精神分裂癥患者甲狀腺激素變化特征及其與白蛋白的相關性
翟媛媛 張輝 馬瑾

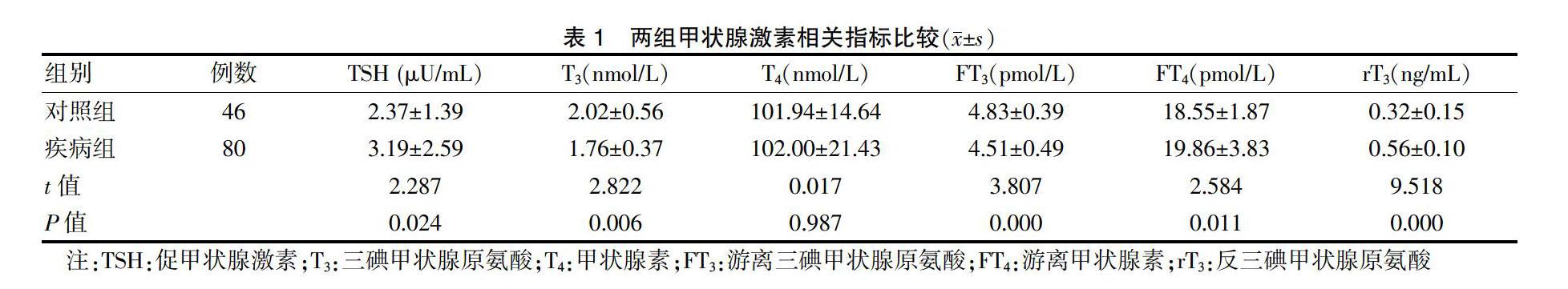
[摘要] 目的 探討精神分裂癥患者血清甲狀腺激素的變化特征及其與白蛋白(ALB)的相關性。 方法 選取西安市精神衛生中心門診接收的精神分裂癥患者80例為疾病組,同時選取西安市友誼醫院的健康體檢者46名為對照組。采用化學發光法檢測兩組的血清促甲狀腺激素(TSH)、三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(T3)、甲狀腺素(T4)、游離三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(FT3)、游離甲狀腺素(FT4)、反三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(rT3)的水平,同時采用溴甲酚紫終點法檢測疾病組患者的ALB水平。 結果 疾病組的TSH、FT4、rT3水平均高于對照組,T3、FT3水平均低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05),兩組間T4比較,差異無統計學意義(P > 0.05)。病程和性別對疾病組患者甲狀腺激素指標(TSH,T3,T4,FT3,FT4,rT3,T3/rT3)的影響差異均無統計學意義(均P > 0.05);疾病組患者T3/rT3比值與ALB水平呈負相關(r = -0.262,P = 0.019)。 結論 精神分裂癥患者存在甲狀腺功能紊亂,rT3升高是其特征性變化,T3/rT3比值與ALB水平呈負相關。
[關鍵詞] 甲狀腺激素;反三碘甲狀腺原氨酸;白蛋白
[中圖分類號] R749.3 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻標識碼] A ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1673-7210(2019)12(c)-0073-04
Characteristics of thyroid hormone changes and their correlation with albumin in patients with schizophrenia
ZHAI Yuanyuan1 ? ZHANG Hui2 ? MA Jin1 ? AO Lei4 ? ZHANG Yan3
1.Clinical Laboratory, Xi′an Mental Health Center, Shaanxi Province, Xi′an ? 710100, China; 2.Medical Department, Xi′an Mental Health Center, Shaanxi Province, Xi′an ? 710100, China; 3.Pharmaceutical Laboratory, Xi′an Mental Health Center, Shaanxi Province, Xi′an ? 710100, China; 4.the Second Division of Women′s Mental Health, Xi′an Mental Health Center, Shaanxi Province, Xi′an ? 710100, China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the change characteristics of serum thyroid hormone and its correlation with albumin (ALB) in patients with schizophrenia. Methods Eighty patients with schizophrenia admitted by the outpatient department of Xi′an Mental Health Center were selected as the disease group, and forty-six healthy patients from Xi′an Friendship Hospital were selected as the control group. Serum levels of thyrotrophin (TSH), triiodinated thyroxine (T3), thyroxine (T4), free triiodinated thyroxine (FT3), free thyroxine (FT4), and reverse triiodothyronine (rT3) in two groups were detected by chemical radiometry. At the same time, the ALB level of patients in the disease group was detected by the end point method of bromocresol purple. Results TSH, FT4 and rT3 levels in the disease group were all higher than those in the control group, while T3 and FT3 levels were lower than those in the control group, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in T4 between the two groups (P > 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the effects of disease course and gender on thyroid hormone indexes (TSH, T3, T4, FT3, FT4, rT3, T3/rT3) in the disease group (all P > 0.05). In the disease group, the T3/rT3 ratio was negatively correlated with ?ALB level (r = -0.262,P = 0.019). Conclusion In schizophrenia patients with thyroid dysfunction, rT3 elevation is the characteristic change, and the T3/rT3 ratio is negatively correlated with ALB level.
[Key words] Thyroid hormone; Reverse triiodothyronine; Albumin
精神分裂癥是重性精神病之一,發病率為0.6%~1.9%,且病程遷延,易反復,嚴重影響患者的正常生活[1]。甲狀腺激素不僅為大腦發育和成熟所必需,也能調節大腦的功能[2]。Radhakrishnan等[3]的報道中發現25.17%精神分裂癥患者有正常甲狀腺病態綜合征(euthyroid sick syndrome,ESS)。一般觀點認為這是機體在各種應激狀態下出現的甲狀腺功能改變。典型的改變是三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(T3)下降,反三碘甲狀腺原氨酸(rT3)升高,甲狀腺素(T4)正常或降低,促甲狀腺激素(TSH)正常或輕度下降。rT3雖然沒有生物活性,但是對調節T3、T4的代謝和維持適當甲狀腺激素水平有一定的作用[4]。另外……

