羥考酮對瑞芬太尼致切口痛大鼠痛覺敏化的干預機制研究
盧洋 王子一 楊秀娟
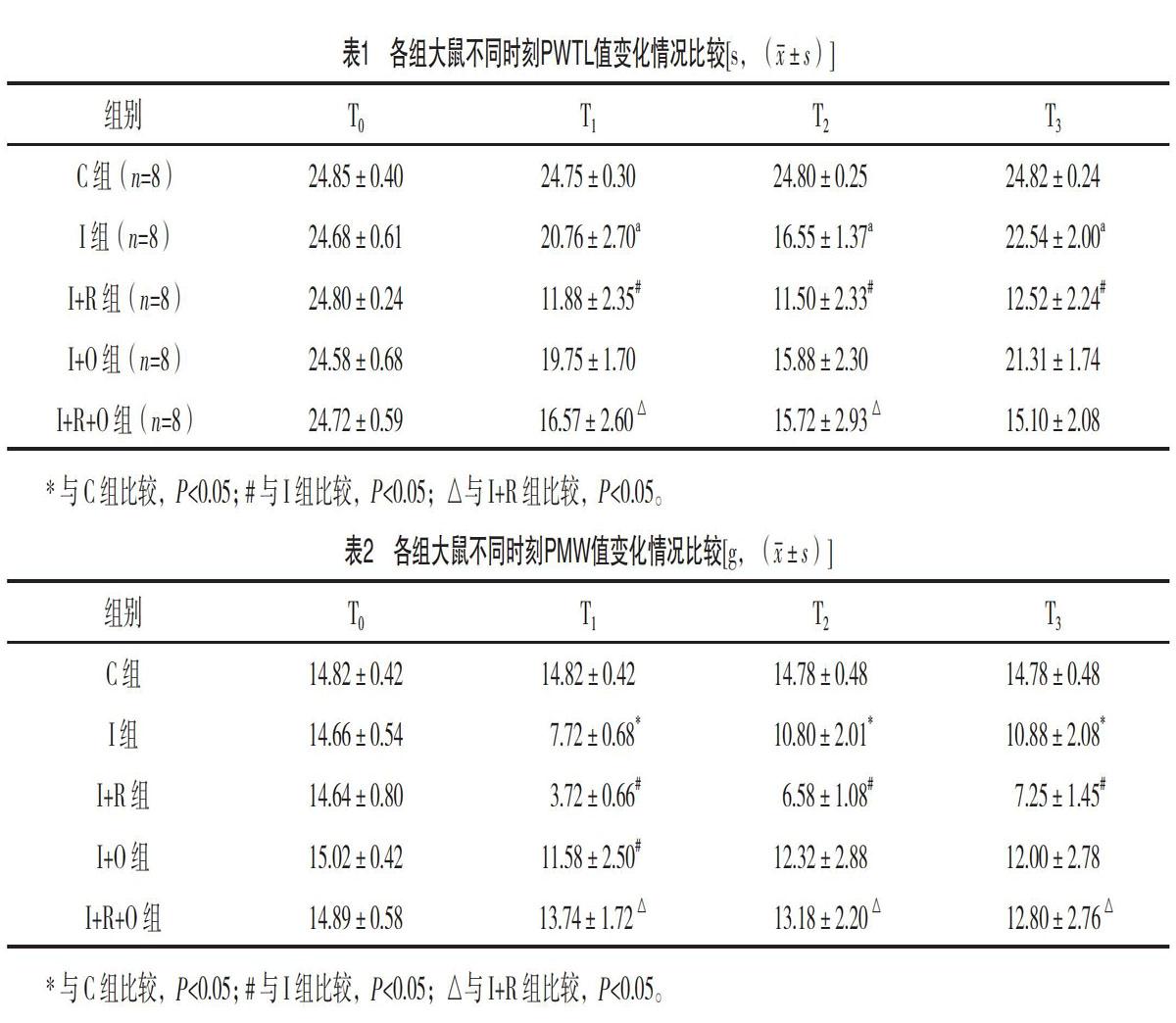
【摘要】 目的:觀察羥考酮對瑞芬太尼致切口痛大鼠痛覺敏化的干預機制。方法:選擇健康雄性SD大鼠40只,按照隨機數字表法分為5組,每組各8只:切口痛+瑞芬太尼+羥考酮組[I+R+O組,切口痛模型建立前30 min皮下注射10 μg/kg羥考酮,建立切口痛模型同時經尾靜脈輸注瑞芬太尼1.2 μg/(kg·min)];切口痛+羥考酮組(I+O組,切口痛模型建立前30 min皮下注射10 μg/kg羥考酮);切口痛+瑞芬太尼(I+R組,建立切口痛模型同時經尾靜脈輸注瑞芬太尼1.2μg/(kg·min)]、切口痛(I組,建立切口痛模型)、空白對照組(C組,皮下注射等量生理鹽水)。采用全自動熱痛刺激儀和Von Frey纖毛機械刺激針測量各組大鼠術前24 h(T0)、術后6 h(T1)、術后24 h(T2)、術后48 h(T3)測定左后足的熱縮足反射潛伏期(PWTL)和機械縮足反射閾值(PMW)。Western免疫印跡檢測L4~5脊髓背角磷酸化NR2B表達。結果:T1~T3時刻,與I組比較,I+R組大鼠PWTL值明顯減小,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);T1~T2時刻,與I+R組比較,I+R+O組大鼠PWTL值明顯增大,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);T1~T3時刻,與I組比較,I+R組大鼠PMW值明顯減小,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);T1~T3時刻,與I+R組比較,I+R+O組大鼠PMW值明顯增大,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。Western免疫印跡檢測顯示,與I組比較,I+R組術后48 h L4~5脊髓背角磷酸化NR2B表達增加,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);與I+R組比較,I+R+O組術后48 h L4~5脊髓背角磷酸化NR2B表達減少,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:瑞芬太尼可誘發切口痛大鼠痛覺敏化,而羥考酮可以有效緩解痛覺敏化,這一作用機制可能與抑制脊髓背角NMDA受體亞基NR2B磷酸化有關。
【關鍵詞】 羥考酮 瑞芬太尼 切口痛 大鼠 痛覺敏化
[Abstract] Objective: To observe intervention mechanism of oxycodone on pain sensitization in rats with incision pain caused by remifentanil. Method:A total of 40 healthy male SD rats were randomly divided into 5 groups (8 cases in each group): incision pain + Remifentanil + Oxycodone group [I + R + O group, subcutaneous injection of 10 μg/kg Oxycodone at 30 min before establishment of incision pain model, instilling Remifentanil
1.2 μg/(kg·min) by tail vein while establishing incision pain model], incision pain + Oxycodone group (I + O group, subcutaneous injection of 10 μg/kg Oxycodone at 30 min before establishment of incision pain model), incision pain + Remifentanil [I + R group, instilling Remifentanil 1.2 μg/(kg·min) by tail vein while establishing incision pain model], incision pain group (I group, establishment of incision pain model) and blank control group (group C, subcutaneous injection of the same amount of normal saline). At 24 h before surgery (T0), at 6 h after surgery (T1), at 24 h after surgery (T2) and at 48 h after surgery (T3), full-automatic heat pain stimulator and Von Frey Hairs were applied to measure paw withdrawal thermal latency (PWTL) and mechanical withdrawal threshold (PMW) of left hindfoot in both groups. Western blotting was applied to detect expression of phosphorylated NR2B in the spinal dorsal horn of L4-5. Result: At T1-T3, compared with group I, the PWTL value of rats in group I + R decreased significantly (P<0.05). At T1-T2, compared with the I + R group, the PWTL value of the I + R + O group increased significantly (P<0.05). At T1-T3, compared with I group, the PMW value of rats in group I+R decreased significantly (P<0.05). At T1-T3, compared with the I + R group, the PMW value of the rats in the I + R + O group increased significantly (P<0.05). Western Blot showed that compared with group I, NR2B phosphorylation in L4-5 dorsal horn of spinal cord in I + R group increased 48 h after surgery, with statistically significant difference (P<0.05). Compared with the I + R group, NR2B phosphorylation in L4-5 dorsal horn of spinal cord decreased 48 h after surgery in the I + R + O group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Remifentanil can induce pain sensitization in rats with incision pain, and oxycodone can effectively alleviate pain sensitization. This action mechanism may be related to inhibiting phosphorylation of NMDA receptor subunit NR2B in spinal dorsal horn.[Key words] Hydroxycodone Ruifentaini The incision is painful Rat Pain sensitivityFirst-authors address: Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154000, China
瑞芬太尼是一種具有較強鎮痛作用的超短效阿片μ受體激動劑,在臨床麻醉及疼痛治療領域應用普遍,但由于其鎮痛效應消失迅速,可能誘發術后痛覺敏化[1]。這一效應在很大程度上限制了瑞芬太尼在臨床的應用,目前對其發生機制尚未完全清楚,如何有效預防及治療瑞芬太尼誘發的痛覺敏化已成為臨床研究的熱點。N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸(NMDA)受體是疼痛傳導的主要調節受體,在中樞敏化過程中背角神經元NMDA受體的激活被認為是關鍵環節[2]。有研究認為,瑞芬太尼致切口痛大鼠痛覺敏化的作用機制可能與促進NMDA受體向胞膜轉運增加及NMDA受體磷酸化有關[3]。……

