脊柱結核伴脊髓損害急診手術后結核桿菌全身擴散的風險評估與應用研究
藍常貢 龍麗珍 謝克恭 涂振陽 高子然 唐毓金
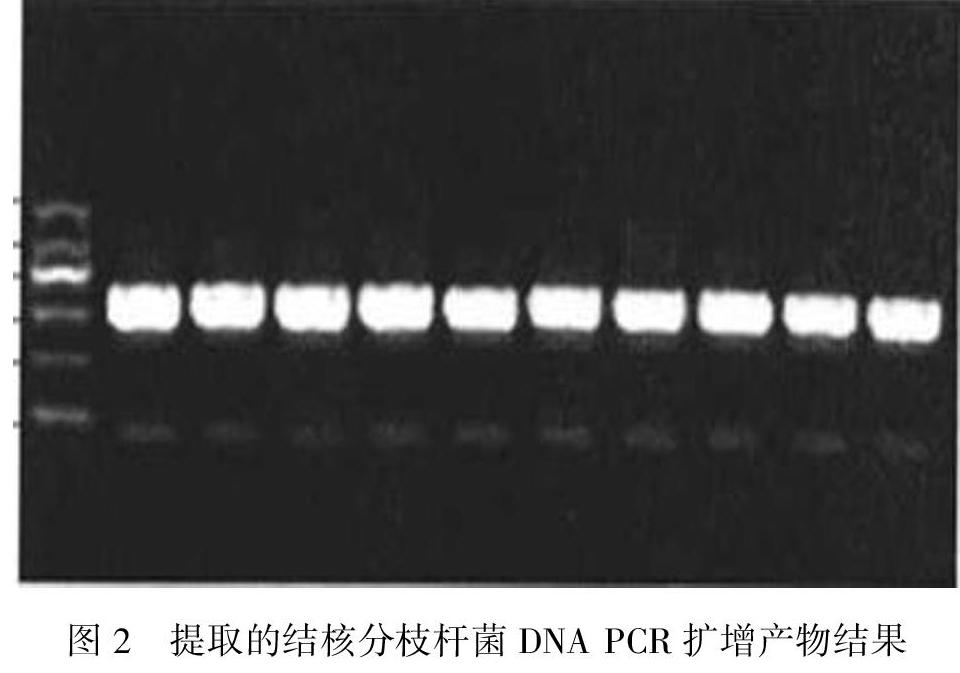

【摘要】 目的 探討脊柱結核伴脊髓損害急診手術后結核桿菌全身擴散的風險。方法 研究組(44例)為脊柱結核伴脊髓損害并進行急診手術治療的患者;對照組(59例)為脊柱結核伴脊髓損害進行擇期手術治療的患者。分別在術前1天、術后第1天和術后第7天抽取外周血提取結核分枝桿菌DNA(Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA,MTBDNA),PCR擴增,進行MTBDNA即時熒光定量檢測,經對比分析研究,評估脊柱結核伴脊髓損害急診手術后結核桿菌全身擴散的風險。結果 術前1天、術后第1天和術后第7天外周血結核桿菌的DNA陽性率研究組分別為50.0%(22/44)、56.8%(25/44)和31.8%(14/44),對照組分別為49.1%(29/59)、52.5%(31/59)和33.9%(20/59);其中,研究組術前1天、術后第1天和術后第7天外周血結核桿菌的含量變化差異無統計學意義(F=0.08,P=0.920);對照組術前1天、術后第1天和術后第7天外周血結核桿菌的含量變化差異無統計學意義(F=1.29,P=0.084);研究組和對照組術前1天、術后第1天和術后第7天的結核桿菌DNA含量組間比較差異無統計學意義(t值分別為1.415、0.158、0.144,P值分別為0.078、0.874、0.889)。結論 脊柱結核伴脊髓損害患者,術前沒有結核桿菌耐藥表現,術后正規抗結核治療,急診及擇期手術前后外周血結核桿菌DNA含量測定無明顯差異,提示脊柱結核伴脊髓損害患者急診手術并沒有造成結核桿菌全身外周血擴散的風險。
【關鍵詞】 脊柱結核;脊髓損害;熒光定量聚合酶鏈反應;脫氧核糖核酸
中圖分類號:R529.2? ?文獻標志碼:A? ?DOI:10.3969/j.issn.10031-383.2019.06.003
【Abstract】 Objective To study the risk of systemic diffusion of mycobacterium tuberculosis after emergency operation for spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord injury.Methods 44 cases of spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord lesion who underwent emergency operation were selected as research group,and 59 cases of spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord injury who underwent selective operation were selected as control group.Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA(MTBDNA) was extracted from peripheral blood on one day before operation,the first day after operation and the seventh day after operation,respectively.Realtime fluorescence quantitative detection of MTBDNA was carried out by PCR amplification.And the risk of systemic diffusion of mycobacterium tuberculosis after emergency surgery for spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord injury was evaluated by comparative analysis.Results The DNA positive rate of mycobacterium tuberculosis in peripheral blood was 50.0%(22/44),56.8%(25/44) and 31.8%(14/44) in the research group on one day before operation,the first day after operation and the seventh day after operation,respectively,and 49.1%(29/59),52.5%(31/59) and 33.9%(20/59) in the control group,respectively.There was no statistically significant difference in the contents of mycobacterium tuberculosis in peripheral blood in the research group on one day before operation,the first day after operation and the seventh day after operation(F=0.08,P=0.920).There was no statistically significant difference in the contents of mycobacterium tuberculosis in peripheral blood in the control group on one day before operation,the first day after operation and the seventh day after operation(F=1.29,P=0.084).In addition,there was no statistically significant difference in the contents of mycobacterium tuberculosis between the research group and the control group on one day before operation,the first day after operation and the seventh day after operation(t=1.415,0.158,0.144,P=0.078,0.874,0.889,respectively).Conclusion There was no drug resistance of mycobacterium tuberculosis in patients with spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord injury before operation,and regular antituberculosis treatment was performed after operation.Difference in the contents of mycobacterium tuberculosis in peripheral blood before and after emergency operation and selective operation was not significant,which shows that emergency operation in patients with spinal tuberculosis with spinal cord injury does not cause the risk of systemic diffusion of mycobacterium tuberculosis.

