右美托咪定加單次小劑量肌松全身麻醉在鼻內窺鏡手術ERAS中應用
董龍禹 劉冰 孫玉明

[摘要] 目的 探討右美托咪定加單次小劑量肌松全身麻醉在鼻內窺鏡手術ERAS中的應用效果。 方法 選擇2018年5月~2019年4月本院收治的擬擇期行鼻內窺鏡手術患者30例,男16例,女14例,隨機分為兩組,每組各15例。觀察組麻醉誘導采用右美托咪定0.5 μg/kg緩慢靜注、丙泊酚2 mg/kg,羅庫溴銨0.8 mg/kg、芬太尼1 μg/kg,全麻插管控制呼吸。麻醉維持:丙泊酚50~60 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼0.3 μg/(kg·min)行麻醉維持,不再使用右美托咪定及肌松劑。對照組采用常規麻醉方法,手術結束麻醉停藥后,待患者意識清醒,TOF≥0.9時,拔除氣管導管,10 min內MAS≥9分,送入外科病房,達不到出室條件患者送入PACU。術中監護HR、MAP,術畢停藥后,記錄患者命令反應時間、拔管時間、MAS≥9時間、有無EA。 結果 兩組HR、MAP改變比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),觀察組術后各項蘇醒指標分別為命令反應時間為(2.5±1.1)min、拔管時間為(2.8±1.0)min、MAS≥9時間為(4.5±2.1)min,與對照組比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。無EA發生,全部患者術后5 min內達到出室條件。對照組患者10 min內全部沒有達到MAS≥9,送入PACU,7例(46.7%)發生EA。兩組無其他麻醉相關并發癥。 結論 右美托咪定加單次小劑量肌松全麻在鼻內窺鏡手術ERAS中應用與常規全麻比較,效果明顯,無須進入PACU,無EA發生,有臨床推廣價值。
[關鍵詞] 右美托咪定;內窺鏡手術;ERAS;全麻;氣管插管
[中圖分類號] R614.2 ? ? ? ? ?[文獻標識碼] B ? ? ? ? ?[文章編號] 1673-9701(2020)31-0118-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application efficacy of dexmedetomidine combined with single and low dose of muscle relaxant for general anesthesia in ERAS of nasal endoscopic surgery. Methods A total of 30 patients(16 males and 14 females were included) who were scheduled to undergo nasal endoscopic surgery and admitted to our hospital from May 2018 to April 2019 were randomLy divided into the observation group(n=15) and the control group(n=15). In the observation group, 0.5 μg/kg dexmedetomidine, 2 mg/kg propofol, 0.8 mg/kg rocuronium and 1 ug/kg fentanyl were used for anesthesia induction, and general anesthesia intubation was used to control breathing. In the anesthesia maintenance, 50-60 μg/(kg·min) propofol and 0.3 μg/(kg·min) remifentanil were used, while dexmedetomidine and muscle relaxant were no longer used. On the other hand, the conventional anesthesia was used in the control group. After the anesthesia was stopped after the operation, when the patient was conscious and TOF≥0.9, the endotracheal tube was removed. Within 10 minutes, when MAS≥9 points, the patient was sent to the surgical ward, and if he could not meet the condition of discharge, he would be sent to PACU. HR and MAP were monitored during operation. After stopping the drug after operation, the patient′s reaction time on command, extubating time, MAS ≥9 time and with or without EA were recorded. Results There were no significant differences in HR and MAP changes between the two groups. The wake-up indexes in the observation group were(2.5±1.1)min after operation,(2.8±1.0)min after extubating, and(4.5±2.1)min after MAS ≥9. Compared with the control group, there was statistically significant difference(P<0.01).No EA occurred, and all patients reached the discharge condition within 5 min after operation. None of the patients in the control group reached MAS≥9 within 10 minutes. And after they were sent to PACU, EA occurred in 7 patients(46.7%). There was no other anesthesia related complications in the two groups. Conclusion Compared with conventional general anesthesia, dexmedetomidine combined with a single and low dose of muscle relaxant for general anesthesia has obvious efficacy. There is no need to enter PACU, no EA occurs. Therefore, it is worthy of clinical promotion.
[Key words] Dexmedetomidine; Endoscopic surgery; ERAS; General anesthesia; Tracheal intubation
1997年,丹麥外科教授Kehlet等[1]提出的術后快速康復(Enhanced recovery after surgery,ERAS)理念,可有效提高病床使用率,減少住院時間[2],患者術后的功能狀態更快恢復。2006年,黎介壽院士首次將ERAS理念引入中國,在我國ERAS積極推廣,特別是普外科及腹腔手術應用ERAS[2-6],其他外科手術也相繼推廣了ERAS,骨科、婦科、創傷外科也有臨床報道[7-10],麻醉科對ERAS報道較少[11],作為麻醉科,麻醉醫師應當在麻醉及手術期間精確使用麻醉劑,維持生命體征穩定,使患者手術后快速蘇醒,降低麻醉及手術后并發癥,并且減少麻醉后監護病房(Post anesthesia care unit,PACU)滯留時間。本研究探討右美托咪定加小劑量肌松全身麻醉在鼻內窺鏡手術在ERAS中應用效果,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
選擇2018年5月~2019年4月本院耳鼻喉科收治的擬擇期行鼻內窺鏡手術患者30例,男16例,女14例,年齡20~55歲,隨機數字法分為兩組,每組各15例。對照組中,男8例,女7例,年齡20~54歲,平均(32.81±7.15)歲,體重(60.51±4.5)kg;觀察組中,男8例,女7例,年齡20~55歲,平均(33.58±6.91)歲,體重(61.03±3.97)kg。兩組患者男女比例、年齡分布、體重比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。所有患者均簽署知情同意書,本研究經醫院醫學倫理委員會審核批準。
納入標準[5]:美國麻醉學會麻醉分級(ASA)Ⅰ~Ⅱ級;體重50~70 kg;無心腦血管疾病;無高血壓及心律失常;無肝腎功能損害;無呼吸道及肺疾病。排除標準[6]:神經精神病史;吸毒史;酒精依賴;藥物依賴;認知功能障礙;體質量過高或過低者。
1.2 方法
兩組患者均不使用術前藥物,觀察組麻醉誘導采用右美托咪定(四川國瑞藥業有限責任公司,國藥準字H20110097,2 mL∶0.2 mg)0.5 μg/kg緩慢靜注,丙泊酚(廣東嘉博制藥有限公司,國藥準字H20051843, 10 mL∶100 mg)2 mg/kg,芬太尼(宜昌人福藥業有限責任公司,國藥準字H42022076,2 mL∶0.1 mg)1 μg/kg、羅庫溴銨(浙江仙琚制藥有限公司,國藥準字 H2009 3186,5 mL∶50 mg)0.8 mg/kg靜脈注射,麻醉誘導后氣管插入加強氣管導管,機械通氣。麻醉維持:丙泊酚50~60 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼(宜昌人福藥業有限責任公司,國藥準字H20030197,粉針劑:1 mg)0.3 μg/(kg·min)連續靜脈注射麻醉維持,不再使用右美托咪定及肌松劑。對照組使用普通誘導方法,靜脈注射丙泊酚2 mg/kg、羅庫溴銨1 mg/kg、芬太尼1 μg/kg,麻醉誘導后插入加強氣管導管,機器控制通氣。丙泊酚60~70 μg/(kg·min),瑞芬太尼0.3 μg/(kg·min)行麻醉維持,術中根據肌松監測結果,四個成串刺激(TOF)≥0.5時,羅庫溴銨0.5 mg/kg靜注維持肌松,兩組控制通氣頻率8~12次/min,機械控制通氣潮氣量8~12 mL/kg,維持呼氣末CO2濃度4.5~5.5 Kpa。手術結束麻醉停藥后,待患者意識清醒,達到拔管條件TOF≥0.9時,拔除氣管導管,10 min內修正的Aldrete 評分(Modfied aldrete score,MAS)[3]達到≥9分,送入外科病房,10 min內達不到MAS≥9分患者送入PACU。
1.3 觀察指標
兩組患者入室后連接邁瑞T5監護儀,記錄麻醉前(T0)、麻醉后5 min(T1)、手術結束(T2)時的心率(HR)和平均動脈壓(MAP)。術畢從停止麻醉用藥開始,觀察患者命令反應時間、拔管時間、MAS≥9時間、有無術后躁動(Emergence agitation,EA)。
1.4 統計學方法
應用SPSS21.0統計學軟件行數據處理,計量資料以均數±標準差(x±s)表示,采用t檢驗,三組以上正態計量資料比較采用方差分析,計數資料采用χ2檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 兩組不同時間MAP、HR比較
手術時間為40~60 min,觀察組平均為(47.5±5.8)min,對照組平均為(45.5±6.8)min,兩組比較,差異無統計學意義(t=0.451,P>0.05)。兩組不同時間MAP、HR比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見表1。
2.2 兩組患者蘇醒時間比較
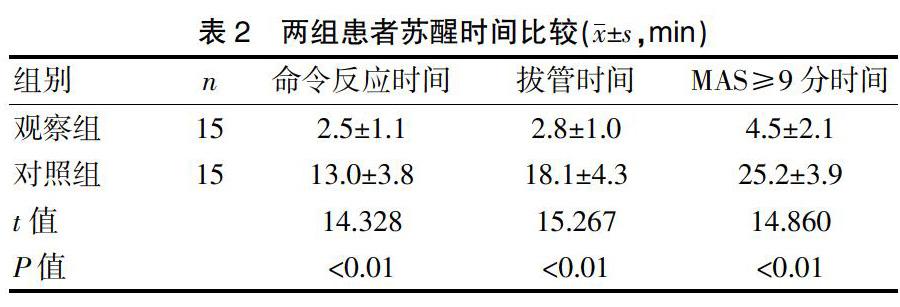
觀察組術后各項蘇醒指標與對照組比較,顯著加快(P<0.01)。見表2。觀察組無術后EA,全部患者術后5 min內達到出室條件,送入病房。對照組10 min內皆沒有達到MAS≥9分,需要進入PACU,7例(46.7%)發生EA。兩組無其他麻醉相關并發癥。
3 討論
ERAS的核心要求呈微創手術、目標導向圍術期處理、術后快速恢復等,ERAS理念用于胃癌手術[2-5]、結腸癌手術[6]、髖膝關節手術[7-8]、產科手術[9]、創傷外科手術[10]等,效果良好。麻醉科是所有外科手術患者最重要關鍵的環節,ERAS強調多學科團隊合作的重要性,麻醉學科貫穿ERAS始終[13],沒有麻醉學科參與ERAS難以實現,麻醉科與外科一同聯手,規范化、系統化地進行ERAS,才能順利開展。加快術后康復是患者和醫師的共同愿望,ERAS應當在麻醉后使患者的功能狀態更快恢復,麻醉管理應當維持麻醉期間HR、MAP平穩,降低麻醉相關并發癥,減少PACU滯留時間。

