水下阻抗球(柱)內部質點振速分布規律研究
趙天吉,陳洪娟
?
水下阻抗球(柱)內部質點振速分布規律研究
趙天吉1,2,陳洪娟1,2
(1. 哈爾濱工程大學水聲工程學院,黑龍江哈爾濱 150001; 2. 哈爾濱工程大學水聲技術重點實驗室,黑龍江哈爾濱 150001)
針對同振式矢量水聽器的物理模型,將其考慮成一個聲場中靜止的阻抗球體或柱體,建立了平面波作用下的聲場模型,并依據簡正波理論推導了球體和柱體內部的聲場特性,得到了阻抗球體和柱體內部各個位置處的振速與水質點振速的關系表達式,分析了不同材料參數和幾何參數下其內部質點振速的分布規律。研究結果對以后矢量水聽器的研制過程中材料的選擇與結構尺寸的設計具有指導意義。
阻抗球;阻抗柱;矢量水聽器;簡正波;
0 引言
目前大多數文獻中,對同振式矢量水聽器的理論模型的研究都將其考慮成剛性球或柱體,采用水下剛性球體(或柱體)的自由振動理論,研究其外部的聲場特性對水聽器整體振動特性的影響。但是在實際的工程設計制作過程中,選取的材料無論是金屬材料還是粘彈性材料,它們的聲阻抗都未能遠遠大于水介質。因此把矢量水聽器當作一個水下自由振動的阻抗球或柱體更為恰當。
對于水下阻抗體的聲場特性問題的分析,與剛性體的聲場類似,以往學者也比較關注其外部的散射特性。例如國外學者Lax和Feshbach[1]利用相移分析的方法計算了阻抗球體和柱體的聲吸收和散射問題;VICTOR C.ANDERSON[2]為了研究海洋生物對聲吶聲束造成的偏轉問題,以及其對聲信號傳播造成的衰減問題,分析了大尺寸阻抗球的遠場散射特性;在此基礎上,H. G. Frey[3]計算了脈沖波聲場下散射波的時間特性,國內學者張攬月[4]、時勝國[5]等分析了導流罩的內部聲場狀態對水聽器測量精度的影響,稽建飛[6]利用阻抗邊界條件分析了阻抗球的散射聲場特性。
對于矢量水聽器而言,阻抗球體和柱體的內部聲場問題更值得關注和研究,而以往學者對其也有過一定的考慮,例如,Benjamin A. Cary[7]利用了粘彈性球體內部各位置處的質點振速的不同發明設計了一種高指向性水聽器,但是其并未對阻抗球體內部的聲場特性加以闡述和推導,尤其是材料聲速對振速響應的相位影響也未見文獻有過分析和計算。本文對阻抗球體和柱體內部振速的頻響特性、材料參數和幾何參數對其頻帶穩定性的影響以及振速分布的均勻性進行了研究和討論。
1 水下阻抗球體和柱體的聲場模型
1.1 阻抗球內部聲場推導
取球坐標系,令其軸與入射平面波(幅值為1)的傳播方向一致,并且坐標系的原點與阻抗球球心重合,如圖1所示。假設阻抗球的半徑為,阻抗球體材料的密度和聲速分別為1、1,水介質的密度和聲速分別為0、0。
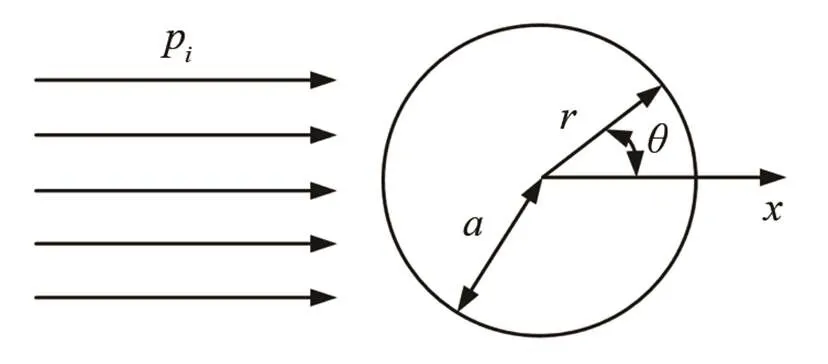
圖1 阻抗球聲場模型

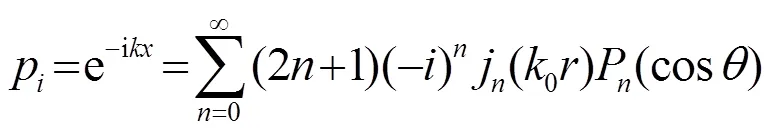
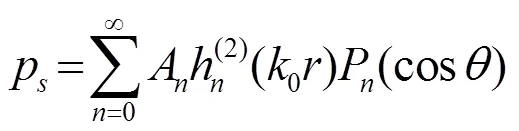
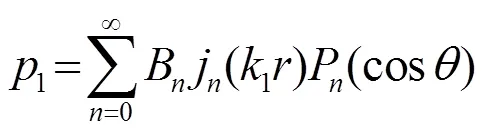
其中,為散射系數,為內聲場系數。
在阻抗球邊界處,內外聲場需要滿足聲壓連續和振速連續條件,將式(1)~(3)式和根據尤拉方程得到的質點振速代入邊界條件得到方程組:
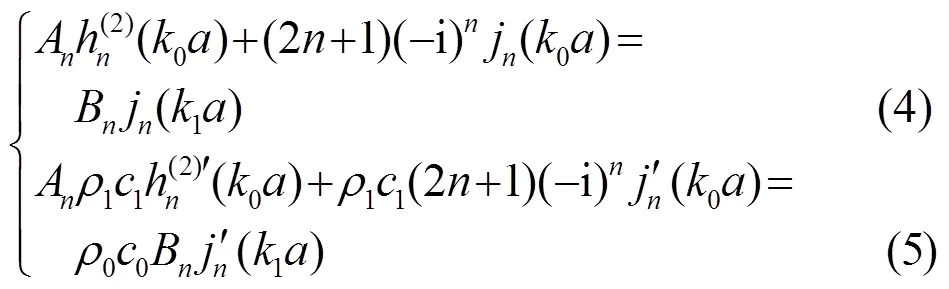
利用克萊姆法則和貝塞爾函數的Wronskian行列式可以得到
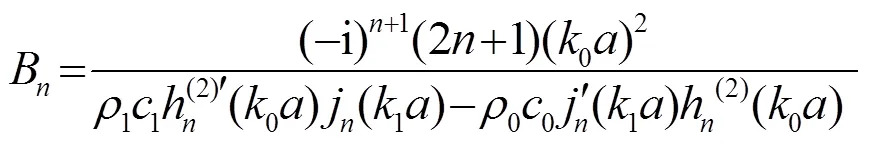
那么,阻抗球內部各位置處質點振速則為
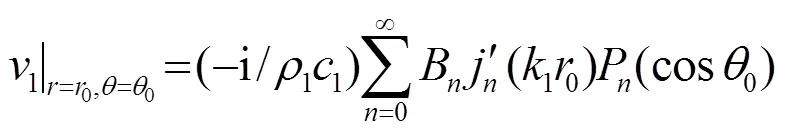
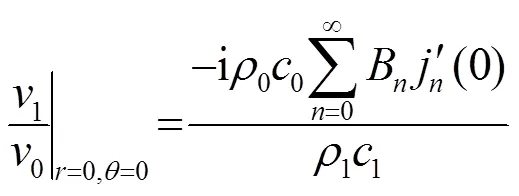
1.2 阻抗柱內部聲場推導
雖然矢量水聽器的實際模型為有限長柱體,但是由文獻[8]可知,對于有限長圓柱體,當柱體長度大于截面直徑時,其內部聲場分布狀態可認為與無限長圓柱體相同,即阻抗柱體內外聲場均與軸方向無關,因此取柱坐標系,令其軸與入射平面波(幅值為1)的傳播方向一致,并且坐標系的原點與阻抗柱中心重合,如圖2所示。假設阻抗柱體的半徑為,阻抗柱體材料的密度和聲速分別為1、1,水介質的密度和聲速分別為0、0。
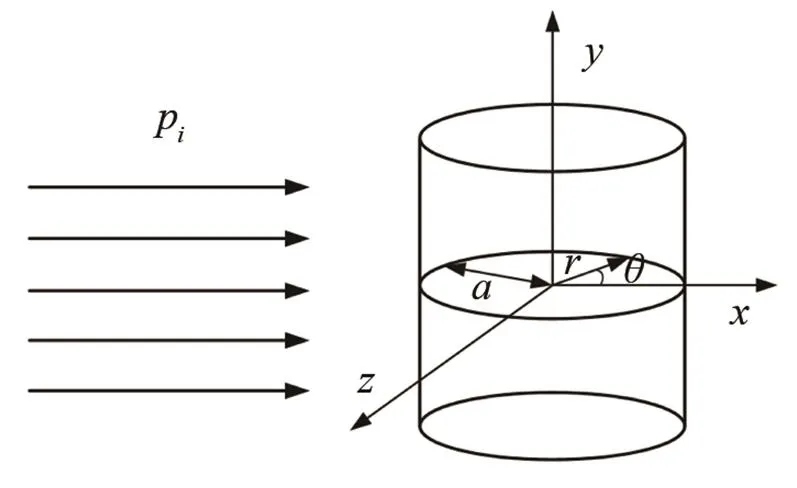
圖2 阻抗柱聲場模型

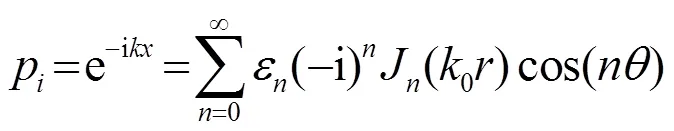
阻抗柱外部散射聲壓為
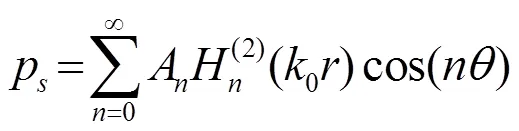
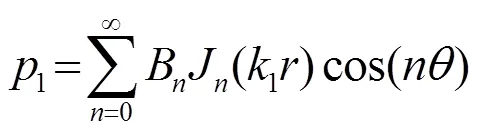
采用與阻抗球一樣的邊界條件處理方法可以得到
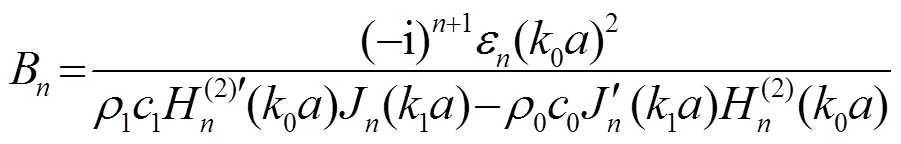
那么,阻抗柱內部各位置處質點振速則為
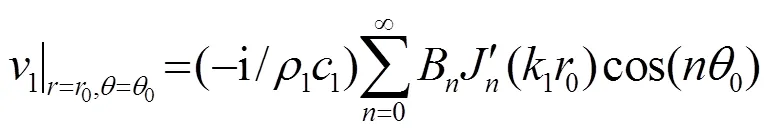
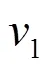
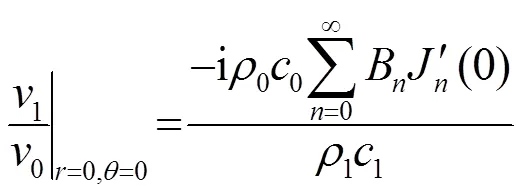
2 數值計算分析
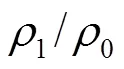
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
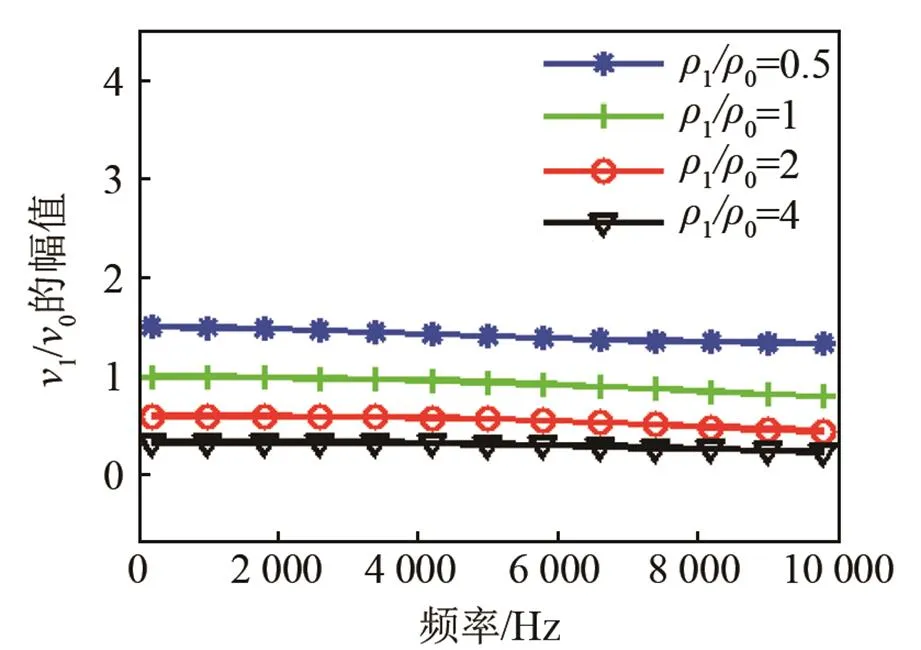
圖3 阻抗球中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的1/0)
Fig.3 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance sphere for different1/0
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
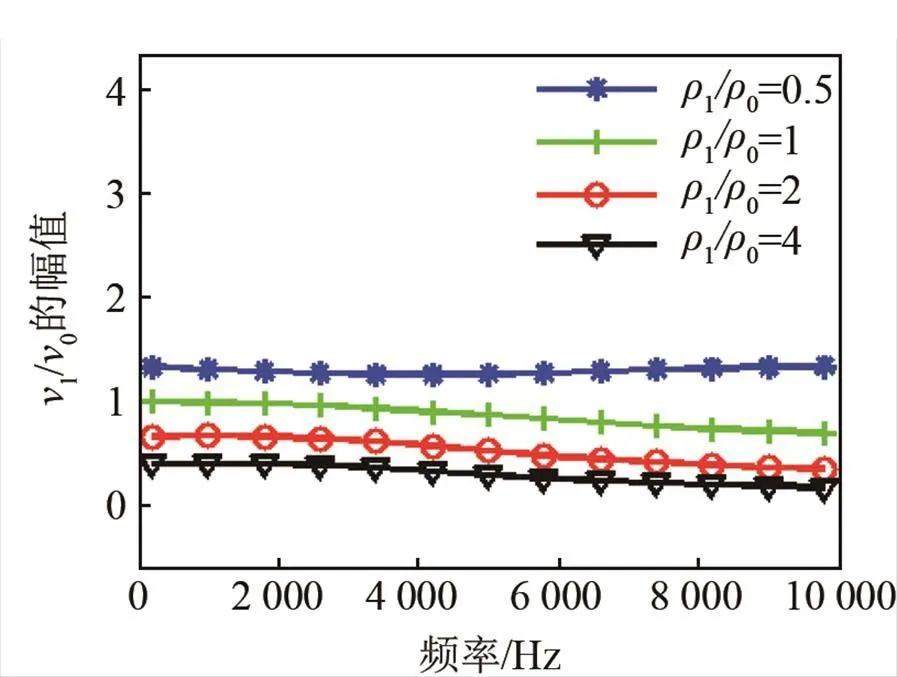
圖4 阻抗柱中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的1/0)
Fig.4 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance cylinder for different1/0
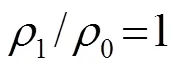
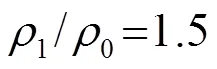
對比圖3~8對應的計算結果可以得出以下結論:
(1) 當聲速一定時,中心處振速幅值隨著材料密度的增大而減小;
(2) 當密度一定時,聲速的變化對振速幅值影響不明顯,在低頻范圍內可以認為是不變的;
(3) 隨著頻率升高,阻抗球體和柱體受外部散射影響變大,振速幅值開始變小,中心處振速與水質點振速的相位差開始變大。這種現象在密度較小時較為明顯,隨著密度的增大,振速頻響曲線變得更平坦;
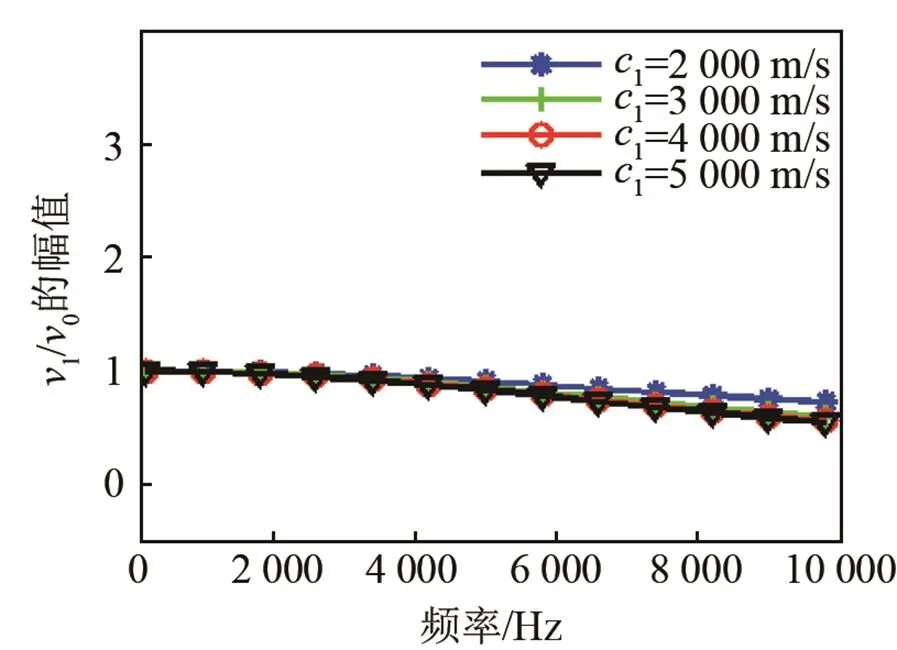
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
圖5 阻抗球中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的1)
Fig.5 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance sphere for different1
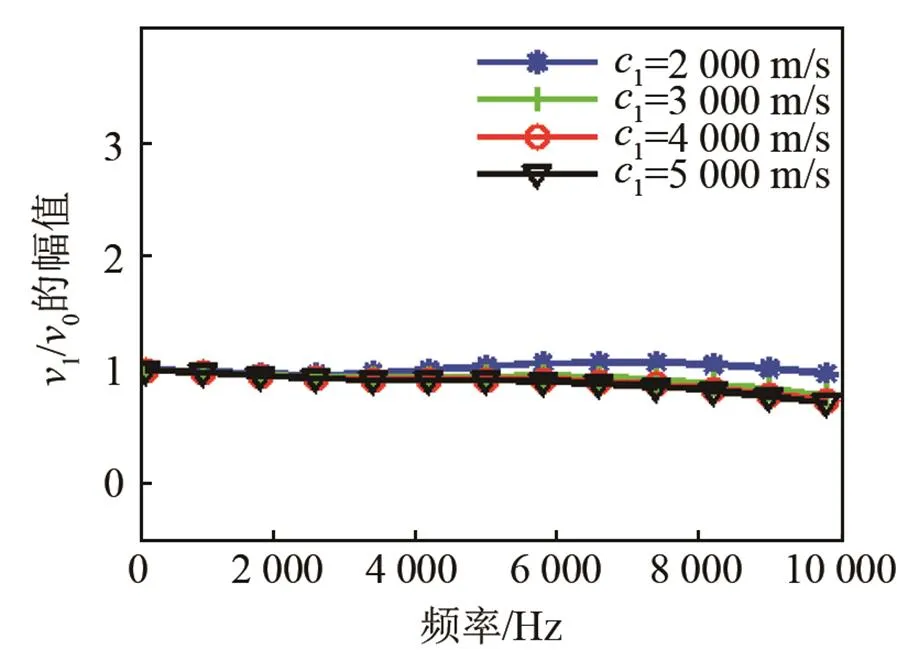
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
圖6 阻抗柱中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的1)
Fig.6 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance cylinder for different1
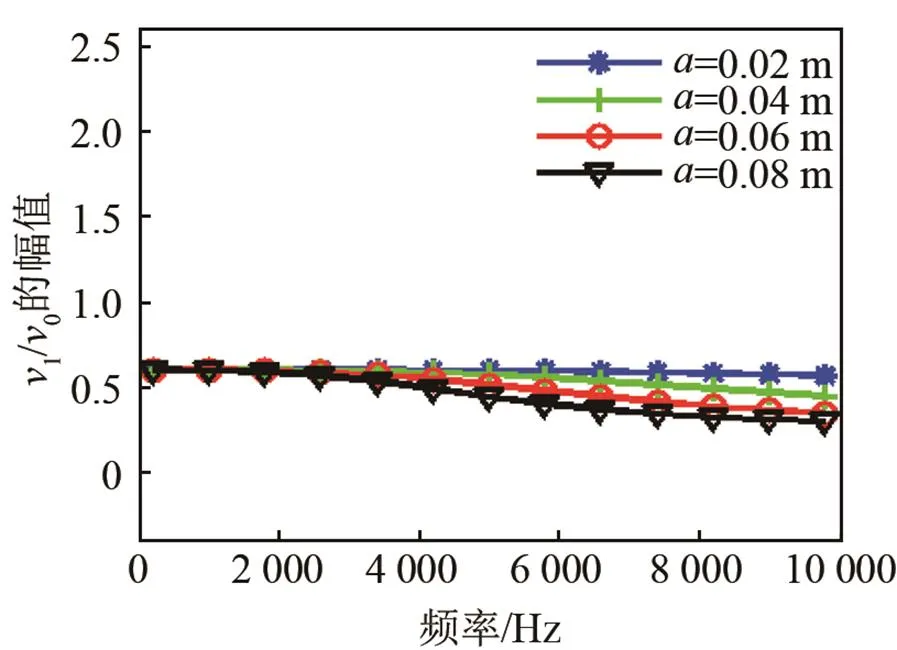
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
圖7 阻抗球中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的)
Fig.7 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance sphere for different
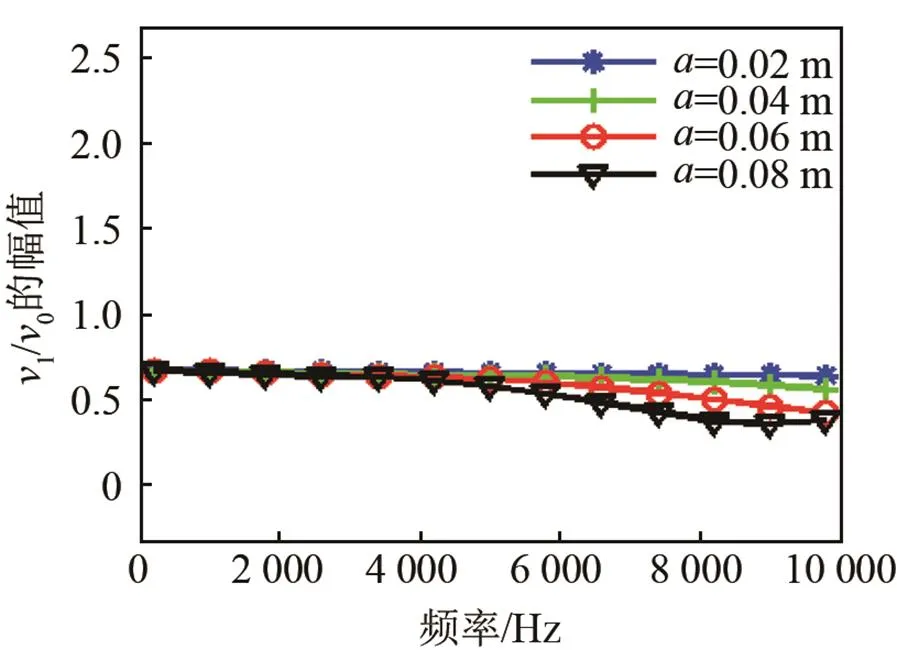
(a) 幅頻特性
(b) 相頻特性
圖8 阻抗柱中心處振速特性曲線(對不同的)
Fig.8 Vibration velocity curves at the center of impedance cylinder for different
(4) 在高頻范圍內,散射影響隨著尺寸的增大而越來越明顯,造成振速衰減越來越明顯, 相位差越來越大。
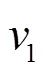
(a) 阻抗球
(b) 阻抗柱
圖9 頻率100 Hz下阻抗球(柱)內部振速分布云圖
Fig.9 Nephograms of internal vibration velocity distribution for impedance sphere and cylinder at 100 Hz
(a) 阻抗球
(b) 阻抗柱
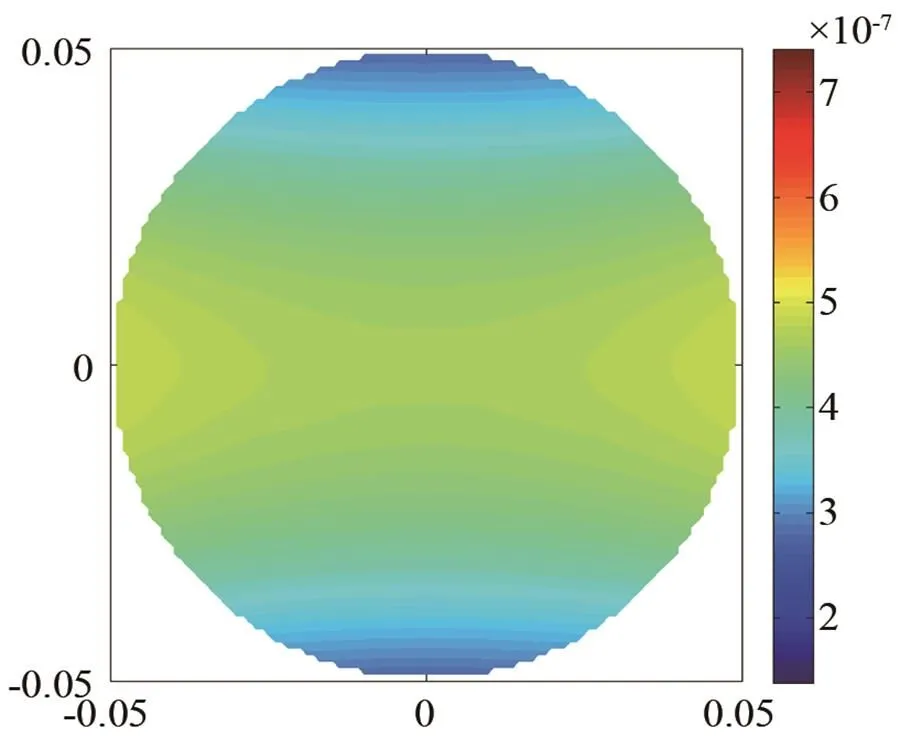
圖10 頻率1 000 Hz下阻抗球(柱)內部振速分布云圖
Fig.10 Nephograms of internal vibration velocity distribution for impedance sphere and cylinder at 1 000 Hz
3 結論
首先從阻抗球體和柱體的聲場模型入手,利用了簡正波理論推導并計算了聲波從水介質進入到固體介質以后,阻抗球體和柱體內部的振速分布規律;其次,通過對比計算結果可以看到不同材料參數和幾何參數下振速的頻率響應的變化規律。本文所得到的分析結果為矢量水聽器的研制提供了新的理論設計依據。
[1] Lax M, Feshbach H. Absorption and scattering for impedance boundary conditions on spheres and circular cylinders[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1948, 20(2): 108-124.
[2] Anderson V C. Sound scattering from a fluid sphere[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1950, 22(4): 426-431.
[3] Frey H G, Goodman R R. Acoustic scattering from fluid spheres[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1962, 34(5): 740-740.
[4] 張攬月. 導流罩對矢量水聽器性能影響研究[C]//全國水聲學學術會議. 2007. ZHANG Lanyue. The performance of vector hydrophone affected by demo[C]//The Underwater Acoustics Academic Meeting. 2007.
[5] 時勝國, 楊德森, 陳志剛. 薄壁球形導流罩對矢量水聽器接收性能的影響[J]. 應用聲學, 2009, 28(5): 342-349.SHI Shengguo, YANG Desen, CHEN Zhigang. Influence of thinwalled spherical dome on the receiving performance of vectorhydrophone[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2009, 28(5): 342-349(inChinese).
[6] 嵇建飛. 聲障板對矢量傳感器指向性的影響研究[D]. 哈爾濱: 哈爾濱工程大學, 2012: 11-14. JI Jianfei. Research on the effect of sound baffle on the directivity of vector sensor[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2012: 11-14.
[7] Cray B A, Evora V F. Highly directive underwater acoustic receiver: Acoustical Society of America Journal: US, 6697302 B1[P]. 2004-02-24.
[8] Stanton T K. Sound scattering by cylinders of finite length. II. Elastic cylinders[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1988, 83(1): 64-67.
The vibration velocity distribution of internal particles in underwater impedance sphere or cylinder
ZHAO Tian-ji1,2, CHEN Hong-juan1,2
(1.Acoustic Science and Technology Laboratory, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001,Heilongjiang, China;2. College of Underwater Acoustic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin,150001,Heilongjiang, China)
Based on the physical model of co-oscillating vector hydrophone, the hydrophone is considered as an impedance sphere or cylinder vibrating freely under the action of sound waves. The sound field models of impedance sphere and cylinder are established and the characteristic of internal sound field is derived based on the normal-mode theory. And then the relationships between the outside water particle vibration velocities and the internal particle vibration velocities at different positions in sphere and cylinder are derived. According to the calculation of frequency response under different materials and geometric parameters, the distribution of internal particle velocity is obtained. The results of the study are helpful for the material selection and the structure size design in developing new vector hydrophone.
impedance sphere; impedance cylinder; vector hydrophone; normal-mode
TB5651
A
1000-3630(2017)-01-0017-06
10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2017.01.004
2016-03-24;
2016-05-22
國家自然科學基金資助項目(11474075); 技術基礎基金項目 (J053915001)。
趙天吉(1988-), 男, 吉林白城人, 博士研究生, 研究方向為水聲換能器及測量技術。
陳洪娟, E-mail: chenhongjuan@hrbeu.edu.cn。

