口腔護(hù)理干預(yù)對(duì)老年糖尿病合并口腔疾病患者護(hù)理滿(mǎn)意度的影響
馮培 王藝瀟 谷婷
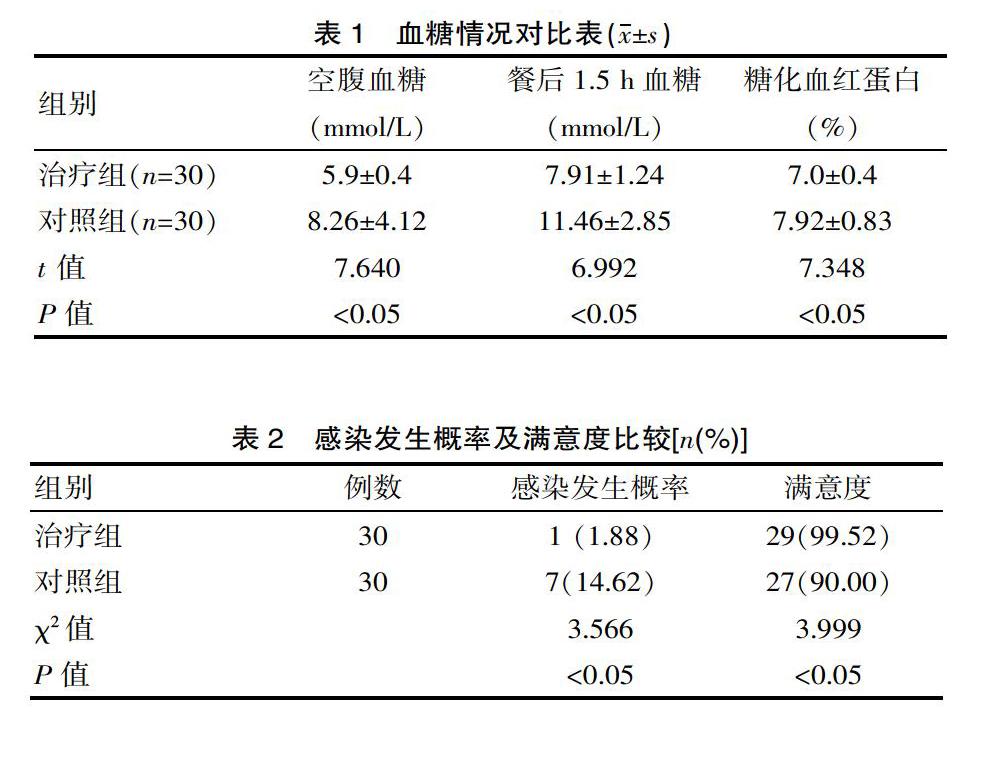
[摘要] 目的 觀察口腔護(hù)理干預(yù)對(duì)老年糖尿病合并口腔疾病患者護(hù)理滿(mǎn)意度的影響。方法 該次選擇2018年2月—2019年3月該院收治老年糖尿病合并的口腔疾病的患者60例,隨機(jī)分為對(duì)照組和治療組組,各30例。對(duì)照組實(shí)施常規(guī)護(hù)理措施,治療組在此基礎(chǔ)上進(jìn)行口腔護(hù)理干預(yù),比較護(hù)理效果。 結(jié)果 治療組與對(duì)照組相比,患者焦慮和抑郁情況顯著改善,治療組護(hù)理滿(mǎn)意度高于對(duì)照組,差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 口腔護(hù)理干預(yù)對(duì)老年糖尿病合并口腔疾病患者護(hù)理滿(mǎn)意度有明顯效果。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 口腔護(hù)理干預(yù);口腔疾病;老年糖尿病
[中圖分類(lèi)號(hào)] R587? ? ? ? ? [文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號(hào)] 1672-4062(2020)01(b)-0156-02
[Abstract] Objective To observe the effect of oral nursing intervention on nursing satisfaction of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus complicated with oral diseases. Methods Sixty patients with oral diabetes mellitus admitted to our hospital from February 2018 to March 2019 were randomly divided into control group and treatment group. The control group was given routine nursing measures, and the treatment group performed oral care intervention on this basis to compare the nursing effects. Results Compared with the control group, the anxiety and depression of the treatment group were significantly improved, and the satisfaction of the treatment group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion Oral care intervention has a significant effect on the satisfaction of nursing patients with diabetes mellitus complicated with oral disease.
[Key words] Oral care intervention; Oral disease; Senile diabetes
相關(guān)醫(yī)學(xué)領(lǐng)域的研究表明[1],口腔護(hù)理的治療對(duì)老年糖尿病聯(lián)合口腔疾病患者的口腔癥狀更加安全高效,且對(duì)血糖水平得以控制,從而使患者生活質(zhì)量顯著提高。老年糖尿病則是一種極為普遍的發(fā)病病狀,盡管如此,許多患者不重視其病的重要性,而糖尿病患者的血糖如果不穩(wěn)定,則易引起口腔的相關(guān)疾病,增加了感染發(fā)病率的風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。故2018年2月—2019年3月該院收治老年糖尿病合并的口腔疾病的患者護(hù)理治療進(jìn)行相關(guān)評(píng)價(jià),報(bào)道如下。
1? 資料與方法
1.1? 一般資料
該院60例收治老年糖尿病的患者,隨機(jī)分為對(duì)照組30 例和治療組 30 例,經(jīng)倫理委員同意,均診斷符合糖尿病臨床指標(biāo)。對(duì)照組患者男女比例:2:1 ,年齡大小60~89歲,平均年齡(69.5±9.3)歲,糖尿病病程2~7年,平均病程(4±2.2)年,含有合并牙齦炎20例、牙周病3例和其他伴隨性牙病7例;治療組男女比例為1:1,年齡大小61~85歲, 平均年齡(73.2±7.9)歲,糖尿病病程 2~7年,平均病程 5.1±3.4)年,含有合并牙齦炎15例、牙周病10例和其他伴隨性牙病5例。……

