Activin-A在人急性布魯菌感染中的作用及與其他炎性因子的關系
奧敦托婭,其其格
·臨床研究·
Activin-A在人急性布魯菌感染中的作用及與其他炎性因子的關系
奧敦托婭,其其格
目的 探討Activin-A在人急性布魯菌感染中的作用及與其他炎性因子的相關性。方法 選擇我院2015年1月—2016年1月收治的布魯菌感染者80例(觀察組),選擇同期體檢健康的成人80例(對照組),觀察兩組血Activin-A、降鈣素原(procalcitonin, PCT)、C反應蛋白(C reactive protein, CRP)和白細胞水平變化,分析Activin-A與PCT、CRP和血白細胞間的相關性,探討影響Activin-A水平的因素。結果 與對照組比較,觀察組Activin-A、PCT、CRP及白細胞水平均顯著升高,差異有統計學意義(P=0.000)。Pearson線性回歸分析顯示Activin-A與PCT、CRP和血白細胞均具有顯著相關性(P<0.05)。多元線性回歸分析顯示PCT、CRP和白細胞水平均可影響Activin-A的表達(P<0.05)。結論 Activin-A對判斷人急性布魯菌感染有一定的臨床價值,且與傳統的炎性指標顯著相關。
Activin-A;布魯桿菌病;C反應蛋白;降鈣素原
Activin-A為細胞間信號傳遞分子,系轉化生長因子-β(transforming growth factor-β, TGF-β)超家族成員之一,在脊椎動物中胚層誘導方面起重要作用,是近年發現的新型炎性指標,在膿毒癥與炎性疾病中具有較好的應用價值[1-2]。布魯菌病是一種人畜共患的傳染病,在內蒙古地區發病率較高,臨床表現復雜[3]。周珣等[4]檢測降鈣素原(procalcitonin, PCT)、C反應蛋白(C reactive protein, CRP)以判斷人急性布魯菌感染情況,結果顯示PCT和CRP在診斷人急性布魯菌病的陽性率僅為67.72%和59.06%。因此,臨床需尋找診斷布魯菌感染的新型指標,且聯合多指標檢測可能更有意義。本文探討Activin-A在人急性布魯菌感染中的價值,并分析其與傳統炎性指標的相關性,現將結果報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選擇我院2015年1月—2016年1月收治的布魯菌感染80例(觀察組),其中男48例,女32例;年齡18~62(43.68±12.57)歲。選擇同期體檢健康的成人80例(對照組),其中男51例,女29例;年齡18~60(43.26±13.72)歲。兩組年齡、性別等比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。觀察組均表現為發熱,其中出現骨關節疼痛65例,多汗45例,乏力28例,淋巴結增大21例,肝脾大11例。所有患者均知情同意并簽署知情同意書,本研究通過我院倫理委員會批準。
1.2 納入及排除標準 觀察組均符合人急性布魯菌感染的診斷標準[5]:①有流行病學接觸史;②有典型臨床表現,如發熱、乏力、多汗、關節疼痛和淋巴結增大等;③布魯菌病食管凝集試驗滴度≥1∶100(++)。排除標準:①7 d內合并其他急性或慢性感染;②傷寒或副傷寒;③結核;④風濕或類風濕;⑤霍亂;⑥瘧疾;⑦自身免疫性疾病;⑧惡性腫瘤。
1.3 觀察指標與檢測方法 觀察兩組血Activin-A、PCT、CRP和白細胞水平變化,分析Activin-A與PCT、CRP和白細胞之間的相關性,探討影響Activin-A水平的因素。Activin-A和PCT檢測方法:所有患者均清晨空腹抽取靜脈血5 ml,3000 r/min離心10 min后取上層血清,使用酶聯免疫吸附測定(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA)法檢測Activin-A和PCT,ELISA試劑盒均購自上海嵐派生物科技有限公司,具體步驟參考試劑盒說明書。CRP檢測使用金斯爾日立7180全自動生化分析儀,白細胞檢測使用MEK-6420P 全自動血液細胞分析儀。
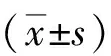
2 結果
2.1 兩組Activin-A、PCT、CRP和白細胞水平比較 與對照組比較,觀察組Activin-A、PCT、CRP及白細胞水平均顯著升高,差異有統計學意義(P=0.000),見表1。
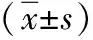
表1 布魯菌感染者和健康者Activin-A、降鈣素原、C反應蛋白和血白細胞水平比較
2.2 Activin-A與PCT、CRP和白細胞的相關性分析 Pearson線性回歸分析顯示Activin-A與PCT、CRP和白細胞均具有顯著相關性(P<0.05),見表2。
2.3 影響Activin-A水平的因素 多元線性回歸分析顯示PCT、CRP和白細胞水平均可影響Activin-A的表達(P<0.05),見表3。

3 討論
布魯菌病是由布魯菌引起的一種人畜共患傳染病,急性感染表現為菌血癥和膿毒血癥,嚴重者可伴多臟器功能衰竭[6]。Lee等[7]研究發現膿毒癥患者血清Activin-A水平與病情嚴重程度密切相關,表現為膿毒癥、重度膿毒癥和膿毒性休克的患者血清Activin-A水平分別為251、319和432 pg/ml,與序貫器官衰竭評分(sequential organ failure assessment, SOFA)、急性生理與慢性健康(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation scoring system, APPACHEⅡ)評分和院內死亡率呈明顯正相關。韓麗紅等[8]研究71例急性布魯菌感染,結果顯示該病可伴肝臟等多臟器功能損傷。
導致急性布魯菌病患者臟器功能損傷的原因與布魯菌感染引起的免疫功能損傷有關,早期表現為過度炎癥反應,晚期表現為免疫抑制。韓丹[9]探討新疆急性布魯菌感染者免疫功能狀況,結果顯示病變早期主要表現為CD4+和CD8+T淋巴細胞升高,晚期表現為CD8+T淋巴細胞升高,部分重癥患者早期即可表現為血白細胞降低等免疫抑制狀態。由于人急性布魯菌感染表現多樣,給臨床診斷帶來一定困難。王敬琦等[10]研究61例布魯菌感染,臨床表現為發熱、多汗、乏力、關節疼痛、胃腸道不適、淋巴結增大及肝脾大等癥狀,表現復雜多樣,缺乏特異性。因此,臨床急需尋找新型觀察指標以協助診斷并判斷布魯菌病病情嚴重程度。
Activin-A又稱免疫抑制素P,具有多種生物活性。作為TGF-β家族的一員,Activin-A與Smads及絲裂原活化蛋白激酶信號通路聯系密切,可促進腫瘤壞死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)和白介素-6(interleukin-6, IL-6)等炎性因子的表達,進而促進炎癥反應[11-12]。人感染布魯菌后可引發全身炎癥反應[13-14],而不可逆性炎癥反應可致機體多臟器功能衰竭,甚至死亡[15]。有研究顯示Avtivin-A在自身免疫性疾病中顯著升高,并參與Foxp3+和Foxp3-CD4+調節性T淋巴細胞的免疫應答過程[16]。本研究將自身免疫性疾病作為排除標準,避免了該病對結果造成的偏差,提高了結果的準確性。Activin-A亦可通過抑制半胱氨酸蛋白酶-1等因子,從而發揮抑制炎癥反應的作用[17-19]。由此可見,Activin-A具有促炎和抗炎的雙重功能,其在人急性布魯菌病中的具體作用機制及動態監測對臨床的指導意義等尚需進一步的研究證實。本研究結果顯示急性布魯菌感染者Activin-A水平顯著升高,與傳統炎性指標(PCT、CRP和白細胞)呈正相關,且傳統炎性指標可影響Activin-A的表達。本文首次探討了Activin-A在人急性布魯菌病中的表達及與傳統炎性指標的相關性,具有一定的創新性和臨床意義。
[1] Rosenberg V A, Buhimschi I A, Dulay A T,etal. Modulation of amniotic fluid activin-A and inhibin-A in women with preterm premature rupture of the membranes and infection-induced preterm birth[J].Am J Reprod Immunol, 2012,67(2):122-131.
[2] Linko R, Hedger M P, Pettila V,etal. Serum activin A and B, and follistatin in critically ill patients with influenza A (H1N1) infection[J].BMC Infect Dis, 2014,14(3):253.
[3] Tiryaki O, Usalan C, Aydin A. An unusual manifestation of brucellosis infection: acute renal failure[J].Ren Fail, 2010,32(6):747-749.
[4] 周珣,趙冬梅,鄭遵榮,等.人急性布魯桿菌病降鈣素原與C-反應蛋白含量研究及其臨床意義[J].職業與健康,2016,32(15):2158-2160.
[5] WS269-2007,布魯桿菌病診斷標準[S].
[6] 李靜,姚文海,張蕊.布魯桿菌感染血清學與細菌學檢測結果的比較[J].現代醫學,2012,40(1):83-85.
[7] Lee J K, Choi S M, Lee J,etal. Serum activin-A as a predictive and prognostic marker in critically ill patients with sepsis[J].Respirology, 2016,21(5):891-897.
[8] 韓麗紅,劉日宏,劉永華.急性布魯菌病患者強化期治療前后肝功能的變化[J].中國臨床研究,2013,26(4):328-330.
[9] 韓丹.新疆布魯氏菌病患者外周血T細胞亞群的臨床分析[D].烏魯木齊:新疆醫科大學,2016.
[10]王敬琦,胡雪靚,馬力揚.61例布魯桿菌病患者流行病學特征、臨床表現及療效分析[J].中國真菌學雜志,2015,10(5):288-290.
[11]Tania N P, Schmidt M, Gosens R. Activin-A: active in inflammation in COPD[J].Eur Respir J, 2014,43(4):954-955.
[12]Hardy J T, Buhimschi I A, McCarthy M E,etal. Imbalance of Amniotic Fluid Activin-A and Follistatin in Intraamniotic Infection, Inflammation, and Preterm Birth[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2016,101(7):2785-2793.
[13]Nullens S, Staessens M, Peleman C,etal. Beneficial Effects of Anti-Interleukin-6 Antibodies on Impaired Gastrointestinal Motility, Inflammation and Increased Colonic Permeability in a Murine Model of Sepsis Are Most Pronounced When Administered in a Preventive Setup[J].PLoS One, 2016,11(4):152914.
[14]Artigas A, Wernerman J, Arroyo V,etal. Role of albumin in diseases associated with severe systemic inflammation: Pathophysiologic and clinical evidence in sepsis and in decompensated cirrhosis[J].J Crit Care, 2016,33:62-70.
[15]Donnelly J P, Locke J E, MacLennan P A,etal. Inpatient Mortality Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients Hospitalized for Sepsis and Severe Sepsis[J].Clin Infect Dis, 2016,63(2):186-194.
[16]Huber S, Schramm C. Role of activin A in the induction of Foxp3+and Foxp3-CD4+regulatory T cells[J].Crit Rev Immunol, 2011,31(1):53-60.
[17]González-Domínguez E, Domínguez-Soto A, Nieto C,etal. Atypical Activin A and IL-10 Production Impairs Human CD16+Monocyte Differentiation into Anti-Inflammatory Macrophages[J].J Immunol, 2016,196(3):1327-1337.
[18]Petrakou E, Fotopoulos S, Anagnostakou M,etal. Activin-A exerts a crucial anti-inflammatory role in neonatal infections[J].Pediatr Res, 2013,74(6):675-681.
[19]Sierra-Filardi E, Puig-Kroger A, Blanco F J,etal. Activin A skews macrophage polarization by promoting a proinflammatory phenotype and inhibiting the acquisition of anti-inflammatory macrophage markers[J].Blood, 2011,117(19):5092-5101.
Effect of Activin-A in Human Acute Brucellosis Infection and Its Relationship with Other Inflammatory Factors
AODUNTUOYA, QIQIGE
(Department of Infection Diseases, Hospital Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, China)
Objective To investigate effect of activin-A in human acute brucellosis infection and its relationship with other inflammatory factors. Methods A total of 80 patients with acute brucellosis infection admitted during January 2015 and January 2016 were selected as observation group, and 80 healthy adults taking medical examination at the same period were collected as control group. Level changes of activin-A, procalcitonin (PCT), C reactive protein (CRP) and white blood cell were detected, and relationships between activin-A and PCT, CRP and white blood cell were analyzed, and influencing factors of activin-A level were studied in two groups. Results Compared with those in control group, activin-A, PCT, CRP and white blood cells levels were significantly increased in observation group (P=0.000). Pearson linear regression analysis showed that activin-A was significantly correlated with PCT, CRP and white blood cells (P<0.05). Multiple linear regression analysis showed that PCT, CRP and white blood cell affected activin-A expression (P<0.05). Conclusion Activin-A has a certain clinical significance in diagnosis of acute brucellosis infection, and it has significant relationship with traditional inflammatory indexes.
Activin-A; Brucellosis; C reactive protein; Procalcitonin
內蒙古衛計委醫療衛生科研項目(201302071)
010050 呼和浩特,內蒙古醫科大學附屬醫院感染科
R516.7
A
1002-3429(2017)06-0081-03
10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2017.06.030
2017-03-01 修回時間:2017-04-05)

