Informationist roles and collaborations in curriculum innovation at the University of Michigan′s A.Alfred Taubman Health Sciences Library
.,
Uniesity of Michigan's A.Alfred Taubman Health Sciences Library
[Abstract]To address the ultimate mission to be "a valued partner, fully integrated into the work of the university and providing leadership in knowledge management for education, research, patient care, and community outreach", the University of Michigan A. Alfred Taubman Health Sciences Library (THL) has transformed from retitling librarians as informationists to shifting from a service to a collaboration focus. Infomationists at THL have spent several years building relationships and expertise to be true partners in curriculum integration and innovation within the health sciences schools and colleges at the University of Michigan and the curricular integration has becoming a constantly evolving process for THL informationists. Current article focus on how THL convert the librarian into informationist and how to make collaborations in curriculum innovation within different departments to furtherly improve the status of THL library in the University.
[Key words]Mission; Integrated; Informationist; Collaboration focus; Curriculum innovation
BACKGROUND
The University of Michigan A.Alfred Taubman Health Sciences Library (THL) has a stated mission to be "a valued partner,fully integrated into the work of the university and providing leadership in knowledge management for education,research,patient care,and community outreach"[1].To fulfill this mission,THL administration,Informationists,and staff take a proactive approach to identify and address emerging roles for the library in academic,research,and clinical activities within the health sciences.From re-titling librarians as Informationists[2]to shifting from a service to a collaboration focus,the Taubman Health Sciences Library continues to work on "transforming the health sciences of the future"[3].
This transformation takes many forms at THL,and is a continual process of innovation and reinvention.Systematic review integration,data management planning,research impact analytics,and global health are just a few of the initiatives that THL Informationists incorporate into their daily work.While library instruction is often considered to be one of the more traditional activities that the library is involved in,Infomationists at THL have spent years building relationships and expertise to become true partners in curriculum integration and innovation within the health sciences schools and colleges at the University of Michigan.
OURPARTNERS:MICHIGANMEDICINE&UMSCHOOLSOFHEALTHSCIENCES
The Taubman Health Sciences Library works with a variety of health-related partners on the University of Michigan Ann Arbor campus.THL Informationists collaborate with the faculty,students,and staff in academic units,which include the Medical School,School of Nursing,School of Dentistry,School of Public Health,School of Kinesiology,and College of Pharmacy.In addition,Informationists work directly with the clinical and research faculty and staff of Michigan Medicine,the University of Michigan′s health system.
Michigan Medicine is comprised of over 26,000 faculty,staff,students,trainees,and volunteers.The main medical campus is located in Ann Arbor,Michigan,but includes satellite locations throughout Michigan and northern Ohio that total more than 11 million square feet of clinical and research space.Michigan Medicine personnel fill three hospitals,multiple specialty centers[4],over 40 outpatient locations,and the North Campus Research Complex (former Pfizer headquarters,purchased by Michigan Medicine).These locations handle over 2.3 million outpatient visits per year,and more than 47,000 hospital stays in 1,000 beds.
Michigan Medicine has a total operating budget of more than $3.3 billion,and boasts one of the United State′s largest research budgets at $466 million[5].Informationists from the Taubman Health Sciences Library use a liaison model to build relationships with faculty,staff,and trainees in the clinical departments and research units that make up Michigan Medicine; each Informationist acts as the primary point person for a collection of clinical and research units that best align with their individual expertise and interests[6].
In addition to their Michigan Medicine clinical departments and research units,THL Informationists work in teams to collaborate with the faculty,staff,and students of the health sciences academic units.The University of Michigan Medical School (UMMS),School of Nursing (SoN),School of Dentistry (SoD),School of Public Health (SPH),School of Kinesiology (SoK),and College of Pharmacy (CoP) are each ranked in the top 5 in the United States.Together,the health sciences schools account for almost 50% of the University of Michigan′s $1.48 billion in research expenditures each year while producing some of the most sought-after graduates in the country[7].
CURRICULUM INTEGRATION & CURRICULUM MAPPING
THL Informationists are currently integrated into the curricula of each of the health sciences schools,through in-person instruction,online modules and distance education,individual consultations,and faculty development.This level of integration is not possible without years of individual relationship-building with faculty,students,and decision-makers within each academic unit,and integration points are constantly and consistently reviewed as pedagogy,content,and delivery methods evolve.The development of Core Teams of Informationists for each academic unit has been important to encouraging longitudinal relationship-building and ensuring that the library has the capacity to deliver new and innovative information skills sessions through various modalities.In general,each Core Team works with its respective school on course instruction,resource integration,faculty development & research,curriculum planning,and accreditation,and other school-specific information needs.
While Core Team membership can fluctuate depending on staffing levels and the educational needs of each academic health sciences unit,team composition is roughly:
Informationists on each Core Team have actively worked to be members of their schools′ respective curriculum committees; four teams have member status,and two actively advise curriculum committee faculty.This successful representation on curriculum committees allows the Core Teams to stay abreast of planned curricular changes while giving the committee members the opportunity to advocate for integration of content that is consistent with the information skills/literacy competencies defined by each school,and with the ACRL Framework for Information Literacy in Higher Education[8].
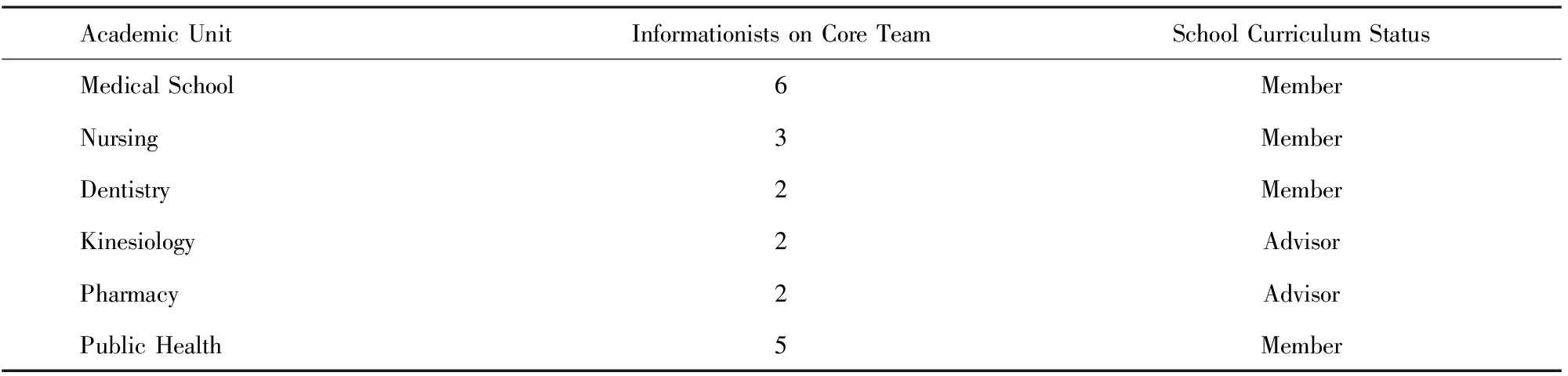
Academic UnitInformationists on Core TeamSchool Curriculum StatusMedical School6MemberNursing3MemberDentistry2MemberKinesiology2AdvisorPharmacy2AdvisorPublic Health5Member
Each school and program has different requirements for accreditation with their program′s governing body; for many,this takes the form of standardized competencies that students are expected to meet upon graduation.THL Informationists from each Core Team are currently mapping school and program competencies related to information to the relevant parts of the ACRL Framework in order to demonstrate and reinforce our efforts to integrate scaffolded,relevant information resources and instruction into each curricular path that a student may take.
The UM School of Kinesiology recently became the sixth school of health sciences that partners with THL; as Core Team members began teaching existing information sessions and integrating new sessions and content,all sessions were mapped to the ACRL Framework:
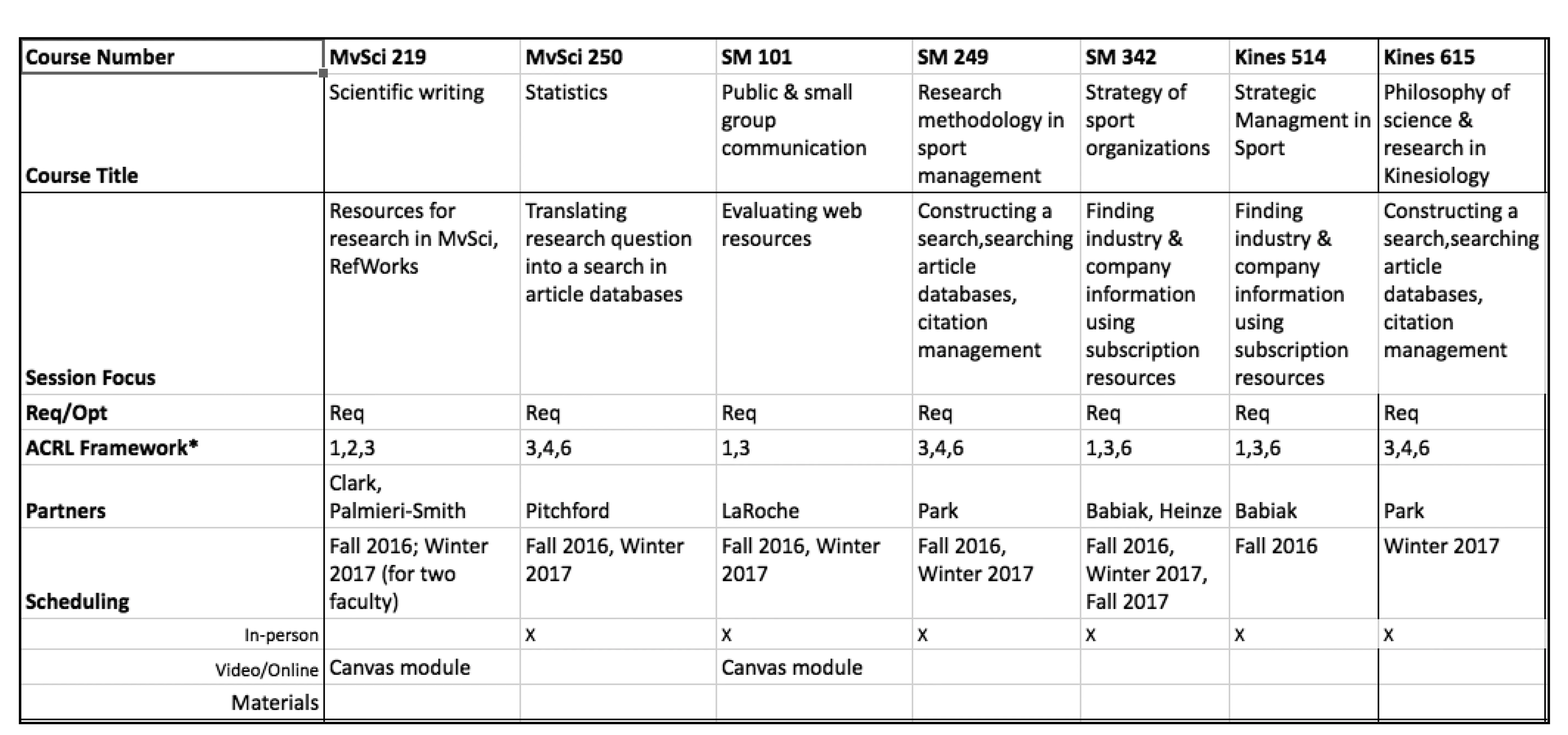
CURRICULUM INTEGRATION CASE STUDY: UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN MEDICAL SCHOOL
While curriculum mapping is taking place within all academic health sciences units,THL Informationists also leveraged their long-standing relationships and collaborations with the Medical School to play a key role in the development of a new,innovative curriculum development project funded by the American Medical Association.The Core Team for Medical Education has a long history of longitudinal curricular integration,with representation and instruction in all four years of the medical school curriculum.At the time,the medical school curriculum followed a traditional format of two years of preclinical education,and two years of clinical education and experience; Informationist-instructed sessions focused on background and foundational resources (textbooks),and high level of evidence publication types (practice guidelines,systematic reviews,and point of care resources) for the first two years.Instruction during the clinical years covered additional evidence-based medicine concepts,clinical resources (including drug databases,patient education resources,and mobile device resources),systematic review appraisal,and advanced database searching[9].
In June 2013,the American Medical Association announced that the UM Medical School was awarded funding to develop a new medical school curriculum,with the goal of fundamentally "transforming the training of tomorrow′s doctors".The UM Medical School,along with 10 other founding awardees,began the process of designing a flexible curriculum focused on developing students as outstanding clinicians,but also leaders in health care change.
The Accelerating Change in Medical Education Consortium schools identified six key areas to develop transformative solutions in medical education; while information skills and literacy can relate to all of them,Medical Education Core Team members immediately identified three to focus our integration efforts and curriculum mapping on: Developing flexible,competency-based pathways; Making technology work for learning; and Envisioning the master adaptive learner[10].
The new curriculum development process began in 2013,with the first full four-year class of students anticipated in 2019[11].THL Informationists took a proactive approach to integrating into the new curriculum; based on our strong relationships with medical education faculty,Informationists were invited to attend the Medical School Faculty Planning Retreat to participate in idea generation and work group formation.When calls went out to Medical School faculty to volunteer for curricular work groups,Informationists responded and were subsequently added to planning groups related to Leadership and Paths of Excellence; Evidence-based Medicine; Clinical Education; Administration; and more.An Informationist was selected to lead the Evidence-based Medicine working group,which positioned the Core Team to develop information-specific objectives and learning outcomes that were incorporated into the new curriculum.
Participation on the working groups continues to place Informationists in roles that allow increased integration into the new curriculum; many members of initial working groups now sit on the established curricular planning groups and we maintain representation on the Medical School Curriculum Policy Committee.Throughout the curriculum development process,all integration points map directly to the defined Medical School Competencies[12].Of particular note,Informationists have seen significant success integrating into specific curricular components:
Optimizing Patient Care Curriculum
The Optimizing Patient Care Curriculum (OPCC) takes the place of traditional EBM education.After leading the initial working group,an Informationist continues to serve as a member of the faculty planning group and other Core Team members act as course planners and instructors in all four years of the planned curriculum.Informationists write and grade formal exam questions related to our delivered content,train medical faculty group leaders on systematic review appraisal,and develop online learning modules and in-person active instructions sessions to meet OPCC objectives and school competencies.In the first two years of the developed curriculum,this has translated into six unique Informationist-led instructions sessions and the integration of multiple online modules.
Adapted 5S Pyramid
Informationists had long utilized RB Haynes′s 5S Evidence Pyramid[13]into instruction.To address additional information resources in the context of evidence-based resources,Core Team Informationists developed an adapted version of the pyramid,along with instructional video modules used in the OPCC curriculum and in other health sciences instruction[14].
Paths of Excellence
As part of the new Medical School curriculum focused on developing physician-leaders,the domain-focused elective Path of Excellence program is available to all medical students[15].Informationist integration into these programs started early,with a dedicated Informationist for Global Health working directly with the Global Health & Disparities Path.Due to the strong relationship and effective integration into the inaugural Path,Informationists were assigned to each subsequent Path as it was developed.Path Informationists work with the faculty and accepted students on longitudinal capstone projects related to their Path.A dedicated LibGuide is created for each Path to direct students to customized,topic-specific resources that they do not encounter during their clinical education[16].
CONCLUSIONS
Curricular integration is a constantly evolving process for THL Informationists,and we continue to foster faculty relationships and build knowledge about school-specific competencies and their relationship to information literacy and emerging information needs.While some components of instruction and integration will likely always be core,like information evaluation and subject-specific resources,it is important to constantly and proactively develop integration points for emerging information needs and trends.Presently,Core Teams for all health sciences units are beginning the work of mapping data education instruction to school competencies,and partnering with faculty to incorporate data use,data stewardship,and data planning into the various health sciences curricula.

