基于Q學(xué)習(xí)異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)干擾協(xié)調(diào)算法
錢進(jìn)++郭士增++王孝
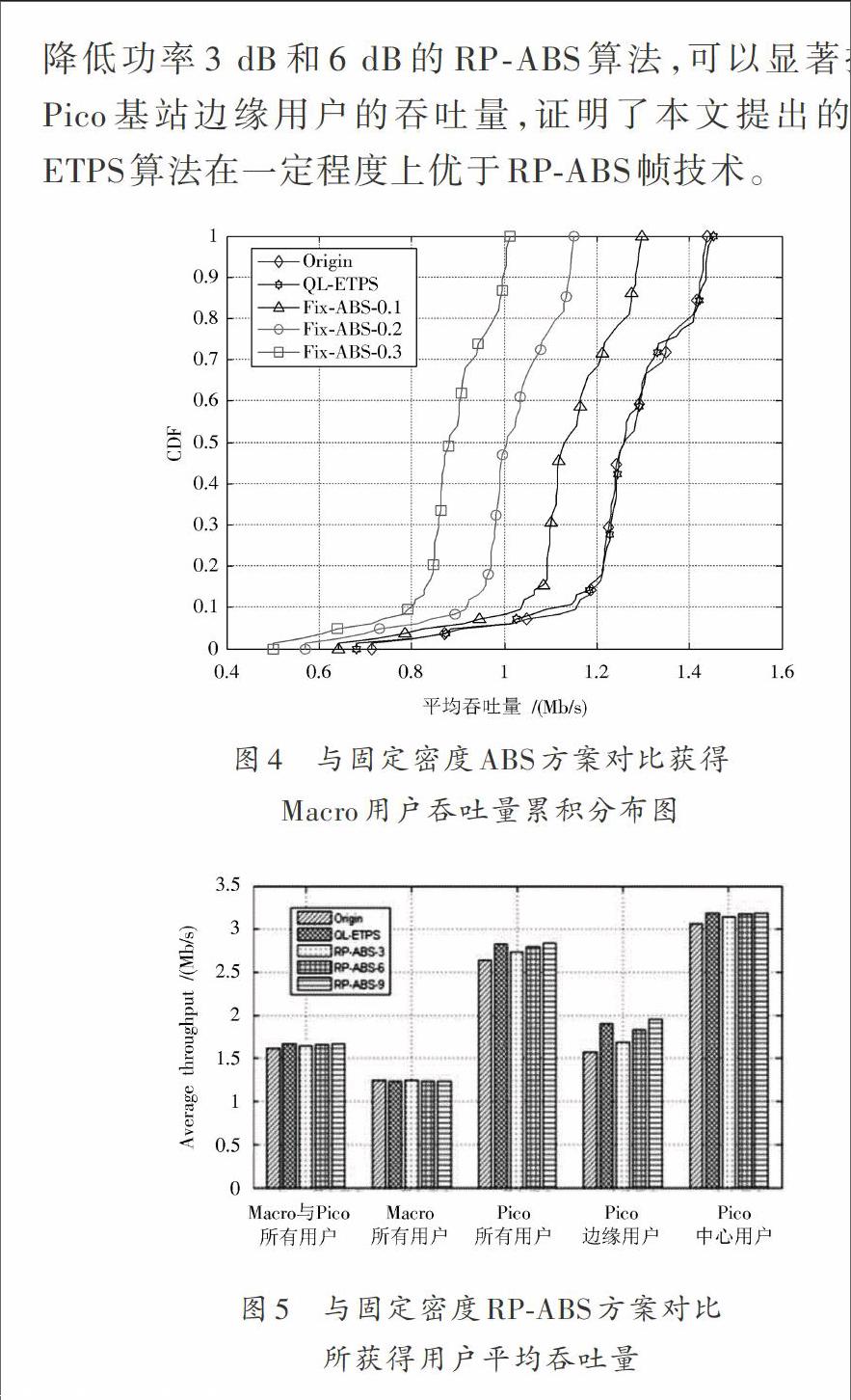


摘 要: 在LTE?A中采用異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)能提高用戶的性能,但是由于小區(qū)間使用相同的頻譜資源,產(chǎn)生了小區(qū)間干擾,影響了用戶性能,從而需要采用小區(qū)間干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)來控制小區(qū)間干擾(ICI)。雖然現(xiàn)有的小區(qū)間干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)可以降低小區(qū)間干擾,但是存在Macro用戶性能影響較大的問題。為此,提出了基于Q學(xué)習(xí)的ETPS算法,在不影響Macro用戶性能的前提下,降低小區(qū)間干擾。仿真結(jié)果表明,QL?ETPS算法較傳統(tǒng)固定ABS/RP?ABS子幀配置方案性能更優(yōu),可以在盡量不影響Macro基站用戶的前提下,提高Pico基站邊緣用戶的吞吐量。
關(guān)鍵詞: 干擾協(xié)調(diào); 異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò); Q學(xué)習(xí)算法; Macro?Pico; 吞吐量
中圖分類號(hào): TN913?34 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼: A 文章編號(hào): 1004?373X(2016)23?0013?04
Q?learning based interference coordination algorithm for heterogeneous network
QIAN Jin1, GUO Shizeng2, WANG Xiao2
(1. Navy Military Representative Office in the 3rd Institute of CASIC, Beijing 100074, China;
2. Communication Research Center, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China)
Abstract: The heterogeneous network adopted by long?term evolution?advance (LTE?A) system can improve the user performance. The inter?cell interference (ICI) is generated and the user performance is influenced due to the shared frequency spectrum among the inter?cells, so it is necessary to adopt the inter?cell interference coordination (IC) technology to control the ICI. Although the existing inter?cell interference coordination technology can reduce the ICI efficiently, but influence the Macro user performance greatly. To solve this problem, a Q?learning based enhance transmission power subframe (QL?ETPS) algorithm is proposed, which can reduce the ICI on the premise of ensuring the Macro user performance. The simulation results show that the performance of the proposed QL?ETPS algorithm is better than that of the conventional fixed ABS/RP?ABS configuration scheme, and can improve the throughput of the Pico base station edge user while ensuring the performance of Macro base station user.
Keywords: interference coordination; heterogeneous network; Q?learning algorithm; Macro?Pico; throughput
0 引 言
LTE?A定義的異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)是在發(fā)射功率較大的Macro基站下,在信號(hào)范圍的死角或者用戶稠密的地方架設(shè)發(fā)射功率較小的低功率基站如Pico基站等,來提高用戶的性能。異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)不僅縮短了網(wǎng)絡(luò)與用戶之間的距離,而且能提升單位面積的頻譜效率。由于頻譜資源的缺乏,同時(shí)也為了提高頻譜效率,LTE?A系統(tǒng)采用頻率復(fù)用的方案同頻組網(wǎng),但是由于Macro基站和Pico基站使用相同的頻譜資源,小區(qū)間復(fù)用的頻譜越多,帶來的小區(qū)間干擾越嚴(yán)重,進(jìn)而影響小區(qū)邊緣用戶的數(shù)據(jù)速率,因此必須采取有效的方法對(duì)小區(qū)間干擾進(jìn)行控制。
3GPP Release 10/11提出了解決異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)中干擾問題的增強(qiáng)型小區(qū)間干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)(enhanced Inter?Cell Interference Coordination,eICIC)。eICIC可以分為功率控制、頻域干擾協(xié)調(diào)和時(shí)域干擾協(xié)調(diào)三類技術(shù)方法。功率控制技術(shù)[1?3]是在Macro基站與低功率基站組成的異構(gòu)網(wǎng)絡(luò)中,通過調(diào)整Macro基站的發(fā)射功率大小來減輕對(duì)低功率基站用戶的干擾以提高這些用戶的性能。頻域干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)[4?6]將不同的資源塊分配給相鄰小區(qū),讓這些資源相互正交,可以減輕小區(qū)間干擾。頻域上也可以使用載波聚合方法進(jìn)行干擾協(xié)調(diào),載波聚合方法通過將多個(gè)連續(xù)或者非連續(xù)的成分載波聚合起來,用來實(shí)現(xiàn)更大的傳輸帶寬,最大可達(dá)100 MHz,能有效提高用戶的上下行傳輸速率并最大限度地利用頻譜資源。時(shí)域干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)[7?9]的基本思想是干擾源基站(如Macro基站)在某些子幀上保持靜默,不發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù)信號(hào),以減小對(duì)被干擾基站用戶的跨層干擾,這些子幀就叫做幾乎空白子幀(Almost Blank Subframe,ABS)。以上小區(qū)間干擾協(xié)調(diào)技術(shù)可以有效降低小區(qū)間干擾,但是對(duì)Macro用戶性能的影響比較大。因此,本文提出了基于Q學(xué)習(xí)的ETPS(Q Learning based Enhance Transmission Power Subframe,QL?ETPS)算法,在盡量不影響Macro基站用戶性能的前提下,降低小區(qū)間干擾,同時(shí)提高Pico基站邊緣用戶的吞吐量。
4 結(jié) 論
本文基于ABS子幀的思想,首先設(shè)計(jì)了一種面向Pico基站的ETPS幀,Pico基站可以根據(jù)自身情況靈活地改變?cè)黾拥墓β蚀笮『虴TPS幀的密度。針對(duì)Macro?Pico網(wǎng)絡(luò)的干擾問題,提出了一種基于Q學(xué)習(xí)的干擾協(xié)調(diào)算法QL?ETPS,將ETPS幀的配置作為Q學(xué)習(xí)的動(dòng)作,Pico基站邊緣用戶的SINR作為Q學(xué)習(xí)的狀態(tài),通過迭代獲得Q值表,選取最優(yōu)值作為ETPS幀的配置。仿真結(jié)果表明,本文提出的QL?ETPS算法較傳統(tǒng)固定的ABS/RP?ABS子幀配置方案性能更優(yōu),可以在盡量不影響Macro基站用戶的前提下,提高Pico基站邊緣用戶的吞吐量。
參考文獻(xiàn)
[1] KOLEVA P, ASENOV O, ILIEV G, et al. Interference limited uplink power control based on a cognitive approach [C]// Proceedings of 2012 35th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2012: 242?246.
[2] TABASSUM H, YILMAZ F, DAWY Z, et al. A statistical model of uplink inter?cell interference with slow and fast power control mechanisms [J]. IEEE transactions on communications, 2013, 61(9): 3953?3966.
[3] BITON E, COHEN A, REINA G, et al. Distributed inter?cell interference mitigation via joint scheduling and power control under noise rise constraints [J]. IEEE transactions on wireless communications, 2014, 13(6): 3464?3477.
[4] LOPEZ?PEREZ D, CHU X, ZHANG J. Dynamic downlink frequency and power allocation in OFDMA cellular networks [J]. IEEE transactions on communications, 2012, 60(10): 2904?2914.
[5] HUANG C H, LIAO C Y. An interference management scheme for heterogeneous network with cell range extension [C]// Proceedings of 2011 13th Asia?Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium. Taoyuan, China: IEEE, 2011: 1?5.
[6] MAO X, MAAREF A, TEO K H. Adaptive soft frequency reuse for inter?cell interference coordination in SC?FDMA based 3GPP LTE uplinks [C]// Proceedings of 2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2008: 1?6.
[7] DEB S, MONOGIOUDIS P, MIERNIK J, et al. Algorithms for enhanced inter?cell interference coordination (eICIC) in LTE HetNets [J]. IEEE/ACM transactions on networking, 2014, 22(1): 137?150.
[8] L?PEZ?P?REZ D, CLAUSSEN H. Duty cycles and load ba?lancing in HetNets with eICIC almost blank subframes [C]// Proceedings of 2013 IEEE 24th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2013: 173?178.
[9] JIANG L, LEI M. Resource allocation for eICIC scheme in he?terogeneous networks [C]// Proceedings of 2012 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Personal Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications. [S.l.]: IEEE, 2012: 448?453.
- 現(xiàn)代電子技術(shù)的其它文章
- 電網(wǎng)企業(yè)全過程技術(shù)監(jiān)督評(píng)價(jià)指標(biāo)體系建設(shè)研究
- 基于人臉特征定位的SNS網(wǎng)站應(yīng)用組件研究與設(shè)計(jì)
- 基于嵌入式向量和循環(huán)神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)的用戶行為預(yù)測(cè)方法
- 基于Raspberry Pi的智能家居系統(tǒng)設(shè)計(jì)
- 無線定位系統(tǒng)中自動(dòng)增益控制電路的設(shè)計(jì)與研究
- 基于6LoWPAN和CoAP的農(nóng)業(yè)環(huán)境信息傳感系統(tǒng)的設(shè)計(jì)與實(shí)現(xiàn)

