腦源性神經營養因子預處理神經干細胞移植對急性缺血性腦卒中小鼠的效果
王棟,楊文楨,侯博儒,康軍林,任海軍
·基礎研究·
腦源性神經營養因子預處理神經干細胞移植對急性缺血性腦卒中小鼠的效果
王棟,楊文楨,侯博儒,康軍林,任海軍
目的 比較腦源性神經營養因子(BDNF)預處理對神經干細胞(NSCs)移植修復急性缺血性腦卒中的作用。方法 出生1 d C57BL/6小鼠,分離NSCs體外培養及鑒定。10周齡健康C57BL/6小鼠150只隨機分為5組,A組(n=20)為假手術組,B(n=20)、C(n=20)、D(n=45)、E(n=45)組采用光化學誘導法建立急性腦缺血模型。造模24 h后,D組行單純NSCs移植,E組行BDNF預處理的NSCs移植,C組移植等量溶劑。移植前1 d,移植后3 d、7 d、14 d、21 d、28 d,行加速轉棒測試及前肢抓力測試,移植后28 d,D、E組取5只小鼠行微管相關蛋白2(MAP-2)、神經膠質纖維酸性蛋白(GFAP)免疫熒光染色。結果 移植后3 d、7 d、14 d、21 d、28 d,加速轉棒時間由長到短依次為E組、D組、B組(p<0.05);移植后14 d、21 d、28 d,前肢抓力由大到小依次為E組、D組、B組(p<0.05)。移植后28 d,D組、E組均發現Edu/GFAP雙陽性細胞及Edu/MAP-2雙陽性細胞。結論 NSCs移植可促進缺血性腦卒中后行為功能恢復,經BDNF預處理后有更好效果。
缺血性腦卒中;神經干細胞;腦源性神經營養因子;體外培養;移植
腦卒中是全球范圍內引起死亡、致殘的重要原因。急性缺血性腦卒中是最常見的卒中類型,占腦卒中80%以上。腦卒中患者多伴有不同程度神經功能缺陷,如肢體運動及語言障礙[1-4]。
卒中后的損害效應不僅涉及神經元,對腦內其他細胞和細胞外基質也會產生影響。由于缺血性腦卒中后機體自身修復能力有限,難以產生新的功能性神經元。將外源性神經干細胞(neural stem cells,NSCs)植入中樞神經系統(central nervous system,CNS)疾病模型動物腦組織后,NSCs會向病灶區域遷移分化,并分泌神經營養因子,產生神經保護作用;同時減小病灶區梗死體積,促進運動、學習、記憶、感覺、認知等功能恢復[5-8]。NSCs移植為臨床治療急性CNS損傷和慢性退行性CNS疾病帶來廣闊應用前景[9-13]。
腦源性神經營養因子(brain-derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)是神經生長及發揮功能所必需的多肽類因子,屬于神經營養生長因子家族,由大腦細胞分泌產生,腦內含量豐富,在神經元生長、存活、分化過程中發揮重要作用。缺血性腦卒中后,BDNF通過促進神經及血管再生,發揮抗缺血損傷作用;通過提高突觸及軸突可塑性,促進學習、記憶和感覺運動等恢復[14-16]。
BDNF對體內外NSCs增殖分化發揮重要調節作用,可影響NSCs存活、增殖、凋亡和遷移。移植高表達BDNF的NSCs到腦內,可增加NSCs存活及血管再生,減少細胞死亡[17-18]。在創傷性腦損傷模型中移植高表達BDNF的NSCs,NSCs存活率增加,神經功能恢復效果更佳[19]。
本研究對比分析單純NSCs移植與BDNF預處理NSCs移植對小鼠缺血性腦卒中的效果,探討其相關機制。
1 材料與方法
1.1 試劑和儀器
表皮生長因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)、堿性成纖維細胞生長因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF):PEPROTECH公司。Edu細胞增殖檢測盒(貨號c10640):THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC公司。胎牛血清、即用型山羊血清:杭州四季青生物試劑公司。DMEM/F12培養液、B27(不含維生素A)、Accutase原液:GIBCO公司。兔抗神經元特異性烯醇化酶(neuron-specific enolase,NSE)多克隆抗體、小鼠抗5-溴脫氧尿嘧啶核苷(5-Bromo-2-deoxyuridine,BrdU)單克隆抗體:ABCAM公司。兔抗小鼠巢蛋白(nestin)單克隆抗體、兔抗微管相關蛋白2(microtubule-associated protein 2,MAP-2)多克隆抗體、BDNF、Hochest33258原液、孟加拉紅玫瑰紅(rose bengal sodium salt,RB)、2,3,5-氯化三苯基四氮唑(2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride,TTC)、 Fluoro-Jade C(FJ-C)染 料 :SIGMA公司。兔抗膠質纖維酸性蛋白(glial fibrillary acidic protein,GFAP)多克隆抗體:BOSTER公司。TRITC標記山羊抗兔IgG:KPL公司。FITC標記山羊抗小鼠IgG:EARTHOX公司。牛血清白蛋白(albumin from bovine serum,BSA):SOLARBIO公司。
磷酸鹽緩沖液(phosphate buffered saline,PBS,pH=7.4);一抗稀釋液(BSA 1.2 g+10%NaN30.4 ml+Triton X-100 0.08 ml+PBS 40 ml);二抗稀釋液(BSA 1.2 g+10%NaN30.4 ml+PBS 40 ml);2%氯胺酮-甲苯噻嗪混合液(鹽酸氯胺酮溶液10 ml+甲苯噻嗪0.075 g+滅菌生理鹽水15 ml)。
激光共聚焦顯微鏡(型號FV1000MPE)、熒光倒置顯微鏡、倒置相差顯微鏡:OLYMPUS公司。JZ300高精度張力換能器:北京新航科技有限公司。BL-420S生物機能實驗系統、ZB-200加速轉棒儀:成都泰盟科技有限公司。VT1000S振動切片機:LEICA公司。
1.2 實驗動物及分組
出生1 d C57BL/6小鼠,體質量1 g,雌雄不限,用于NSCs體外分離及培養;10周齡C57BL/6小鼠,雌雄不限,體質量20~25 g,用于免疫組化及行為學實驗。實驗動物由蘭州大學實驗動物中心提供,實驗過程嚴格按照動物倫理學規范要求進行。
加速轉棒預訓練3 d,轉棒爬行時間>220 s小鼠150只納入研究。隨機分為5組:A組(n=20)切開頭皮,暴露硬腦膜;B組(n=20)建模后不做干預;C組(n=20)建模后移植等量溶劑;D組(n=45)建模后單純NSCs移植;E組(n=45)建模后移植BDNF預處理的NSCs。
實驗過程中死亡或不列入統計學分析的小鼠,按相等的數量和相同的實驗方法予以補充。
1.3 NSCs體外分離培養及鑒定
1.3.1 體外分離培養
出生1 d C57BL/6小鼠2只,無菌條件分離兩側海馬,無菌預冷PBS漂洗后剪碎,4倍體積0.25%胰酶37℃水浴8 min,500 r/min離心5 min;棄上清,加入DMEM/F12基礎培養液;改良拋光巴氏吸管吹打成細胞懸液,400目濾網過濾;500 r/min離心5 min,棄上清;加入提前預熱的NSCs完全培養基2 ml(DMEM/F12基礎培養液49 ml+B27 1 ml+EGF 1μg+bFGF 1μg)重懸細胞。1×109/L接種于25 cm2培養瓶,37℃、體積分數5%CO2、平衡濕度培養箱培養。原代培養至第3天出現懸浮細胞球,半量換液;1周后細胞球直徑達100~130μm,收集細胞。Accutase原液2 ml消化10 min,1000 r/min離心5 min,棄上清;37℃預熱的NSCs完全培養基吹打混勻,1×109/L接種培養。
1.3.2 鑒定
第3代細胞在傳代過程加入BrdU(終濃度10 μmol/L),培養48 h后接種于24孔板中(含多聚賴氨酸包被的無菌玻片)繼續培養12 h。撤除培養基,4℃預冷的4%PFA室溫固定15 min,PBS室溫搖床洗滌3次,每次5 min。0.5%Triton X-100室溫搖床孵育20 min,PBS洗滌3次,每次5 min。每孔加入2 mol/L鹽酸500μl,37℃搖床20 min。去除鹽酸,加入硼酸緩沖液,室溫搖床洗滌3次,每次15 min。每孔加即用型山羊血清200μl室溫搖床封閉1.5 h。移除血清,分別加入兔抗小鼠Nestin一抗(1∶100)、小鼠抗BrdU一抗(1∶100),4℃搖床孵育12 h,PBS洗滌3次,每次10 min。分別避光加入TRITC標記的山羊抗兔IgG二抗(1∶100)、FITC標記的山羊抗小鼠IgG二抗(1∶100),搖床孵育1.5 h(37℃,90 r/min)。PBS洗滌3次,每次10 min。每孔加Hoechst33258(1∶2000)200 μl復染細胞核,室溫搖床15 min;PBS洗3次,每次5 min。甘油-PBS封片,熒光顯微鏡下觀察拍照。加入二抗以后所有步驟均需避光操作。
1.3.3 體外誘導分化及鑒定
取BrdU標記的第三代NSCs,1×104/L接種于24孔板(內含多聚賴氨酸包被的無菌玻片),每孔加NSCs促分化培養基(DMEM/F12基礎培養液45 ml+10%胎牛血清5 ml)1 ml,輕晃培養板使細胞分散均勻;培養箱內繼續培養,每2 d半量換液。2 d后細胞呈散射狀向四周遷移,突起逐漸變長。培養10 d行NSE、GFAP免疫熒光染色。加兔抗小鼠NSE一抗(1∶500)、兔抗小鼠GFAP一抗(1∶100)、TRITC標記的山羊抗兔IgG二抗(1∶100)。染色、封片步驟同1.3.2。
1.4 模型建立及造模后NSCs移植
1.4.1 模型建立
在Watson等光化學誘導法基礎上改進[20-24]。2%氯胺酮-甲苯噻嗪溶液0.5 ml/kg腹腔注射至小鼠完全麻醉,暴露顱骨,剝離骨膜。以Bregma點為原點,矢狀縫右側2.2 mm、冠狀縫后0.8 mm,解剖鏡下打磨顱骨暴露硬腦膜,至滴加PBS可見清晰大腦淺表血管為止,保持硬膜完整。眼眶下靜脈注射10 mg/ml RB溶液2 μl/g,熒光顯微鏡下綠色激發光定點照射,照射面積1 mm2,時間4.25 min[25]。A組眼眶下靜脈注射等量PBS溶液。術后4 h行神經功能缺損評分(Neurological Severity Scores,NSS),3分以上小鼠納入實驗。
1.4.2 模型鑒定
1.4.2.1 尼氏染色
造模后3 d取3只小鼠灌流取腦組織,切片厚30 μm,粘于多聚賴氨酸包被的載玻片上,室溫過夜干燥;蒸餾水漂洗1 min,梯度酒精脫水(70%乙醇1 min,95%乙醇1 min,100%乙醇1 min,二甲苯20 min)。梯度酒精復水(100%乙醇5 min,95%乙醇1 min,50%乙醇1 min),1%甲分酚紫37℃染色10 min,蒸餾水漂洗3次,每次1 min;乙酸分化1 min。100%乙醇2 min(觀察顏色脫去即可終止),二甲苯透明10 min,中性樹膠封片后避光保存。
1.4.2.2 TTC染色
造模后3 d,取3只小鼠氨基甲酸乙酯麻醉,斷頭取腦。TTC溶液浸入15 min(37℃恒溫,避光),每3~5 min翻動1次,期間注意觀察(顏色要鮮紅,不能變成暗紅色),15 min后取出腦組織,放入模具,-20℃冰凍30 min,切成厚1 mm腦片;轉移出模具后繼續用TTC溶液染色10 min(37℃恒溫,避光),注意觀察翻動,保證每個腦片都能充分接觸染料。4%PFA終止染色。
1.4.2.3 FJ-C染色
造模后3 d取3只小鼠灌流取腦組織,切片厚30 μm,粘于多聚賴氨酸包被的載玻片上,室溫過夜干燥。依次浸潤于無水乙醇3 min、95%乙醇1 min、75%乙醇1 min,蒸餾水漂洗1 min,0.06%高錳酸鉀避光搖15 min,蒸餾水浸潤2 min;0.0001%FJ-C工作液避光染色30 min,蒸餾水漂洗3次,每次1 min;37℃干燥30 min。二甲苯浸潤10 min,中性樹膠封片。高錳酸鉀搖床后步驟均需嚴格避光。
1.4.3 NSCs移植
移植前24 h,用終濃度10μmol/L Edu標記NSCs[26]。造模后24 h,D組移植NSCs 2×106[27]。E組NSCs移植前用BDNF 100 ng/ml預處理1 h[28],基礎培養基洗滌濃縮后再移植。
立體定向儀定位前囟后0.46 mm,矢狀縫右旁1.0 mm,硬膜下2.5 mm[29],1 μl/min速度注射,留針5 min,5 min內緩慢拔出針頭。
1.5 行為學測試
1.5.1 加速轉棒測試
造模前1 d,移植后3 d、7 d、14 d、21 d、28 d,小鼠置于靜止轉棒上3 min,然后于5 min內將轉速從0加速到40 r/min,記錄從轉棒上掉落的時間(兩次被動旋轉認為掉落)。測試3次,間隔5 min,取平均值。
1.5.2 前肢抓力測試
造模前1 d,移植后3 d、7 d、14 d、21 d、28 d,將小鼠其前肢放于張力換能器三腳架上,水平均勻牽拉小鼠尾巴,直到小鼠前肢完全松開三腳架。實驗過程保持小鼠與三腳架處于水平位。連續測試5次,記錄每次峰值,取5次平均值。
1.6 移植后免疫熒光染色
1.6.1 組織標本制備
NSCs移植后28 d,行為學測試結束后,D、E兩組分別取5只小鼠,氨基甲酸乙酯0.17 ml/20 g腹腔注射麻醉,打開胸腔,暴露心臟,于右心耳橫向剪一小口,左心室快速灌注4℃預冷PBS 20 ml,灌注4℃預冷4%PFA 20 ml。取腦組織浸入4%PFA,4℃固定48 h。振動切片機連續冠狀切片,厚30 μm。
1.6.2 免疫熒光染色
腦片置24孔板內,3%BSA 1 ml室溫搖床洗滌2次,每次5 min。每孔加0.5%TritonX-100 1 ml,室溫搖床孵育20 min;3%BSA洗滌2次,每次5 min。每孔加入Edu反應混合液(1×Click-iT?reaction buffer 440 μl+Copper protectant 10 μl+Alexa Fluor?picolyl azide 1.2 μl+Reaction-buffer additive 50 μl)500 μl,室溫避光孵育30 min。3%BSA洗滌2次,每次5 min。
避 光 , 加 MAP-2(1∶ 100)、 GFAP(1∶ 100)、Hoechst33342(1∶2000)一抗,TRITC標記山羊抗兔IgG二抗(1∶100)。染色、封片步驟同1.3.2。
1.6.3 尼氏染色和TTC染色
移植后28 d,各組取3只小鼠行尼氏染色和TTC染色,方法同前。
1.7 統計學分析
采用SPSS 21.0進行統計分析。組間比較采用單因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA)。顯著性水平α=0.05。Image J軟件進行圖像處理分析。
2 結果
2.1 NSCs體外分離培養鑒定
原代NSCs接種后2 h,倒置相差顯微鏡下可見大量散在單細胞(圖1A);3 d可見大小不一神經球形成(圖1B);7 d可見大神經球形成,由大量透光良好、形態圓潤的單細胞聚集而成(圖1C)。
第 3 代細胞行 BrdU(圖 2A)、Nestin(圖 2B)、Hochest33258(圖2C)熒光染色,均呈陽性。Image J軟件疊加后(圖2D)呈混合陽性。
2.2 NSCs體外誘導分化鑒定
培養10 d時,細胞BrdU/GFAP(圖3)、BrdU/NSE(圖4)免疫熒光染色均陽性。BrdU/GFAP陽性細胞呈多樣性,胞體多角形,突起較多且單個細胞間突起有相互交織呈網狀的趨勢。細胞核形態隨著胞體形態而變化,呈大而圓或長而扁形狀,位于胞體中央或周邊。BrdU/NSE陽性細胞胞體呈橢圓形、梭形、三角形,突起細長呈雙極樣。
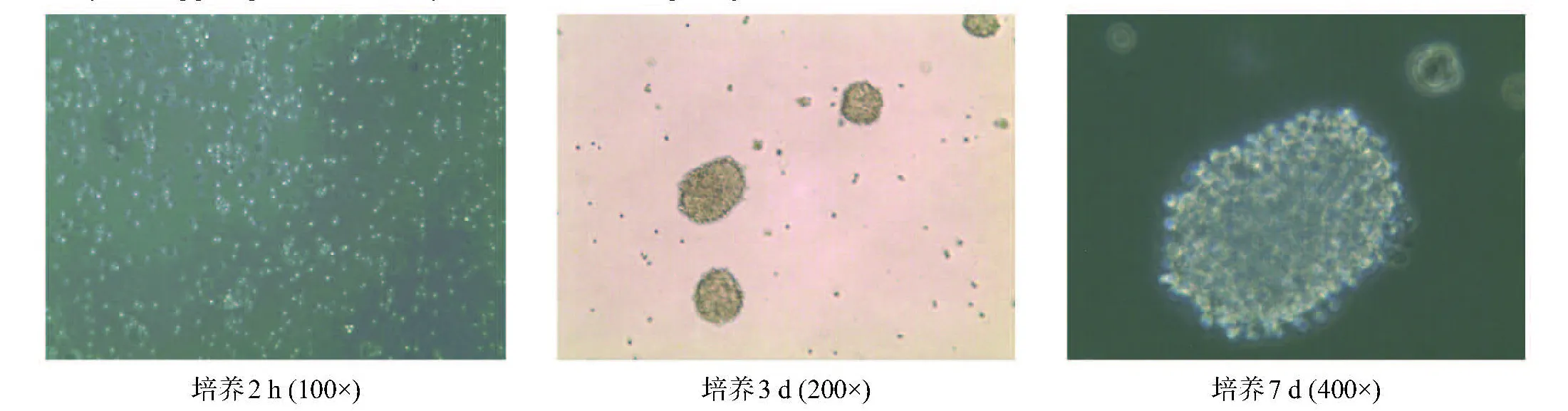
圖1 NSCs體外培養的形態變化(倒置相差顯微鏡)
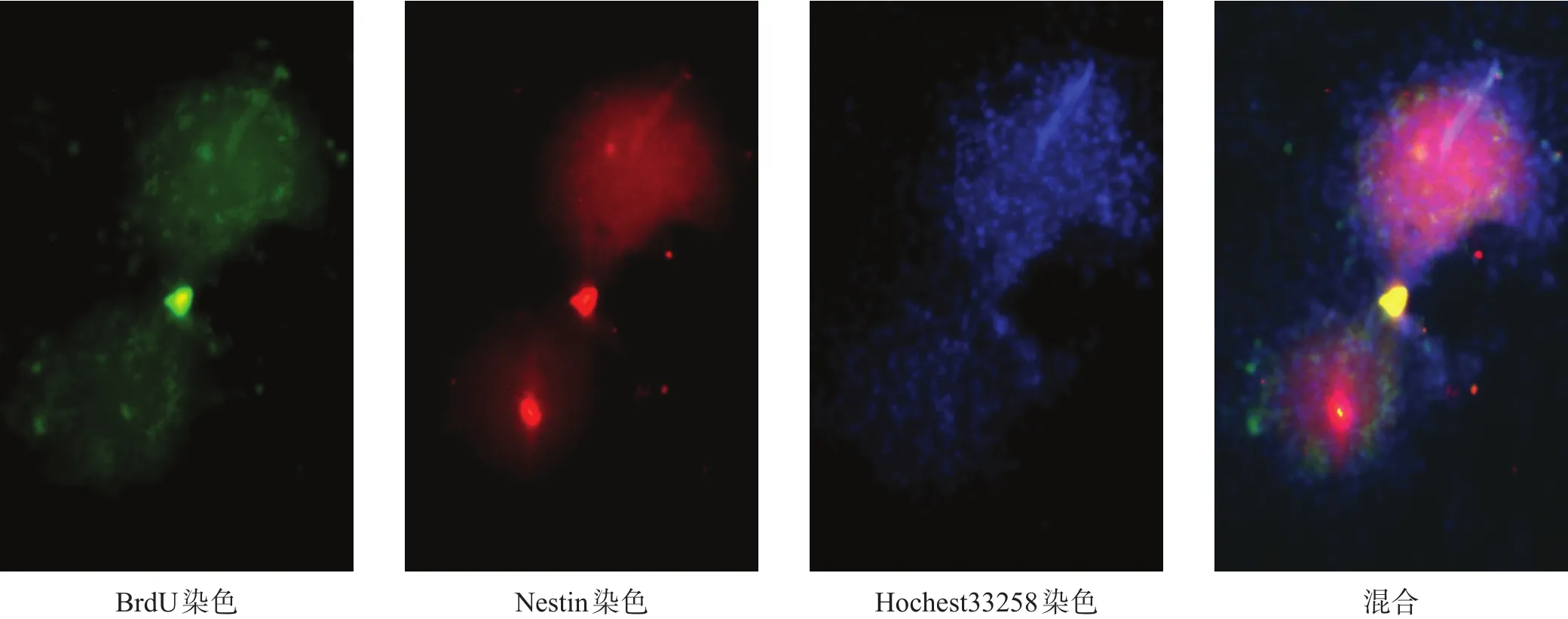
圖2 NSCs體外培養鑒定(免疫熒光染色,200×)

圖3 NSCs體外分化成星形膠質細胞(免疫熒光染色,200×)
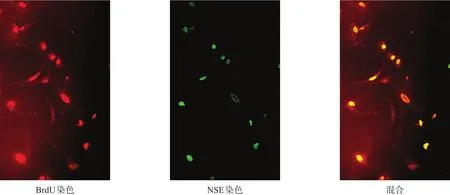
圖4 NSCs體外分化成神經元(免疫熒光染色,200×)
2.3 急性缺血性腦卒中模型鑒定
2.3.1 大體觀察
熒光照射后,血管內血液高速流動,隨后血流減慢,血管逐漸被阻塞,熒光變暗(圖5)。
2.3.2 模型鑒定
尼氏體是神經元的特征性結構之一,存在于神經元胞體粗面內質網及核糖體上,在病理情況下會溶解或消失[30]。造模后3 d,尼氏染色可見損傷區尼氏體數量減少,神經元壞死、數目減少,周圍細胞水腫明顯,部分細胞核固縮,細胞間隙增大,微血管內皮細胞腫脹(圖6)。
TTC染色后正常組織顯示為紅色,壞死組織由于琥珀酸脫氫酶失活,不能與TTC發生反應,顯示為白色(圖6)。
FJ-C染色可在大腦急性損傷病變時標記退行性神經元,而正常神經元不染色[31-32](圖6)。
染色結果表明,光化學誘導法建立模型成功。
2.4 NSCs移植后的存活及分化
移植后28 d,D、E兩組均可見Edu/MAP-2陽性、Edu/GFAP陽性細胞,E組Edu陽性細胞數量更多(圖7、圖8)。
2.5 移植后尼氏、TTC染色
D、E組尼氏體數量較C組有所增加,神經元形態較完整。E組尼氏體及神經元數量多于D組(圖9)。E組TTC白色區域小于D組(圖10)。

圖5 光栓法缺血模型建立示意圖
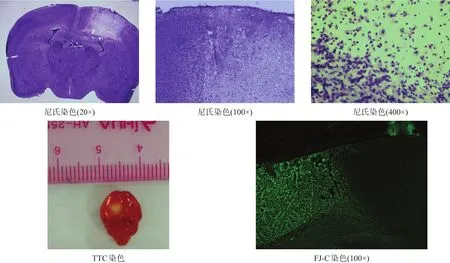
圖6 光栓法缺血模型鑒定

圖8 E組NSC移植后分化情況(免疫熒光染色,200×)
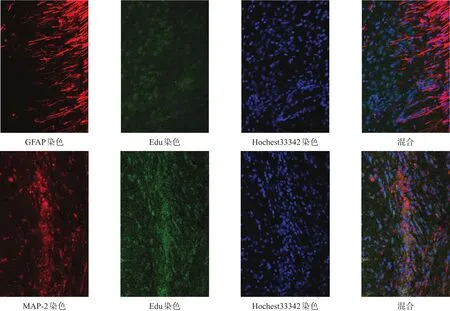
圖7 D組NSC移植后分化情況(免疫熒光染色,200×)
2.6 加速轉棒測試
加速轉棒測試可評估小鼠平衡及協調能力[33-34]。造模前1 d,各組間轉棒時間均無顯著性差異(P>0.05);移植后3 d,A組轉棒時間較造模前略有下降,B、C、D、E組明顯下降,移植后7 d各組轉棒時間有所上升,B、C兩組各時間點比較均無顯著性差異(P>0.05),D、B兩組及E、D兩組間均有顯著性差異(p<0.05)。見圖11。
2.7 前肢抓力測試
造模前1 d,各組間抓力均無顯著性差異(P>0.05)。移植后各時間點,B、C兩組比較均無顯著性差異(P>0.05);移植后7 d,D、B兩組間有顯著性差異(p<0.05),而E、D兩組間無顯著性差異(P>0.05);移植后14 d、21 d、28 d,D、B兩組及E、D兩組間均有顯著性差異(p<0.05)。見圖12。
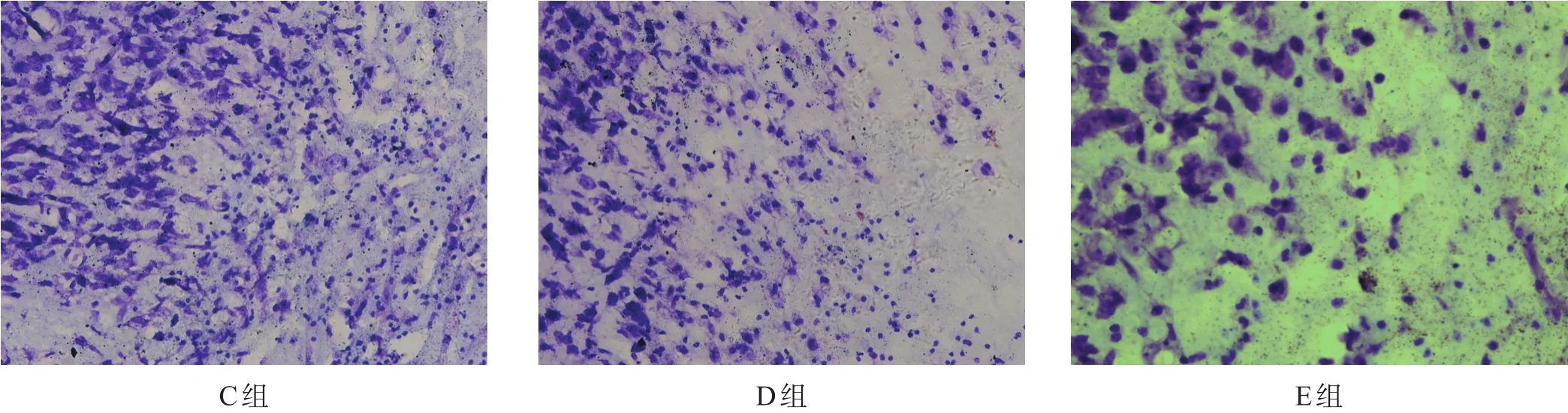
圖9 NSC移植后C組、D組、E組尼氏體數目(尼氏染色,400×)

圖10 NSC移植后D組、E組損傷體積(TTC染色)
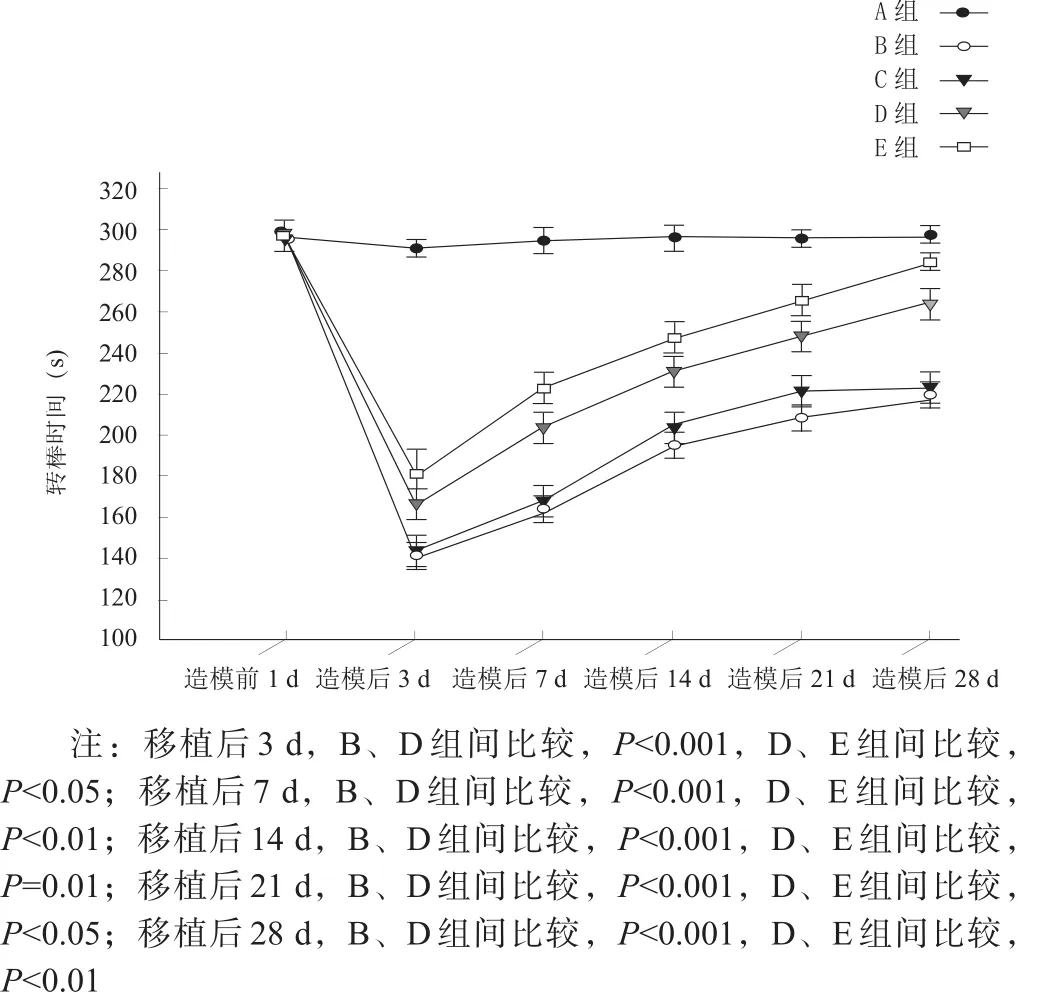
圖11 造模前及移植后各時間點加速轉棒測試結果
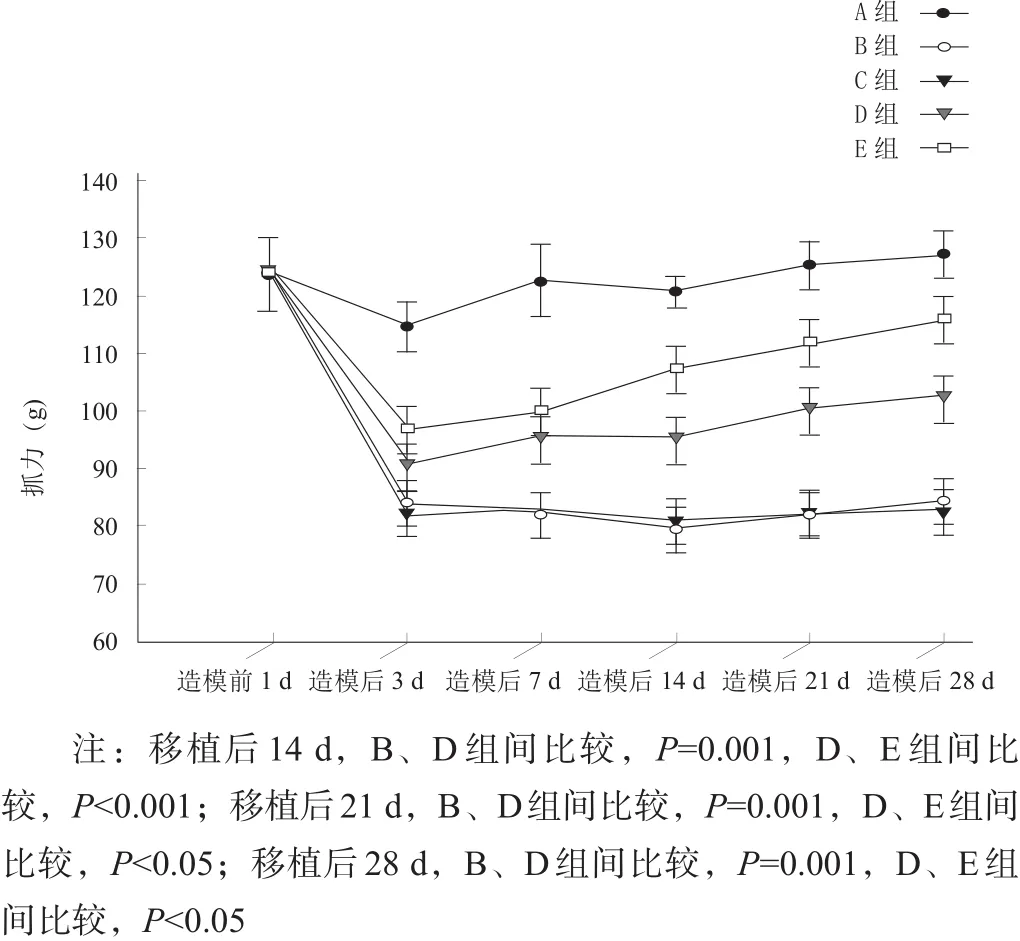
圖12 造模前及移植后各時間點前肢抓力測試結果
3 討論
NSCs是居存于CNS的前體細胞,主要分布于腦、脊髓、視網膜;在成年哺乳動物大腦中,NSCs主要存在于側腦室下區及海馬齒狀回顆粒下區[35],胚胎期小鼠嗅球、海馬、側腦室室周等部位也存在NSCs[36-37]。NSCs具有多潛能分化及自我更新能力,可通過對稱及不對稱分裂分化產生子代NSCs及神經元、星形膠質細胞和少突膠質細胞[38-39]。NSCs植入體內后,在EGF、FGF、白血病抑制因子(leukemia inhibitory factor,LIF)刺激下增殖,進而通過視黃酸誘導分化為神經元、星形膠質細胞、少突膠質細胞,替代損傷丟失的神經細胞,為腦卒中等CNS疾病臨床治療帶來新的希望[40]。
加速轉棒測試主要反映運動協調能力。本研究顯示,從移植后7 d起,B、C、D、E各組加速轉棒時間有所上升;A組造模后轉棒時間短暫下降,隨后恢復正常,推測可能由于打磨顱骨時機械振動擠壓腦組織所引起,未對小鼠腦組織產生實質性損害。B、C兩組轉棒時間上升有限,且無顯著性差異,說明卒中后腦內注射基礎培養基不會對小鼠行為恢復產生明顯作用;卒中后小鼠存在一定神經自我修復功能,其機制可能是卒中后內源性NSCs激活,分化出新的神經元,替代梗死區壞死或無功能性的神經元、膠質細胞,通過膠質瘢痕修復促進神經功能恢復[41-43]。D組與B、C組比較,轉棒時間明顯增加,同時腦內出現Edu/GFAP、Edu/MAP-2陽性細胞,并向缺血半暗帶區域遷移,證實體外培養的NSCs在體內依舊保持自我更新、增殖及多潛能分化能力,NSCs移植是治療缺血性腦卒中的有效方法,可以促進卒中后小鼠神經功能恢復,也與之前其他研究結果一致[5,44-45]。
體內外相關研究證實,血管內皮生長因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)在神經保護中發揮重要作用,經過BNDF處理后,VEGF表達顯著上升。移植后存活的NSCs可以分泌BDNF、睫狀神經生長因子(ciliary neurotrophic factor,CNTF)、膠質細胞源性神經營養因子(glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor,GDNF)等多種神經營養因子,并使其表達量上調,從而減少細胞凋亡,促進損傷灶局部受損神經元存活,增加移植后NSCs存活;BNDF對NSCs向神經元分化起推動作用,有利于神經突觸重塑[46-49]。
本研究顯示,E組行為恢復明顯優于D組,同時E組腦內也存在Edu/GFAP、Edu/MAP-2陽性細胞,且E組神經元分化數多于D組,說明BDNF預處理對NSCs增殖、存活、分化、遷移有更好效果。具體機制有待深入研究。
抓力測試結果與加速轉棒測試呈大致相同趨勢,但起效時間略有延遲。
綜上所述,外源性NSCs移植后,可在梗死區域發生遷移和分化,對缺血性腦卒中后腦組織修復及神經功能恢復發揮重要作用;而移植經BNDF預處理的NSCs,可在腦組織形態修復和神經功能恢復方面有更好療效。
[1]Feigin VL,Norrving B,George MG,et al.Prevention of stroke:a strategic global imperative[J].Nat Rev Neurol,2016,12(9):501-512.
[2]Moskowitz MA,Lo EH,Iadecola C.The science of stroke:mechanisms in search of treatments[J].Neuron,2010,67(2):181-198.
[3]Marks MP,Lansberg MG,Mlynash M,et al.Effect of collateral blood flow on patients undergoing endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke[J].Stroke,2014,45(4):1035-1039.
[4]Detante O,Jaillard A,Moisan A,et al.Biotherapies in stroke[J].Rev Neurol(Paris),2014,170(12):779-798.
[5]Mine Y,Tatarishvili J,Oki K,et al.Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats[J].Neurobiol Dis,2013,52:191-203.
[6]Tang Y,Wang J,Lin X,et al.Neural stem cell protects aged rat brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury through neurogenesis and angiogenesis[J].J Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2014,34(7):1138-1147.
[7]Doeppner TR,Ewert TA,Tonges L,et al.Transduction of neural precursor cells with TAT-heat shock protein 70 chaperone:therapeutic potential against ischemic stroke after intrastriatal and systemic transplantation[J].Stem Cells,2012,30(6):1297-1310.
[8]Andres RH,Horie N,Slikker W,et al.Human neural stem cells enhance structural plasticity and axonal transport in the ischaemic brain[J].Brain,2011,134(Pt 6):1777-1789.
[9]Karussis D,Petrou P,Kassis I.Clinical experience with stem cells and other cell therapies in neurological diseases[J].J Neurol Sci,2013,324(1-2):1-9.
[10]Minnerup J,Kim JB,Schmidt A,et al.Effects of neural progenitor cells on sensorimotor recovery and endogenous repair mechanisms after photothrombotic stroke[J].Stroke,2011,42(6):1757-1763.
[11]Buchet D,Garcia C,Deboux C,et al.Human neural progenitors from different foetal forebrain regions remyelinate the adult mouse spinal cord[J].Brain,2011,134(Pt 4):1168-1183.
[12]Naegele JR,Maisano X,Yang J,et al.Recent advancements in stem cell and gene therapies for neurological disorders and intractable epilepsy[J].Neuropharmacology,2010,58(6):855-864.
[13]Brundin P,Barker RA,Parmar M.Neural grafting in Parkinson's disease:problems and possibilities[J].Prog Brain Res,2010,184:265-294.
[14]Liu X,Zhang J,Sun D,et al.Effects of fluoxetine on brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum concentration and cognition in patients with vascular dementia[J].Clin IntervAging,2014,9:411-418.
[15]Jeong CH,Kim SM,Lim JY,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic stroke model[J].Biomed Res Int,2014,2014:129145.
[16]Pikula A,Beiser AS,Chen TC,et al.Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and vascular endothelial growth factor levels are associated with risk of stroke and vascular brain injury:Framingham Study[J].Stroke,2013,44(10):2768-2775.
[17]PetridisAK,El MaaroufA.Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels influence the balance of migration and differentiation of subventricular zone cells,but not guidance to the olfactory bulb[J].J Clin Neurosci,2011,18(2):265-270.
[18]Lee HJ,Lim IJ,Lee MC,et al.Human neural stem cells genetically modified to overexpress brain-derived neurotrophic factor promote functional recovery and neuroprotection in a mouse stroke model[J].J Neurosci Res,2010,88(15):3282-3294.
[19]Ma H,Yu B,Kong L,et al.Neural stem cells over-expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor(BDNF)stimulate synaptic protein expression and promote functional recovery following transplantation in rat model of traumatic brain injury[J].Neurochem Res,2012,37(1):69-83.
[20]Klaric TS,Jaehne EJ,Koblar SA,et al.Alterations in anxiety and social behaviour in Npas4 deficient mice following photochemically-induced focal cortical stroke[J].Behav Brain Res,2017,316:29-37.
[21]Tsiminis G,Klaric TS,Schartner EP,et al.Generating and measuring photochemical changes inside the brain using optical fibers:exploring stroke[J].Biomed Opt Express,2014,5(11):3975-3980.
[22]Lozano JD,Abulafia DP,Danton GH,et al.Characterization of a thromboembolic photochemical model of repeated stroke in mice[J].J Neurosci Methods,2007,162(1-2):244-254.
[23]Zhang S,Boyd J,Delaney K,et al.Rapid reversible changes in dendritic spine structure in vivo gated by the degree of ischemia[J].J Neurosci,2005,25(22):5333-5338.
[24]Watson BD,Dietrich WD,Busto R,et al.Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis[J].Ann Neurol,1985,17(5):497-504.
[25]Wang J,Feng X,Du Y,et al.Combination treatment with progesterone and rehabilitation training further promotes behavioral recovery after acute ischemic stroke in mice[J].Restor Neurol Neurosci,2013,31(4):487-499.
[26]Chehrehasa F,Meedeniya AC,Dwyer P,et al.EdU,a new thymidine analogue for labelling proliferating cells in the nervous system[J].J Neurosci Methods,2009,177(1):122-130.
[27]Wang LQ,Lin ZZ,Zhang HX,et al.Timing and dose regimens of marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation affect the outcomes and neuroinflammatory response after ischemic stroke[J].CNS Neurosci Ther,2014,20(4):317-326.
[28]Rosenblum S,Smith TN,Wang N,et al.BDNF pretreatment of human embryonic-derived neural stem cells improves cell survival and functional recovery after transplantation in hypoxic-ischemic stroke[J].Cell Transplant,2015,24(12):2449-2461.
[29]Paxinos G,Franklin BJ.The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates,Compact.Third Edition:The Coronal Plates and Diagrams in Stereotaxic Coordinates[M].San Diego,California:A Harcourt Science and Technology Company,2001:80-86.
[30]Gittins R,Harrison PJ.Neuronal density,size and shape in the human anterior cingulate cortex:a comparison of Nissl and NeuN staining[J].Brain Res Bull,2004,63(2):155-160.
[31]Damjanac M,Rioux Bilan A,Barrier L,et al.Fluoro-Jade B staining as useful tool to identify activated microglia and astrocytes in a mouse transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease[J].Brain Res,2007,1128(1):40-49.
[32]Schmued LC,Stowers CC,Scallet AC,et al.Fluoro-Jade C results in ultra high resolution and contrast labeling of degenerating neurons[J].Brain Res,2005,1035(1):24-31.
[33]Ferrara A,El Bejaoui S,Seyen S,et al.The usefulness of operant conditioning procedures to assess long-lasting deficits following transient focal ischemia in mice[J].Behav Brain Res,2009,205(2):525-534.
[34]Bouet V,Freret T,Toutain J,et al.Sensorimotor and cognitive deficits after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the mouse[J].Exp Neurol,2007,203(2):555-567.
[35]Doetsch F.The glial identity of neural stem cells[J].Nat Neurosci,2003,6(11):1127-1134.
[36]Ahmed S.The culture of neural stem cells[J].J Cell Biochem,2009,106(1):1-6.
[37]Walker MR,Patel KK,Stappenbeck TS.The stem cell niche[J].J Pathol,2009,217(2):169-180.
[38]Ming GL,Song H.Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain:significant answers and significant questions[J].Neuron,2011,70(4):687-702.
[39]Gage FH.Mammalian neural stem cells[J].Science,2000,287(5457):1433-1438.
[40]Hao L,Zou Z,Tian H,et al.Stem cell-based therapies for ischemic stroke[J].Biomed Res Int,2014,2014:468748.
[41]Sabelstrom H,Stenudd M,Reu P,et al.Resident neural stem cells restrict tissue damage and neuronal loss after spinal cord injury in mice[J].Science,2013,342(6158):637-640.
[42]Benner EJ,Luciano D,Jo R,et al.Protective astrogenesis from the SVZ niche after injury is controlled by Notch modulator Thbs4[J].Nature,2013,497(7449):369-373.
[43]Erlandsson A,Lin CH,Yu F,et al.Immunosuppression promotes endogenous neural stem and progenitor cell migration and tissue regeneration after ischemic injury[J].Exp Neurol,2011,230(1):48-57.
[44]Jensen MB,Yan H,Krishnaney-Davison R,et al.Survival and differentiation of transplanted neural stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a rat stroke model[J].J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis,2013,22(4):304-308.
[45]Liu H,Cao J,Zhang H,et al.Folic acid stimulates proliferation of transplanted neural stem cells after focal cerebral ischemia in rats[J].J Nutr Biochem,2013,24(11):1817-1822.
[46]Piltonen M,Planken A,Leskela O,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor C acts as a neurotrophic factor for dopamine neurons in vitro and in vivo[J].Neuroscience,2011,192:550-563.
[47]Lee HJ,Kim KS,Park IH,et al.Human neural stem cells over-expressing VEGF provide neuroprotection,angiogenesis and functional recovery in mouse stroke model[J].PLoS One,2007,2(1):e156.
[48]Zimmermann T,Remmers F,Lutz B,et al.ESC-derived BDNF-overexpressing neural progenitors differentially promote recovery in Huntington's disease models by enhanced striatal differentiation[J].Stem Cell Reports,2016,7(4):693-706.
[49]Wu CC,Lien CC,Hou WH,et al.Gain of BDNF function in engrafted neural stem cells promotes the therapeutic potential for Alzheimer's disease[J].Sci Rep,2016,6:27358.
Effect of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation Pretreated with Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor on Acute Ischemic Stroke in Mice
WANG Dong,YANG Wen-zhen,HOU Bo-ru,KANG Jun-lin,REN Hai-jun
Department of Neurosurgery,Second HospitalAffiliated to Lanzhou University,Lanzhou,Gansu 730000,China
REN Hai-jun.E-mail:baiyunguan@hotmail.com
Objective To explore the effect of transplantation of neural stem cells(NSCs)pretreated with brain-derived neurotrophic factor(BDNF)on acute ischemic stroke in mice.Methods NSCs from a newborn(one day)C57BL/6 mouse were isolated and cultured in vitro.A total of 150 healthy C57BL/6 mice,ten-week-old,were randomly divided into five groups,that group A accepted sham operation,and groups B,C,D and E were subjected to focal ischemia by photothrombosis.Group D was transplanted NSCs 24 hours after ischemia,while group E transplanted NSCs pretreated with BDNF and group C accepted same volume of medium.All the groups were tested with rotarod test and grip strength one day before transplantation and three,seven,14,21 and 28 days after transplantation.The differentiation of NSCs in groups D and E were observed immunofluorescence staining of microtubule-associated protein-2(MAP-2)and glial fibrillary acidic protein(GFAP).Results The time on rotarod arranged from more to less was groups E,D and B(p<0.05)three,seven,14,21 and 28 days after transplantation,as well as grip strength 14,21 and 28 days after transplantation(p<0.05).The Edu/GFAP positive cells and Edu/MAP-2 positive cells were found in both groups D and E.Conclusion Transplanting NSCs can promote the behavioral recovery after ischemic stroke,and it is more effective as pretreated with BDNF.
ischemic stroke;neural stem cells;brain-derived neurotrophic factor;in vitro;transplantation
10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2017.11.006
R743.3
A
1006-9771(2017)11-1263-10
[本文著錄格式] 王棟,楊文楨,侯博儒,等.腦源性神經營養因子預處理神經干細胞移植對急性缺血性腦卒中小鼠的效果[J].中國康復理論與實踐,2017,23(11):1263-1272.
CITEDAS:Wang D,Yang WZ,Hou BR,et al.Effect of neural stem cell transplantation pretreated with brain-derived neurotrophic factor on acute ischemic stroke in mice[J].Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun Yu Shijian,2017,23(11):1263-1272.
1.甘肅省高等學校科研項目(No.2014B-001);2.甘肅電信萃英科研基金資助項目(No.lzudxcy-2014-8)。
蘭州大學第二醫院神經外科,甘肅蘭州市730000。作者簡介:王棟(1989-),男,漢族,陜西西安市人,碩士研究生,主要研究方向:重型顱腦損傷及腦血管病。通訊作者:任海軍(1962-),男,漢族,甘肅蘭州市人,主任醫師、教授,碩士研究生導師,主要研究方向:重型顱腦損傷。E-mail:baiyunguan@hotmail.com。
2016-11-01
2017-01-23)

