夜間陰莖勃起功能監測結果與代謝綜合征的相關性研究
康樂 劉曉冬 李成文
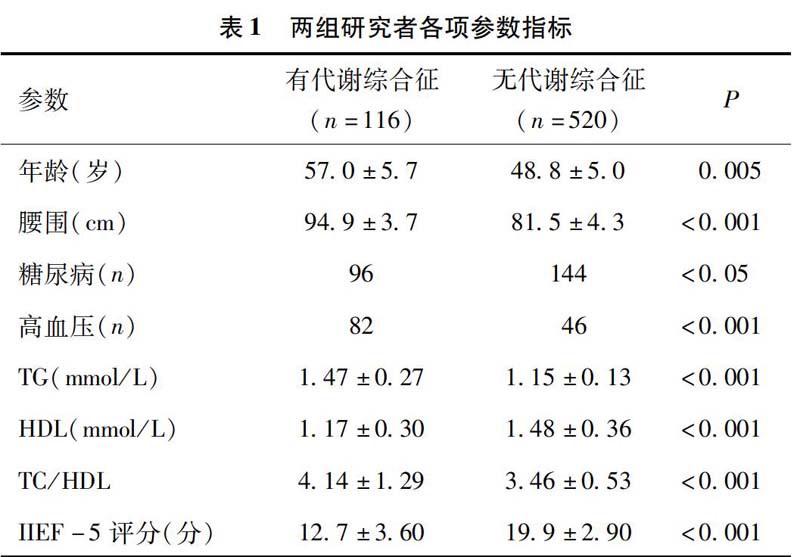
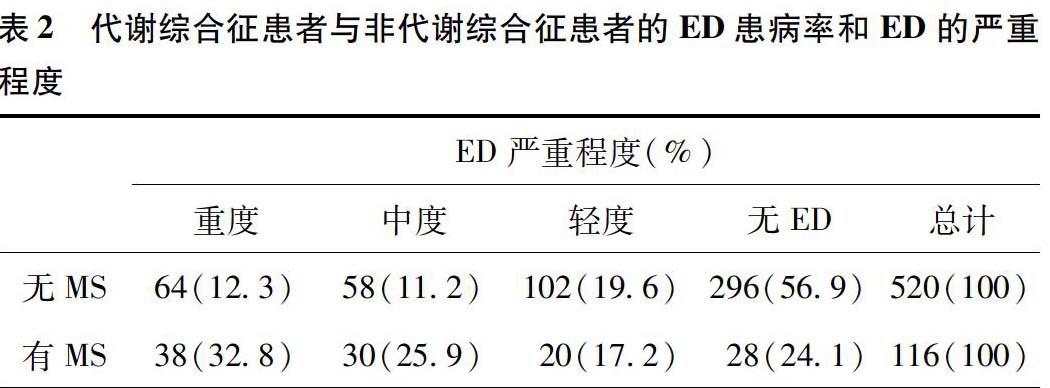
【摘要】目的:研究夜間陰莖勃起功能檢測結果與代謝綜合征的相關性分析。方法:對黑龍江省牡丹江醫學院第二附屬醫院2012年5月至2014年5月間636例男性夜間陰莖勃起功能進行監測,根據其有無代謝綜合征將其分為兩組,所有患者均需要依據國際勃起功能指數(IIEF-5)填寫問卷,代謝綜合征(MS)的診斷標準依據2005年國際糖尿病聯盟頒布的國際學術界第一個MS的全球統一定義,這一定義的核心是中心性肥胖,中心性肥胖的診斷指標為腰圍。結果:觀察組的116名被調查者為存在代謝綜合征的患者,IIEF-5為(12.7±3.6)分,有76%的患者存在程度不等的夜間陰莖勃起功能障礙;對照組的520名被調查者為不存在代謝綜合征患者,IIEF-5為(19.8±2.8)分,有43%的患者存在程度不等的夜間陰莖勃起功能障礙;兩組患者ED發生率差異顯著(P<0.05),且隨著代謝危險因素的不斷提升,勃起功能評分明顯下降。結論:夜間陰莖勃起功能障礙中存在的潛在危險因素為代謝綜合征,對于代謝綜合征就診的患者應認真詢問陰莖勃起功能障礙的病史,可將腰圍測量納入評價中的一個指標。
【關鍵詞】夜間陰莖勃起;功能檢測;代謝綜合征;相關性分析
Correlation between function monitoring results of nocturnal penile tumescence and metabolic syndromeKANG Le1, LIU Xiaodong2△, LI Chengwen3. 1.Department of Medical Education, Hospital Affiliated to College of Armed Police Logistics, Tianjin 300162, China; 2.Medical Insurance Department, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Mudanjiang Medical University, Mudanjiang 157000, Heilongjiang, China; 3.Urology Department, Hospital Affiliated to College of Armed Police Logistics, Tianjin 300162, China
【Abstract】Objectives: To study the correlation between function monitoring results of nocturnal penile tumescence and metabolic syndrome. Methods: The nocturnal penile erectile function of 636 patients in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Mudanjiang Medical University from May 2012 to May 2014 was monitored, and according to the metabolic syndrome those patients were divided into two groups. All the patients were required to fill in the questionnaire according to the international index of erectile function (IIEF-5), and the metabolic syndrome diagnosis standard was referenced to the 2005 International Diabetes Federation issued by the international academic community of the worlds first MS unified definition, whose core was central obesity with diagnosis index of waist. Results: The 116 patients in the observation group had metabolic syndrome, with IIEF-5 score of (12.7 ± 3.6), and 76% of them had varying degrees of nocturnal penile erectile dysfunction. The 520 patients in the control group were with no metabolic syndrome, with IIEF-5 score of (19.8 ± 2.8), and 43% of them had varying degrees of nocturnal penile erectile dysfunction. Difference in the two groups were of statistical significance (P<0.05). With the continuous improvement of metabolic risk factors, erectile function scores decreased significantly. Conclusion: The potential risk factor for nocturnal penile erectile dysfunction is the presence of metabolic syndrome, and the treatment of patients with metabolic syndrome should seriously ask their erectile dysfunction history, and the waist circumference measurement can be included as an index.
【Key words】Nocturnal penile tumescence; Function tests; Metabolic syndrome; Correlation analysis
【中圖分類號】R589【文獻標志碼】A
代謝綜合征(metabolic syndrome, MS)是機體出現的多項代謝功能紊亂的一個總稱,患者臨床上主要表現為高血壓、腹型肥胖、高空腹血糖、高密度脂蛋白降低以及高血甘油三脂等[1,2]。由于生活條件的逐漸提升,患有MS的男性患者數量逐漸增多。大量研究指出,MS是一種引起心血管疾病以及陰莖勃起功能障礙的重要危險因素。勃起功能障礙(Erectile dysfunction, ED)是陰莖無法維持和達到足夠勃起而得到的理想的性生活狀態。器質性ED的危險因素包括:高血脂、高血壓、冠狀動脈、糖尿病以及外周血管疾病等[3]。然而,對于正是生育年齡的青年男性ED患者,實施治療的意義更加重要。……

