優(yōu)質(zhì)護理在部隊療養(yǎng)院糖尿病患者中的應(yīng)用效果
游小彧 洪美楊 潘曉蒙
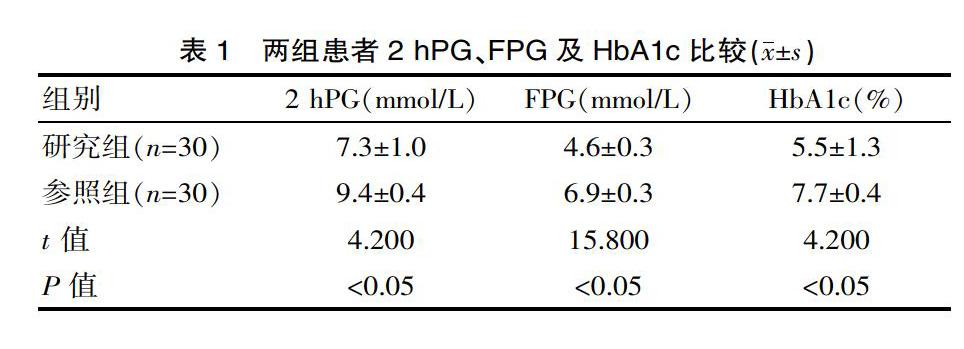

[摘要] 目的 探討優(yōu)質(zhì)護理在部隊療養(yǎng)院糖尿病患者中的應(yīng)用效果。方法 選擇2017年3月—2019年3月在該療養(yǎng)院療養(yǎng)的糖尿病患者60例,按照護理方式的不同分為兩組,參照組(n=30)與觀察組(n=30),分別采取常規(guī)護理與優(yōu)質(zhì)護理。對兩組空腹血糖、糖化血紅蛋白,餐后2 h血糖水平及護理滿意度進行分析。 結(jié)果 研究組餐后2 h血糖、空腹血糖及糖化血紅蛋白低于參照組,護理滿意度高于對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 對部隊療養(yǎng)院糖尿病患者實施優(yōu)質(zhì)護理能夠顯著幫助患者控制血糖水平,臨床效果滿意,值得推薦。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 優(yōu)質(zhì)護理;療養(yǎng)院;糖尿病
[中圖分類號] R473.5? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)01(b)-0167-02
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application effect of quality nursing in diabetic patients in military nursing homes. Methods Sixty patients with diabetes mellitus who were convalesced in the nursing home from March 2017 to March 2019 were divided into two groups according to the different nursing methods. The reference group (n=30) and the observation group (n=30), respectively with routinely nursing care and quality care. The fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, 2 h postprandial blood glucose level and nursing satisfaction were analyzed. Results The blood glucose, fasting blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the study group were lower than the reference group at 2 h after the meal. The nursing satisfaction was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The implementation of quality nursing care for patients with diabetes in military nursing homes can significantly help patients to control blood glucose levels, and the clinical results are satisfactory. It is worthwhile to promote.
[key words] Quality nursing; Nursing home; Diabetes
糖尿病屬于一種慢性疾病,是一種糖代謝紊亂誘發(fā)的一種代謝性疾病,近年來,糖尿病發(fā)病率呈逐年升高趨勢,引起醫(yī)學界及社會的關(guān)注[1]。糖尿病需終身治療,治療不及時會產(chǎn)生嚴重并發(fā)癥。報道指出單純藥物治療難以控制血糖,需結(jié)合有效護理方式,才能獲得滿意效果[2]。該研究選取在2017年3月—2019年3月就診該療養(yǎng)院糖尿病患者60例作為研究對象,收到滿意效果,報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1? 一般資料
于該療養(yǎng)院就診的糖尿病患者中選取60例作為研究對象,按照護理方式不同分為參照組與觀察組,均30例。參照組實施常規(guī)護理,觀察組實施優(yōu)質(zhì)護理。納入標準:①空腹血糖水平>11.10 mmol/L; ②糖化血紅蛋白>10%。排除標準:①難以完成該項研究患者;②妊娠或哺乳期孕婦;③合并肝腎等實質(zhì)臟器損害。參照組中男22例,女8例;年齡66~90歲,平均(77.28±6.60)歲。觀察組中男24例,女6例;年齡67~92歲,平均(77.30±6.62)歲。兩組一般資料差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05),具有可比性。

