MONOTONICITY IN ORLICZ-LORENTZ SEQUENCE SPACES EQUIPPED WITH THE ORLICZ NORM?
Wanzhong GONG(鞏萬中) Daoxiang ZHANG(張道祥)
Department of Mathematics,Anhui Normal University,Wuhu 241000,China
MONOTONICITY IN ORLICZ-LORENTZ SEQUENCE SPACES EQUIPPED WITH THE ORLICZ NORM?
Wanzhong GONG(鞏萬中)?Daoxiang ZHANG(張道祥)
Department of Mathematics,Anhui Normal University,Wuhu 241000,China
E-mail:gongwanzhong@shu.edu.cn;zdxiang1012@163.com
In Orlicz-Lorentz sequence space λ??,ωwith the Orlicz norm,uniform monotonicity,points of upper local uniform monotonicity and lower local uniform monotonicity are characterized.Moreover,the monotonicity coefcient in λ??,ωare discussed.
Orlicz-Lorentz sequence space;Orlicz norm;point of upper(lower)local uniform monotonicity;uniform monotonicity;monotone coefcient
2010 MR Subject Classifcation46B20
1 Introduction
A Banach lattice X with a lattice norm k·k is said to be strictly monotone(STM for short) [1]if for any x∈X+(positive cone in X)and any y∈X+{0},we have kx+yk>kxk.A point x∈S(X+):=S(X)∩X+is said to be upper monotone[2]if,for any y∈X+{0},kx+yk>1. A point x∈S(X+)is said to be lower monotone[2]if,for any y∈X+{0}and y≤ x, kx?yk<1.An equivalent condition for X being strictly monotone[1]is that any point x∈S(X+)is lower monotone.But lower monotone points and upper monotone points are diferent,see[2].X is called upper locally uniformly monotone(ULUM)[3]if for any ε>0 and x∈S(X+),there exists δ(x,ε)>0 such that y∈X+and kyk≥ε imply kx+yk≥1+δ(x,ε). If for any ε>0 and x∈S(X+),there is δ(x,ε)>0 such that kx?yk≤1?δ(x,ε)whenever y∈X+,kyk≥ε and y≤x,then X is said to be lower locally uniformly monotone(LLUM) [3].We can analogously defne points of lower local uniform monotonicity and points of upper local uniform monotonicity.We say that X is uniformly monotone(UM)[4]if for any ε∈(0,1) there exists δ(ε)∈(0,1)such that kx+yk>1+δ(ε)whenever x∈S(X+),y∈X+and kyk≥ε.For ε∈[0,1],defne ηX(ε)=inf{kx+yk?1:x,y∈X+,kxk=1,kyk≥ε}.We call m(X)=sup{ε∈[0,1]:ηX(ε)=0}the monotone coefcient[5]of X.
It is well known that some rotundity properties of Banach spaces were widely applied in ergodic theory,fxed point theory,probability theory and approximation theory,and in many cases these rotundity properties can be replaced by respective monotonicity properties when werestrict ourselves to a Banach space being a Banach lattice[3].Roughly speaking,monotonicity properties played in Banach lattices similar role as rotundity properties in Banach spaces, and so for monotonicity points and rotundity points.Therefore in recent years monotonicity properties and monotonicity points were widely investigated in Musielak-Orlicz,Orlicz-Lorentz, Orlicz-Sobolev,Calder′on-Lozanovskiˇi spaces[2,3,7,8,19].In addition,some geometric properties concerning with the dual spaces of Orlicz-Lorentz spaces were researched by many mathematicians,where the Orlicz norm play a important role.In this paper we mainly give the criteria for Orlicz-Lorentz sequence spaces λ??,ωwith the Orlicz norm being UM,a point in the space being upper locally uniformly monotone and lower locally uniformly monotone.At last we get the monotone coefcients of Orlicz-Lorentz sequence spaces with the Luxemburg norm and the Orlicz norm.

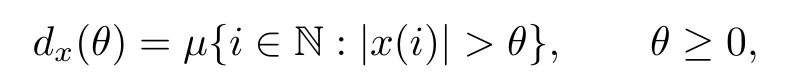
and the non-increasing rearrangement of x,
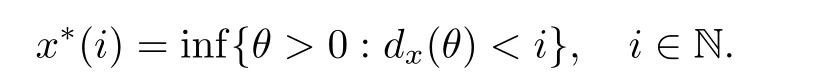

endowed with the Orlicz norm[9]

or the Banach space λ?,ωequipped with the Luxemburg norm[10]
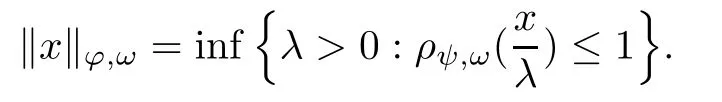
Similarly as in the Orlicz space theory[11],denote
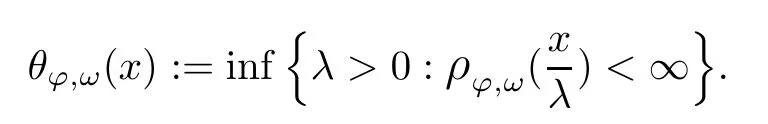
Recall that ? satisfes δ2-condition if there exist k>0 and u0>0 such that ?(2u)≤k?(u) for all 0 In recent years,Wang and Ning extended some properties in Orlicz space to Orlicz-Lorentz spaces[9]. Lemma 2.1(see[9]) Let x∈λ??,ω,we have where k?=inf{h>0:ρψ,ω(p(h|x|))≥1},and k??=sup{h>0:ρψ,ω(p(h|x|))≤1}. Lemma 2.2(see[9]) By Lemma 1.1 in[23],and similarly as the proof of Lemma 1.40 in[11],we can get Lemma 2.3Suppose ?∈δ2,then for any L>0 and ε>0,there exists δ>0 such that whenever ρ?,ω(u)≤L and ρ?,ω(v)≤δ. Lemma 2.4Let x∈(λ??,ω)+with ρ?,ω(x)< ∞.Then ρ?,ω(x?[x]n)→ 0,where [x]n=(x(1),x(2),···,x(n),0···). Lemma 2.5Suppose x∈(λ??,ω)+and δ>0 be such that the set A:={j∈N:δ≤x?(j)} is nonempty.Then for any i∈A,there exists a constant b=b(x,δ,i)>0 such that ProofCase 1δ Since we only need to check that Otherwise,x?(i)=x?(i+1)=x?(i+2)=···=x?(n)=x?(i)?δ since ω is non-increasing. This contradiction yields that the inequality above holds.It follows the inequalityρ?,ω(x)> ρ?,ω(x??δei).Set b:=12(ρ?,ω(x)?ρ?,ω(x??δei)).Then b=b(x,δ,i)>0 satisfes Lemma 2.6Suppose x∈(λ??,ω)+and δ>0 satisfy that A:={j∈N:δ≤x?(j)}is nonempty.Then there exists a constant c=c(x,δ)>0 such that the inequality holds for all h∈A. ProofThere is a bijection σ:N→N(ifμSx<∞)or σ:Sx→N(ifμSx=∞)such that x=x??σ.Clearly h∈H:={σ?1(j):x?(j)≥δ}andμH<∞.By Lemma 2.5,one get where b′(x,δ,h)>0.Set c=min{b′(x,δ,h):h∈H}.Then c=c(x,δ)>0 satisfes the demand. ? 2.1Monotonicity inλ??,ω Theorem 2.7λ??,ωis STM. ProofLet us choose arbitrary x∈S?(λ??,ω)+?:=S(λ??,ω)T(λ??,ω)+and y∈λ??,ω,y?0, and let k∈K(x)and h∈K(x+y).In the following we will consider two cases. Case Ih 6∈K(x).By Lemma 2.1,we have Case IIh∈K(x).For y?0,there exists i0∈N such that y(i0)>0.We know that there is a bijection σ:N→N(ifμSx<∞)or σ:Sx→N(ifμSx=∞)such that x=x??σ. If i0∈Sx,assuming that σ(i0)=j0,one can get If i06∈Sx,then h0:=μ{i∈N:x(i)≥y(i0)}<∞.Without loss of generality,we may assume that h0≥1.So x?(h0+1) Hence it follows that kx+yk??,ω=1h(1+ρ?,ω(h(x+y)))>1h(1+ρ?,ω(hx))=kxk??,ω=1,i.e., x is upper monotone,and λ??,ωis STM. Theorem 2.8A point x∈S?(λ??,ω)+is upper locally uniformly monotone if and only if ?∈δ2. ProofSufciencyIf ?∈δ2and x is not upper locally uniformly monotone,then there exist{xn}?λ??,ω,xn≥0 such that kxnk??,ω≥ε0∈R+for any n∈N and kx+xnk??,ω→1 as n→∞.Now denoting k=k?x,kn=k?x+xn,by the defnition we can get kn≤k.Without loss of generality,we can assume that kn→k0as n→∞. If k0 a contradiction!Therefore we may assume that kn→k as n→∞. By Corollary 5.1 in[24],we know that λ?,ωis ULUM.Hence for the above ε0>0,there exists δ=δ(ε0)>0 such that ρ?,ω(k(x+xn))> ρ?,ω (kx)+δ.Set u=kn(x+xn),v= (k?kn)(x+xn).By kn→k and Lemma 2.3,there exist N∈N such that when n>N.Therefore,by the defnition of the Orlicz norm,we have,for n>N, a contradiction which shows that x is upper locally uniformly monotone. If ? 6∈δ2,in view of the proof of Theorem 8 in[25],There exists a w0satisfying Sw0= N,ρ?,ω(w0)<∞and θ?,ω(w0)=1.For the above subset I0,there exists a w=w|I0such thatFrom Lemma 2.4 and the orthogonally sub-additive convexity of ρ?,ωwe get where An={n+1,n+2,···}∩I0.Thus kx+ynk→1,a contradiction with x being upper locally uniformly monotone. Theorem 2.9x∈S((λ??,ω)+)is lower locally uniformly monotone if and only if θ?,ω(x)= 0. ProofNecessityIf θ?,ω(x)=ε>0,denote yn:=x?[x]n.Then θ?,ω(yn)=θ?,ω(x). So kynk??,ω≥θ?,ω(yn)=ε0>0.But kx?ynk??,ω=k[x]nk??,ω→kxk??,ω=1,a contradiction with x being lower locally uniformly monotone. SufciencyIf x is not lower locally uniformly monotone,then there exist ε>0 and {xn:0?xn≤x}satisfying kxnk??,ω≥2ε and kx?xnk??,ω→1. Thus kxnk??,ω≤2kxnk?,ω≤ε,a contradiction with kxnk??,ω≥2ε. So there exist an ε0>0,a subsequence of{xn}still denoted by{xn},and{in:in=i(n)} such that xn(in)≥ε0for any n∈N.Since ρ?,ω(x)<∞,n0:=μ{i∈Sx:x(i)≥ε0}<∞.In virtue of Lemma 2.6,there is a δ=δ(x,ε0)>0 independent of n,such that ρ?,ω(kx?kxn)≤ρ?,ω(kx?kε0ein)≤ρ?,ω(kx)?kδ. By θ?,ω(x)=0 implying ρ?,ω(2x)<∞,we have where k∈[k?,k??],a contradiction with kx?xnk??,ω→1. Corollary 2.10The following conditions are equivalent: 1.?∈δ2; 2.λ??,ωis ULUM; 3.λ??,ωis LLUM. Theorem 2.11λ??,ωis UM if and only if ?∈δ2,and ω is regular. Set fi=μ({1,2,···,ei}∩A)and gi=μ({1,2,···,ei}A),then fi+gi=ei.Choosing arbitrarily k0∈K(x),we have k0>1, and Defning and so When i∈N2,combiningfi2p≤gi≤fiwith fi+gi=eiwe get ei≥2gi.So using the regularity and monotonicity of ω,we have For i∈N3,by fi Therefore Which follows that Obviously δ:=ah(ε)satisfes the demand. 2.2Monotone Coefcients in Orlicz-Lorentz Sequence Space In 1999,L¨u,Wang and Wang gave the monotone coefcients in Orlicz function space [5].Here we investigate similarly the monotone coefcients in Orlicz-Lorentz sequence space. Combining Theorem 4.4 in[26]with our Theorem 2.11 we immediately get Theorem 2.12If ?∈δ2and ω be regular,then m(λ??,ω)=0 and m(λ?,ω)=0. Theorem 2.13For the Orlicz-Lorentz sequence space λ?,ωwith the Luxemburg norm, if ? 6∈δ2,or ω is not regular,then m(λ?,ω)=1. which shows kx+yk≤1,so kx+yk=1.Therefore ηλ?,ω(1?ε)=0,and so by the arbitrariness of ε>0 we have m(λ?,ω)=1. that is ρ?,ω(xn+yn)→1,which means that kxn+ynk?,ω→1 since xn+yn≥xn.From the defnition of the monotonicity coefcient we know that m(λ?,ω)=1. Theorem 2.14For Orlicz-Lorentz sequence space λ??,ωwith the Orlicz norm,if ? 6∈δ2, or ω is not regular,then m(λ??,ω)=1. and for any α=(α1,α2,···)∈l∞. (b1,b2,···).Certainly a,b∈l∞and kak∞=1=kbk∞.So by(2.11)and(2.12),one can get Denote Therefore,by the arbitrariness of ε>0 and the defnition of the monotonicity coefcient we can easily get m(λ??,ω)=1. Then similarly as the proof of Theorem 2.13 one can get [1]Kurc W.Strictly and uniformly monotone Musielak-Orlicz spaces and applications to best approximation. J Approx Theory,1992,69:173–187 [2]Hudzik H,Liu X B,Wang T F.Points of monotonicity in Musielak-Orlicz function spaces endowed with the Luxemburg norm.Arch Math,2004,82:534–545 [3]Hudzik H,Kurc W.Monotonicity properties of Musielak-Orlicz spaces and domained best approximation in Banach lattices.J Approx Theory,1998,95:353–368 [4]BirkhofG.Lattice Theory.Providence,RI:Amer Math Soc,1988 [5]L¨u Y M,Wang J M,Wang T F.Monotone coefcients and monotonicity of Orlicz spaces.Rev Mat Complut, 1999,12:105–114 [19]Chen S T,He X,Hudzik H,Kami′nska A.Monotonicity and best approximation in Orlicz-Sobolev spaces with the Luxemburg norm.J Math Anal Appl,2008,344:687–698 [7]Hudzik H,Kami′nska A.Monotonicity properties of Lorentz spaces.Proc Amer Math Soc,1995,123: 2715–2721 [8]Kolwicz P.Rotundity properties in Calder′on-Lozanovskiˇi spaces.Houston J Math,2005,31:883–912 [9]Wang J C,Ning Z.Rotundtity and uniform rotundity of Orlicz-Lorentz sequence spaces with the Orlicz norm.Math Nachr,2011,284:2297–2311 [10]Kami′nska A.Some remarks on Orlicz-Lorentz spaces.Math Nachr,1990,147:29–38 [11]Chen S T.Geometry of Orlicz spaces.Dissertationes Math,356,1996 [12]Bennett C,Sharpley R.Interpolation of Operators.New York:University of Sorth Carolina,1988 [13]Zhang C Z,Pan Y,Zhang X Y.Interpolation of Lorentz-Orlicz martingale spaces.Acta Math Sci,2015, 35B:1467–1474 [14]Foralewski P,Hudzik H,Kaczmarek R,Krbec M.Moduli and characteristics of monotonicity in some Banach lattices.Fixed Point Theory Appl,2010:Art ID 852346 [15]Foralewski P,Hudzik H,Kaczmarek R,Krbec M,W′ojtowicz M.On the moduli and characteristic of monotonicity in Orlicz-Lorentz function spaces.J Convex Anal,2013,20:955–970 [16]Foralewski P,Hudzik H,Kaczmarek R,Krbec M.Characteristic of monotonicity of Orlicz function spaces equipped with the Orlicz norm.Comment Math,2013,53:421–432 [17]Cui Y A,Hudzik H,Wis la M.Monotonicity properties and dominated best approximation problems in Orlicz spaces equipped with the p-Amemiya norm.J Math Anal Appl,2015,432:1095–1105 [18]Hudzik H,Kaczmarek R.Monotonicity characteristic of K¨othe-Bochner spaces.J Math Anal Appl,2009, 349:459–468 [19]Chen S T,He X,Hudzik H.Monotonicity and best approximation in Banach lattices.Acta Math Sin(Engl Ser),2009,25:785–794 [20]Hudzik H,Narloch A,Local monotonicity structure of Calder′on-Lozanovskiˇi spaces.Indag Math,2004,15: 245–255 [21]Hudzik H,Kaczmarek R,Krbec M.In some symmetric spaces monotonicity properties can be reduced to the cone of rearrangements.Aequationes Math,2016,90:249–261 [22]Hudzik H,Kurc W.Monotonicity properties of Musielak-Orlicz spaces and dominated best approximation in Banach lattices.J Approx Theory,1998,95:353–368 [23]Choi C,Kami′nska A,Lee H.Complex convexity of Orlicz-Lorentz spaces and its applications.Bull Polish Acad Sci Math,2004,52:19–38 [24]Kolwicz P,P luciennik R.Points of upper local uniform monotonicity in Calder′on-Lozanowskiˇi spaces.J Convex Anal,2010,17:111–130 [25]Cerda J,Hudzik H,Kami′nska A,Masty lo M.Geometric properties of symmetric spaces with applications to Orlicz-Lorentz spaces.Positivity,1998,2:311–337 [26]Foralewski P.On Some geometric properties of generalized Orlicz-Lorentz sequence spaces.Indag Math, 2013,24:346–372 [27]Hudzik H,Kami′nska A,Masty lo M.Monotonicity and rotundity properties in Banach lattices.Rocky Mountain J Math,2000,30:933–950 ?Received June 25,2015;revised May 5,2016.This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China(11271248 and 11302002),the National Science Research Project of Anhui Educational Department (KJ2012Z127),and the PhD research startup foundation of Anhui Normal University. ?Corresponding author:Wanzhong GONG.2 Lemmas
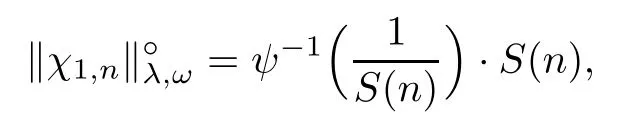
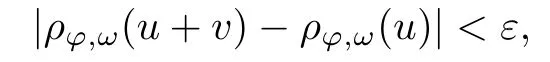
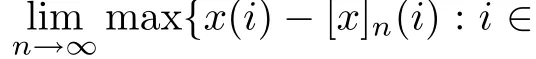
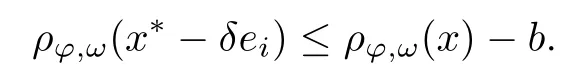


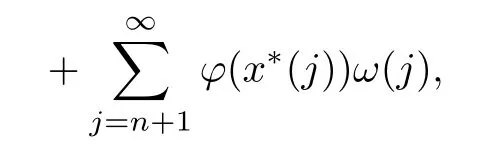

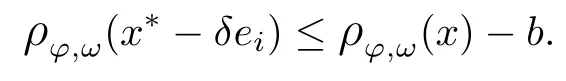
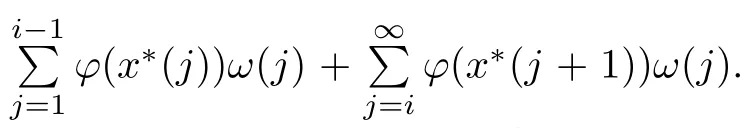

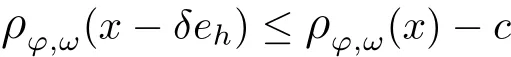
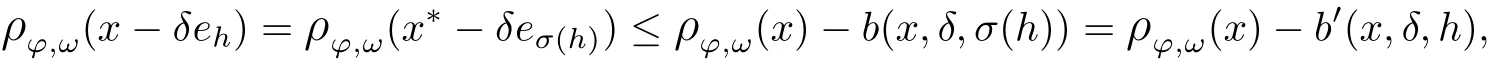
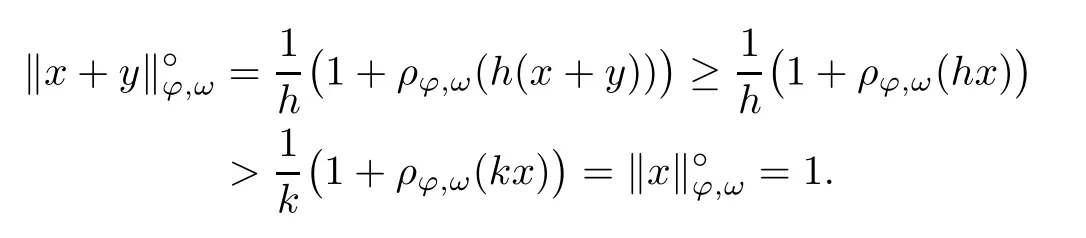

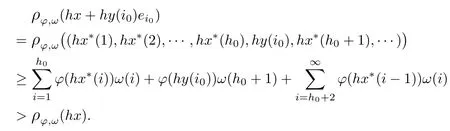
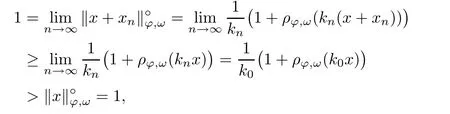

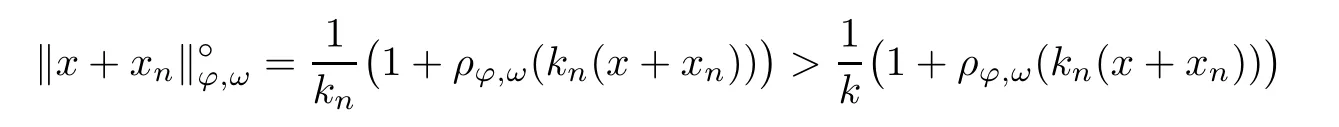
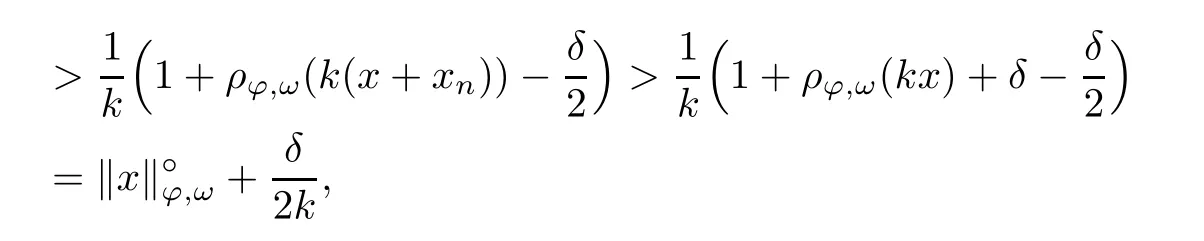
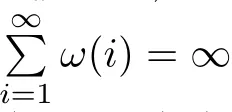

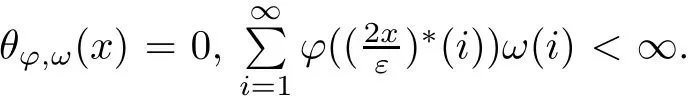
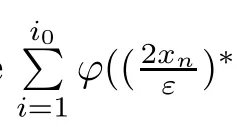
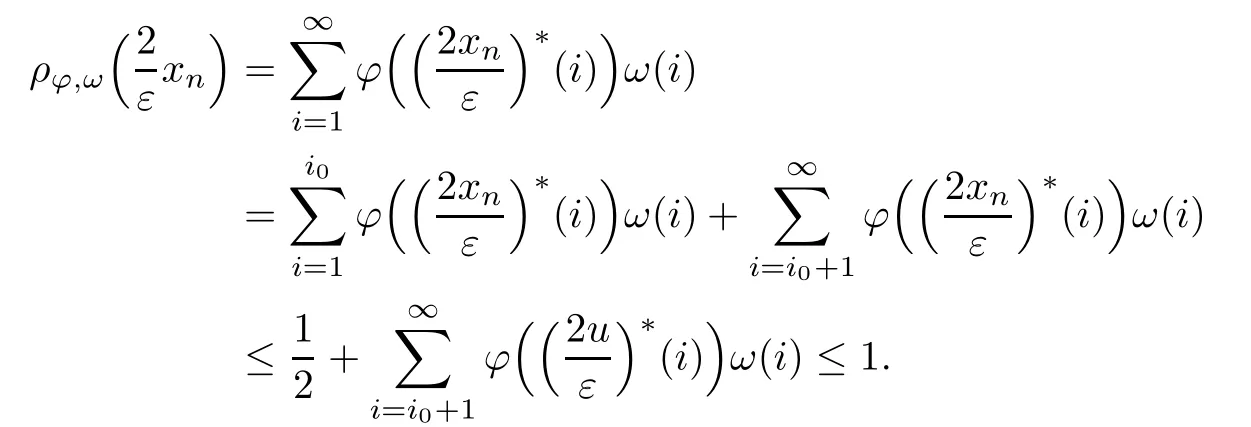
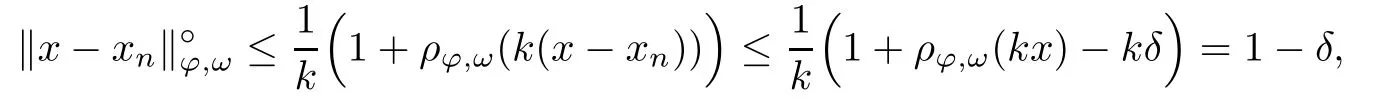


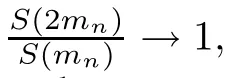
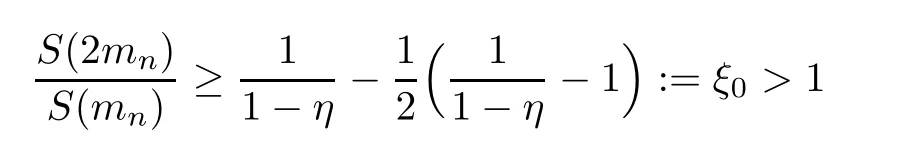

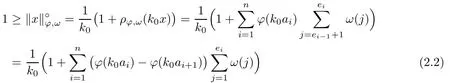
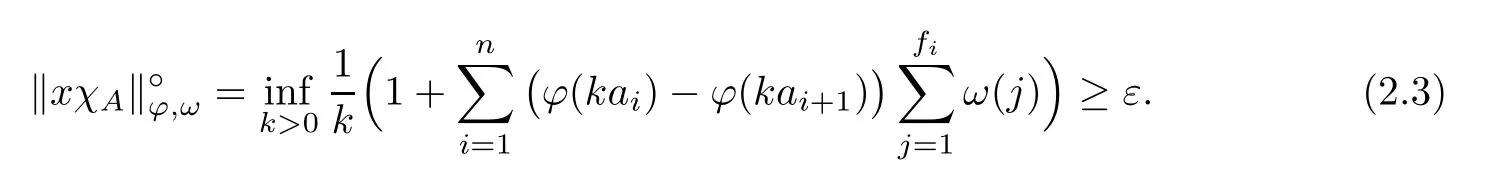
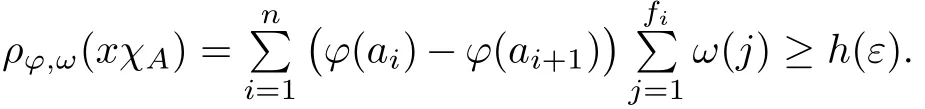
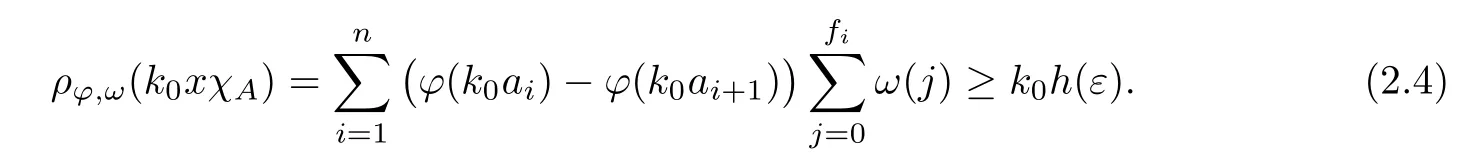
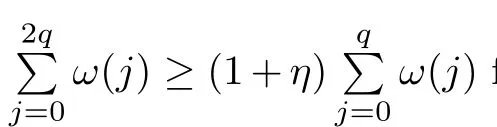


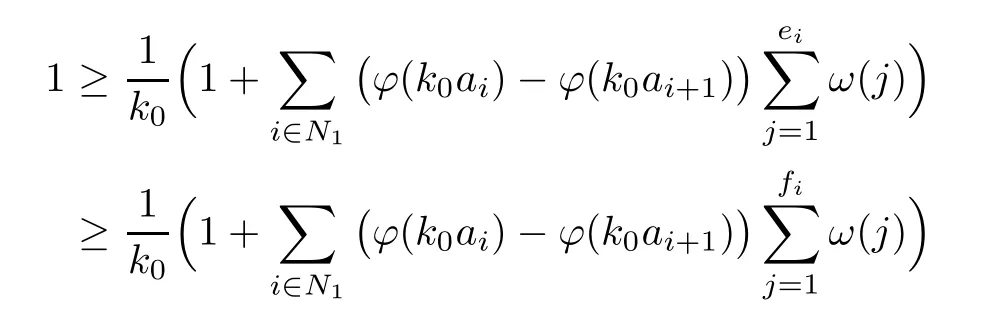
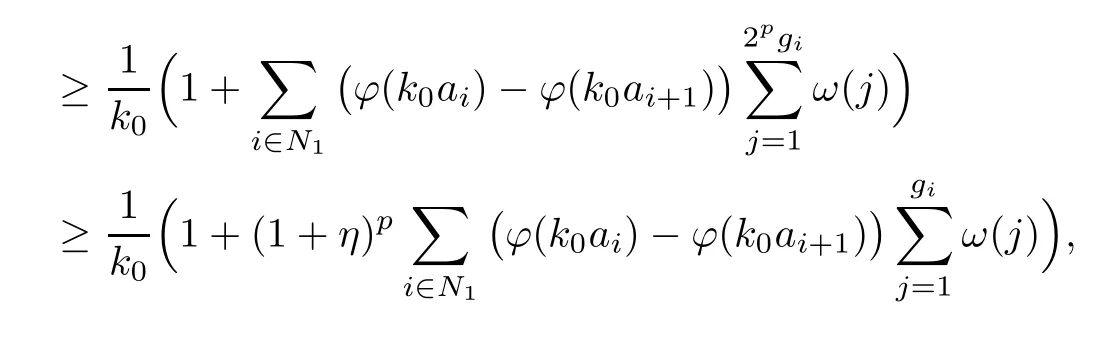


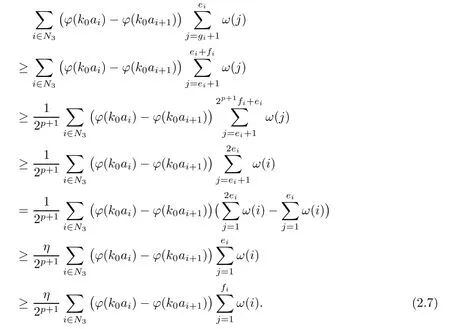
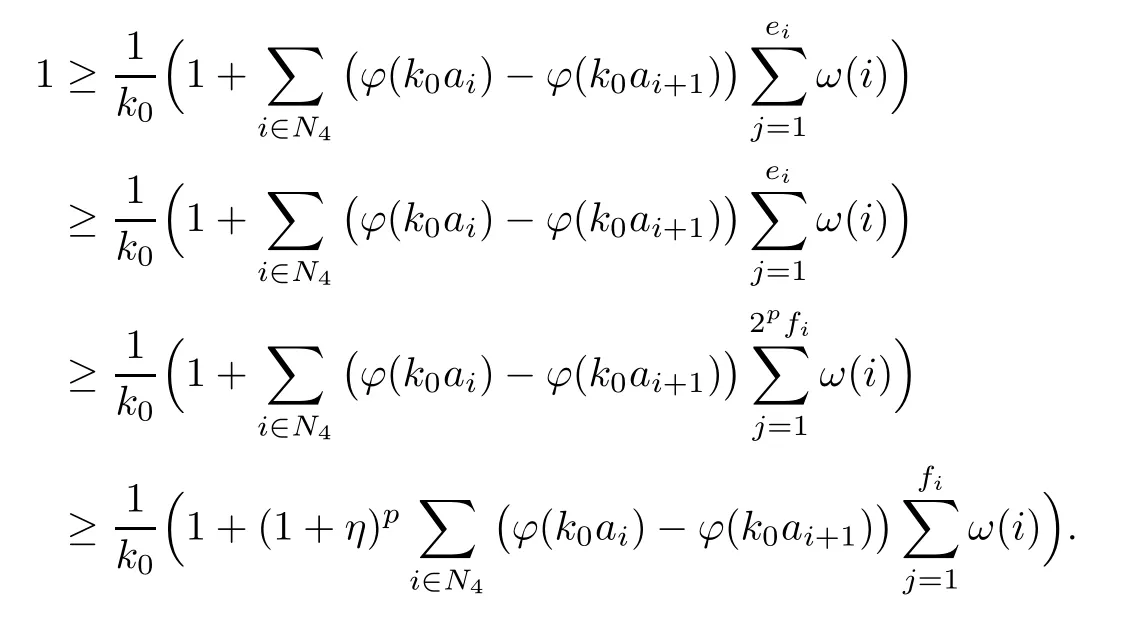
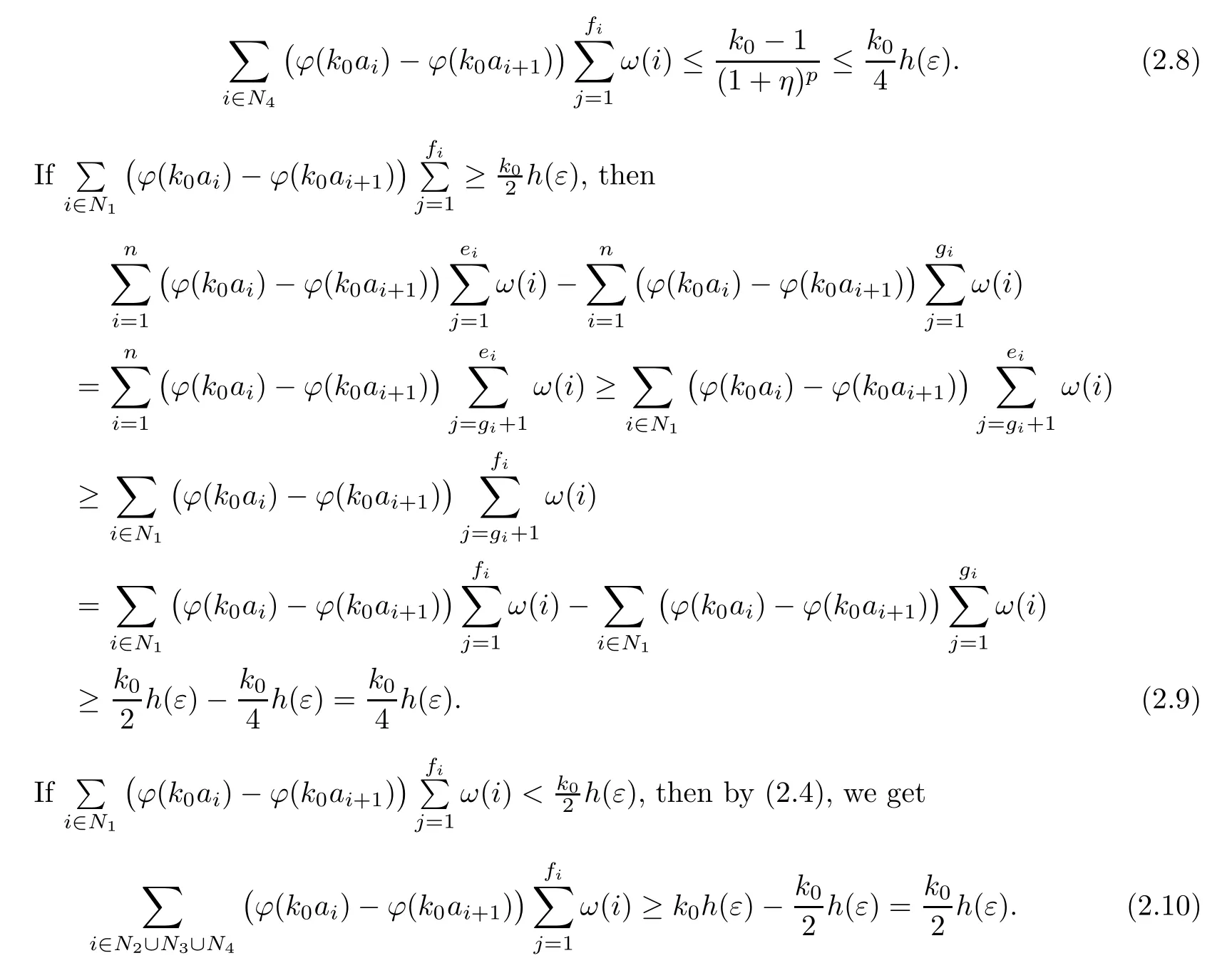
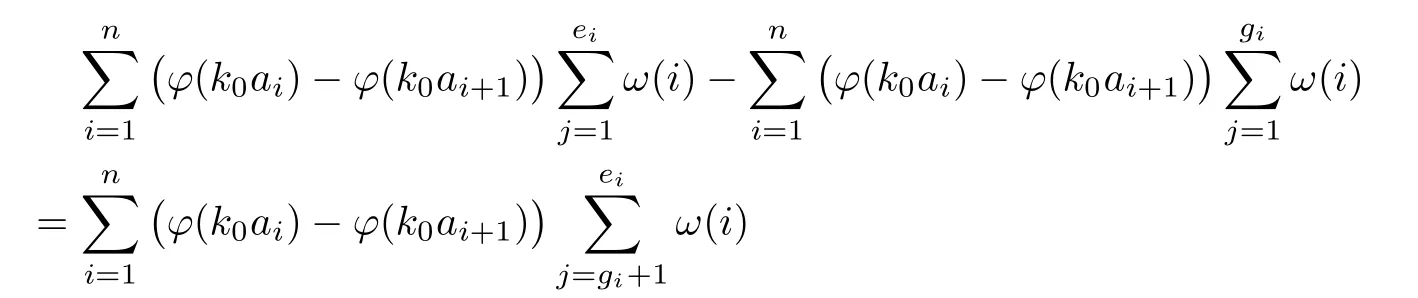

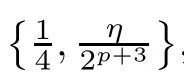
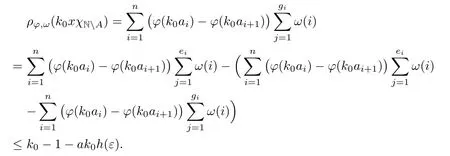
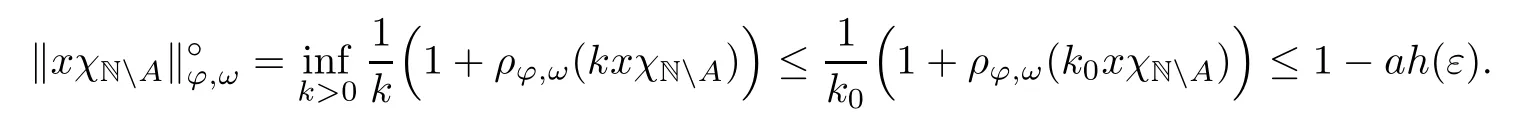
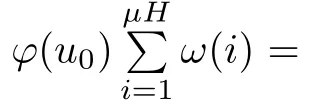
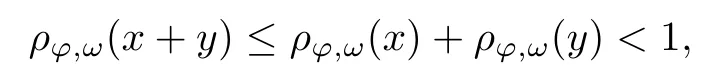
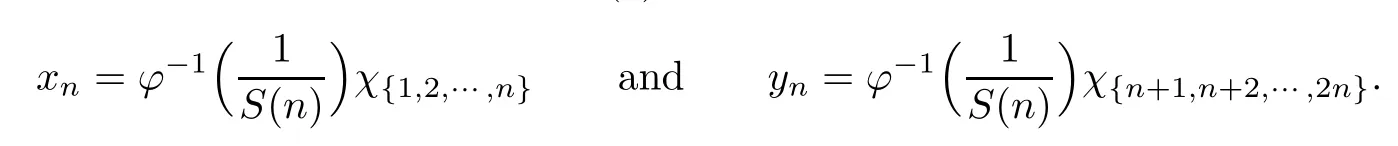
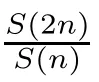
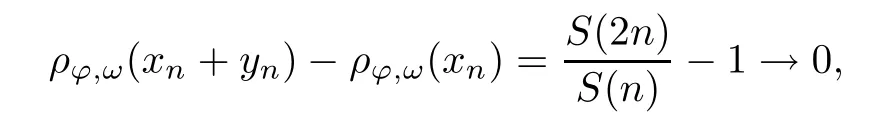
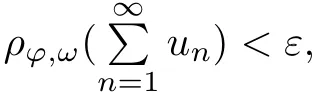
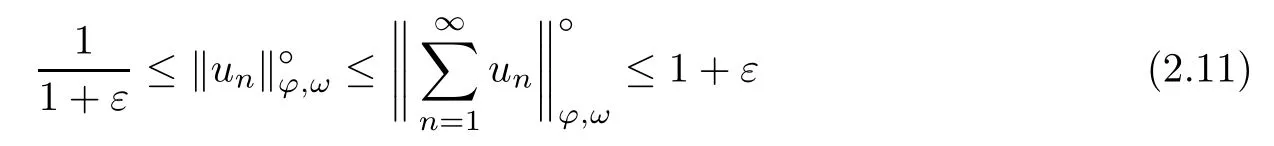
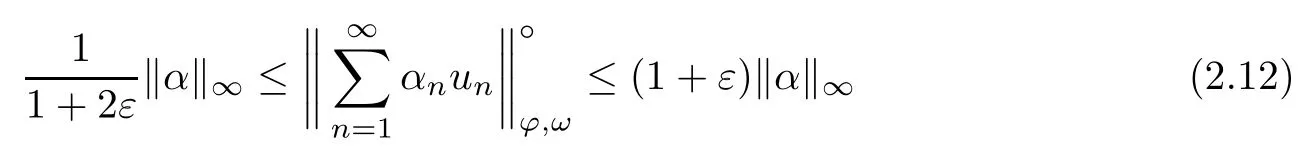

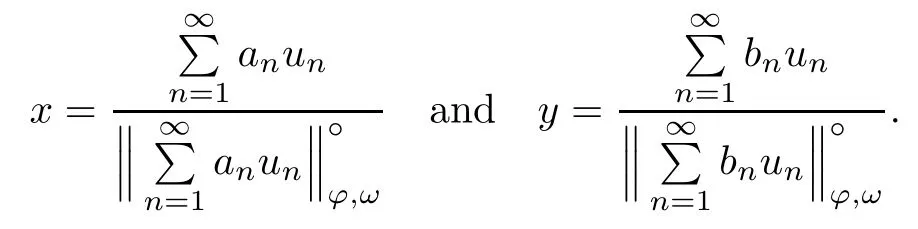
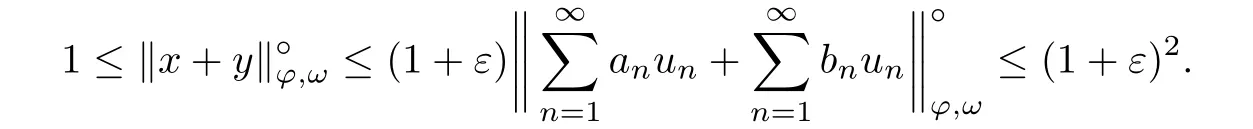
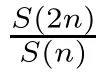
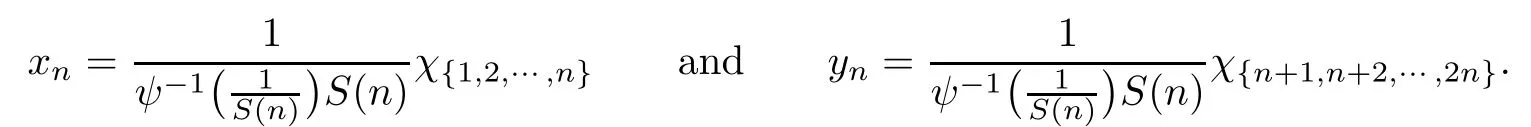
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
