食管癌患者術后院內感染的危險因素分析與護理干預研究
石際杰 弓潔 張文靜 趙瑋
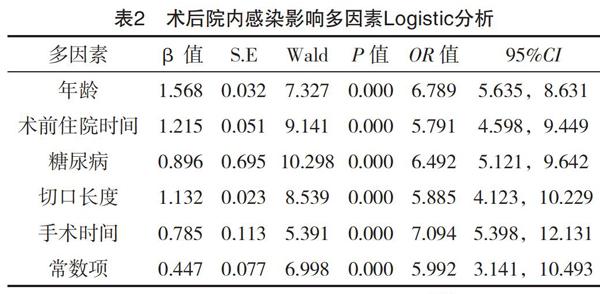
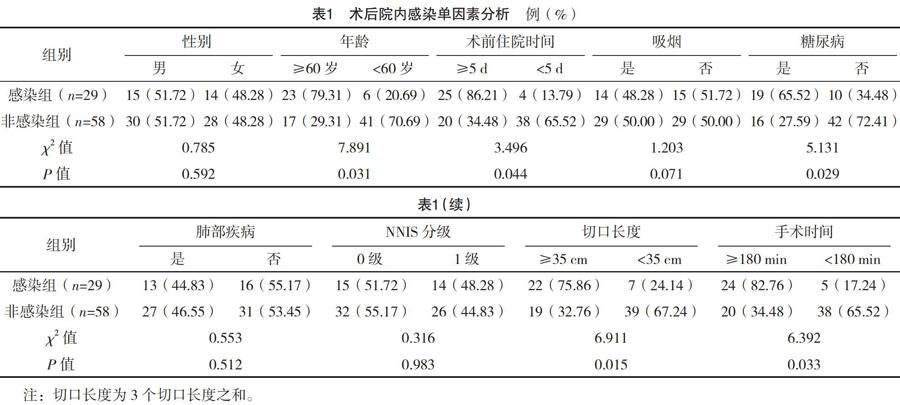
【摘要】 目的:探討食管癌患者術后院內感染的危險因素及護理干預措施。方法:選擇2017年5月-2018年11月治療的食管癌手術患者87例,根據患者術后是否發生院內感染分為感染組(n=29)與非感染組(n=58)。所有患者入院后均查閱患者病例資料,記錄患者性別、年齡、術前住院時間、是否吸煙、糖尿病、肺部疾病、NNIS分級、切口長度、手術時間,并對上述危險因素進行單因素及多因素Logistic分析,針對上述危險因素制定有效的護理措施進行干預。結果:87例患者中29例術后發生院內感染,感染率為33.33%。兩組性別、是否吸煙、肺部疾病、NNIS分級比較,差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),年齡、術前住院時間、糖尿病、切口長度、手術時間為術后院內感染危險因素(P<0.05)。結論:食管癌患者術后院內感染率較高,年齡、糖尿病、切口長度及手術和住院時間為術后院內感染危險因素,應加強危險可控因素干預,降低院內感染率。
【關鍵詞】 食管癌; 院內感染; 危險因素; 多因素Logistic分析
Analysis of Risk Factors and Nursing Intervention of Postoperative Nosocomial Infection in Patients with Esophageal Cancer/SHI Jijie,GONG Jie,ZHANG Wenjing,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2019,16(25):-165
【Abstract】 Objective:To investigate the risk factors and nursing interventions for postoperative nosocomial infection in patients with esophageal cancer.Method:87 patients with esophageal cancer surgery treated from May 2017 to November 2018 were selected.They were divided into the infection group(n=29) and the non-infected group(n=58).Data of all of the patients were consulted after admission,and the gender,age, preoperative hospital stay,smoking status,diabetes,pulmonary disease,NNIS grade,length of incision and operation time were recorded.The above risk factors were analyzed by single and multiple Logistic analysis,and effective nursing measures were formulated for the above risk factors for intervention.Result:Of the 87 patients,29 cases developed nosocomial infection after surgery,the infection rate was 33.33%.There was no significant difference in gender,smoking status,pulmonary disease,and NNIS grade between the two groups(P>0.05).Age,preoperative hospitalization time,diabetes mellitus,incision length and operation time were all risk factors for nosocomial infection after surgery(P<0.05).Conclusion:The postoperative in-hospital infection rate of patients with esophageal cancer is high,and the age,diabetes,length of incision and operation and hospitalization time are risk factors for nosocomial infection.It is necessary to strengthen the intervention of risk controllable factors and reduce the infection rate in hospital.
【Key words】 Esophageal cancer; Nosocomial infection; Risk factors; Multivariate Logistic analysis
First-authors address:Taian City Tumor Prevention and Cure Hospital,Taian 271000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.25.041
食管癌是臨床上常見的惡性腫瘤,好發于40歲以上人群中,且不同國家、地區發病率及死亡率存在明顯的差異性[1]。患者發病早期臨床癥狀缺乏典型性,隨著病情的不斷發展,多表現為難以咽干的食物、繼而半流質食物,甚至連水或唾液均無法下咽,影響患者健康、生活[2-3]。手術治療是食管癌首選方法,能切除病灶組織,延緩病情發展[4-5]。但是,食管癌手術風險性較高,導致患者術后院內感染率較高,影響患者手術預后[6]。因此,本文采用隨機對照方法進行研究,探討食管癌患者術后院內感染的危險因素及護理干預措施,現報道如下。
[3]謝琴,莫占端,華潤,等.老年食管癌患者術后肺部感染影響因素與預防干預研究[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2016,26(2):346-348.
[4]錢霄君,黃黎明,陳巍,等.乳腺癌術后化療患者感染的高危因素分析及干預措施[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2016,26(11):2553-2555.
[5] Carcillo J A,Dean J M,Holubkov R,et al.Inherent Risk Factors for Nosocomial Infection in the Long Stay Critically Ill Child Without Known Baseline Immunocompromise:A Post-Hoc Analysis of the CRISIS Trial[J]. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal,2016,35(11):1182-1186.
[6]郭孟剛,周海寧,李麗.老年食管癌患者術后并發肺部感染危險因素的臨床分析[J].檢驗醫學與臨床,2016,13(16):2317-2319.
[7]劉娟,霍連蘋,付婷婷,等.宮頸癌患者行腹腔鏡手術感染的危險因素分析[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2017,27(6):1377-1379.
[8]尹麗霞,陳寶敏,袁啟峰,等.頸部吻合食管癌切除術手術部位感染危險因素分析及預測模型研究[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2017,27(8):1799-1801.
[9]魯為鳳,彭潔,曹勍,等.白內障術后患者發生感染性眼內炎的相關因素分析及圍術期護理的預防效果研究[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2017,27(23):5437-5440.
[10] Li L,Ding J,Han J,et al.A nomogram prediction of postoperative surgical site infections in patients with perihilar cholangiocarcinoma[J].Medicine,2017,96(25):e7198.
[11]劉菲,張啟新,劉文佳,等.直腸癌患者腹腔鏡根治術后感染的臨床分析與預防[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2016,26(15):3481-3483.
[12]陳桂珍,葛綠玲,劉玉蓮,等.婦科腹腔鏡手術患者醫院感染的危險因素分析[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2016,26(5):1129-1131.
[13] Aquina C T,Probst C P,Becerra A Z,et al.High Variability in Nosocomial Clostridium difficile Infection Rates Across Hospitals After Colorectal Resection[J].Diseases of the Colon & Rectum,2016,59(4):323-331.
[14]俞霞,曹珍,王麗春,等.全髖關節置換術患者醫院感染的干預措施研究[J].中華醫院感染學雜志,2016,26(7):1593-1594.
[15] Yoshida N,Baba Y,Hiyoshi Y,et al.Duration of Smoking Cessation and Postoperative Morbidity After Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer: How Long Should Patients Stop Smoking Before Surgery?[J].World Journal of Surgery,2016,40(1):142-147.
[16] Hyun S Y,Han S H,Kim S J,et al.Pretreatment Lymphopenia,Poor Performance Status, and Early Courses of Therapy Are Risk Factors for Severe Bacterial Infection in Patients with Multiple Myeloma during Treatment with Bortezomib-based Regimens[J].Journal of Korean Medical Science,2016,31(4):510-518.
[17]劉麗娟,王海燕.護理干預對降低乳腺癌化療患者PICC置管感染發生率的應用體會[J].中國醫藥導刊,2017,19(2):203-205.
[18]樊榮,蔣玉梅,張娜,等.膀胱全切術后泌尿系感染的危險評估及護理干預對策[J].實用臨床醫藥雜志,2017,21(14):101-103.
[19] Algethamy M M,Faidah H S,Ademola H A,et al.Risk factors associated with multi-drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii nosocomial infections at a tertiary care hospital in Makkah,Saudi Arabia - a matched case-control study[J].Journal of International Medical Research,2017,45(3):1181-1189.
[20]朱瑞芳,馮文靜,王建敏,等.腦出血術后氣管切開合并肺部感染患者行霧化吸入聯合振動排痰的護理干預及心理因素分析[J].山西醫藥雜志,2017,46(23):2838-2840.
(收稿日期:2019-03-11) (本文編輯:田婧)

