DEPTOR—mTOR信號通路介導的自噬在多發性骨髓瘤中對破骨細胞分化的調控作用
張浩然 喬旭旭 畢明宏 翟云芝 錢立宇 潘成武 趙論
[摘要] 目的 探討沉默RPMI-8226 DEPTOR基因表達在非接觸式共培養體系下,對破骨細胞分化因子(RANKL)蛋白表達及THP-1細胞向破骨樣分化的作用,并研究其可能機制。 方法 構建DEPTOR shRNA重組慢病毒載體轉染RPMI-8226細胞。通過Western blot技術從蛋白水平檢測RPMI-8226細胞中DEPTOR及RANKL的表達,Western blot檢測自噬相關蛋白LC-3和Atg5表達。構建共培養體系,分三組:THP-1細胞單培養組、THP-1+RPMI-8226細胞組和THP-1+DEPTOR shRNA組。應用抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(TRAP)染色法檢測THP-1向破骨樣細胞分化過程中抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶活性改變,應用RT-PCR法檢測THP-1細胞降鈣素受體(CTR)和組織蛋白酶(Cathepsin)-K mRNA表達水平。 結果 DEPTOR shRNA可明顯抑制RPMI-8226細胞中DEPTOR及RANKL蛋白表達(P < 0.05),DEPTOR shRNA組自噬相關蛋白LC-3和Atg5的蛋白的表達水平較陰性對照轉染組及未轉染組下降(P < 0.05)。THP-1細胞與RPMI-8226細胞共培養條件下可誘導THP-1細胞破骨樣分化,CTR和Cathepsin-K基因表達上調(P < 0.05);DEPTOR shRNA共培養條件下可抑制THP-1細胞向破骨樣細胞分化,CTR和Cathepsin-K基因表達減弱,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。 結論 DEPTOR shRNA能明顯抑制共培養體系中THP-1細胞的破骨樣分化,該作用可能與DEPTOR下調RPMI-8226細胞RANKL有關,抑制自噬可阻礙破骨細胞的分化成熟。
[關鍵詞] 骨髓瘤骨病;DEPTOR;RNA干擾;自噬;THP-1
[中圖分類號] R733.3 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2018)02(a)-0018-04
The role of DEPTOR-mTOR signaling pathway-mediated autophagy on osteoclasts differentiation and maturation in multiple myeloma
ZHANG Haoran1 QIAO Xuxu1 BI Minghong1 ZHAI Yunzhi1 QIAN Liyu2 PAN Chengwu2 ZHAO Lun1
1.Department of Medical Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Anhui Province, Bengbu 233004, China; 2.Department of Surgical Oncology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College, Anhui Province, Bengbu 233004, China
[Abstract] Objective To study the role of DEPTOR knockdown in RPMI-8226 cells on the protein expression of RANKL and differentiation of THP-1 into osteoclast-like cells in a contactless co-culture system and its possible mechanism. Methods Constructed DEPTOR shRNA expression vector GV115-shRNA was transferred into RPMI-8226 cell to produce packaged lentivirus. Western blot was applied to measure the protein levels of DEPTOR and RANKL. The expression of autophagy-associated proteins LC-3 and Atg5 were confirmed by Western blot analysis. Three groups were divided:THP-1 group, THP-1 + RPMI-8226 group and THP-1 + DEPTOR shRNA group. Osteoclast-like cells were identified by TRAP. The mRNA levels of calcitonin receptor (CTR) and Cathepsin-K were examined using RT-PCR. Results The results showed that protein expression levels of DEPTOR and RANKL were significantly lower in RPMI-8226 cells transfected with GV115 DEPTOR shRNA compared with that in untransfected cells (P < 0.05). The expression levels of autophagy-associated proteins LC-3 and Atg5 in the DEPTOR shRNA group were significantly lower than those in the control shRNA group and the parental group (P < 0.05). In the co-culture system, THP-1 cell could differentiate into TRAP positive multinuclear cells. RPMI-8226 promoted mRNA expression of CTR and Cathepsin-K (P < 0.05). DEPTOR shRNA suppressed osteoclast-like cells formation and decreased CTR and Cathepsin-K mRNA expression in co-cultures, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion In the coculture system, DEPTOR shRNA inhibits the differentiation of THP-1 cells into TRAP positive multinuclear cells, which may be due to its inhibition on RANKL expression in RPMI-8226 cells, and the inhibition of autophagy will restrain osteoclast maturation.
[Key words] Myeloma bone disease; DEPTOR; RNA interference; Autophagy; THP-1
多發性骨髓瘤(multiple myeloma,MM)居血液系統惡性腫瘤第二位,占10%~15%[1]。70%~80%的MM患者可出現不同程度的骨質破壞即骨髓瘤骨病(myeloma bone disease,MBD)。目前認為在骨髓微環境中,破骨細胞(osteoclast,OC)是MBD的主要效應細胞,其起源于骨髓單核/巨噬細胞系[2]。目前認為有多種機制參與OC的分化[3-5]。
自噬是廣泛存在于真核細胞中的生命現象,細胞自噬與腫瘤的關系十分復雜,研究顯示在人類腫瘤中存在自噬活性的改變[6]。且有研究提示自噬可能參與OC的形成[7]。研究顯示DEPTOR基因高表達于大部分多發性骨髓瘤細胞系[8],DEPTOR是mTOR的負性因子,我們前期研究發現在MM細胞株中DEPTOR基因沉默對自噬有抑制作用[9]。
本研究從骨髓微環境入手,使用人外周血的THP-1細胞株,shRNA抑制RPMI-8226細胞DEPTOR表達,通過建立共培養模型,觀察其對OC分化因子(RANKL)蛋白表達及THP-1細胞向破骨樣分化的作用,并研究其可能機制,以期更好地揭示MBD發生的分子機制。
1 材料與方法
1.1 主要材料
DEPTOR shRNA由蚌埠醫學院第一附屬醫院中心實驗室構建。Transwell小室(孔徑0.4 μm)(2500655)購于Millipore,抗體DEPTOR(09463)購自美國Millipore公司,兔抗人RANKL多克隆抗體(GTX59855)購于GeneTex。Atg5(sc33210)、LC-3:(sc271625)和GAPDH抗體(sc47724)購自Santa Cruz公司。PCR引物由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成,RT-PCR試劑盒(20140801)購自美國Promega公司。PMA(佛波醇)(ICA1042)及TRAP(抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶)染色試劑盒(SLBJ7300V)購于美國Sigma公司。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 細胞培養 THP-1細胞及人MM細胞株RPMI-8226細胞用含10%小牛血清的RPMI 1640培養液培養,在37℃、5%CO2飽和濕度的細胞培養箱內培養。
1.2.2 DEPTOR shRNA載體轉染RPMI-8226細胞 特異DEPTOR shRNA的篩選及慢病毒載體的構建見本課題組的先前報道[10],將感染復數為10的DEPTOR shRNA病毒液加入RPMI-8226細胞中,在37℃、5%CO2飽和濕度的細胞培養箱培養,經鑒定轉染成功后收集細胞進行下面的實驗。
1.2.3 Western blot檢測RPMI-8226細胞中DEPTOR、RANKL、LC-3及Atg5蛋白水平 在RPMI-8226細胞感染72 h后收集DEPTOR shRNA處理的細胞提取總蛋白,RIPA裂解液與蛋白酶抑制劑PMSF混合液提取蛋白質,測定濃度。凝膠電泳并常規轉膜,脫脂奶粉封閉2 h,一抗(DEPTOR、RANKL、Atg5及LC-3抗體)4℃孵育過夜,二抗室溫孵育2 h,ECL化學發光顯像,以GAPDH為對照。
1.2.4 建立非接觸式共培養體系 培養THP-1細胞,1×105/mL接種24孔板中。使用Transwell小室進行細胞共培養,上室接種1×105/mL RPMI-8226細胞,Transwell小室下室接種有貼壁THP-1細胞。在37℃、5%CO2飽和濕度的細胞培養箱內培養。
1.2.5 TRAP染色及細胞計數 培養10 d后,應用4%多聚甲醛固定各組細胞后,進行TRAP染色,按試劑盒操作步驟進行染色。觀察TRAP染色陽性細胞數目。
1.2.6 RT-PCR檢測CTR和Cathepsin-K mRNA的表達 以前述條件培養48 h后,提取細胞總RNA,逆轉錄為cDNA,以RT-PCR法檢測CTR和Cathepsin-K mRNA表達水平。PCR反應條件:95℃ 2 min,95℃ 30 s,60℃ 30 s,72℃ 45 s,共35個循環。PCR引物序列,CTR序列:5′-TGGCGACTATCTACTGCTTCTG-3′(上游);5′-GTTGTTGCTGATTGGAGGATTC-3′(下游);Cathepsin-K序列:5′-GTTGTATGTATAACGCCACGGC-3′(上游);5′-CTTTCTCGTTCCCCACAGG?鄄A-3′(下游);內參GAPDH序列:5′-TGACTTCAACAG?鄄CGACACCCA-3′(上游);5′-CACCCTGTTGCTGTAG?鄄CCAAA-3′(下游)。
1.3 統計學方法
采用SPSS 17.0統計學軟件進行數據分析,計量資料用均數±標準差(x±s)表示,兩組間比較采用t檢驗,多組間比較采用單因素方差分析,以P < 0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 DEPTOR shRNA對RPMI-8226細胞DEPTOR蛋白表達的影響
Western blot檢測顯示,慢病毒感染RPMI-8226細胞72 h后,DEPTOR shRNA組DEPTOR蛋白表達量[(33.0±1.7)%]較陰性對照轉染組(Control shRNA組)[(89.3±1.5)%]顯著下降,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。見圖1。
2.2 Western blot檢測RANKL蛋白
DEPTOR shRNA組RANKL的蛋白表達水平[(36.0±2.1)%]較Control shRNA組[(92.5±1.8)%]顯著下降,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。見圖2。
2.3 Western blot技術檢測自噬相關蛋白LC-3和Atg5
DEPTOR shRNA組Atg5蛋白[(18.6±2.1)%]表達量與Control shRNA組[(48.5±1.8)%]相比顯著下降,DEPTOR shRNA組LC-3Ⅱ的蛋白表達水平[(11.3±1.6)%]與Control shRNA組[(22.6±1.9)%]相比下調,差異均有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。見圖3。
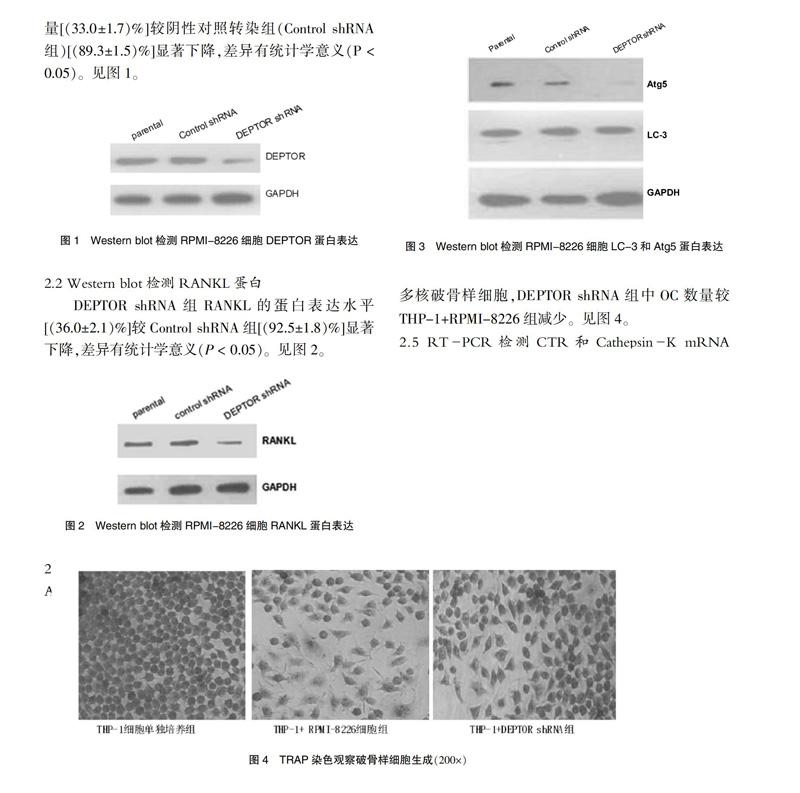
2.4 DEPTOR shRNA對破骨樣細胞生成的影響
本研究顯示,THP-1細胞單培養組TRAP染色呈陰性;THP-1+RPMI-8226組中可見TRAP染色陽性多核破骨樣細胞,DEPTOR shRNA組中OC數量較THP-1+RPMI-8226組減少。見圖4。
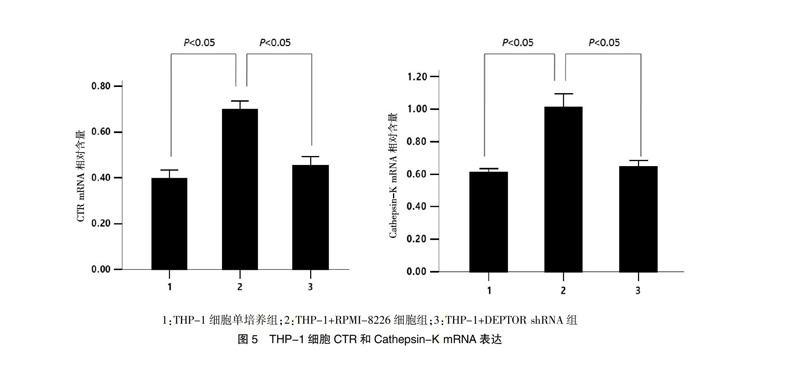
2.5 RT-PCR檢測CTR和Cathepsin-K mRNA表達
RT-PCR檢測顯示,THP-1+RPMI-8226細胞組中CTR和Cathepsin-K基因表達水平均較THP-1細胞單培養組升高(P < 0.05);THP-1+DEPTOR shRNA組中CTR和Cathepsin-K基因表達水平較THP-1+RPMI-8226細胞組均降低(P < 0.05);THP-1+DEPTOR shRNA組中CTR和Cathepsin-K基因表達水平與THP-1細胞單培養組比較差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05)。見圖5。
3 討論
人外周血中的OC前體細胞,在M-CSF與RANKL的共同刺激下,可分化為OC[11]。M-CSF能夠與OC前體細胞表面的c-Fms受體結合,并維持OC前體細胞的生存。RANKL通過激活OC前體細胞上的受體使其分化成OC,并增強OC活力。OC與MM細胞相互作用所導致的惡性循環是MBD發生進行性骨質破壞最主要的原因[12]。
自噬具有維持細胞自穩的功能。近年來研究表明,細胞自噬與發育、氧化性損傷保護、神經退行性疾病及腫瘤細胞的增殖有關,并且多種人類腫瘤細胞中存在自噬活性的改變[13],發現在MM細胞中存在較高的自噬活性[14],調節自噬可能會為MM治療提供新角度。目前研究顯示DEPTOR-mTOR信號通路在調控細胞生長、分化、凋亡、自噬等活動中起重要作用[15-16]。位于mTOR信號通路下游的核糖體蛋白p70S6K抑制細胞自噬發生,其活性受mTOR調節。有研究發現自噬活性改變參與了骨髓間充質干細胞向成骨細胞的分化過程,研究也提示自噬參與了K562細胞向巨核細胞的分化演變進程[17]。
自噬和OC功能關系密切,有研究發現OC產生自噬可能是OC的一種生存保護機制,自噬對機體骨形成及骨骼發育有重要調節作用[18],但相關分子機制并不清楚。目前發現,自噬主要受mTOR信號通路的調節,DEPTOR是mTOR的負性因子,在MM細胞株中DEPTOR基因沉默后下調自噬[9]。調節自噬活性可能對MM微環境下OC分化有重要影響,從而可通過調節自噬阻斷OC-MM惡性循環。
本研究采用RNA干擾技術,沉默DEPTOR基因,研究了在非接觸式共培養模式下觀察OC分化的過程。目前已知PMA刺激THP-1可使其分化為貼壁的巨噬細胞,在RANKL和M-CSF誘導下,可分化形成TRAP染色陽性的OC[19]。本研究顯示,MM細胞RPMI-8226可誘導THP-1細胞破骨樣分化,形成TRAP陽性多核破骨樣細胞,OC特征性基因CTR和Cathepsin-K的mRNA表達也增高。
本研究表明沉默DEPTOR蛋白表達后可明顯下調RPMI-8226細胞RANKL蛋白表達。沉默DEPTOR可抑制細胞的自噬功能,MM細胞株可表達RANKL。而RANKL有誘導單核巨噬細胞系分化為OC的功能。本研究顯示DEPTOR shRNA能明顯抑制共培養體系中THP-1細胞的破骨樣分化,該作用可能與DEPTOR下調RPMI-8226細胞RANKL有關,DEPTOR-mTOR信號通路參與的自噬可能在RANKL介導的OC分化過程中發揮重要影響,抑制自噬可阻礙OC的分化成熟。
[參考文獻]
[1] Gay F,Palumbo A. Management of older patients with mul?鄄tiple myeloma [J]. Blood Rev,2011,25(2):65-73.
[2] Edwards JR,Weivoda MM. Osteoclasts:malefactors of disease and targets for treatment [J]. Discov Med,2012,13(70):201-210.
[3] McManus S,Bisson M,Chamberland R,et al. Autophagy and 3-Phosphoinositide-Dependent Kinase 1(PDK1)-Rel?鄄ated Kinome in Pagetic Osteoclasts [J]. J Bone Miner Res,2016,31(7):1334-1343.
[4] Owen HC,Vanhees I,Gunst J,et al. Critical illness-induced bone loss is related to deficient autophagy and histone hypomethylation [J]. Intensive Care Med Exp,2015,3(1):52.
[5] Gómez-Puerto MC,Verhagen LP,Braat AK,et al. Activation of autophagy by FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic differentiation [J]. Autophagy,2016,12(10):1804-1816.
[6] Puissant A,Robert G,Auberger P. Targeting autophagy to fight hematopoietic malignancies [J]. Cell Cycle,2010,9(17):3470-3478.
[7] Hadji P,Coleman R,Gnant M. Bone effects of mammalian target of rapamycin(mTOR)inhibition with everolimus [J]. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology,2013,87(2):101-111.
[8] Peterson TR,Laplante M,Thoreen CC,et al. DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival [J]. Cell,2009, 137(5):873-886.
[9] Zhang H,Chen J,Zeng Z,et al. Knockdown of DEPTOR induces apoptosis,increases chemosensitivity to doxorubicin and suppresses autophagy in RPMI-8226 human multiple myeloma cells in vitro [J]. Int J Mol Med,2013, 31(5):1127-1134.
[10] 張浩然,曾志勇,陳君敏.體外RNA干擾下調DEPTOR表達對人多發性骨髓瘤細胞增殖和凋亡能力的影響[J].中國生物工程雜志,2013,33(5):13~21.
[11] S?rensen MG,Henriksen K,Schaller S,et al. Characterization of osteoclasts derived from CD14+ monocytes isolated from peripheral blood [J]. J Bone Miner Metab,2007, 25(1):36-45.
[12] Fowler JA,Edwards CM,Croucher PI. Tumor-host cell interactions in the bone disease of myeloma [J]. Bone,2011,48(1):121-128.
[13] Mizushima N. Autophagy:process and function [J]. Genes Dev,2007,21(22):2861- 2873.
[14] Hoang B,Benavides A,Shi Y,et al. Effect of autophagy on multiple myeloma cell viability [J]. Mol Cancer Ther,2009,8(7):1974-1984.
[15] Yang Z,Klionsky DJ. Mammalian autophagy:core molec?鄄ular machinery and signaling regulation [J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol,2010,22(2):124-131.
[16] 黃漫華,葛鴻慶,陳文治,等.葛根素誘導破骨細胞自噬的機制研究[J].中國醫藥導報,2015,12(15):20-23.
[17] Colosetti P,Puissant A,Robert G,et al. Autophagy is an important event for megakaryocytic differentiation of the chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell line [J]. Autop?鄄hagy,2009,5(8):1092-1098.
[18] Usategui-Martín R,García-Aparicio J,Corral-Gudino L,et al. Polymorphisms in autophagy genes are associated with paget disease of bone [J]. PLoS One,2015,10(6):e0128984.
[19] Munoz-Pacheco P,Ortega-Hernandez A,Miana M,et al. Ezetimibe inhibits PMA-induced monocyte/macrophage differentiation by altering microRNA expression:a novel anti-atherosclerotic mechanism [J]. Pharmacol Res,2012, 66(6):536-543.
(收稿日期:2017-11-07 本文編輯:任 念)

