厄米-高斯光束在飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性
姜其暢,蘇艷麗,聶合賢,馬紫微,李永宏
(運城學院 物理與電子工程系,運城 044000)
厄米-高斯光束在飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性
姜其暢,蘇艷麗,聶合賢,馬紫微,李永宏
(運城學院 物理與電子工程系,運城 044000)
為了研究厄米-高斯光束在光折變飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性,采用有限差分方法數值求解了光波演化方程,理論分析了厄米-高斯光束的傳輸特性。結果表明,1維1階、2階和3階厄米-高斯光束在光折變非線性介質中傳輸時,在合適的非線性條件下,均可以形成呼吸模式的孤子;隨著非線性的加大,厄米-高斯光束的光場分量之間的相互分離趨勢將逐漸變弱,同時,每個光場分量的振幅起伏效應會更加明顯;改變厄米-高斯光束的入射位置、入射角度對其傳輸特性沒有影響;2維厄米-高斯光束的傳輸特性和1維情況是類似的。厄米-高斯光束的這些特性在光開關領域有一定的應用前景。
非線性光學;厄米-高斯光束;光折變效應;空間孤子
引 言
1998年,CASPERSON和TOVAR給出了近軸近似直角坐標下亥姆霍茲方程的一類特解,即所謂厄米-正弦類-高斯光束,它是具有廣泛代表性意義的一類光束[1-5]。厄米-高斯光束被認為是厄米-正弦類-高斯光束的特例。目前,人們對厄米-高斯光束的研究重要集中在兩個方面,一方面是研究厄米-高斯光束對各種介質圓柱、介質球的散射問題[6-8];另一方面是研究厄米-高斯光束在大氣湍流[9-11]和非線性介質[12-15]中的傳輸問題。近幾年,人們報道了厄米-高斯光束在強非局域非線性介質中的傳輸特性,發現厄米-高斯光束可以在一定條件下形成厄米-高斯孤子,由于厄米多項式的調制作用,厄米-高斯孤子相比于傳統的基模高斯孤子[16-17]表現出更豐富的傳輸特性,但是關于厄米-高斯光束在光折變飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性還少有相關報道。本文中借助光波演化的非線性薛定諤方程,數值研究了厄米-高斯光束在光折變飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性。
1 基本理論
考慮厄米-高斯光束在光折變晶體中沿z軸傳輸,其偏振沿x方向;假定光束只在x方向衍射,晶體光軸和外加電場均沿x方向。為了便于數值分析,取歸一化的坐標參量s=x/x0,ξ=z/(kx02)。其中,x0是任意空間寬度,k=k0ne=(2π/λ0)ne,λ0是自由空間波長,ne是未受擾動的非尋常光折射率。光波傳輸的歸一化方程可以表示為:
式中,U(s,ξ)是歸一化光波包絡,非線性系數β=(k0x0)2(ne4r33/2)E0,r33是電光系數,E0是外加電場強度。入射面處的厄米-高斯光束可以表示為:
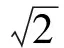
式中,Hn是厄米多項式,n表示厄米多項式的階數。如果x0=w0=50μm(w0表示高斯光束的光斑大小),λ0=0.5μm,相應的高斯光束的瑞利距離ZR=πw02/λ0=15.7mm。下面基于(1)式和(2)式數值分析各階厄米-高斯光束的傳輸特性。
2 數值結果
當厄米多項式H0=1時,(2)式即退化為基模高斯光束的表達式。如果外加電場為零,則非線性參量β=0,可得到圖1a所示結果,圖中橫縱坐標均是歸一化的無量綱坐標。ξ=1對應實際傳輸距離大約是70mm,可以看到超過瑞利距離(約ξ=0.2),由于光束的衍射效應,高斯光束的光斑能量逐漸彌散。為了抑制光束的這種衍射效應,增加外加電場強度,當非線性系數β=5.5,基本可以抑制光束的衍射,形成呼吸模式的高斯孤子,為了更清楚看到其呼吸模式,可以將傳輸距離增加到ξ=6,如圖1b和圖1c所示。
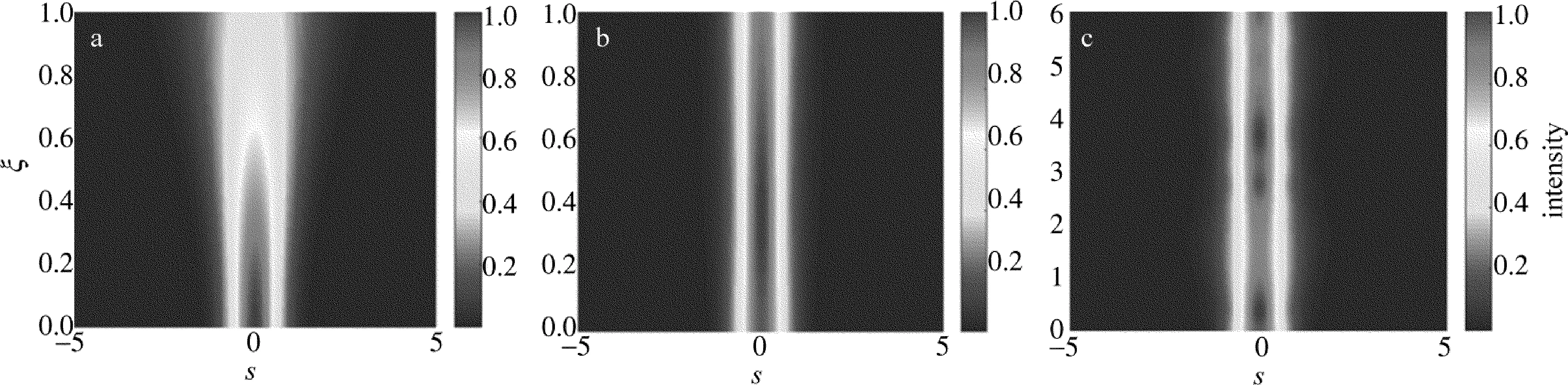
Fig.1 Natural diffraction and soliton propagation of fundamental-mode Gaussian beama—β=0 b—β=5.5 c—β=5.5
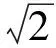

Fig.2 Propagation of first-order Hermite-Gaussian beam
如果加大非線性即加大外加電場,兩個光場分量之間的分離距離可以明顯減小,但是相應的每個光場分量的起伏效應會顯著加大,如圖3所示。通過改變外加電場的大小可以靈活調節兩個光場分量之間的距離,從而可以控制出射面某一點處光信號的有無,這在光開關領域有一定的應用前景。
同樣,當厄米多項式取H2=8s2-2時,(2)式就是2階厄米-高斯光束的表達式。此時,在初始入射面,2階厄米-高斯光束呈現對稱的3個光場分量,取合適的外加電場強度如β=15,同樣可以形成呼吸模式的孤子,中間光場分量直線傳輸,兩側的光場分量彼此分離,而且分離的距離隨著傳輸距離的加大而增加;當外加電場強度加大時,比如β=25,兩側光場分量之間的分離距離明顯減小,但是3個光場分量振幅的起伏效應會更加明顯(見圖4)。
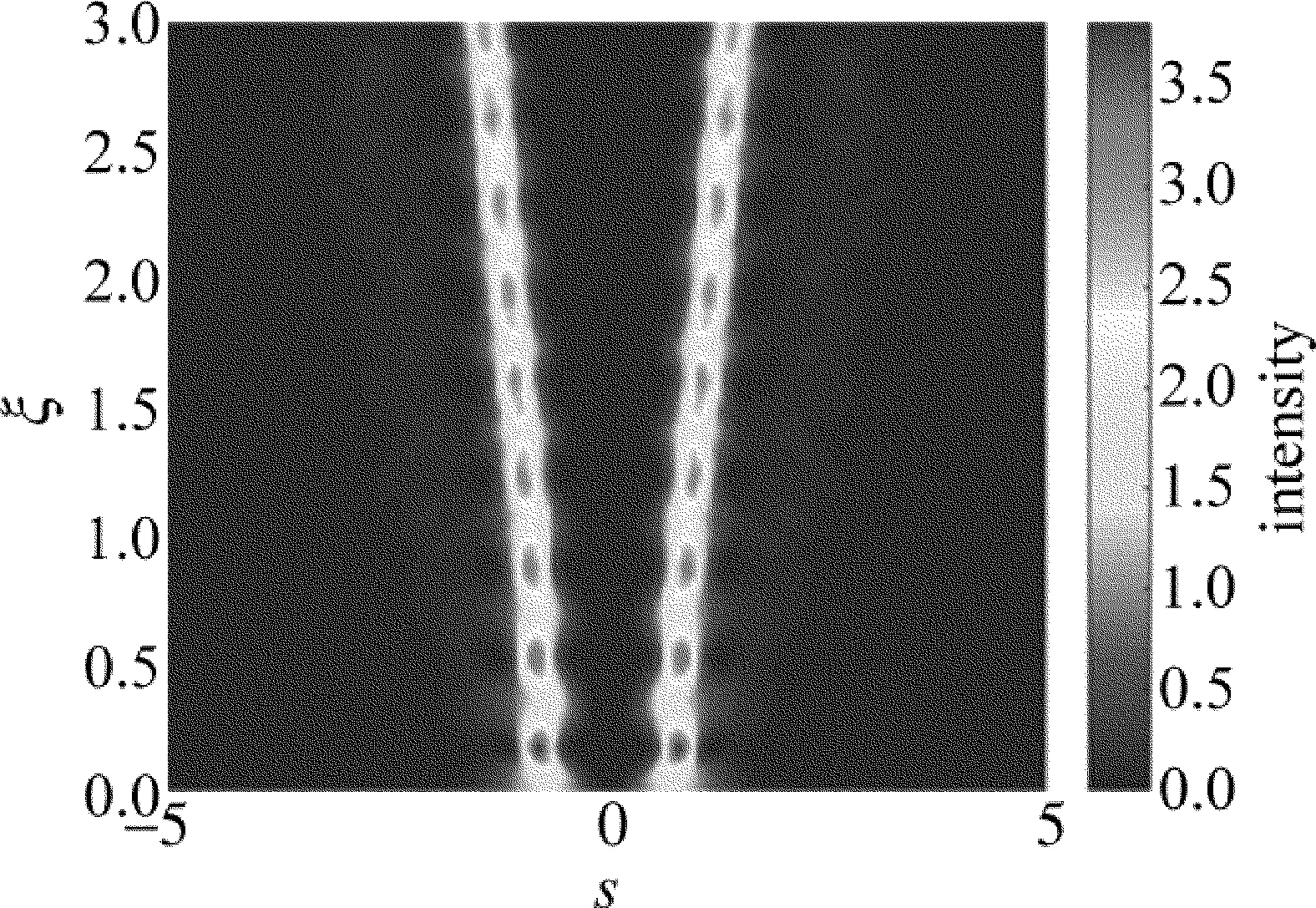
Fig.3 Propagation of the first-order Hermite-Gaussian beam at β=40
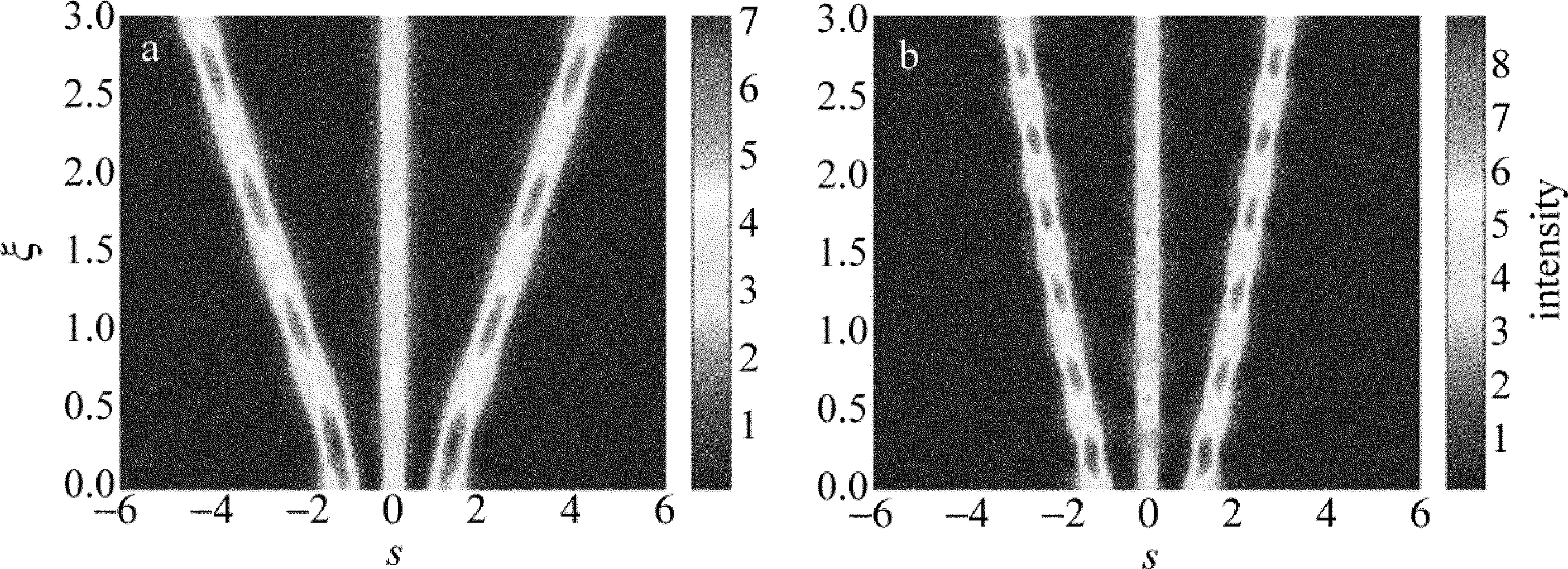
Fig.4 Propagation of the second-order Hermite-Gaussian beam under different nonlinear conditions
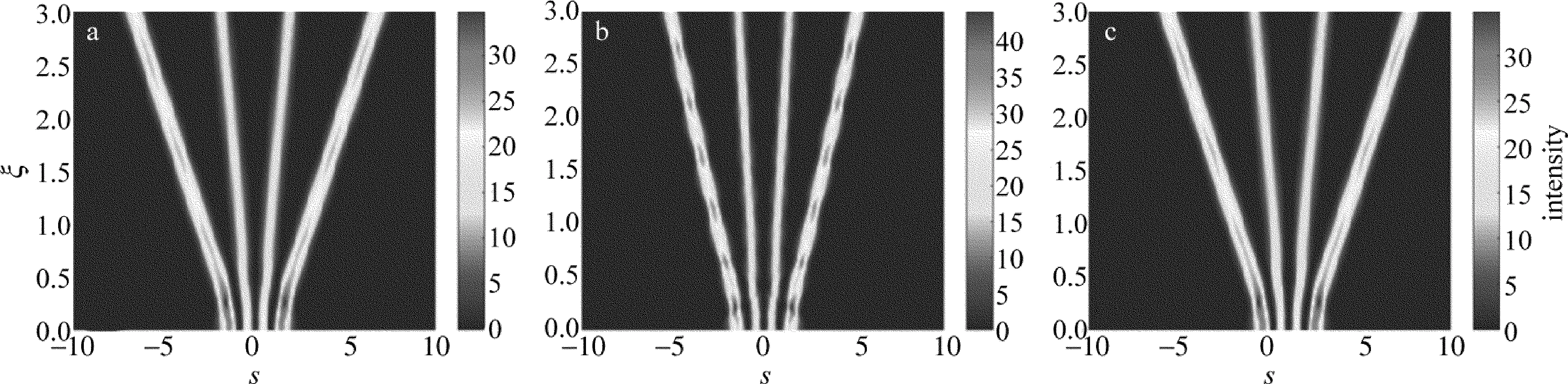
Fig.5 Propagation of the third-order Hermite-Gaussian beam under different conditions
光波傳輸的歸一化方程(1)式在2維情況時可以表示為[15]:
式中,sx=x/x0,sy=y/x0,分別是x方向和y方向的歸一化坐標。其它參量的意義和(1)式相同。這里以2階厄米-高斯光束為例,2維厄米-高斯光束表示為U(sx,sy,0)=(8sx2-2)(8sy2-2)exp(-sx2-sy2),同樣取非線性參量β=15,2維厄米-高斯光束在ξ=0,ξ=1.5和ξ=3處的橫截面強度分布如圖6所示。可以看到,在合適非線性條件下,2階厄米-高斯光束的每一個光場分量都以呼吸模式的孤子形式傳輸,而且隨著傳輸距離的加大,各個光場分量之間的距離會逐漸增加。
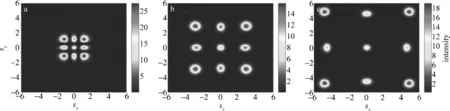
Fig.6 Propagation of 2-D second-order Hermite-Gaussian beam
3 結 論
分析了1階、2階和3階厄米-高斯光束在光折變飽和非線性介質中的傳輸特性,在合適的外加電場強度條件下,厄米-高斯光束的各個光場分量都可以形成呼吸模式的孤子,各個光場分量之間的分離距離可以由外加電場強度靈活操控。厄米-高斯光束的這些特性在光開關領域有一定的應用前景。
[1] CASPERSON L W, TOVAR A A. Hermite-sinusoidal-Gaussian beams in complex optical systems [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1998, A15(4):954-961.
[2] TOVAR A A, CASPERSON L W. Production and propagation of Hermite-sinusoidal-Gaussian laser beams [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1998, A15(9):2425-2432.
[3] ZHAO D, MAO H, LIU H. Propagation of off-axial Hermite cosh-Gaussian laser beams [J]. Journal of Optics, 2004, A6(1):77-83.
[4] YU S, GUO H, FU X,etal. Propagation properties of elegant Hermite-cosh-Gaussian laser beams [J]. Optics Communications, 2002, 204(1/6):59-66.
[5] ZHAO Q, HAO H Y, FAN H Y,etal. Focusing characteristics of partially coherent cosh-Gaussian beams propagating through turbulent atmosphere [J]. Laser Technology, 2016, 40(5):750-755 (in Chinese).
[6] YOKOTA M, KUDOU T, FUKUMITSU O. High-frequency scattering of a Hermite-Gaussian beam by a perfectly conducting cylinder [J]. Electronics Letters, 1987, 23(4):174-175.
[7] YOKOTA M, HE S, TAKENAKA T. Scattering of a Hermite-Gaussian beam field by a chiral sphere [J]. Journal of Optical Society American, 2001, A18(7):1681-1689.
[8] QU T, WU Zh S, SHANG Q Ch,etal. Far-field scattering of a chiral sphere located in a Hermite-Gaussian beam [J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2016, 36(4):0429001 (in Chinese).
[9] JI X L, CHEN X W, Lü B D. Spreading and directionality of partially coherent Hermite-Gaussian beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 2008, A25(1):21-28.
[10] JI X L, LI X Q. Effective radius of curvature of partially coherent Hermite-Gaussian beams propagating through atmospheric turbulence [J]. Journal of Optics, 2010, 12(3):035403.
[11] HUANG Y P, GAO Z H, WANG F H,etal. The effective radius of curvature of partially coherent Hermite-Gaussian linear array beams passing through non-Kolmogorov turbulence [J]. Optics Communications, 2014, 315(19):130-137.
[12] DENG D, ZHAO X, GUO Q,etal. Hermite-Gaussian breathers and solitons in strongly nonlocal nonlinear media [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 2007, B24(9):2537-2544.
[13] WANG Q, LI J Z. Elliptic Hermite-Gaussian soliton in anisotropic strong nonlocal media [J]. Optics Communications, 2016, 359:31-37.
[14] ZHONG L H, YANG J, REN Z M,etal. Hermite-Gaussian stationary solutions in strongly nonlocal nonlinear optical media [J]. Optics Communications, 2017, 383:274-280.
[15] LI Sh H, YANG Zh J, LU D Q,etal. Numerical study of Hermite-Gaussian beams in nonlocal thermal media [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2011, 60(2):024214 (in Chinese).
[16] KANG J, TANG Y L, LI D Y,etal. Propagation characteristics of Gaussian beam in logarithmically nonlinear media [J]. Laser Technology, 2000, 24(2):118-121 (in Chinese).
[17] SU Y L, JIANG Q C, JI X M,etal. The temperature properties of matching Gaussian beam in biased two-photon centrosymmetric paraelectric photorefractive crystals [J]. Optics and Quantum Electronics, 2012, 44(14):649-655.
PropagationcharacteristicsofHermite-Gaussianbeaminsaturablenonlinearmedia
JIANGQichang,SUYanli,NIEHexian,MAZiwei,LIYonghong
(Department of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Yuncheng University, Yuncheng 044000, China)
In order to study propagation properties of Hermite-Gaussian beams in photorefractive saturable nonlinear media, finite difference method was used to solve the evolution equation of light wave numerically and analyze the propagation properties of Hermite-Gaussian beams theoretically. The results show that, under suitable nonlinear conditions, 1-D Hermite-Gaussian beams of 1-order, 2-order and 3-order can form the solitons in respiratory mode during the propagation in photorefractive nonlinear media. With the increase of nonlinearity, the separation tendency among light field components of Hermite-Gaussian beams would become weaker. At the same time, the amplitude fluctuation effect of each light field component would be more obvious. The changes of incident position and incident angle of Hermite-Gaussian beams have no influence on its propagation characteristics. The transmission characteristics of 2-D Hermite-Gaussian beams are similar to those of 1-D. These properties of Hermite-Gaussian beams have certain application prospects in the field of optical switching.
nonlinear optics; Hermite-Gaussian beam; photorefractive effect; spatial solitons
1001-3806(2018)01-0141-04
山西省自然科學基金資助項目(2011011003-2)
姜其暢(1980-),男,博士,副教授,主要從事非線性光學和光場調控方面的研究。
E-mail:jiangsir009@163.com
2017-02-13;
2017-03-17
O437.5
A
10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.01.028

