日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因全長cDNA克隆及表達分析
鄭征帆,呂艷杰,王 佩,寧黔冀
( 河南師范大學 生命科學學院,河南 新鄉(xiāng) 453007 )
日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因全長cDNA克隆及表達分析
鄭征帆,呂艷杰,王 佩,寧黔冀
( 河南師范大學 生命科學學院,河南 新鄉(xiāng) 453007 )
為探究甲殼動物表皮蛋白多樣性及其功能,根據(jù)表皮轉(zhuǎn)錄組資料,利用RACE技術擴增得到日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因的cDNA全長序列,分析其生物信息學、不同蛻皮時期的表達特征以及KK-42對其表達特征的影響。日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因的cDNA全長796 bp,開放閱讀框477 bp,編碼158個氨基酸,含RR基序,預測蛋白等電點為4.22,分子量為16.46 ku;氨基酸序列比對發(fā)現(xiàn)日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5與克氏原螯蝦Casp-2相似性最高,為76%,與其他甲殼動物表皮蛋白相似性為41%~53%。實時熒光定量PCR結(jié)果顯示,日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因在3個時期——蛻皮間期、蛻皮前早期和蛻皮前晚期均有表達,其中在脫皮前晚期的相對表達量最高,為蛻皮間期的1400倍,與之有極顯著差異(P<0.01)。KK-42處理顯著上調(diào)日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因在蛻皮前早期的表達,在處理后3、6 h和48 h表達量分別是對照組的6.3、4.8和11.4倍。KK-42誘導日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因的表達,使峰值前移,這可能是KK-42縮短日本沼蝦幼蝦蛻皮周期的機制之一。
日本沼蝦;表皮蛋白;基因克隆;表達;KK-42
由于堅硬表皮的限制,甲殼動物必須經(jīng)過蛻皮才能生長,蛻皮是一個周期性的動態(tài)過程,包括舊表皮降解和新表皮的形成。作為表皮組成成分的幾丁質(zhì)是和蛋白質(zhì)以結(jié)合的形式存在,此蛋白即為表皮蛋白(CPs),是甲殼動物表皮中重要的結(jié)構(gòu)性蛋白,由蛻皮激素的靶組織——表皮上皮細胞按照一定的周期和步驟表達合成[1-2]。
表皮蛋白的表達與蛻皮周期的關系是研究此類蛋白功能的重要方面。采用分離純化方法獲得表皮蛋白,根據(jù)氨基酸測序結(jié)果推定堿基序列,在轉(zhuǎn)錄水平分析相關基因表達在蛻皮周期中的變化趨勢[3-5]。近年來應用高通量測序技術大大加快了新表皮蛋白基因發(fā)現(xiàn)的進程,在日本囊對蝦(Marsupenaeusjaponicus)[6-7]、藍蟹(Callinectessapidus)[8]、克氏原螯蝦(Procambarusclarkii)[9-11]少數(shù)幾個物種獲得9個甲殼動物表皮蛋白基因全長。尚未見到日本沼蝦(Macrobrachiumnipponense)表皮蛋白的相關報道。
前期研究發(fā)現(xiàn)咪唑類物質(zhì)KK-42能縮短日本沼蝦幼蝦蛻皮周期[12],機制尚不明確,推測與表皮蛋白表達有關。本試驗采用cDNA 末端快速擴增技術首次從日本沼蝦尾扇中克隆出一個表皮蛋白基因全長,命名為日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5(MnCP-5,GenBank 登錄號:KU356774),對其進行序列分析、不同蛻皮時期表達分析以及KK-42處理等相關研究,探究甲殼動物表皮蛋白的多樣性,也為闡明KK-42縮短蛻皮周期的作用機制積累資料。
1 材料與方法
1.1 試驗材料及KK-42處理
日本沼蝦幼蝦捕撈于河南衛(wèi)輝市順城關公園,實驗室暫養(yǎng)后選取400尾體長(3.0±0.5) cm,體質(zhì)量約0.30 g個體分為2組:KK-42試驗組和對照組,其蛻皮周期的鑒定依據(jù)Cesar等[13]顯微形態(tài)學觀察的方法。試驗組用1.95×10-4mol/L的KK-42溶液浸泡處理1 min,取出后迅速去除水分,立刻置于水族箱中,室溫全天通氧飼養(yǎng);對照組用不含KK-42溶液做相同的處理[14]。
1.2 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因全長克隆
用MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit (TaKaRa) 試劑盒提取尾扇總RNA,微量紫外分光光度儀檢測RNA含量,1%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測RNA完整性。按照SMARTerTMRACE 5′/3′Kit (Clontech) 試劑盒說明, 合成cDNA第一鏈,用于全長cDNA 5′和3′端序列快速擴增的模板。根據(jù)表皮轉(zhuǎn)錄組資料及甲殼動物表皮蛋白RR保守序列,設計降落PCR特異性引物RMnCP-5-R和RMnCP-5-F(表1)。
PCR產(chǎn)物經(jīng)1%的瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測后,用BIOMIGA Gel/PCR Extraction Kit回收,采用pUC19, Linearized(Clontech)連接,利用DH5α(TaKaRa)感受態(tài)細胞進行轉(zhuǎn)化,培養(yǎng)得到的陽性克隆經(jīng)過菌液PCR驗證后由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司進行序列測序。

表1 基因克隆和實時定量所用引物
1.3 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因序列特征分析
將5′-RACE片段和3′-RACE片段序列進行拼接,開放閱讀框利用ORF finder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html)查詢;Conserved Domain Search Service (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi)在線工具進行保守域分析;Protparam程序(http://web.expasy.org/protparam/)預測氨基酸等電點、分子量等參數(shù);TMHMM、SingalP 3.0 Server(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/、http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-3.0/)等在線軟件分析蛋白的跨膜結(jié)構(gòu)和預測信號肽。MEGA 6.0軟件鄰接法構(gòu)建系統(tǒng)進化樹。SMS工具包(http://www.bio-soft.net/sms/)進行氨基酸多序列比對。
1.4 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因的表達分析
MiniBEST Universal RNA Extraction Kit(TaKaRa)試劑盒提取蛻皮間期、蛻皮前早期和蛻皮前晚期以及KK-42處理后0、3、6、12、24 h和48 h日本沼蝦步足RNA,反轉(zhuǎn)錄合成cDNA。根據(jù)表皮轉(zhuǎn)錄組資料設計特異性引物QMnCP-5-F和QMnCP-5-R (表1),18S rRNA 基因作為內(nèi)參進行實時熒光定量PCR, 每個樣本做3個平行。數(shù)據(jù)處理采用相對值2-△△CT計算,SPSS 13.0進行統(tǒng)計分析。
2 結(jié) 果
2.1 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因cDNA全長克隆
日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因cDNA全長796 bp,ORF包含158個氨基酸殘基,基因第1~136 bp為5′UTR區(qū),第137~151位編碼以起始密碼子ATG為開端的信號肽序列,覆蓋15個氨基酸殘基,幾丁質(zhì)結(jié)合結(jié)構(gòu)域——RR基序從第90位氨基酸開始至第124位氨基酸結(jié)束,覆蓋35個氨基酸殘基,終止密碼子TAG,3′UTR區(qū)有表明序列完整性的加尾信號AATAAA及polyA尾(圖1)。預測該蛋白等電點為4.22,分子量為16.46 ku,無跨膜結(jié)構(gòu)。
2.2 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5氨基酸序列同源性分析
利用MEGA 6.0軟件鄰接法將日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5氨基酸與相關代表甲殼動物和昆蟲的表皮蛋白氨基酸序列共同構(gòu)建發(fā)育樹(圖2),參與構(gòu)建發(fā)育樹的表皮蛋白均包含RR-1基序。結(jié)果顯示,日本沼蝦和其他甲殼動物聚為1支,節(jié)肢動物另聚3支,其中日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5和克氏原螯蝦表皮蛋白Csap-2單獨聚為1小支,二者相距最近。經(jīng)BLASTP比對表明,日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5氨基酸序列與紅螯螯蝦(Cheraxquadricarinatus)、美洲螯龍蝦(Homarusamericanus)、黃道蟹(Cancerpagurus)、藍蟹、日本囊對蝦相似度41%~53%,其中與克氏原螯蝦Casp-2相似度最高,達76%(圖3)。

圖1 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因核苷酸序列及推測的氨基酸序列實線方框:起始密碼子(ATG)和終止密碼子(TAG);灰底框:poly(A)加尾信號(AATAAA);*:終止密碼;下劃線:信號肽;虛線:RR基序;圓圈:RR基序中保守的氨基酸.

圖2 鄰接法構(gòu)建的日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5與其他物種表皮蛋白的系統(tǒng)進化樹

圖3 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5與其他物種表皮蛋白的氨基酸序列比對日本沼蝦CP-5:KU356774;藍蟹AMP6.0:AAV28477.1;藍蟹CP14.1:ABB91676.1;紅螯螯蝦M15:AIN36963.1;日本囊對蝦DD9A:BAA90875.1;克氏原螯蝦Casp-2:BAF73806.1;克氏原螯蝦SCBP-1:BAM99303.1;美洲螯龍蝦AMP1A:P81384.1;美洲螯龍蝦AMP4:P81388.1;黃道蟹AM1159:P81576.1.RR一致序列標注于多序列下方.
2.3 蛻皮周期不同階段日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因表達分析
實時熒光定量PCR結(jié)果表明,日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因在蛻皮間期、蛻皮前早期和蛻皮前晚期均有表達,但表達量存在差異(圖4),在蛻皮前晚期急劇升高,是蛻皮間期的1400倍,與之呈極顯著差異(P<0.01)。
2.4 KK-42對日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因表達的影響
KK-42處理能顯著上調(diào)基因的表達,尤其是蛻皮前早期和蛻皮間期。K-42處理后48 h,蛻皮間期的表達量是對照組的2.1倍(圖5a);在3、6 h和48 h,蛻皮前早期表達極顯著升高,分別是對照組的6.3、4.8倍和11.4倍(圖5b);在蛻皮前晚期,處理組的轉(zhuǎn)錄水平明顯降低(圖5c)。
3 討 論
RR基序[Gx8Gx6YxAxExGYx7Px2P](x代表任意氨基酸,阿拉伯數(shù)字代表任意氨基酸的數(shù)目)最先在昆蟲中發(fā)現(xiàn),是表皮蛋白中分布最廣、研究最為深入的基序[15-18]。離體研究顯示,該基序能結(jié)合幾丁質(zhì),覆蓋35個氨基酸殘基。甲殼動物表皮蛋白是含RR基序、與蛻皮周期相關且種內(nèi)和種間相似度較低的一類結(jié)構(gòu)性蛋白。本試驗首次克隆出日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因cDNA全長,含RR基序(圖1)。對甲殼動物表皮蛋白的研究表明,RR基序可以鑒別表皮蛋白,是其特征性保守序列[1]。日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因編碼蛋白預測分子量是16.46 ku,與克氏原螯蝦、藍蟹的全長cDNA編碼蛋白類似[8-11];蛋白呈酸性(等電點為4.22),可能與表皮鈣化相關[9]。甲殼動物表皮蛋白常含有12~19個aa不等的信號肽,日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5含15個aa的信號肽,表明其屬于基質(zhì)蛋白,由上皮細胞分泌至胞外,參與表皮結(jié)構(gòu)的形成[9]。

圖4 日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5 在不同蛻皮時期的表達n=5/蛻皮時期.**表示與蛻皮間期比P<0.01.
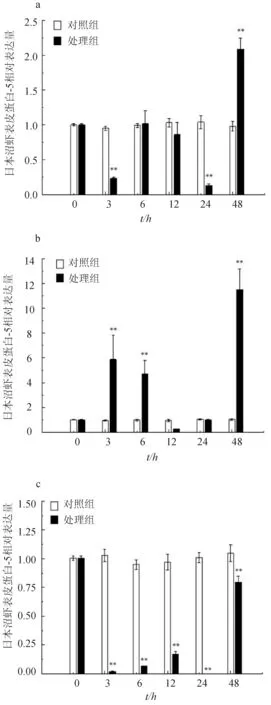
圖5 KK-42處理后日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5在不同蛻皮時期的表達變化n=5/組/時間點.a:蛻皮間期;b:蛻皮前早期;c:蛻皮前晚期.**表示與對照組比P<0.01.
在甲殼動物周期性蛻皮過程中,表皮結(jié)構(gòu)也不斷地變化,蛻皮前新的上表皮和外表皮已經(jīng)形成,蛻皮后內(nèi)表皮逐漸形成[19]。日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因在蛻皮前晚期顯著表達(圖4),與克氏原螯蝦[10]、藍蟹[8,20]表皮蛋白的表達特征相一致,因此推測日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5參與外表皮的形成。
前期研究顯示,KK-42能顯著提高日本沼蝦血淋巴中蛻皮激素20-羥蛻皮酮的滴度[21],合成表皮蛋白的表皮上皮細胞是蛻皮激素的靶組織,推測KK-42 上調(diào)日本沼蝦表皮蛋白-5基因的表達是間接效應;而蛻皮前晚期該基因表達顯著降低的原因,可能是KK-42促使蛻皮激素的峰值從蛻皮前晚期前移至蛻皮前早期,進而加速了新表皮的形成,蛻皮周期縮短[12]。
[1] Roer R,Abehsera S, Sagi A. Exoskeletons across the Pancrustacea: comparative morphology, physiology, biochemistry and Genetics. [J]. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2015, 55(5):771-791.
[2] Roer R,Dillaman R.The structure and calcification of the crustacean cuticle[J].Integrative and Comparative Biology, 1984, 24(4):893-909.
[3] Jacobsen S L, Andersen S O, Hojrup P. Amino acid sequence determination of a protein purified from the shell of the shrimp,Pandalusborealis[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, 1994, 109(2/3):209-217.
[4] Andersen S O.Characterization of proteins from arthrodial membranes of the lobster,Homarusamericanus[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 1998, 121(4):375-383.
[5] Andersen S O.Exoskeletal proteins from the crab,Cancerpugurus[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A, 1999, 123(2):203-211.
[6] Ikeya T,Persson P,Kono M,et al.The DD5 gene of the decapods crustaceanPenaeusjaponicasencodes a putative exoskeletal protein with a novel tandem repeat structure[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, 2001, 128(3):379-388.
[7] Endo H,Persson P,Watanabe T.Molecular cloning of the crustacean DD4 cDNA encoding a Ca2+-binding protein[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 2000, 276(1):286-291.
[8] Wynn A,Shafer T H.Four differentially expressed cDNAs inCallinectessapiduscontaining Rebers-Riddiford consensus sequence[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, 2005, 141(3):294-306.
[9] Inoue H,Ohira T,Ozaki N,et al.Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding a matrix peptide associated with calcification in the exoskeleton of the crayfish[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, 2003, 136(4):755-765.
[10] Inoue H, Yuasa-Hashimoto N, Suzuki M, et al.Structure determination and functional analysis of a soluble matrix protein associated with calcification of exoskeleton of the crayfish,Procambarusclarkii[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2008, 72(10):2697-2707.
[11] Suzuki M,Sugisaka-Nobayshi A,Kogure T,et al.Structural and functional analyses of a strong chitin-binding protein-1 (SCBP-1) from the exoskeleton of the crayfishProcambarusclarkii[J]. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 2013, 77(2):361-368.
[12] Guan J,Lv Y,Zhang Y,et al.A shortening effect of KK-42 on the moult cycle of juvenileMacrobrachiumnipponense(De Haan, 1849) (Decapoda, Palaemonidae)[J].Crustaceana, 2016, 89(1):85-95.
[13] Cesar J,Zhao B,Malecha S,et al.Morphological and biochemical changes in the muscle of the marine shrimpLitopenaeusvannameiduring the molt cycle[J].Aquaculture, 2006, 261(2):688-694.
[14] Ning Q,Fu S,Xu X,et al.A new and practical application of JH antagonist KK-42 to promoting growth of shrimpPenaeusvannamei[J].Aquaculture, 2007, 270(1/4):422-426.
[15] Togawa T,Dunn W A,Emmons A C,et al.Developmental expression patterns of cuticular protein genes with the R&R Consensus fromAnophelesgambiae[J].Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2008, 38(5):508-519.
[16] Charles J P.The regulation of expression of insect cuticle protein genes[J].Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 40(3):205-213.
[17] Willis J H.Structural cuticular proteins from arthropods: annotation, nomenclature, and sequence characteristics in the genomics era[J].Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 40(3):189-204.
[18] Zhu K Y,Merzendorfer H,Zhang W,et al.Biosynthesis, turnover, and functions of chitin in insects[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2016(61):177-196.
[19] Nagasawa H.The crustacean cuticle: structure, composition and mineralization[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience, 2012, 4(1):711-720.
[20] Faircloth L M,Shafer T H.Differential expression of eight transcripts and their roles in the cuticle of the blue crab,Callinectessapidus[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B, 2007, 146(3):370-383.
[21] 劉方,陳香麗,郭愛蓮,等. KK-42對日本沼蝦蛻皮激素及其受體表達的影響[J]. 河南師范大學學報: 自然科學版,2013,41(4):124-127.
Full-lengthcDNACloningandExpressionofCuticularProtein-5inFreshwaterPrawnMacrobrachiumnipponense
ZHENG Zhengfan, Lü Yanjie, WANG Pei, NING Qianji
( College of Life Science, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, China )
To explore the diversity and functions of cuticular proteins in crustacean, full-length cDNA of cuticular protein-5 in freshwater prawnMacrobrachiumnipponense(MnCP-5) was cloned using epidermis transcriptome by RACE technique. The bioinformatics, expression profile and effects of KK-42 for the expression of MnCP-5 were analyzed in different molt stages. The full sequence is 796bp containing a complete 477 bp ORF which encodes 158 amino acids with RR motif, a calculated molecular mass of 16.46 ku and pI of 4.22. Comparison of amino acid sequences in crustacean, MnCP-5 shared 41%-53% identity with others, and the maximal similarity of 76% with swamp red prawnProcambarusclarkiiCasp-2. The Quantitative Real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) showed that MnCP-5 was expressed on all 3 stages—C, D0-2and D3-4, while the relative expression level at stage D3-4was 1400 times as the level at stage C with very significant difference (P<0.01). KK-42 treatment can up-regulate the expression of MnCP-5 at stage D0-2, and the expression levels at 3, 6 and 48 h were 6.3, 4.8 and 11.4 times as the levels in control group. KK-42 can importantly move forward the peak expression of MnCP-5 from stage D3-4to D0-2, which is involved in one of the potential molecular mechanisms of KK-42 for shortening the molt cycle of juvenile freshwater prawn.
Macrobrachiumnipponense; cuticular protein; gene cloning; expression; KK-42
10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2017.06.009
S917.4
A
1003-1111(2017)06-0747-06
2017-01-16;
2017-03-09.
河南省基礎與前沿技術研究項目(142300410021).
鄭征帆(1990—),女,碩士研究生;研究方向:甲殼動物生長發(fā)育的體液調(diào)節(jié). E-mail: zhengzhengfan@163.com. 通訊作者:寧黔冀(1964—),女,教授,博士;研究方向:甲殼動物激素調(diào)控. E-mail: nqjnqj1964@163.com.

