尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗對糖尿病早期腎損傷的診斷作用分析
張軍 何新文
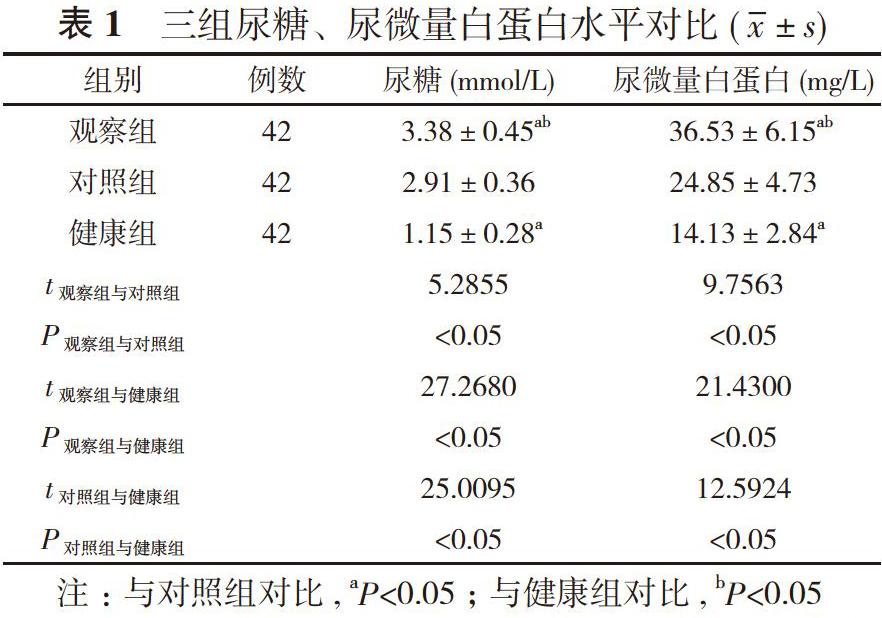
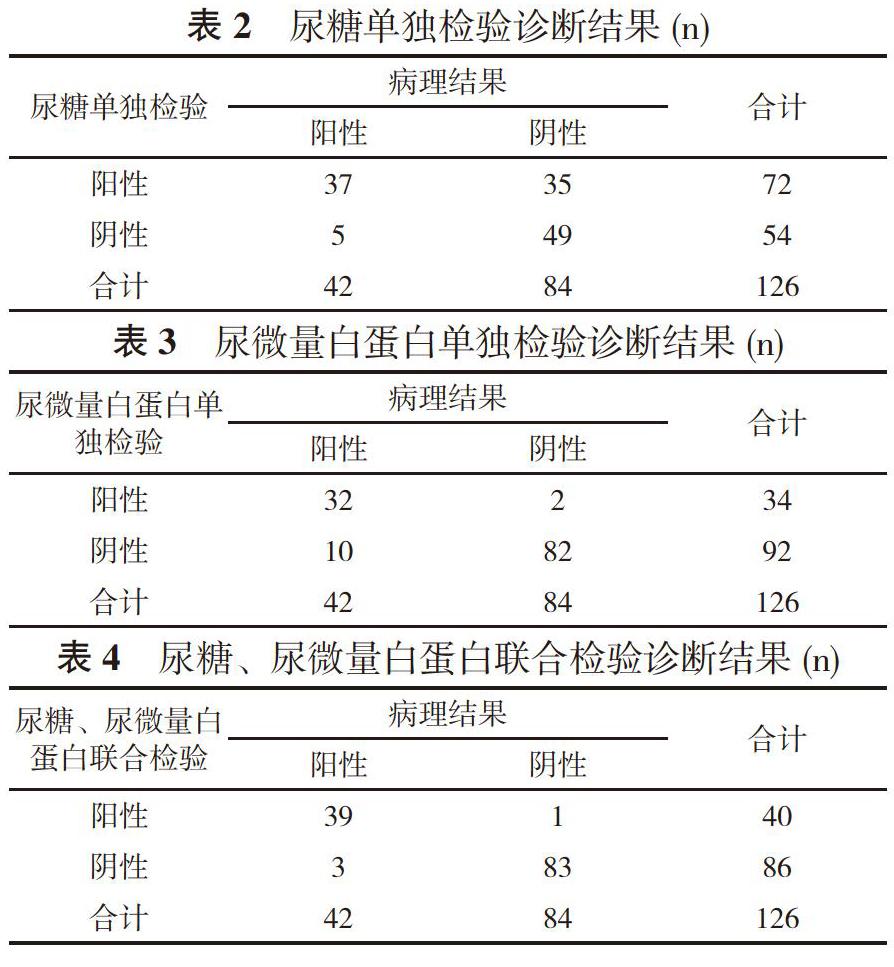
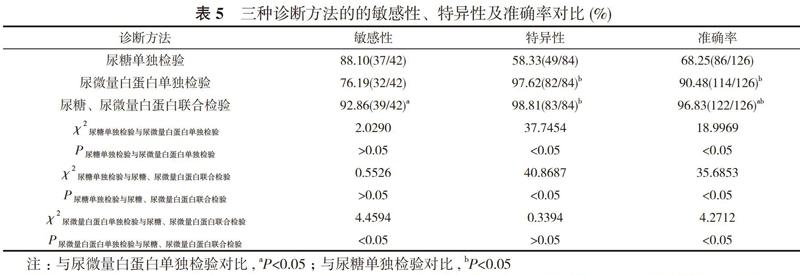
【摘要】 目的 探究尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗對糖尿病早期腎損傷的診斷價值。方法 選取42例糖尿病早期腎損傷患者作為觀察組, 42例糖尿病非腎損傷患者作為對照組, 42例健康體檢患者作為健康組。檢測對比三組尿糖、尿微量白蛋白水平, 統(tǒng)計尿糖單獨檢驗、尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗及尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗的診斷結(jié)果。對比尿糖單獨檢驗、尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗及尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗的敏感性、特異性及準(zhǔn)確率。結(jié)果 觀察組尿糖、尿微量白蛋白水平分別為(3.38±0.45)mmol/L、(36.53±6.15)mg/L;對照組尿糖、尿微量白蛋白水平分別為(2.91±0.36)mmol/L、(24.85±4.73)mg/L;健康組尿糖、尿微量白蛋白水平分別為(1.15±0.28)mmol/L、(14.13±2.84)mg/L;觀察組尿糖、尿微量白蛋白水平均顯著高于對照組和健康組, 對照組顯著高于健康組, 差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。尿糖單獨檢驗檢出陽性72例, 陰性54例;尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗檢出陽性34例, 陰性92例;尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗檢出陽性40例, 陰性86例;病理結(jié)果顯示:陽性42例, 陰性84例。尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗及尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗的特異性、準(zhǔn)確率顯著高于尿糖單獨檢驗, 尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗的敏感性、準(zhǔn)確率顯著高于尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗, 差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 尿糖、尿微量白蛋白是糖尿病早期腎損傷的重要指標(biāo), 尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗診斷糖尿病早期腎損傷效果良好, 顯著優(yōu)于單獨檢驗, 宜于臨床推廣。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 糖尿病腎損傷;尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗;尿糖單獨檢驗;尿微量白蛋白單獨檢驗
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.09.005
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To investigate the diagnostic value of combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin in the diagnosis of early renal damage in diabetic patients. Methods? ?There were 42 diabetes mellitus patients with early renal damage selected as the observation group, 42 diabetes mellitus patients without early renal damage selected as the control group, and another 42 healthy physical examination patients as healthy group. The levels of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin in three groups were measured and compared, and the diagnosis results of separate urinary glucose test, separate urinary microalbumin test and combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin were statistically analyzed. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of separate urinary glucose test, separate urinary microalbumin test and combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin were compared. Results? ?The levels of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin were (3.38±0.45) mmol/L and (36.53±6.15) mg/L respectively in the observation group, which were (2.91±0.36) mmol/L and (24.85±4.73) mg/L in the control group, and (1.15±0.28) mmol/L and (14.13±2.84) mg/L in healthy group. The levels of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group and healthy group, and the control group was significantly higher than the healthy group. The difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). 72 cases were positive and 54 cases were negative in separate urinary glucose test , 34 cases were positive and 92 cases were negative in separate urinary microalbumin test, 40 cases were positive and 86 cases were negative in combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin. Pathological results showed that 42 cases were positive and 84 cases were negative. The specificity and accuracy of separate urinary microalbumin test and combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin were significantly higher than those of separate urinary glucose test, and the specificity and accuracy of combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin were significantly higher than those of separate urinary microalbumin test. The difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion? ?Urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin are important indicators of early renal damage in diabetes. The combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin has a good effect in diagnosing early renal damage in diabetes mellitus, which is significantly better than separate test and is suitable for clinical promotion.
【Key words】 Diabetic renal injury; Combined test of urinary glucose and urinary microalbumin; Separate urinary glucose test; Separate urinary microalbumin test
糖尿病是一種發(fā)病率較高的基礎(chǔ)代謝疾病, 容易引發(fā)多種并發(fā)癥, 糖尿病腎病是糖尿病常見的嚴(yán)重并發(fā)癥之一, 發(fā)病原因主要是患者糖代謝異常引發(fā)的腎功能損傷, 若得不到及時的診斷治療容易發(fā)展為終末期腎病, 導(dǎo)致糖尿病患者死亡, 糖尿病早期腎損傷較為隱蔽, 診斷較為困難。本文分別選取42例糖尿病早期腎損傷患者、42例糖尿病非腎損傷患者及42例健康體檢患者作為研究對象, 旨在分析尿糖、尿微量白蛋白聯(lián)合檢驗對糖尿病早期腎損傷的診斷價值[1], 報告如下。
1 資料與方法

