早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力的影響
熊艷+江育英+何淑琴+熊玉芳+黃燕+吳小蓮

摘 要 目的:探討早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力的影響。方法:收集2014年8月—2015年1月收治的腦梗死患者60例,隨機分為試驗組和對照組各30例。對照組進行常規護理,包括飲食指導、安全教育等;試驗組在對照組基礎上,為患者制定個體化的康復護理計劃,進行早期康復訓練。觀察患者美國國家衛生研究院腦卒中量表(NIHSS)評分、Barthel指數、生活質量、并發癥發生情況。結果:隨訪6個月時,試驗組NIHSS評分和Barthel指數分別為(4.55±0.99)分和50.91±8.55,對照組分別為(10.24±2.22)分和(7.41±1.04)分,組間差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。干預后試驗組生活質量高于對照組(P<0.05),并發癥總發生率為13.33%(4/30),低于對照組的43.33%(13/30,P<0.05)。結論:早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力有積極影響,可改善患者神經功能缺損情況,提高患者的日常生活能力。
關鍵詞 腦梗死 早期康復護理 神經功能缺損 日常生活能力
中圖分類號:R743.3 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:1006-1533(2016)20-0056-03
Influence of early rehabilitation nursing on neurological deficit and daily life ability of patients with cerebral infarction
XIONG Yan, JIANG Yuying, HE Shuqin, XIONG Yufang, HUANG Yan, WU Xiaolian(Department of Neurosurgery of Peoples Hospital, Yichuan City, Jiangxi 336000, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the effect of early rehabilitation nursing on neurological deficit and daily life ability of patients with cerebral infarction. Methods: From January 2015 to August 2014, 60 cases of cerebral infarction were collected and randomly divided into an experiment group and a control group with 30 cases each. The control group was cared by the routine nursing, including diet guide and safety education. On the basis of the control group, the individualized rehabilitation nursing plan was made for the patients in the experiment group and the early rehabilitation training was carried on. The stroke scale score of the National Institutes of Health in the United States (NIHSS), Barthel index, quality of life and complication occurrence were observed in the patients. Results: The score of NIHSS and Barthel index of the experiment group were (4.55±0.99) and(50.91±8.55) points, respectively, and those of the control group were (10.24±2.22) and (7.41±1.04) points, respectively, and the difference between the groups was statistically significant(P<0.05). The quality of life of the experiment group were higher than that of the control group(P<0.05). The total rate of complication of the experiment group were 13.33%(4/30) lower than that of the control group 43.33%(13/30), (P<0.05). Conclusion: Early rehabilitation nursing has positive effect on neurological deficit and daily living ability of patients with cerebral infarction, and can improve the patients neurological deficit and daily life ability.
KEY WORDS cerebral infarction; early rehabilitation nursing; neurological deficit; daily life ability
急性腦血管病的發病率在不斷增加,且以急性腦梗死發病率最高,患者在急性發病后,常有不同程度的后遺癥,以神經功能缺損為主要表現,嚴重影響患者的生活質量[1]。對患者進行適當的護理干預,可提高患者的生活質量,有重要意義。本文報道我院對腦梗死患者開展早期康復護理的效果。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選取我院2014年8月—2015年1月收治的腦梗死患者60例,按入院順序隨機分為試驗組和對照組各30例。試驗組男20例,女10例,年齡49~77歲,平均(65.48±8.77)歲;對照組男19例,女11例,年齡50~76歲,平均(66.47±8.58)歲。兩組患者的的一般臨床資料差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。患者均簽署知情同意協議書。排除昏迷、嚴重癡呆、精神疾病患者。
1.2 方法
兩組患者均進行常規治療,改善水、電解質平衡等。對照組進行常規護理,包括飲食指導、安全教育等。試驗組在對照組基礎上,為患者制定個體化的康復護理計劃,進行早期康復訓練。①良肢位置的擺放:護理人員要注意患者良肢位置擺放的正確姿勢,為患者取上肢伸展為下肢屈曲位,可減少肢體攣縮變形情況發生。②言語功能訓練:對于運動性失語患者,要鼓勵多說話,多與家人進行交流。對于感覺性失語患者,通過手勢、表情等,教會患者不同手勢的意思。③步行訓練:指導患者逐步增加鍛煉難度,并指導家屬進行輔助鍛煉。④對患者進行日常生活能力鍛煉,包括洗漱、進食、穿衣等,從簡單到復雜,逐步得到改善。兩組均隨訪6個月,觀察患者干預前后美國國家衛生研究院腦卒中量表(NIHSS)NIHSS評分、Barthel指數、生活質量等。
1.3 評估標準
NIHSS評分低于4分為輕度神經功能障礙,4~15分為中度神經功能障礙,高于15分為重度神經功能障礙。Barthel指數分值滿分為100分,分值越低,患者自理能力越差。生活質量采用腦卒中影響量表310(SIS-310)評估,包括力量、手功能、行動能力、日常生活能力、記憶與思維、交流、情感、社會參與8項內容,分值越高,患者生活質量越好。
1.4 統計學分析
2 結果
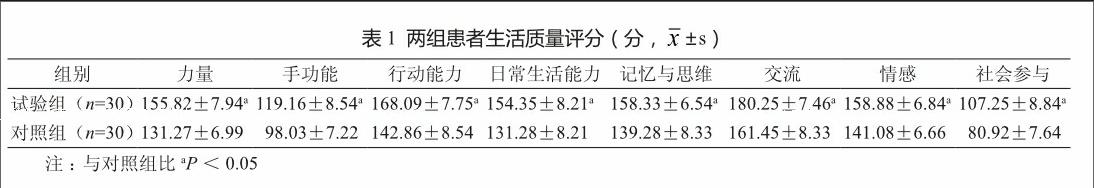
試驗組干預前和隨訪6個月后的NIHSS評分分別為(10.37±2.44)分和(4.55±0.99)分,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);對照組分別為(10.24±2.22)分和(7.41±1.04)分,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。試驗組干預前和隨訪6個月后的Barthel指數分別為32.53±7.66和50.91±8.55,對照組分別為33.25±5.64和45.91±8.77,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。試驗組隨訪6個月后的NIHSS評分和Barthel指數均優于對照組(P<0.05)。從表1可見,試驗組生活質量高于對照組(P<0.05)。
試驗組中,肩痛2例,肌肉萎縮1例,膝關節痛1例,總發生率為13.33%;對照組中,肩痛5例,肌肉萎縮4例,膝關節痛4例,總發生率43.33%,組間差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
3 討論
對患者進行早期康復護理,可以誘發來自皮膚、關節處深淺感受器的大量信息傳入性活動,使大腦皮質功能得到恢復重組,利于患者運動功能的恢復[2-3]。對腦梗死偏癱患者進行康復訓練,可以減少患者肌肉痙攣的發生[4]。本研究顯示,出院后6個月,試驗組患者NIHSS評分低于對照組和護理前,Barthel指數高于對照組和護理前(P<0.05)。患者的神經功能缺損情況改善較好, Barthel指數較高。
腦梗死患者進行訓練往往開始較晚,且功能鍛煉方法不對,發生肌肉萎縮等的可能較高[5-6]。對患者進行早期康復訓練,可以減少壓瘡、墜積性肺炎的發生,提高患者生活質量。本研究中,試驗組生活質量高于對照組(P<0.05),并發癥總發生率為13.33%,低于對照組43.33%(P<0.05),提示早期康復訓練效果較好。
老年急性腦梗死發病率較高,患者經治療后,往往會留下不同程度的后遺癥[7-8]。傳統的治療方法以搶救患者生命為重點。現階段,改善患者的生活質量越發引起重視[9-10]。對患者進行早期康復訓練,對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力有積極影響,能提高患者的肢體運動功能,降低并發癥發生,提高患者的日常生活能力。
參考文獻
[1] Pallesen LP, Ragaller M, Kepplinger J, et al. Diagnostic impact of transesophageal echocardiography in patients with acute cerebral ischemia[J]. Echocardiography, 2016, 33(4): 555-561.
[2] Yaghmour W, Kurdi ME, Baeesa SS. De novo glioblastoma in the territory of a recent middle cerebral artery infarction and a residual meningioma: pathogenesis revisited[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2016, 14(1): 112.
[3] 劉玉蓮, 賴育芳, 羅慶. 早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力的影響[J]. 護理實踐與研究, 2011, 8(24): 14-15.
[4] Kanaoka Y, Ohki T, Maeda K, et al. Multivariate analysis of risk factors of cerebral infarction in 439 patients undergoing thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2016, 95(15): e3335.
[5] 趙艷, 薛嘉. 早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能缺損及日常生活能力的影響[J]. 中國現代藥物應用, 2013, 7(10): 142-143.
[6] Low MS, Vilcassim S, Fedele P, et al. Anabolic androgenic steroids, an easily forgotten cause of polycythaemia and cerebral infarction[J]. Intern Med J, 2016, 46(4): 497-499.
[7] 任燕, 顧艷葒, 金小紅, 等. 路徑式早期康復護理對腦梗死患者上肢功能恢復的影響[J]. 護理研究: 上旬版, 2015, 29(11): 3911-3913.
[8] Maeshima S, Okamoto S, Okazaki H, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation in patients with cerebral infarction referred to a rehabilitation hospital[J]. Interv Neurol, 2016, 4(3-4): 69-74.
[9] 陜海麗, 王妮娜, 支楠, 等. 早期系統化康復護理對老年急性腦梗死患者神經功能缺損和日常生活能力的影響[J].中國實用神經疾病雜志, 2015, 18(23): 143-144.
[10] 金小紅, 任燕, 陳美華, 等. 路徑式早期康復護理對腦梗死患者神經功能恢復的影響[J]. 江蘇醫藥, 2016, 42(2): 237-238.

