血清C肽和糖化血紅蛋白聯(lián)合檢測對糖尿病診斷的臨床價值研究
楊玉勤
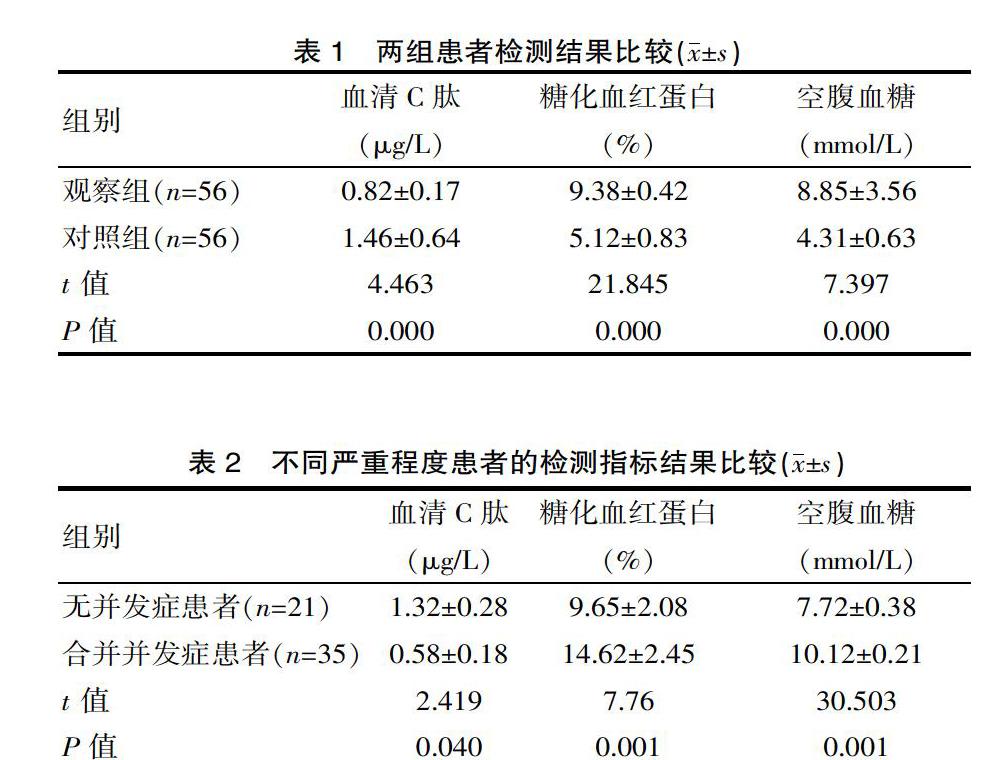
[摘要] 目的 探究血清C肽、糖化血紅蛋白二者聯(lián)合檢測在糖尿病臨床診斷中的臨床價值。方法 整理2018年1月—2019年2月期間該院內(nèi)二科收治的56例糖尿病患者設(shè)為觀察組,同期選擇56名身體健康的老年人設(shè)為對照組。對兩組進行血清C肽檢測與糖化血紅蛋白檢測,分析兩種檢測方法的檢測結(jié)果及臨床檢測價值。 結(jié)果 觀察組的糖化血紅蛋白、空腹血糖水高于對照組,觀察組的血清C肽水平低于對照組。合并并發(fā)癥患者的糖化血紅蛋白、空腹血糖水高于無并發(fā)癥患者,而合并并發(fā)癥患者的血清C肽低于無并發(fā)癥的患者。以上差異有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 在糖尿病臨床診斷中進行血清C肽、糖化血紅蛋白檢測,可顯著提高診斷效果,有利于臨床醫(yī)師有效判斷患者的病情嚴(yán)重程度,了解其血糖水平變化,為臨床診治提供有價值的依據(jù)。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 血清C肽;糖化血紅蛋白;糖尿病;臨床價值
[中圖分類號] R587.1? ? ? ? ? [文獻標(biāo)識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)01(b)-0057-02
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical value of combined detection of serum C-peptide and glycated hemoglobin in the clinical diagnosis of diabetes. Methods A total of 56 patients with diabetes mellitus admitted to the hospital from January 2018 to February 2019 were enrolled in the observation group. 56 healthy individuals were selected as the control group. Serum C-peptide detection and glycosylated hemoglobin were detected in both groups, and the detection results and clinical detection value of the two detection methods were analyzed. Results The glycated hemoglobin and fasting blood glucose in the observation group were higher than those in the control group. The serum C-peptide level of the observation group was lower than that of the control group. Glycated hemoglobin and fasting blood glucose were higher in patients with complications than in uncomplicated patients, and patients with complications had lower serum C-peptide than patients without complications. The above differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The detection of serum C-peptide and glycosylated hemoglobin in the clinical diagnosis of diabetes can significantly improve the diagnostic effect, which is helpful for clinicians to effectively judge the severity of the patient's condition and understand the changes of blood glucose level, which provides a valuable basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
[Key words] Serum C-peptide; Glycated hemoglobin; Diabetes; Clinical value
糖尿病是常見的基礎(chǔ)疾病之一,也是最為常見的一種代謝系統(tǒng)疾病,臨床表現(xiàn)以血糖水平升高為主。于糖尿病患者而言,控制血糖是治療該病癥的治療原則[1]。臨床上常以胰島素藥物控制治療為主要治療方式控制病情。近年來,醫(yī)學(xué)領(lǐng)域?qū)μ悄虿∨R床診治效果的關(guān)注度較高,并做了許多創(chuàng)新與努力[2]。該研究對糖尿病患者進行血清C肽檢測與糖化血紅蛋白檢測,旨在探究兩種檢測方法聯(lián)合檢測的效果。現(xiàn)分析2018年1月—2019年2月間該院內(nèi)二科收治的56例糖尿病患者為臨床資料,報道如下。
1? 資料與方法
1.1? 一般資料
整理在該院內(nèi)二科住院期間的56例糖尿病患者的臨床資料,包括30例男性、26例女性;年齡最大88歲,最小38歲,平均(58.63±2.15)歲;病程最長26年,最短7個月,平均(13.74±1.03)年;平均空腹血糖值>7.0 mmol/L,餐后2 h血糖值>12.0 mmol/L。對照……

