阻塞性睡眠呼吸暫停低通氣綜合征與勃起功能障礙的相關(guān)性研究
胡海翔 孫梯業(yè) 方紅 顏偉 徐少強(qiáng) 劉紅明 沈傳運(yùn) 孫哲 張啟龍 韋仕福
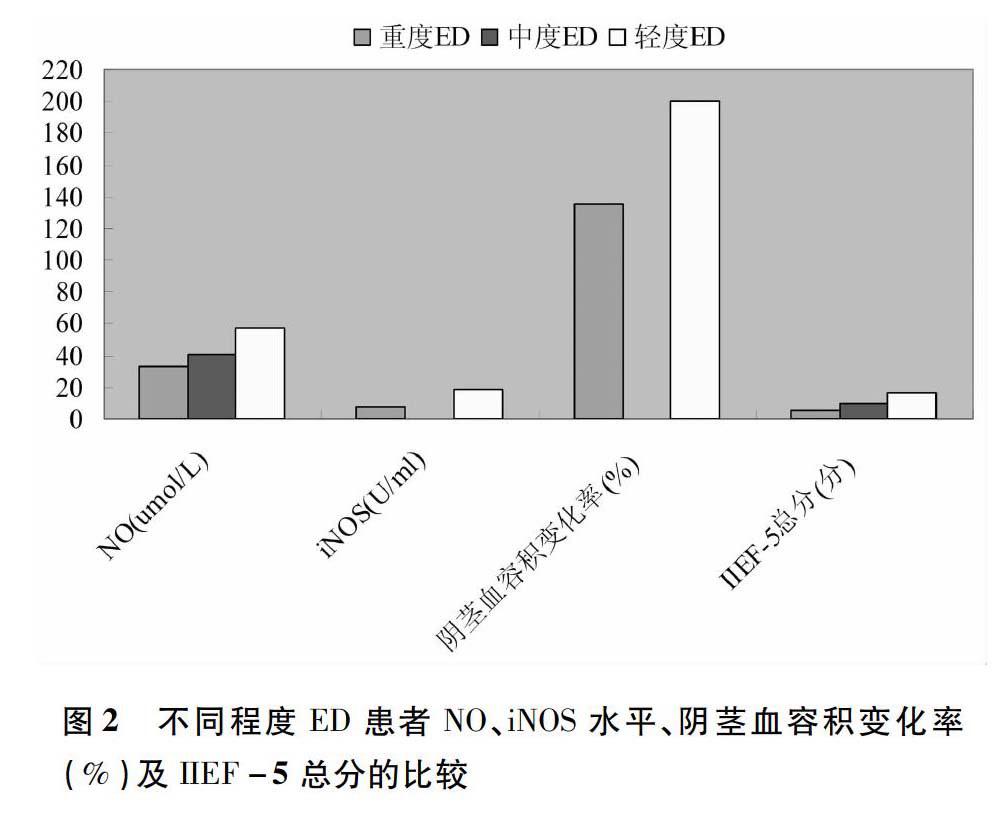


【摘要】目的:探討阻塞性睡眠呼吸暫停低通氣綜合征(OSAHS)患者與勃起功能障礙(ED)之間的相關(guān)性。方法:OSAHS患者60例,納入觀察組;門診體檢健康志愿者60例,納入對照組,采用PSG睡眠監(jiān)測儀和NPT同步監(jiān)測兩組患者睡眠狀態(tài)及陰莖勃起情況,包括呼吸暫停低通氣指數(shù)(AHI)、最低動(dòng)脈血氧飽和度(minSaO2)和陰莖血容積變化率(%)。硝酸還原酶法、比色法分別檢測NO、iNOS濃度,ECLIA法檢測血清睪酮(T)、游離睪酮(FT)、卵泡刺激素(FSH)、黃體生成激素(LH)、催乳素(PRL)水平,國際勃起功能指數(shù)評(píng)分5項(xiàng)(IIEF-5)評(píng)估男性O(shè)SAHS患者ED的發(fā)病率,并對數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行相關(guān)分析。結(jié)果:OSAHS組T(2.10±2.42)、FT(9.76±2.33)、NO(72.51±11.74)、iNOS(25.32±11.57)、minSaO2(71.23±5.71)、陰莖血容積變化率(158.36±32.87),與對照組相比,差異有非常顯著的統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.01),OSAHS組AHI(45.75±11.92)顯著高于對照組(P<0.05)。OSAHS患者ED的發(fā)生率顯著高于對照組(P<0.01),重度ED患者NO(32.57±6.33)、iNOS(8.06±1.01)、陰莖血容積變化率(135.56±16.92)及IIEF-5總分(5.3±2.3)明顯低于輕中度ED患者(P<0.01)。結(jié)論:OSAHS與ED有明顯的相關(guān)性,NO升高、低氧血癥、T降低可能是OSAHS患者導(dǎo)致ED的機(jī)制。
【關(guān)鍵詞】阻塞性睡眠呼吸暫停低通氣綜合征;勃起功能障礙;相關(guān)性;研究
Correlation between obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome and erectile dysfunctionHU Haixiang1, SUN Tiye1, FANG Hong2, YAN Wei3, XU Shaoqiang1, LIU Hongming1, SHEN Chuanyun1, SUN Zhe1, ZHANG Qilong1, WEI Shifu1. 1. Department of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine Andrology, General Hospital of PLA Airforce, Beijing 100142, China; 2. Department of Radiology, General Hospital of PLA Airforce, Beijing 100142, China; 3. Forth Cadres Ward, General Hospital of PLA Airforce, Beijing 100142, China
【Abstract】Objectives: To investigate the correlation of obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) with erectile dysfunction. Methods: 60 OSAHS patients were selected as observation group and 60 healthy subjects as controls group. The dormancy and penile erection of two groups were determined synchronously by polysomnography and nocturnal penile tumeascence, including appnea hypopnea index (AHI), minimal arterial blood oxygen saturation (minSaO2) and change rate of penis blood volume (%). NO was measured by nitrate reduction enzymatic method, and iNOS by colorimetric assay, testosterone, T, FT, FSH, LH, PRL by electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA), and the incidence of erectile dysfunction among OSAHS patients was evaluated by 5-item version of the international index of erectile function (IIEF-5). Results: For OSAHS group, the results included testosterone (2.10±2.42), flow testosterone (9.76±2.33), nitric oxide (72.51±11.74), inducible nitric oxide synthase (25.32±11.57), minimal arterial blood oxygen saturation (71.23±5.71) and change rate of penis blood volume (158.36±32.87), with significant difference from the control group (P<0.01); the appnea hypopnea index of OSAHS group was significantly higher than that in control group (P<0.05). The incidence rate of OSAHS with erectile dysfunction was higher than the control group (P<0.01), NO (32.57±6.33), iNOS (8.06±1.01), change rate of penis blood volume (135.56±16.92) and IIEF-5 (5.3±2.3) in patients with severe erectile dysfunction were significantly less than those in patients with slight and midrange erectile dysfunction (P<0.01). Conclusions: There is apparent correlation between OSAHS and erectile dysfunction, and the increase in NO, hypoxemia and decrease of testosterone may be the mechanism of OSAHS patient with erectile dysfunction.
【Key words】Obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS); Erectile dysfunction; Correlation; Study
【中圖分類號(hào)】R167【文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼】A
阻塞性睡眠呼吸暫停低通氣綜合征(obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome,OSAHS)是有各種原因?qū)е碌乃吆粑鼤和V笖?shù)(appnea hypopnea index,AHI)大于等于5次/h,從而引起低氧血癥、高碳酸血癥和睡眠結(jié)構(gòu)紊亂等多臟器功能障礙的呼吸疾患癥候群[1-3],嚴(yán)重影響患者的生活和生存質(zhì)量,是全身多種疾患的獨(dú)立危險(xiǎn)因素[4],包括性功能障礙,而最常見的是勃起功能障礙(erectile dysfunction,ED)。一項(xiàng)流行病學(xué)調(diào)查資料顯示,OSASH已成為一種發(fā)病率較高的慢性睡眠呼吸疾病,患病率為2%~4%,且多見于男性,表明該病已成為一種常見病[1]。ED是成年男性的常見病,美國MMAS對1290名40~70歲男性的研究表明ED患病率為52%,在中國ED發(fā)病率可能會(huì)更高,ED是男性O(shè)SAHS患者的常見癥狀,有時(shí)可能是就診的主要癥狀。……

