EDI-OCT對老年黃斑變性脈絡膜厚度的研究
潘 昕,楊 麗,賈志芳,陳哲慧,張大光*
(1.吉林大學第二醫院,吉林 長春130041;2.吉林大學第一醫院,吉林 長春130021)
EDI-OCT對老年黃斑變性脈絡膜厚度的研究
潘 昕1,楊 麗1,賈志芳2,陳哲慧1,張大光2*
(1.吉林大學第二醫院,吉林 長春130041;2.吉林大學第一醫院,吉林 長春130021)
目的 利用OCT加強深度掃描模式測量比較濕性和干性老年黃斑變性(AMD)脈絡膜厚度。方法 采用回顧性病例對照研究。對經眼底熒光造影(fundus fluorescein angiography,FFA)確診的以單側眼為濕性AMD且對側眼為干性AMD 的28例患者(56眼)作為研究組,另選取與AMD組年齡與性別相匹配的正常人30例30眼作為對照。使用光學相干斷層掃描的加強深度掃描模式(coherence tomography with enhanced depth imaging,OCT-EDI) 水平位及垂直位掃描黃斑區,測量黃斑中心凹下(subfoveal choroidal thickness,SFCT),距中心凹上方(S)、下方(I)、鼻側(N)及顳側(T)1.5 mm處5個不同點的脈絡膜厚度(Choroidal thickness,CT)。對所收集的數據均采用SPSS18.0統計軟件進行統計分析,以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。結果 SFCT厚度:濕性型老年黃斑變性組為203.29±14.98 μm、干性型老年黃斑變性組為155.86±25.19 μm、正常對照組為279.67±23.65 μm,濕性型組與其他組比較有顯著性差異(P<0.05)。結論 EDI-OCT是觀察AMD脈絡膜形態的有效方法。運用EDI-OCT對黃斑區脈絡膜厚度進行測量,有助于理解AMD 的病理生理機制。但仍需要大量前瞻性研究來探求濕性AMD中SFCT增厚的原因。
老年黃斑變性;脈絡膜厚度;EDI-OCT
(ChinJLabDiagn,2017,21:1128)
老年黃斑變性(AMD)是遺傳和環境因素共同誘發的與年齡相關的一組退行性黃斑病變,是當前60歲以上人口致盲的重要疾病,分為濕性型與干性型兩種類型[1]。AMD主要是由于視網膜色素上皮細胞(RPE)的形態和功能的改變而導致對視細胞外節盤膜吞噬消化功能下降,導致在視網膜下代謝物(drusen)的堆積[2]。脈絡膜富有豐富的血流,主要為RPE和視網膜外層提供營養及代謝支持,在眼后節的重大疾病的發病機制起著重要的作用,比如AMD,中心性漿液性脈絡膜視網膜病變,息肉狀脈絡膜血管病變和病理性近視性視網膜病變[3]。因此,脈絡膜血液循環障礙在drusen的形成起了重要的作用。頻域相干光斷層深度增強成像 (EDI -OCT )是在頻域相干光斷層成像技術(SD-OCT )的基礎上通過深度增強成像技術 ,可以清楚的觀察網膜、脈絡膜組織形態的變化及對脈絡膜厚度進行測量[4,5]。為此,我們利用EDI-OCT分別對濕性與干性AMD患者的中心凹下脈絡膜厚度(SFCT)進行測量,來評價脈絡膜在AMD中的改變。
1 資料與方法
1.1 研究對象
回顧性研究。研究獲得本院單位倫理委員會批準并獲取患者知情同意。選擇我院2016年1月至2016年9月首次就診并確診的以單側眼為濕性AMD且對側眼為干性AMD 的28例患者(56眼)作為研究組,另選取與AMD組年齡,性別和屈光度相匹配的正常人30例30眼作為對照。測量結果在亞組間進行統計學對比研究。干性AMD組研究對象是黃斑區有玻璃疣和/或色素變化眼,而濕性AMD組研究對象是由于脈絡膜新生血管而致視網膜下或視網膜內有滲出液和/或脂性滲出眼。
1.2 方法
所有患者均行最佳矯正視力(BCVA)、間接檢眼鏡、熒光素眼底血管造影(FFA)、頻域光相干斷層掃描(SD-OCT)檢查。BCVA檢查采用國際標準對數視力表進行,檢測結果轉換為最小分辨角對數(logMAR)記錄。參考文獻[6]確立本組患者的納入標準。排除標準:(1)合并或患有DR、葡萄膜炎、高度近視黃斑變性等眼底血管性疾病;(2)既往接受過眼內藥物注射,視網膜激光光凝或眼科手術;(3)屈光間質混濁影響眼底成像,如嚴重的白內障或玻璃體積血;(4)有眼外傷史。
我們運用SD-OCT(Heidelberg Spectralis,海德堡)的EDI模式對AMD組和對照組黃斑區脈絡膜進行檢測,由同一操作者完成。為了獲得清晰的圖像,被檢者在檢測前均用0.5% 復方托吡卡胺散瞳。對黃斑部水平和垂直方向進行高清 25線光柵(HD12Line Raster12-line radial scan)模式掃描。每個掃描線為20度,掃描深度為2 mm,掃描長度隨病變范圍而調整(6-9 mm)。
脈絡膜厚度的定義為視網膜色素上皮細胞(retinal pigment epithelium,RPE)高反射線外緣至鞏膜內層反射線的垂直距離(圖1)。測量SFCT以及距中心凹1 500 μm處上方(S)、下方(I)、鼻側(T)和顳側(N)5個位點的脈絡膜厚度(圖2),所有測量由同一位有經驗的醫生獨立完成,每個值分別測量3次,取平均值作為測量結果。

圖1 黃斑區OCT-EDI 圖像
黃斑中心凹脈絡膜厚度如圖所示,為中心凹位置 RPE 外界和鞏膜內界之間的距離

a:濕性AMD黃斑區OCT的圖像,SFCT值為145 μm;b:干性AMD黃斑區OCT圖像,SFCT值為135 μm; c:正常對照組黃斑區的OCT圖像,SFCT值為288 μm。
圖2 濕性AMD、干性AMD和對照組的 OCT-EDI圖像
1.3 統計學方法
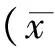
2 結果
2.1 研究對象的一般資料分析
本研究共納入28 例56 眼AMD患者做為研究組,正常對照組 30例 30眼。兩組之間的性別、年齡和屈光度比較均無統計學差異(P=0.75,0.50,0.67;表1)。

表1 AMD組與正常對照組臨床資料分析
2.2 濕性AMD組和干性AMD組、正常對照組的脈絡膜厚變比較
濕性型AMD患眼、干性型AMD患眼和正常對照組SFCT、T、N、S和I的平均CT值見表2。濕性型AMD患眼組的SFCT和對側干性型AMD患眼組與正常對照組比較均有顯著性降低(P<0.05,表3)。

表2 平均脈絡膜厚度CT值(μm)
AMD:老年黃斑變性; SFCT:中心凹下脈絡膜厚度; N1500:中心凹鼻側1 500 μm; S1500:中心凹上方1 500 μm; T1500:中心凹顳側1 500 μm; I1500:中心凹下方1 500 μm

表3 各組間脈絡膜厚度比較的P值
AMD:老年黃斑變性; SFCT:中心凹下脈絡膜厚度; N1500:中心凹鼻側1 500 μm; S1500:中心凹上方1 500 μm; T1500:中心凹顳側1 500 μm; I1500:中心凹下方1 500 μm ;P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
3 討論
近年來,很多學者應用OCT-EDI 來測量研究脈絡膜厚度。影響脈絡膜厚度的主要原因就是年齡。Margolis等[7]認為脈絡膜的厚度是隨年齡的增長而下降,平均年齡每增加10 歲,黃斑中心凹下脈絡膜厚度下降15.6 μm。此外, 脈絡膜厚度還與屈光度[8],性別[9],日波動[10]相關。所以為了避免這些因素對SFCT測量值的影響,我們在選擇病例時,正常對照組與病例組在年齡、性別和屈光度上完全匹配,避免了因選擇病例造成的結果偏差。
本研究表明濕性型AMD組的SFCT(203.29±14.98 μm)和干性型AMD組(155.86±25.19 μm)與正常對照組(279.67±23.65 μm)比較均有顯著性降低。濕性型AMD組的SFCT與干性型AMD組比較沒有顯著性差異。我們發現干性型AMD的SFCT降低是和其他的學者的研究是一致的。Ko等[11]報道玻璃膜疣的面積和脈絡膜厚度是成負相關的。Lee等[12]認為黃斑中心凹下脈絡膜厚度與非滲出型AMD的嚴重程度和視力密切相關。干性型AMD患者的SFCT降低是脈絡膜的血容量降低和異常的血流,導致了脈絡膜毛細血管官腔縮小,細胞喪失,脈絡膜萎縮,并且隨著病情的發展而惡化[13]。這可以通過AMD患者ICGA 的脈絡膜充盈延遲來證實[14]。Chen等[15]也發現AMD患者的FA顯示脈絡膜血管充盈延遲,他們認為脈絡膜血管循環異常在AMD的發病機制中起到一定的作用。
濕性AMD患者的SFCT降低也被先前的一些學者證實。Chung等[16]認為相同年齡下新生血管AMD患者早期非新生血管AMD患者的SFCT較正常對照組降低。 McCourt等[13]研究表明新生血管AMD的SFCT為209.9 μm,非新生血管AMD為162.4 μm,正常對照組為305.7 μm,新生血管和非新生血管AMD的SFCT比正常對照組比較,明顯降低。濕性型AMD患者SFCT降低的原因可能因為AMD患者黃斑區下脈絡膜大血管層萎縮,而小血管層密度相對增加。那么同一患者濕性AMD眼的脈絡膜為什么沒有對側干性AMD眼的脈絡膜厚度更明顯減少呢? 有研究認為早期AMD的脈絡膜開始變薄,隨著脈絡膜血流的減少,支持RPE及外層網膜營養下降,導致促新生血管生長因子的大量分泌,引起脈絡膜新生血管生長,這些血管的通透性增加,從而導致脈絡膜間質的水腫造成[17]。
關于AMD中脈絡膜厚度的變化目前還頗有爭議。Jonas等[18]發現在年齡、屈光度、眼軸長匹配的204眼新生血管型和中間型AMD中,SFCT較228眼正常對照組并沒有明顯改變。Yiu等[19]研究了測量了161例322 眼早期和進展期AMD的SFCT,與154眼正常對照比較后,認為脈絡膜厚度并未因AMD的進展而改變。然而與此相反,Unsal 等[17]卻發現新生血管性AMD組中平均 SFCT (310±90.16 μm)較非新生血管性 AMD 組(221±36.87 μm)和對照組(259±19.25 μm)明顯增厚,認為這是由于新陳代謝增強的需要進而繼發脈絡膜新生血管活動而導致。
[1]Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group.A simplified severity scale for age-related macular degeneration[J].Arch Ophthalmol,2005,123(11):1570.
[2]Linsenmeier RA,Padnick-Silver L.Metabolic dependence of photoreceptors on the choroid in the normal and detached retina[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2000,41(10):3117.
[3]Gass JD.A clinicopathologic study of a peculiar foveomacular dystrophy[J].Trans Am Ophthalmology Soc,1974,72:139.
[4]Wei WB,Xu L,Jonas JB et al.Subfoveal choroidal thickness:the Beijing Eye Study[J].Ophthalmology,2013,120(1):175.
[5]Shao L,Xu L,Chen CX,et al.Reproducibility of subfoveal choroidal thickness measurements with enhanced depth imaging by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2013,54(1):230.
[6]Group AR,Chew EY,Clemons T,et al.The Age-Related Eye Disease Study 2 (AREDS2):study design and baseline characteristics (AREDS2 report number 1)[J].Ophthalmology,2012,119(11):2282.
[7]Margolis R,Spaide RF.A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2009,147(5):811.
[8]曾 婧,丁小燕,李加青,等.中國人黃斑區脈絡膜厚度值及其影響因素分析[J].中華眼底病雜志,2011,27(5):450.
[9]Li XQ,Larsen M,Munch IC.Subfoveal choroidal thickness in relation to sex and axial length in 93 Danish university students[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2011,52(11):8438.
[10]Tan CS,Ouyang Y,Ruiz H,et al.Diurnal variation of choroidal thickness in normal,healthy subjects measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2012,53(1):261.
[11]Ko A,Cao S,Pakzad-Vaezi K,et al.Optical coherence tomography-based correlation between choroidal thickness and drusen load in dry age-related macular degeneration[J].Retina,2013,33(5):1005.
[12]Lee JY,Lee DH,Lee JY,et al.Correlation between subfoveal choroidal thickness and the severity or progression of nonexudative age-related macular degeneration[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2013,54(12):7812.
[13]McCourt EA,Cadena BC,Barnett CJ,et al.Measurement of sub - fovealchoroidal thickness using spectral domain optical coherence tomography[J].Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging,2010,41:S28.
[14]吳德正,文 峰,黃時洲,等.滲出型老年黃斑變性的吲哚青綠血管造影特征[J].中華眼底病雜志,1998,14(2):76.
[15]ChenJE,FitzkeFW,PauleikhoffD,et al.Functional loss in agerelated Bruchs membrane change with choroidal perfusion defect[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,1992,33(2):334.
[16]Chung SE,Kang SW,Lee JH,et al.Choroidal thickness in polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and exudative age-related macular degeneration[J].Ophthalmology,2011,118(5):840.
[17]Unsal E,Eltutar K,Osmanbasoglu OA,et al.Evaluation of choroidal thickness in cases with age-related macular degeneration[J].International Eye Science 2014,14(9):1561.
[18]Jonas JB,Forster TM,Steinmetz P,et al.Choroidal thickness in age-related macular degeneration[J].Retina,2014,34(6):1149.
[19]Yiu G,Chiu SJ,Petrou PA,et al.Relationship of central choroidal thickness with age-related macular degeneration status[J].Am J Ophthalmol,2015,159(4):617.
Assessment of choroidal thickness of age related macular degeneration by optical coherence tomography with enhanced depth imaging
PANXin,YANGLi,JIAZhi-fang,etal.
(TheSecondHospitalofJilinUniversity,Changchun,Jilin130041,China)
Objective To compare choroidal thickness in patients with dry-or wet -age-related macular degeneration (AMD) using enhanced-depth imaging optical coherence tomography (EDI-OCT).Methods This was a retrospective study including 28 patients who had wet AMD in one eye and dry AMD in the other eye diagnosed by fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA).30 healthy controls (30 eyes) with age,gender and diopter - matched were selected as the control group.EDI-OCT were used to measure the subfoveal choroidal thickness (SFCT) in wet AMD eyes,the fellow eyes and also the control eyes.Choroidal thickness (CT) was measured at 5 different points,from 1.5 mm nasal(N),temporal(T),superior(S),and inferior(I) to the subfovea (subfoveal choroidal thickness,SFCT) in the study groups and compared statistically between subgroups using SPSS 18.0 software.Results The mean age of patients was72.4±8.97 (60-82)y.The mean age of healthy individuals was 71.2±8.8 (58-81) y.The mean SFCT of wet AMD group,dry AMD group and the controls was 203.29±14.98 μm,155.86±25.19 μm and 279.67±23.65 μm,respectively.Mean SFCT of wet AMD group were significantly thicker compared to the dry AMD group and the controls.(P=0.008 and 0.013,respectively).Conclusion EDI- OCT is a useful method to assess the choroidal topographic changes of AMD.Choroidal thickness measurements with EDI-OCT can make a contribution to the understanding the phatophysiology of AMD.Large prospective studies should be conducted to validate why SFCT was thicker in wet AMD
age-related macular degeneration;choroidal thickness;EDI-OCT
吉林省教育廳“十三五”科學技術研究資助[吉教科合字(2016)473號]
1007-4287(2017)07-1128-04
R774.5
A
2016-11-16)
*通訊作者

