure wireless communications. In particular, the four-terminal relay-eavesdropper channel is introduced and an outer-bound on the optimal rate-equivocation region is derived. Several cooperation strategies are then devised and the corresponding achievable rate-equivocation region are characterized. Of particular interest is the novel noise-forwarding(NF)strategy, where the relay node sends codewords independent of the source message to confuse the eavesdropper. This strategy is used to illustrate the deaf helper phenomenon, where the relay is able to facilitate secure communications while being totally ignorant of the transmitted messages. Furthermore, NF is shown to increase the secrecy capacity in the reversely degraded scenario, where the relay node fails to offer performance gains in the classical setting. The gain offered by the proposed cooperation strategies is then proved theoretically and validated numerically in the additive white Gaussian noise(AWGN) channel.
cooperation; eavesdropper; noise-forwarding(NF); relay; security
Wireless mesh networks(WMNs) consist of mesh routers and mesh clients, where mesh routers have minimal mobility and form the backbone of WMNs. They provide network access for both mesh and conventional clients. The integration of WMNs with other networks such as the Internet, cellular, IEEE 802.11, IEEE 802.15,IEEE 802.16, sensor networks, etc., can be accomplished through the gateway and bridging functions in the mesh routers. Mesh clients can be either stationary or mobile,and can form a client mesh network among themselves and with mesh routers. WMNs are anticipated to resolve the limitations and to significantly improve the performance of ad hoc networks, wireless local area networks(WLANs), wireless personal area networks(WPANs), and wireless metropolitan area networks(WMANs). They are undergoing rapid progress and inspiring numerous deployments. WMNs will deliver wireless services for a large variety of applications in personal, local, campus, and metropolitan areas. Despite recent advances in wireless mesh networking, many research challenges remain in all protocol layers. This paper presents a detailed study on recent advances and open research issues in WMNs. System architectures and applications of WMNs are described, followed by discussing the critical factors influencing protocol design. Theoretical network capacity and the state-of-the-art protocols for WMNs are explored with an objective to point out a number of open research issues. Finally, testbeds, industrial practice, and current standard activities related to WMNs are highlighted.
wireless mesh networks; ad hoc networks;wireless sensor networks; medium access control; routing protocol; transport protocol; scalability; security; power management and control; timing synchronization
Wireless sensor networks will be widely deployed in the near future. While much research has focused on making these networks feasible and useful,security has
little attention. We present a suite of security protocols optimized for sensor networks: SPINS. SPINS has two secure building blocks: SNEP and muTESLA. SNEP includes: Data confidentiality, twoparty data authentication, and evidence of data freshness. muTESLA provides authenticated broadcast for severely resource-constrained environments. We implemented the above protocols, and show that they are practical even on minimal hardware: The performance of the protocol suite easily matches the data rate of our network. Additionally,we demonstrate that the suite can be used for building higher level protocols.
secure communication protocols; sensor networks; mobile ad hoc networks; MANET; authentication of wireless communication; secrecy and confidentiality;cryptography
Ad hoc networks are a new wireless networking paradigm for mobile hosts. Unlike traditional mobile wireless networks, ad hoc networks do not rely on any fixed infrastructure. Instead, hosts rely on each other to keep the network connected. Military tactical and other security-sensitive operations are still the main applications of ad hoc networks, although there is a trend to adopt ad hoc networks for commercial uses due to their unique properties. One main challenge in the design of these networks is their vulnerability to security attacks. In this article, we study the threats an ad hoc network faces and the security goals to be achieved. We identify the new challenges and opportunities posed by this new networking environment and explore new approaches to secure its communication. In particular; we take advantage of the inherent redundancy in ad hoc networks-multiple routes between nodes-to defend routing against denial-of-service attacks. We also use replication and new cryptographic schemes, such as threshold cryptography, to build a highly secure and highly available key management service,which forms the core of our security framework.
We describe Bro, a stand-alone system fordetecting network intruders in real-time by passively monitoring a network link over which the intruder’s traffic transits. We give an overview of the system’s design, which emphasizes high-speed(FDDI-rate) monitoring, real-time notification, clear separation between mechanism and policy, and extensibility. To achieve these ends, Bro is divided into an ‘event engine’ that: reduces a kernelfiltered network traffic stream into a series of higher-level events, and a ‘policy script interpreter’ that interprets event handlers written in a specialized language used to express a site's security policy. Event handlers can update state information, synthesize new events, record information to disk, and generate real-time notifications via syslog. We also discuss a number of attacks that attempt to subvert passive monitoring systems and defenses against these, and give particulars of how Bro analyzes the six applications integrated into it so far: Finger, FTP, Portmapper, Ident,Telnet and Rlogin. The system is publicly available in source code form.
network intrusion detection; passive network monitoring; network monitoring evasion; domain-specific languages
Security has become a primary concern in order to provide protected communication between mobile nodes in a hostile environment. Unlike the wireline networks, the unique characteristics of mobile ad hoc networks pose a number of nontrivial challenges to security design, such as open peer-to-peer network architecture, shared wireless medium, stringent resource constraints, and highly dynamic network topology. These challenges clearly make a case for building multifence security solutions that achieve both broad protection and desirable network performance. In this article we focus on the fundamental security problem of protecting the multihop network connectivity between mobile nodes in a MANET. We identify the security issues related to this problem, discuss the challenges to security design, and review the state-of-the-art security proposals that protect the MANET link- and network-layer operations of delivering packets over the multihop wireless channel. The complete security solution should span both layers, and encompass all three security components of prevention, detection, and reaction.
A mobile ad hoc network consists of a collection of wireless mobile nodes that are capable of communicating with each other without the use of a network infrastructure or any centralized administration. MANET is an emerging research area with practical applications. However, wireless MANET is particularly vulnerable due to its fundamental characteristics, such as open medium, dynamic topology, distributed cooperation,and constrained capability. Routing plays an important role in the security of the entire network. In general, routing security in wireless MANETs appears to be a problem that is not trivial to solve. In this article we study the routing security issues of MANETs, and analyze in detail one type of attack - the “black hole” problem - that can easily be employed against the MANETs. We also propose a solution for the,black hole problem for ad hoc on-demand distance vector routing protocol.
Security in mobile ad hoc networks is difficult to achieve, notably because of the vulnerability of wireless links, the limited physical protection of nodes,the dynamically changing topology, the absence of a certification authority, and the lack of a centralized monitoring or management point. Earlier studies on mobile ad hoc networks(MANETs) aimed at proposing protocols for some fundamental problems, such as routing,and tried to cope with the challenges imposed by the new environment. These protocols, however, fully trust all nodes and do not consider the security aspect. They are consequently vulnerable to attacks and misbehavior. More recent studies focused on security problems in MANETs,and proposed mechanisms to secure protocols andapplications. This article surveys these studies. It presents and discusses several security problems along with the currently proposed solutions(as of July 2005) at different network layers of MANETs. Security issues involved in this article include routing and data forwarding, medium access, key management and intrusion detection systems(IDSs). This survey also includes an overview of security in a particular type of MANET, namely, wireless sensor networks(WSNs).
Wireless Sensor Networks(WSNs) are used in many applications in military, ecological, and healthrelated areas. These applications often include the monitoring of sensitive information such as enemy movement on the battlefield or the location of personnel in a building. Security is therefore important in WSNs. However, WSNs suffer from many constraints, including low computation capability, small memory, limited energy resources, susceptibility to physical capture, and the use of insecurewireless communicationchannels.These constraints make security in WSNs a challenge. In this article we present a survey of security issues in WSNs. First we outline the constraints, security requirements, and attacks with their corresponding countermeasures in WSNs. We then present a holistic view of security issues. These issues are classified into five categories: cryptography, key management, secure routing, secure data aggregation, and intrusion detection. Along the way we highlight the advantages and disadvantages of various WSN security protocols and further compare and evaluate these protocols based on each of these five categories. We also point out the open research issues in each subarea and conclude with possible future research directions on security in WSNs.
There is virtually universal agreement that it is necessary to upgrade the electric grid to increase overall system efficiency and reliability. Much of the technology currently in use by the grid is outdated and in many cases unreliable. There have been three major blackouts in the past ten years. The reliance on old technology leads to inefficient systems, costing unnecessary money to the utilities, consumers, and taxpayers. To upgrade the grid,and to operate an improved grid, will require significant dependence on distributed intelligence and broadband communicationcapabilities.Theaccessand communications capabilities require the latest in proven security technology for extremely large, wide-area communications networks. This paper discusses key security technologies for a smart grid system, including public key infrastructures and trusted computing.
attestation; public key infrastructure(PKI);supervisory control and data acquisition(SCADA); security;smart grid; trusted computing
Wireless sensor networks(WSNs) use small nodes with constrained capabilities to sense, collect, and disseminate information in many types of applications. As sensor networks become wide-spread, security issues become a central concern, especially in mission-critical tasks. In this paper, we identify the threats and vulnerabilities to WSNs and summarize the defense methods based on the networking protocol layer analysis first. Then we give a holistic overview of security issues. These issues are divided into seven categories: cryptography, key management, attack detections and preventions, secure routing, secure location security,secure data fusion, and other security issues. Along the way we analyze the advantages and disadvantages of current secure schemes in each category. In addition, we also summarize the techniques and methods used in these categories, and point out the open research issues and directions in each area.
sensor networks; security; ad hoc networks;survey; key management; attack detections and preventions;secure routing; secure location; secure data aggregation;node compromise
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the domain of physical layer security in multiuser wireless networks. The essential premise of physical layer security is to enable the exchange of confidential messages over a wireless medium in the presence of unauthorized eavesdroppers, without relying on higher-layer encryption. This can be achieved primarily in two ways: without the need for a secret key by intelligently designing transmit coding strategies, or by exploiting the wirelesscommunication medium to develop secret keys over public channels. The survey begins with an overview of the foundations dating back to the pioneering work of Shannon and Wyner on information-theoretic security. We then describe the evolution of secure transmission strategies from point-to-point channels to multiple-antenna systems,followed by generalizations to multiuser broadcast, multipleaccess, interference, and relay networks. Secret-key generation and establishment protocols based on physical layer mechanisms are subsequently covered. Approaches for secrecy based on channel coding design are then examined, along with a description of inter-disciplinary approaches based on game theory and stochastic geometry. The associated problem of physical layer message authentication is also briefly introduced. The survey concludes with observations on potential research directions in this area.
physical layer security; information-theoretic security; wiretap channel; secrecy; artificial noise;cooperative jamming; secret-key agreement
Understanding security failures of cryptographic protocols is the key to both patching existing protocols and designing future schemes. In this work, we investigate two recent proposals in the area of smart-card-based password authentication for security-critical real-time data access applications in hierarchical wireless sensor networks(HWSN). Firstly, we analyze an efficient and DoS-resistant user authentication scheme introduced by Fan et al. in 2011. This protocol is the first attempt to address the problems of user authentication in HWSN and only involves lightweight cryptographic primitives, such as one-way hash function and XOR operations, and thus it is claimed to be suitable for the resource-constrained HWSN environments. However, it actually has several security loopholes being overlooked, and we show it is vulnerable to user anonymity violation attack, smart card security breach attack, sensor node capture attack and privileged insider attack, as well as its other practical pitfalls. Then, A.K. Das et al.’s protocol is scrutinized, and we point out that it cannot achieve the claimed security goals:(1) It is prone to smart card security breach attack;(2) it fails to withstand privileged insider attack; and(3) it suffers from the defect of server master key disclosure. Our cryptanalysis results discourage any practical use of these two schemes and reveal some subtleties and challenges in designing this type of schemes. Furthermore, using the above two foremost schemes as case studies, we take a first step towards investigating the underlying rationale of the identified security failures,putting forward three basic principles which we believe will be valuable to protocol designers for advancing more robust two-factor authentication schemes for HWSN in the future.
password authentication; hierarchical wireless sensor networks; user anonymity; smart card; non-tamper resistant
Pervasive mobile and low-end wireless technologies, such as radio-frequency identification(RFID), wireless sensor networks and the impending vehicular ad-hoc networks(VANETs), make the wireless scenario exciting and in full transformation. For all the above(and similar) technologies to fully unleash their potential in the industry and society, there are two pillars that cannot be overlooked: security and privacy. Both properties are especially relevant if we focus on ad-hoc wireless networks, where devices are required to cooperate -e.g. from routing to the application layer-to attain their goals. In this paper, we survey emerging and established wireless ad-hoc technologies and we highlight their security/privacy features and deficiencies. We also identify open research issues and technology challenges for each surveyed technology.
wireless networks; ad-hoc networks; security;privacy; survey
High demands for broadband mobile wireless communications and the emergence of new wireless multimedia applications constitute the motivation to the development of broadband wireless access technologies in recent years. The Long Term Evolution/System ArchitectureEvolution(LTE/SAE) system has been specified by the Third Generation Partnership Project(3GPP) on the way towards fourth-generation(4G) mobile to ensure 3GPP keeping the dominance of the cellular communication technologies. Through the design and optimization of new radio access techniques and a further evolution of the LTE systems, the 3GPP is developing the future LTE-Advanced(LTE-A) wireless networks as the 4G standard of the 3GPP. Since the 3GPP LTE and LTE-A architecture are designed to support flat Internet Protocol(IP) connectivity and full interworking with heterogeneous wireless access networks,the new unique features bring some new challenges in the design of the security mechanisms. This paper makes a number of contributions to the security aspects of the LTE and LTE-A networks. First, we present an overview of the security functionality of the LTE and LTE-A networks. Second, the security vulnerabilities existing in the architecture and the design of the LTE and LTE-A networks are explored. Third, the existing solutions to these problems are classically reviewed. Finally, we show the potential research issues for the future research works.
LTE security; LTE; LTE-A; IMS security;HeNB security; MTC security
The security issue of complex networks has drawn significant concerns recently. While pure topological analyzes from a network security perspective provide some effective techniques, their inability to characterize the physical principles requires a more comprehensive model to approximate failure behavior of a complex network in reality. In this paper, based on an extended topological metric, we proposed an approach to examine the vulnerability of a specific type of complex network, i.e.,the power system, against cascading failure threats. The proposed approach adopts a model called extended betweenness that combines network structure with electrical characteristics to define the load of power grid components. By using this power transfer distribution factor-based model, we simulated attacks on different components(buses and branches) in the grid and evaluated the vulnerability of the system components with an extended topological cascading failure simulator. Influence of different loading and overloading situations on cascading failures was also evaluated by testing different tolerance factors. Simulation results from a standard IEEE 118-bus test system revealed the vulnerability of network components, which was then validated on a dc power flow simulator with comparisons to other topological measurements. Finally, potential extensions of the approach were also discussed to exhibit both utility and challenge in more complex scenarios and applications.
complex network security; cascading failure;structural vulnerability; extended topological analysis
Game theory can provide a useful tool to study the security problem in mobile ad hoc networks(MANETs). Most of existing works on applying game theories to security only consider two players in the security game model: an attacker and a defender. While this assumption may be valid for a network with centralized administration,it is not realistic in MANETs, where centralized administration is not available. In this paper, using recent advances in mean field game theory, we propose a novel game theoretic approach with multiple players for security in MANETs. The mean field game theory provides a powerful mathematical tool for problems with a large number of players. The proposed scheme can enable an individual node in MANETs to make strategic security defence decisions without centralized administration. In addition, since security defence mechanisms consume precious system resources(e. g., energy), the proposed scheme considers not only the security requirement of MANETs but also the system resources. Moreover, each node in the proposed scheme only needs to know its own state information and the aggregate effect of the other nodes in the MANET. Therefore, the proposed scheme is a fully distributed scheme. Simulation results are presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
mean field game; security; mobile ad hoc network(MANET)
Mobile social networking is a pervasive communication platform where users with smartphones can search over the Internet and query neighboring peers to obtain the desired information. In this article, we examine the architecture, communication patterns, and especially the security and privacy of MSN. We first study three categories of mobile applications with a focus on two autonomous mobile applications, business card and service review. We then explore the possible methods to deal with the associated security and privacy challenges. By discussing the shortages of the methods, we finally provide several promising research directions.
By enabling a direct comparison of different security solutions with respect to their relative effectiveness,a network security metric may provide quantifiable evidences to assist security practitioners in securing computer networks. However, research on security metrics has been hindered by difficulties in handling zero-day attacks exploiting unknown vulnerabilities. In fact, the security risk of unknown vulnerabilities has been considered as something unmeasurable due to the less predictable nature of software flaws. This causes a major difficulty to security metrics, because a more secure configuration would be of little value if it were equally susceptible to zero-day attacks. In this paper, we propose a novel security metric, k-zero day safety, to address this issue. Instead of attempting to rank unknown vulnerabilities,our metric counts how many such vulnerabilities would be required for compromising network assets; a larger count implies more security because the likelihood of having more unknown vulnerabilities available, applicable, and exploitable all at the same time will be significantly lower. We formally define the metric, analyze the complexity of computing the metric, devise heuristic algorithms for intractable cases, and finally demonstrate through case studies that applying the metric to existing network security practices may generate actionable knowledge.
security metrics; network security; attack graph; network hardening
The fifth generation(5G) network will serve as a key enabler in meeting the continuously increasing demands for future wireless applications, including an ultra-high data rate, an ultrawide radio coverage, an ultralarge number of devices, and an ultra-low latency. This article examines security, a pivotal issue in the 5G network where wireless transmissions are inherently vulnerable to security breaches. Specifically, we focus on physical layer security, which safeguards data confidentiality by exploiting the intrinsic randomness of the communications medium and reaping the benefits offered by the disruptive technologies to 5G. Among various technologies, the three most promising ones are discussed: heterogenous networks,massive multiple-input multiple-output, and millimeter wave. On the basis of the key principles of each technology,we identify the rich opportunities and the outstanding challenges that security designers must tackle. Such an identification is expected to decisively advance the understanding of future physical layer security.
This letter proposes several relay selection policies for secure communication in cognitive decodeand-forward relay networks, where a pair of cognitive relays is opportunistically selected for security protection against eavesdropping. The first relay transmits the secrecy information to the destination, and the second relay, as a friendly jammer, transmits the jamming signal to confound the eavesdropper. We present new exact closed-form expressions for the secrecy outage probability. Our analysis and simulation results strongly support our conclusion that the proposed relay selection policies can enhance the performance of secure cognitive radio. We also confirm that the error floor phenomenon is created in the absence of jamming.
cognitive radio; cooperative networks;physical layer security
Cognitive radio has emerged as an essential recipe for future high-capacity, high-coverage multitier hierarchical networks. Securing data transmission in these networks is of the utmost importance. In this paper, we consider the cognitive wiretap channel and propose multiple antennas to secure the transmission at the physical layer, where the eavesdropper overhears the transmission from the secondary transmitter to the secondary receiver. The secondary receiver and the eavesdropper are equipped with multiple antennas, and passive eavesdropping is considered where the channel state information(CSI) of the eavesdropper's channel is not available at the secondary transmitter. We present new closed-form expressions for the exact and asymptotic secrecy outage probability. Our results reveal the impact of the primary network on the secondary network in the presence of a multiantenna wiretap channel.
cognitive radio; multiple antennas; physicallayer security; wiretap channel
This paper investigates the secrecy performance of full-duplex relay(FDR) networks. The resulting analysis shows that FDR networks have better secrecy performance than half duplex relay networks, if the self-interference can be well suppressed. We also propose a full duplex jamming relay network, in which the relay node transmits jamming signals while receiving the data from the source. While the full duplex jamming scheme has the same data rate as the half duplex scheme, the secrecy performance can be significantly improved, making it an attractive scheme when the network secrecy is a primary concern. A mathematic model is developed to analyze secrecy outage probabilities for the half duplex, the full duplex and full duplex jamming schemes, and the simulation results are also presented to verify the analysis.
physical layer secrecy; cooperative relay networks; full duplex relay; secrecy outage probability
As a new networking paradigm, opportunistic networking communications have great vision in animal migration tracking, mobile social networking, network communicationsinremoteareasandintelligent transportation, and so on. Opportunistic networks are one of the evolutionary mobile ad hoc networks, whose communication links often suffer from frequent disruption and long communication delays. Therefore, many opportunistic forwarding protocols present major security issues, and the design of opportunistic networks faces serious challenges such as how to effectively protect data confidentiality and integrity and how to ensure routing security, privacy, cooperation, and trust management. In this paper, we first systematically describe the security threats and requirements in opportunistic networks; then propose a general security architecture of opportunistic networks; and then make an in-depth analysis on authentication and access control, secure routing, privacy protection, trust management, and incentive cooperation mechanisms; and at the same time, we present a comparison of various security and trust solutions for opportunistic networks. Finally, we conclude and give future research directions.
opportunistic networks; security; authentication;privacy; trust management; incentive mechanism
Software Defined Networking(SDN) has emerged as a new network architecture for dealing with network dynamics through software-enabled control. While SDN is promoting many new network applications,security has become an important concern. This paper provides an extensive survey on SDN security. We discuss the security threats to SDN according to their effects, i.e.,Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information disclosure,Denial of Service, and Elevation of Privilege. We also review a wide range of SDN security controls, such asfirewalls, IDS/IPS, access control, auditing, and policy management. We describe several pathways of how SDN is evolving.
software defined networking; security; software defined security; networking; network security
A growing number of deployments of wireless sensor networks(WSNs) position the nodes as multipurpose albeit limited platforms. These platforms offer services to a set of applications of different owners. This view introduces security problems complementary to protection against outsiders requiring mechanisms beyond the existing physical, base crypto and network-level protection. Limited trust in the different applications mandates a security solution providing granular control over resources and data. Because of the constrained nature of network-embedded systems, transferring solutions from the distributed systems domain to the embedded system requires optimization. Distributed monitors can provide adequate security but must be concise and controllable by lightweight run-time artifacts as well as be deployed only where needed. Presented research consists of an operational model that inserts controls by instrumentation of local or remote interaction in the resource-rich back end,subsequently enforcing control at the nodes by using scaled down policy engines. The selective injection is achieved through aspect-oriented techniques. The solution is demonstrated for two paradigms encountered when building WSN applications, thus achieving local resource protection and protection of distributed event-based data flow. The costs and benefits of the selective injection approach are validated and quantified through a river monitoring case and associated simulation experiments.
sensor network; security; monitor; policy;aspect oriented
Leveraging software-defined networking for security policy enforcement
Liu, Jiaqiang; Li, Yong; Wang, Huandong; et al.
Network operators employ a variety of security policies for protecting the data and services. However,deploying these policies in traditional network is complicated and security vulnerable due to the distributed network control and lack of standard control protocol. Software-defined network provides an ideal paradigm to address these challenges by separating control plane and data plane, and exploiting the logically centralized control. In this paper, we focus on taking the advantage of softwaredefined networking for security policies enforcement. We propose a two layer OpenFlow switch topology designed to implement security policies, which considers the limitation of flow table size in a single switch, the complexity of configuring security policies to these switches, and load balance among these switches. Furthermore, we introduce a safe way to update the configuration of these switches one by one for better load balance when traffic distribution changes. Specifically, we model the update process as a path in a graph, in which each node represents a security policy satisfied configuration, and each edge represents a single step of safely update. Based on this model, we design a heuristic algorithm to find an optimal update path in real time. Simulations of the update scheme show that our proposed algorithm is effective and robust under an extensive range of conditions.
software defined network; security; network update
本領域經典文章題目第一作者來源出版物1SPINS: Security protocols for sensor networksPerrig AWireless Networks, 2002, 8(5): 521-534 2 Security in wireless sensor networks Perrig A Communications of the ACM, 2004, 47(6): 53-57 3 A survey of security issues in mobile ad Hoc and sensor Djenouri,IEEE Communications Surveys and networks Djamel Tutorials, 2005, 7(4): 2-28 4 Sensor network security: A survey Chen, Xiangqian IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2009, 11(2): 52-73 5 The relay-eavesdropper channel: Cooperation for secrecy Lai, Lifeng IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,2008, 54(9): 4005-4019

