A Brief Introduction to the Development Process of Conceptual Structure
【Abstract】This paper aims to explore the theory of conceptual semantics to answer the question of how conceptual structure is proposed. The introduction is the theoretical background of this paper, which includes a development method from decomposition to composition. The conclusion is that the process of how to express a conceptual structure should follow the method of correspondence between syntactic structure and conceptual structure first, and then insert the fragmentary conceptual categories into one of the five general ontological categories to finally present a conceptual structure.
【Key words】Conceptual Structure; Conceptual Semantics; categories
【作者簡介】韓婧婧(1996-),女,漢族,甘肅臨夏人,南京師范大學,碩士研究生在讀,研究方向:認知語言學。
1. Introduction
Conceptual semantics is a framework for semantic analyses which is mainly proposed and developed by Jackendoff in 1977. It is the formal linguistic approach of exploring the way of how meaning is constructed in humans mind. Jackendoff (1987) stands for the statement that describing meaning involves the description of mental representation, which means there is no distinction between meaning and conceptualization. In order to explore the conceptualization and analyze the conceptual semantics, Jackendoff argues that a decompositional method should be adopted. Inspired by this logic of decomposition, Jackendoff started to construct a similar study method, in which he believes that the progress of decomposition cannot go on forever, there must be a ‘bottom that meanings cannot be broken down any longer. This is the level of conceptual structure.
2. The Development Process of Conceptual structure
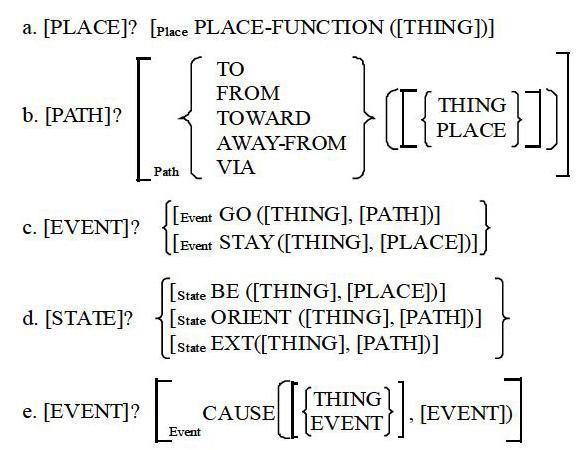
As student of Noam Chomsky, Jackendoff also aims to propose ‘a finite set of mental primitives and a finite set of principles of mental combination governing their interaction to be the mental representations which encode the human understanding of the world (Jackendoff, 1990: 9). This indicates that some technical primitives to analyse word-meaning must be developed, and Jackendoff poses that any concept in the human brain can be expressed using these semantic primitives. It is argued that the essential units of conceptual structure are conceptual constituents which are the basic units of semantic meaning the sentence conveys. Each of these constituents belongs to one of a small set of major ontological categories (or conceptual “parts of speech”) from which a sentence is built due to the necessity to represent lexical semantic information to understand Conceptual Semantics. These include, but are not limited to: Thing, Event, State, Action, Place, Path, Property, Amount and Time. Similar to the categories of parts of speech like Noun, Verb and Adjective, to which words can be assigned based on distributional criteria, the ontological categories constitute the major groupings to which our concepts can be assigned on the basis of what they mean. But how are the ontological categories classified? Jackendoff in 1990 has detected that it is particularly necessary to pay attention to the analysis ‘tools - to classify the ontological categories as seen below (Jackendoff, 1990: 43):
(1)He presents some interpretations of the categories above that each of these can be elaborated into a function-argument organization and each category permits a variety of more specific elaborations, which can be stated as specialized formation rules. Speaking in detail, (1a) says that a conceptual constituent pertaining to the category Place can be illustrated as a Place-function plus an argument that belongs to the category Thing. The Place-function defines a region where the argument as a spatial reference point was mapped into. This illustration goes similar to (1b)-(1e). These functions in (1) are treated as conceptual primitives. Below is an example (this is a sample used frequently by Jackendoff (1992: 13)) of formulaic conceptual structure of the sentence Bill went into the house.
(2) [EVENT GO ([THING BILL], [PATH TO ([PLACE IN ([THING HOUSE])])])]
This leads to a more significant question: how is the conceptual structure analyses developed? Jackendoff believes that there is a level of linguistic structure is related to syntactic structure by a set of rules which Jackendoff called correspondence rules (1983:18). He states that conceptual structure lays on a further level beyond semantic structure and relates to it by pragmatics. Alternatively, semantic structures could be simply a subset of verbally expressible conceptual structures. This point of view claims that the correspondence rules map directly between syntactic structure and conceptual structure. So what are the mapping principle between syntactic structure and conceptual structure? The fundamental principle of correspondence presented by Jackendoff (1990, 44) illustrates that every content-bearing major phrasal constituent of a sentence (S, NP, AP, PP, etc.) corresponds to a conceptual constituent of some major conceptual category in the meaning of the sentence. Taking sentence Nina went into the room as an example, the following is the syntactic structure and the formulaic conceptual structure of the sentence .
(3) a. Syntactic structure
[S [NP Nina] [VP [V went] [PP [P into] [NP the room]]]]
b. Conceptual structure
[EVENT GO ([THING NINA], [PATH TO ([PLACE IN ([THING ROOM])])])]
In (3), the NPs Nina and the room correspond to Thing slots in the conceptual structure, the verb went corresponds to the Event slot, the prepositional phrase into the room corresponds to the Path slot. However, after the decomposition of revealing the conceptual structures of lexicons, it is the time to manage the problem of how these conceptual constituents are constructed together to be a sentential constituent as in (3b). According to the ontological categories classified by Jackendoff in (1), Event and State are the basic conceptual situations and (3b) is a basic example of an Event utterance. In accordance with the classification, it is not very hard to detect that there are some categories like Path and Place can be nested into some more general categories like Event and State. This is because each conceptual categories can take arguments-other elements of conceptual content which have to be inserted into positions in the formalism in order to make them complete. This is also illustrated in (1) in detail that which category contains which arguments.
3. Conclusion
It is obvious that the process of the proposition of the hypothesis of conceptual structure consists of decomposition and composition. It is a procedure from the former to the latter. Although the framework allows interesting connections to be made between seemingly unrelated meanings, it is still a rather controversial theory. Some researchers believe it draws attention to the arbitrary nature, therefore, it is difficult to say how effectively the Conceptual Structure captures the way in which humans create meaning.
References:
[1]Jackendoff, R.. Semantics and Cognition[M]. MIT Press, Cambridge,1983.
[2]Jackendoff, R.. Consciousness and the Computational Mind[M]. MIT Press, Cambridge,1987.
[3]Jackendoff, R.. Semantic Structures[M]. MIT Press, Cambridge, 1990.
[4]Katz, J. &J.. Fodor The Structure of a Semantic Theory[J]. Language,1963(39):2.

