基于光斑位置傳感器的長導軌準直系統
羅 凱,陳培鋒,王 英
(華中科技大學 光學與電子信息學院,武漢 430074)
基于光斑位置傳感器的長導軌準直系統
羅 凱,陳培鋒*,王 英
(華中科技大學 光學與電子信息學院,武漢 430074)
為了檢測長導軌的直線度,采用激光作為參考基準線,將2維光斑位置傳感器作為光電轉換器件。當固定在導軌滑塊上的2維光斑位置傳感器沿著導軌移動時,光斑的位置數據會通過藍牙模塊傳輸到終端上,輸入位置信息之后,軟件會自動繪制出導軌的2維直線度曲線。結果表明,計算出激光偏角帶來的誤差遠小于1μm;通過高精度位移平臺,實驗驗證了系統的精度可達到3.4μm;實際使用中,檢測了7.2m的長導軌,取得了長導軌的直線度數據,重復精度可達5μm。這一結果對長導軌直線度測量的研究是有幫助的。
激光技術;激光準直;比對實驗;光斑位置傳感器
引 言
導軌直線度[1-2]是評價機床質量的重要指標,直接影響機床加工出來的產品精度和機床質量。在機床生產過程中,檢測機床直線度并進行修正[3-5]是提升機床質量關鍵的環節。
導軌直線度的傳統檢測方法有平尺法、鋼絲法等。目前國內普遍采用的通用工具如水平儀、自準直儀等[6],多是以測量元件的精度為基準,人為引入的誤差較大,其檢測精度難以滿足目前工業界的需要[7]。激光具有高方向性以及高亮度等優點,非常適合作為測量的基準。使用激光作為測量基準的測量方法與傳統測量方法相比,具有測量精度高、體積小、幾乎不受被測導軌長度的制約等優點[8]。隨著科技的發展,直線度檢測發展至自動測量[9],其中,以圖像控制器(charge-coupled device,CCD) 或光斑位置傳感器[10](position-sensitve device,PSD)等光電傳感器為核心的激光準直技術被不斷應用在直線度檢測領域中[11-13],使得直線度準直精度至少提升了一個數量級[14]。本文中介紹的基于PSD的長導軌準直系統,以精度為3.4μm的PSD為接收器,測量長度為7.2m的導軌,重復精度優于5μm。
1 工作原理
圖1為系統原理圖。導軌直線度測量系統主要分為3個部分:發射模塊、接收模塊和處理模塊。發射模塊發出激光,接收模塊探測激光光斑重心,并且固定在導軌滑塊上隨之一起運動,處理模塊負責處理、展示數據。向處理模塊中輸入導軌的坐標后,處理模塊會顯示導軌的直線度偏差曲線,標出導軌不同位置的直線度偏差。
發射模塊由He-Ne激光器和透鏡組組成。He-Ne激光器發出激光之后,經過透鏡組的準直與放大,與導軌平行地發射到接收模塊上。經過處理之后的激光準直性良好[15],光斑直徑不超過2mm,功率約為5mW[16-17]。
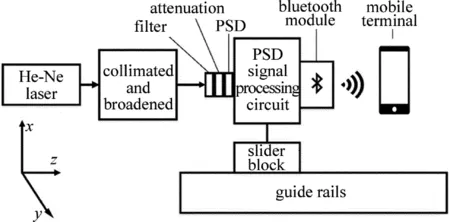
Fig.1 Sketch map of the system
接收模塊主要由紅光濾光片、衰減片、PSD、PSD處理電路和藍牙模塊組成,其主要功能是檢測出光斑的重心坐標并通過藍牙模塊發送給移動終端。紅光濾光片的作用在于把自然光和He-Ne激光器發出的紅光(632.8mm)分離。衰減片的作用在于將接收到的激光功率控制在1mW以下。PSD主要功能是檢測光斑的重心位置,中心區域的檢測精度可以達到3.4μm。由于PSD輸出信號會受到暗電流、非線性失真等因素的負面影響,給PSD配套使用了一塊處理電路板(濱松公司C9069)用于提高PSD檢測的精確性。藍牙模塊用于和移動終端的遠程通信。整個接收模塊用鋁制外殼包裹用于使用現場屏蔽電磁干擾和灰塵。
處理模塊即移動終端,可以是安卓手機或者筆記本電腦。安裝了為實驗特制的軟件之后即可接收實驗數據,在輸入導軌坐標之后,能夠繪制導軌的直線度曲線,并標明導軌每個位置的直線度偏差,精確到5μm。圖2為手機上繪制直線度曲線的軟件圖。
Fig.2 Software interface
2 硬件設計
用Reallight公司生產的He-Ne激光器輸出單模激光,功率約為5mW[18]。擴束準直分別使用焦距為8mm以及200mm的凸面鏡,80mm鏡片焦點處放置直徑為0.1mm的小孔進行空間濾波。濾波后激光準直性和單色性得到增強。
接收模塊核心部件PSD為日本濱松公司生產的S1880型2維位置傳感器,光斑重心測量精度為3.4μm。PSD安裝在C9069型電路板上,PSD接收光斑后輸出光斑的重心坐標給電路板,由于PSD本身的枕形結構[19],電路板使用特定的算法[20-21]修正了這一結構帶來的誤差[22]。輸出接口為RS232串行接口,接上藍牙模塊即可在30m內進行數據的無線傳輸。
3 驗證實驗
3.1 關于PSD傾斜帶來的誤差分析
從圖1中可以看出,接收模塊的核心部件PSD是固定在滑塊上的,PSD始終垂直于導軌,而導軌并不是完美的直線,存在著左右與上下的起伏,因此隨著滑塊在導軌上的滑動,PSD和激光不再是垂直的關系,兩者之間存在一個偏角α,這個偏角會對PSD測量的坐標產生影響[23]。
圖3為激光偏角的原理圖。其中直線AC代表激光,A點是滑塊移動之前激光與PSD的交點,C點是滑塊移動之后激光與PSD的交點。直線AB,BD是輔助線,AB平行于導軌,BD垂直于AC。
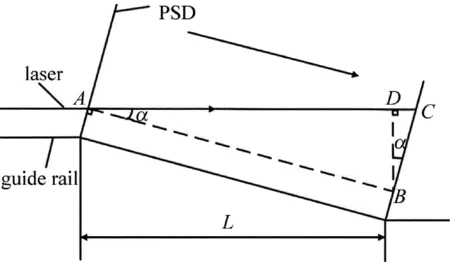
Fig.3 Measurement error caused by laser deflection angle
當導軌出現傾斜時,測量系統測得的光斑位移為線段BC(設為d1),實際上的導軌偏差位移為線段BD(設為d2),測量誤差設為δ,直線AC和直線AB之間的夾角設為α,則有以下關系:
導軌在直線度測量之前都會經過普通水平尺的測量,精度為0.029°,等于0.5mm/m,所以,α<0.029°。另外d1(即線段BC長度)被PSD的直徑限制,小于6mm。由此可以算出:

δ?1μm,相對于PSD的精度3.4μm來說可以忽略不計。因此,激光偏角對直線度測量造成的誤差可以忽略不計。
3.2 PSD精度驗證實驗
日本濱松公司給出PSD的參考精度為3.4μm。為了驗證長距離情況下PSD的使用精度,采取了高精度位移平臺來進行驗證實驗,位移平臺精度達到1μm,激光器固定在距離PSD 10m處,檢測裝置和位移平臺一起移動,讀出位移平臺上的數據和PSD導軌準直系統給出的位移數據,接著進行比較,觀察PSD的精度,如表1所示。
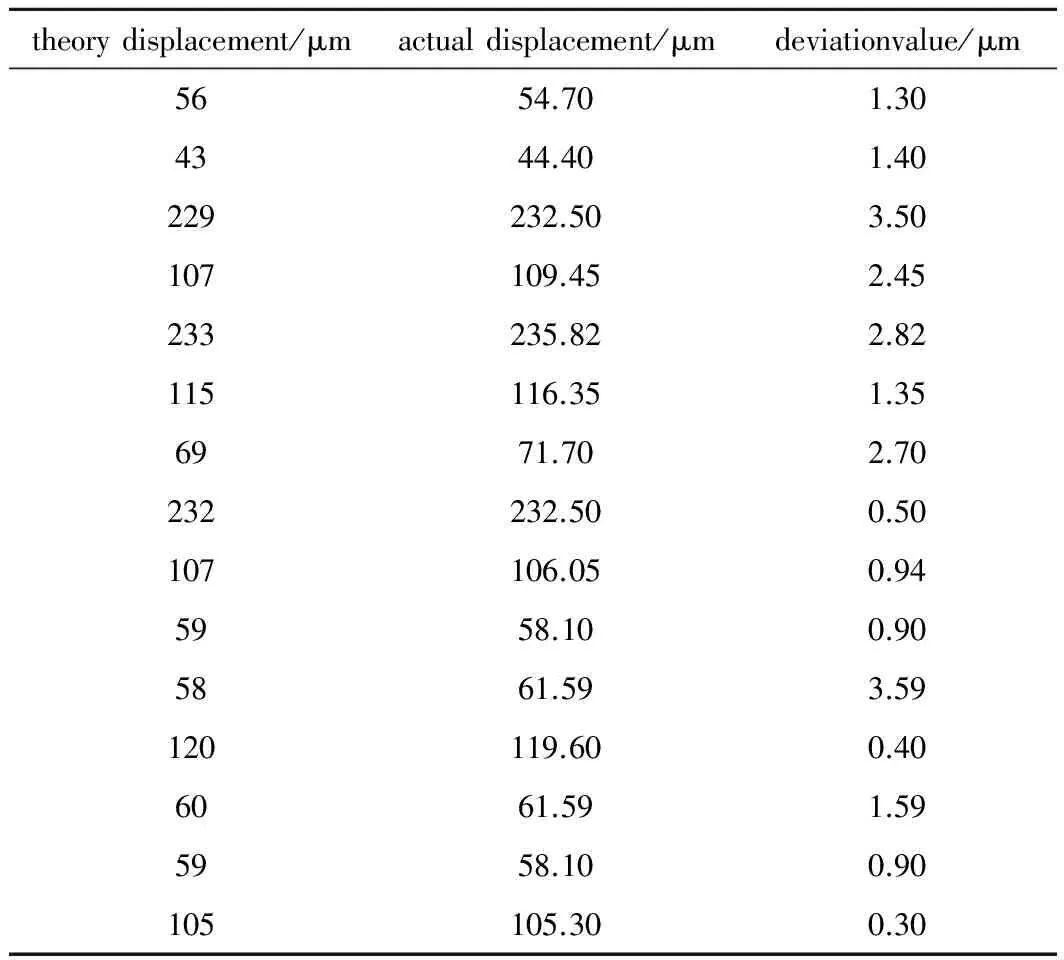
Table 1 Displacement of micro-displacement platform and PSD
從表1中可以看出,一共15組數據,平均誤差為1.64μm,最大誤差為2.70μm,標準差為1.06μm,小于3.4μm。基于以上數據可以得出結論:PSD的測量精度達到了3.4μm。
3.3 導軌精度檢測實驗
為了檢驗導軌準直系統的實際使用情況,在河南某數控機床有限公司開展了現場實驗,檢測了還沒有經過準直的機床。導軌長度為8m,由于接收模塊在導軌上的滑塊本身長30cm,不可以移出導軌,所以只測了7.2m的長度。每隔30cm測一個點,一共測了25組數據,重復測試了3次。
導軌在x,y方向上的直線度如圖4所示。導軌3次測量的標準差如圖5所示。
從圖4中可以看出機床導軌在x(水平)方向、y(垂直)方向上的直線度。x方向上的偏差較小,y方向上偏差較大,這是由于導軌安裝的方式決定的,x方向沒有螺絲固定,精度主要依賴于導軌出廠時的精度,本身不易產生偏移。y方向由螺絲固定,螺絲的松緊會造成導軌的形變,從而引起導軌的起伏,即y方向上的誤差。
從圖5中可以看出,導軌x方向、y方向重復精度都小于4μm,滿足5μm的精度要求。這意味著工人可以根據這些數據進行機床準直的調節,預期調節精度可以達到5μm。
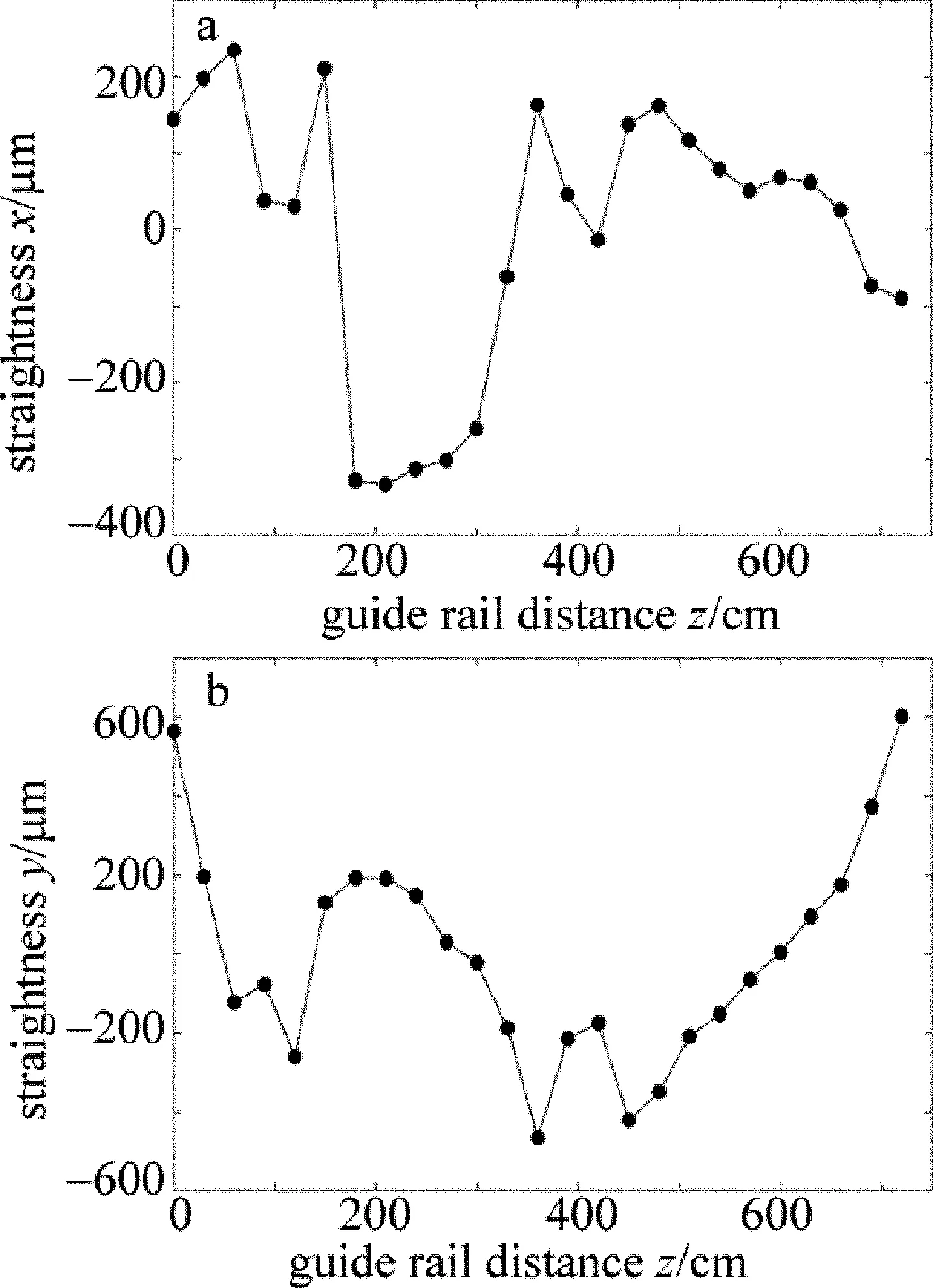
Fig.4 Straightness of guide rail
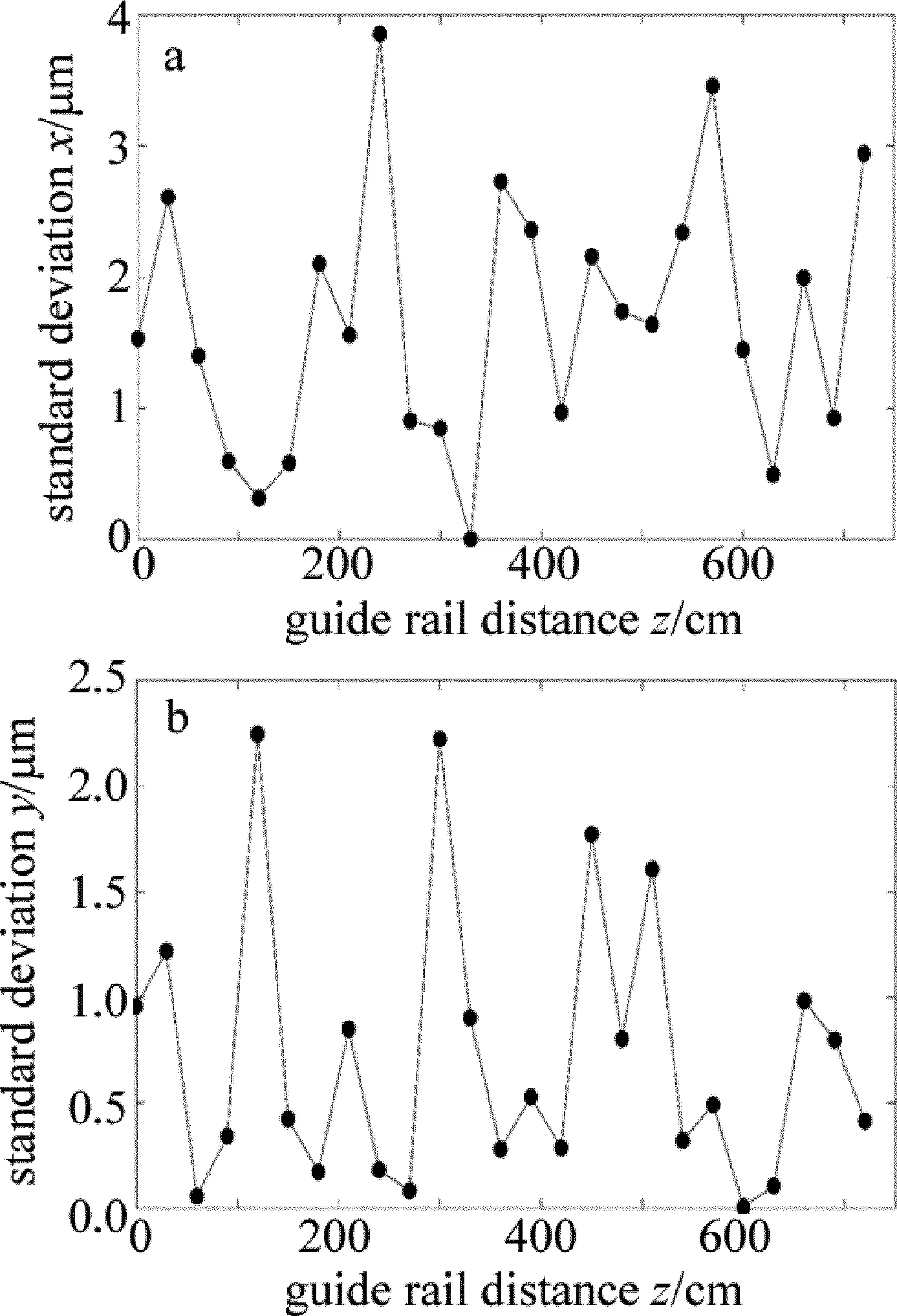
Fig.5 Standard deviation of the straightness
4 結 論
設計出了一套安裝簡單、使用方便的導軌準直系統,能夠滿足高精度導軌直線度的測量要求。通過理論計算,排除了激光偏角的影響,通過實驗驗證了PSD的精度,達到了3.4μm;通過工廠的實驗,證明導軌準直系統在測量7.2m長的導軌時,重復精度可以達到5μm,滿足高精度導軌直線度的測量要求。
[1] WANG Y P. Research of flatness and linearity testing system[D].Shenyang: Shenyang University of Technology,2004:9-38(in Chin-ese).
[2] YUE W L, WU Y. A fast evaluation method for flatness and straightness tolerance by means of incremental algorithm[J].Acta Metrologica Sinica, 2008, 29(2): 120-123(in Chinese).
[3] HUANG F G, CUI Ch C. Comparison of evaluating precision of straightness error between least square method and least envelope zone method[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2007, 15(6):879-893(in Chinese).
[4] LI Y J, ZHENG Z G. Calculation of straightness error and computerization[J].China Measurement Technology,2007,33(3):67-69(in Chinese).
[5] HU Zh X. Research on digitized evaluation theory and algorithm for the straightness error[D].Hunan: Hunan University,2012:15-94(in Chinese).
[6] SONG Q. Research on straightness measurement system of long rails based on 2D-PSD[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2014: 2-20(in Chinese).
[7] LI F. Study on straightness testing system of super-length guideway[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2002: 2-15(in Chinese).
[8] Lü A M, WANG Zh X, HE A Zh,etal. Measuring the straightness of the long slideway using PSD[J].Journal of Transducer Technology,1996(5):55-56(in Chinese).
[9] JIA T X, XU X P, DONG W B. Design of automatic testing system for 2-D position sensitive detector(PSD)[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor,2012(10):67-69(in Chinese).
[10] MA Ch G, YUAN H X, HE A Zh. Research of anti-jamming in facula orientation[J]. Laser Technology, 2002, 26(4): 308-310(in Chinese).
[11] MOU L N. Displacement detection system design based on PSD[D]. Taiyuan: North Central University, 2007:2-30(in Chinese).
[12] LIU P, GAO L M, LE K D. Laser measurement system for rail linearity[J]. Laser Technology, 2009, 33(6): 575-578(in Chinese).
[13] HU Ch D, LI Y Q, Zh X,etal. Laser alignment measuring and testing equipment based on interference fringe[J]. Laser Technology, 2009, 33(5): 522-525(in Chinese).
[14] YANG Sh L, SU Y B, HE J T,etal. Study of measurement accuracy of position sensitive detectors[J]. Laser Technology, 2014, 38(6): 830-834(in Chinese).
[15] FENG Q B, LIANG J W. Development of a single mode fiber laser collimator[J]. Laser Technology, 1994, 18(6): 357-360(in Ch-inese).
[16] Lü A M, YUAN H X, HE A Zh. The research in the influence of beam spot on the precision of PSD[J]. Laser Technology, 1998, 22(5): 294-297(in Chinese).
[17] Lü A M, YUAN H X, HE A Zh. Experimental study of the effect of light source on position precision of PSD[J]. Laser Technology, 2000, 24(3): 192-195(in Chinese).
[18] FENG Q B, ZHANG B, KUANG C F. A straightness measurement system using a single-mode fiber-coupled laser module[J]. Optics & Laser Techology,2004,36(4):279-283.
[19] SONG C, YENG Ch S. Linearity indices and linearity improvement of 2-D tetralateral position-sensitive detector[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, September,2010,57(9):2310-2316.
[20] LIU Ch, MA Y. Nonlinear correction of PSD with genetic algorithm based on neural network[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument,2015,29(8):1157-1163(in Chinese).
[21] LIN Q S, YANG X J, WANG J X,etal. 2-D nonlinear correction in an improved BP neural network[J]. Laser Technology,2012,36(1):124-130(in Chinese).
[22] LI Zh K, QIN Y Y. Research of on-line measurement and non-linearity correction of two dimention PSD device[J]. Laser Technology, 2004, 28(4): 370-372(in Chinese).
[23] EKINCI O, MAYER J R R. Relationships between straightness and angular kinematic errors in machines[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2007,47(12/13):1997-2004.
Longguiderailalignmentsystemsbasedonpositionsensitivedetectors
LUOKai,CHENPeifeng,WANGYing
(School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China)
In order to detect the long rail straightness, laser was used as the reference line, and 2-D position sensitive detector was used as photoelectric converter. When 2-D position sensitive detector was fixed on the guide rail slider and moved along the guide rail, the spot position data was transmitted to the terminal through bluetooth module. After entering the location information, the curve of 2-D straightness was drawn by the software automatically. The results show that, through theoretical analysis, the error of laser deflection angle is calculated and is less than 1μm. The system accuracy is verified by high-precision displacement platform experiment and reaches 3.4μm. In practical appliaction, a long rail of 7.2m is detected and the straightness data of long guide rail is obtained. The repeatability precision can reach 5μm. The study is helpful for straightness measurement of long rails.
laser technique; laser alignment; contrast experiment; position sensitive detector
1001-3806(2018)01-0030-04
羅 凱(1993-),男,碩士研究生,現主要從事光學電子器件的研究。
*通訊聯系人。E-mail:pfchen@hust.edu.cn
2017-02-22;
2017-04-13
TH741
A
10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.01.006

