哈爾濱手術室吸入麻醉廢氣污染狀況及防護措施
廉愛玲++馬鴻雁++興東梅+楊帆+王丹
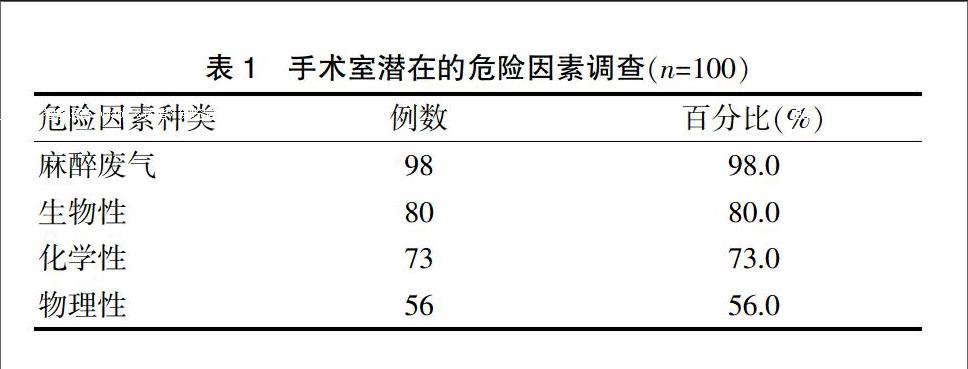
[摘要] 目的 探討哈爾濱手術室吸入麻醉廢氣污染情況,為制訂相應的防護措施提供依據。 方法 采用便利抽樣法選擇2015年1~5月哈爾濱市20家醫院的180個手術間。按照是否采用吸入麻醉分為吸入組(55間)和非吸入組(125間)。比較兩組廢氣檢出率和廢氣超標率。采用自制的調查問卷對醫護人員對麻醉廢氣的認知情況進行調查。 結果 吸入組的廢氣檢出率(98.2%)高于非吸入組(72.8%),差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。吸入組的廢氣超標率(58.2%)高于非吸入組(22.4%),差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。手術室醫護人員中選擇麻醉廢氣為手術室潛在危險因素的比例(98.0%)明顯高于生物性危險因素(80.0%)、物理性因素(56.0%)和化學性因素(73.0%)。 結論 吸入麻醉可造成手術間麻醉廢氣的污染,手術室醫護人員對麻醉廢氣的認知度較高,采取有效的防護措施至關重要。
[關鍵詞] 手術室;麻醉廢氣;防護
[中圖分類號] R472 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2017)11(c)-0183-04
Pollution conditions and protective measures of anesthetic waste gas inhalation in Harbin operation room
LIAN Ailing1 MA Hongyan2 XING Dongmei2 YANG Fan3 WANG Dan2
1.Center of Outpatient Operating Room, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150001, China; 2.Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150001, China; 3.Department of Occupational Health Assessment, the Second Hospital of Heilongjiang Province, Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150010, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the pollution conditions of anestheic waste gas inhalation in Harbin operation room and develop protective measures accordingly. Methods From January to May 2015, 180 operation room in Harbin were selected from 20 hospitals by convenient sampling method and divided into inhalation group and non-inhalation group according to inhalation anesthesia. The detection rate of exhaust gas and the exhaust gas exceeding rate were compared between the two groups. The self-designed questionnaire was used to assess the congnitive of the operating room staff. Results The detection rate of exhaust gas in inhalation group (98.2%) was higher than that of non-inhalation group (72.8%), with statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The exhaust gas exceeding rate in inhalation group (58.2%) was higher than that of non-inhalation group (22.4%), with statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The proportion of choosing anesthetic exhaust gas (98.0%) as the potential risk factors was significantly higher than biological risk factor (80.0%), physical factors (56.0%) and chemical factors (73.0%) in operating room staff. Conclusion Inhalation anestheic waste gas can cause the pollution of the operation room. The staff in the operating room have higher awareness of anesthetic waste gas. It is necessary to take active and effective protective measures.endprint
[Key words] Operation room; Anesthetic waste gas; Protection
手術室既是一個對空氣質量有較高要求的場所,也是一個空氣質量堪憂的場所[1]。隨著醫療技術的不斷提高,吸入麻醉劑在臨床上的應用也十分廣泛,尤其是在手術治療過程中,吸入麻醉劑儼然已經成為主要的麻醉手段[2]。手術室內麻醉廢氣可作為手術室空氣質量受到影響的重要因素之一。大量資料顯示,吸入麻醉廢氣對人體具有致突變性、致癌性、降低生育能力等影響[3]。如果手術室內麻醉廢氣不能及時排除,手術室的醫護人員長期暴露在這種惡劣空氣環境中,將對其身心健康造成不同程度的影響,甚至影響技術的正常發揮。因此改善手術室的空氣環境,保護醫務人員的身心健康成為當務之急。本文就此進行了研究與分析,結果報道如下:
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
采用便利抽樣法選取2015年1~5月哈爾濱市20家醫院,其中三級醫院5家,二級醫院15家,共有手術間180間。按照采樣期間是否采用吸入麻醉分為吸入組和非吸入組,其中吸入組共55間手術室,二級醫院8家,三級醫院3家,非吸入組共125間手術室,二級醫院7家,三級醫院2家。……

