豬基因表達調控數據庫(GereDB)的構建
石博妹 姚敏 余平 黃廷華

摘要:【目的】構建豬基因表達調控數據庫(GereDB),為從基因水平解釋豬的生長發育規律、遺傳育種和疾病防控等提供科學依據。【方法】從NCBI下載小鼠和豬的RNA序列原始數據進行序列比對,根據序列同源性將小鼠的基因表達調控信息轉移給豬,并建立豬基因表達調控信息網絡,整理加工后根據區域結構,以Linux為操作系統、Apache為Web服務器、MySQL為數據庫、Python為服務器端腳本解釋器構建豬GereDB數據庫。【結果】從NCBI下載的Fast數據共包含291182條豬核苷酸序列,通過序列比對和手工整理,注釋篩選出67000多條豬核苷酸序列;將小鼠的基因表達調控信息轉移給豬,獲得的豬基因表達調控關系鏈接有67027條,構建了豬GereDB數據庫(http://www.thua45.cn/geredb-wp/),并開發GEREA生物信息學分析工具以發現豬基因表達調控因子。在豬GereDB數據庫中有116個調控因子可調控100多個基因,說明其在豬轉錄組調控中發揮重要作用。GEREA生物信息學分析工具在已發表的豬乳腺組織數據集上進行測試,結果顯示,與母豬分娩前14 d相比,分娩后1 d母豬乳腺中26個調控因子的靶基因顯著差異表達(FDR<0.05),其中FGF2調控因子在母豬泌乳方面發揮重要作用。【結論】豬GereDB數據庫能提供豬基因表達和調控間關系的信息,且能使用GEREA生物信息學分析工具發掘豬基因表達調控數據,有助于揭示調控因子對高通量測序差異表達基因的調控機制,為從基因水平探究豬的生長發育及疾病防控提供數據信息。
關鍵詞: 豬;基因表達;調控因子;GereDB數據庫
Abstract:【Objective】To construct the pig gene expression and regulation database(GereDB) for providing a scientific basis to explain the growth and development, genetic breeding and disease treatment of pigs at the gene level. 【Me-thod】Original RNA sequence data of mouse and pig were downloaded for sequence alignment from NCBI and transferred gene expression and regulation information from mouse to pig according to the sequence homology, analyzed pig gene expression and regulation data to establish the pig gene expression and regulation information network. According to the regional structure after processing, GereDB database of pig was established with Linux operating system, Apache Web server, MySQL database management system,Python for server-side script interpreter. 【Result】A total of 291182 pig nucleotide sequences were contained in Fast data downloaded form NCBI. The mouse gene expression regulation information was transferred to pig, 67027 relationship links in regulating gene expression of pig were obtained , and the pig GereDB database(http://www.thua45.cn/geredb-wp/) was built, GEREA bioinformatics analysis tools were developed to find gene expression regulators of pig. There were 116 regulators could regulate more than 100 genes in pig GereDB database, indica-ting that they played an important role in the transcriptome regulation of pig. The GEREA bioinformatics analysis tool was tested on a published data set of pig breast tissue and the result showed that 26 target genes of regulatory factors appeared significantly differential expression(FDR<0.05) on the sow 1 d after delivery compared with the 14 d before delivery. Moreover, FGF2 was as an? vital regulatory factor for the milking of sows. 【Conclusion】Pig GereDB database can provide relationships between pig gene expression and regulation, and GEREA bioinformatics tool can explore pig gene expression regulation data. The database is useful for exploring how differentially expressed genes detected by high throughput experiments are regulated by certain regulator genes and can provide valid data to explore the growth and development, disease control and prevention at gene level.
0 引言
【研究意義】基因表達調控是一個復雜而又重要的過程,在過去的幾十年里已取得重大進展(Wachter,2014;Jones,2015),但針對豬的研究相對滯后,尚未形成基因表達調控數據庫(GereDB)。GereDB數據庫能實現將同一物種轉錄因子—靶基因相互作用的關系信息進行整理歸納,有助于科技人員快速準確地提取與目的基因相關的基因或蛋白資料,因此,以小鼠GereDB數據為基礎,利用序列同源性比對構建豬GereDB數據庫,可為掌握豬的生長發育規律和疾病防控機理等提供便捷的分析工具。【前人研究進展】近年來,在人類和小鼠的基因表達調控系統,包括先天免疫系統、代謝系統和信號轉導等方面已取得突破性進展(Wachter,2014;Jones,2015),許多重要的基因表達調控因子如TNF、IFNG和MAPK也被發現(Arthur and Ley,2013;Croft and Siegel,2017;Green et al.,2017),但仍有許多問題亟待進一步探究,包括關鍵調節因子對特定刺激的響應方式及有效發現關鍵調節因子的方法等(Subramanian et al.,2005;Shojaie and Michailidis,2010)。基因表達調控涉及到復雜的網絡,且受多個重要的正、負效應因子控制,而這些效應因子可影響轉錄組的組成(Huang et al.,2011;Zhao et al.,2016)。為此,數個先進的數據庫應運而生,包括TFactS(Essaghir et al.,2010)、HTRIdb(Bovolenta et al.,2012)和TRRUST(Han et al.,2018)。Bovolenta等(2012)建立的HTRIdb數據庫整理了人類轉錄因子—靶基因相互作用關系的信息,研究者可通過此數據庫快速準確地提取與研究基因相關的基因或蛋白資料。Essaghir和Demoulin(2012)利用TfactS數據庫對已發表的惡性腫瘤基因表達數據及癌癥基因組圖譜進行分析,篩選出TFRC、MET和VEGFA基因可作為惡性腫瘤標志物候選基因,因此檢測患者血清中TFRC、MET和VEGFA基因的表達量對惡性腫瘤確診有重要意義。Han等(2018)將人源TRRUST數據庫升級為TRRUST v2數據庫,升級后的TRRUST數據庫不僅包含800個人類轉錄因子調控的8444多個靶基因,還增加了828個小鼠轉錄因子調控的6552個靶基因,該數據庫存儲了大量人類和小鼠基因表達調控信息,為篩選調控人類疾病發生過程的關鍵轉錄因子提供了參考依據。【本研究切入點】TfactS、HTRIdb和TRRUST數據庫是專門針對人類或小鼠的基因表達調控信息,因此,亟需構建豬GereDB數據庫以使有效發掘豬基因表達調控的關鍵調節因子。【擬解決的關鍵問題】將豬的RNA序列與小鼠的RNA序列進行比對,利用序列同源性將小鼠基因表達調控信息轉移給豬,構建豬GereDB數據庫,為從基因水平解釋豬的生長發育規律、遺傳育種和疾病防控等提供科學依據。
1 材料與方法
1. 1 豬和小鼠基因序列獲取及比對分析
小鼠RNA序列和豬RNA序列的原始數據(Fasta格式)從美國國立生物技術信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)下載;本地化的BLAST軟件也從NCBI網頁下載,然后在本地安裝配置并運行,建立本地化的網頁BLAST比對服務。打開命令提示符,切換至保存核苷酸序列的文件夾,同時運行以下命令建立數據庫文件:makeblastdb -in db.fasta -dbtype prot -parse_seqids -out dbnam,運行以下命令將豬RNA序列與小鼠RNA序列進行比對:blastp -query seq.fasta-out seq.blast-db dbname-outfmt 6-evalue 1e-5-num_descriptions 10-num_ threads 8,查看比對結果,根據相似性和P確定豬與小鼠間的同源基因,即比對結果序列相似性越高,期望值越小,其同源性越高。本研究最終選擇豬和小鼠中的最佳匹配基因對,其最佳匹配原則為P小于10-6,且相似性大于70%。
1. 2 豬基因功能注釋
根據豬與小鼠的基因序列比對結果,篩選出序列同源性高的基因序列,將小鼠的基因表達調控信息轉移給豬并建立豬基因表達調控信息網絡,小鼠GereDB數據庫已由GereDB團隊開發并發布使用(Huang et al.,2019)。根據小鼠基因表達調控信息(三列數據)在豬基因里查找對應的基因,建立豬基因表達調控信息(三列數據)。小鼠的A序列與豬的a序列相似,小鼠的A1序列與豬的a1序列相似,由于小鼠的A序列正調控A1序列,故推測豬中的a序列和a1序列也存在正調控關系。
1. 3 GereDB數據庫系統形成與發布
1. 3. 1 GereDB數據庫構建 手工提取的豬基因表達調控相互關系包含3個要素,即基因表達調控因子、靶基因及調控因子與靶基因的直接連接。GereDB數據庫以Linux為操作系統,Apache為Web服務器,MySQL為數據庫,Python為服務器端腳本解釋器,并由這4個軟件組建一個穩定、免費的網站系統。
1. 3. 2 GEREA生物信息學分析工具開發 對豬基因表達調控信息網絡進行整理加工,并進一步收集整理相關的數據資源,開發GEREA生物信息學分析工具以發現基因表達調控因子,進而對豬基因表達數據進行分析。本研究將活性調控因子定義為一個基因,該基因具有發生在不同表達基因列表中的目標,其頻率顯著高于預期基因表達,基因表達調控因子—靶基因鏈接建成后,基因表達分析數據加載于調控因子的靶基因上(圖1-A)。基于網絡數據可被組織為一個3×3列聯表,分析結果中大寫字母所代表的含義見圖1-B,通過Fisher精確性檢驗分析可得到一個全局的顯著性檢驗P0、上調表達顯著性檢驗P1及下調表達顯著性檢驗P2(Sun and Yu,2016),然后采用本杰明和霍克伯格方法(FDR)進行校正(Gui et al.,2015)。若P1<0.05說明靶基因的表達變化由該調控因子上調表達引起,若P2<0.05說明靶基因的表達變化是由該調控因子下調表達引起。
1. 3. 3 采用真實豬基因表達數據集測試GEREA生物信息學分析工具 GEREA生物信息學分析工具在已發表的豬乳腺組織數據集上進行測試。母豬乳腺組織受分娩的刺激(Essaghir and Demoulin,2012),在母豬分娩前后分別取其活體乳腺組織進行高通量測序分析。原始轉錄組數據來自NCBI的GEO數據庫,登錄號GSE101983。采用Bioconductor中的分位數法對數據進行歸一化處理(Bolstad et al.,2003),分析分娩刺激對乳腺中基因調控因子調節靶基因的表達情況。
2 結果與分析
2. 1 豬和小鼠基因序列的獲取及比對分析結果
從NCBI genome FTP下載的Fast數據共包含291182條豬核苷酸序列,通過序列比對和手工整理,注釋篩選出67000多條豬核苷酸序列。表1列出豬和小鼠前50個相似性最高的基因序列,根據最佳匹配原則,可判定表中數據顯著性良好。
2. 2 豬基因表達調控信息網絡構建
通過將小鼠的基因表達調控信息轉移給豬,建立與豬基因表達調控信息相關的數據庫,豬的基因表達調控關系鏈接有67027條,其中豬和小鼠前50個基因表達調控關系的比對結果見表2。
2. 3 GereDB數據庫的形成與發布
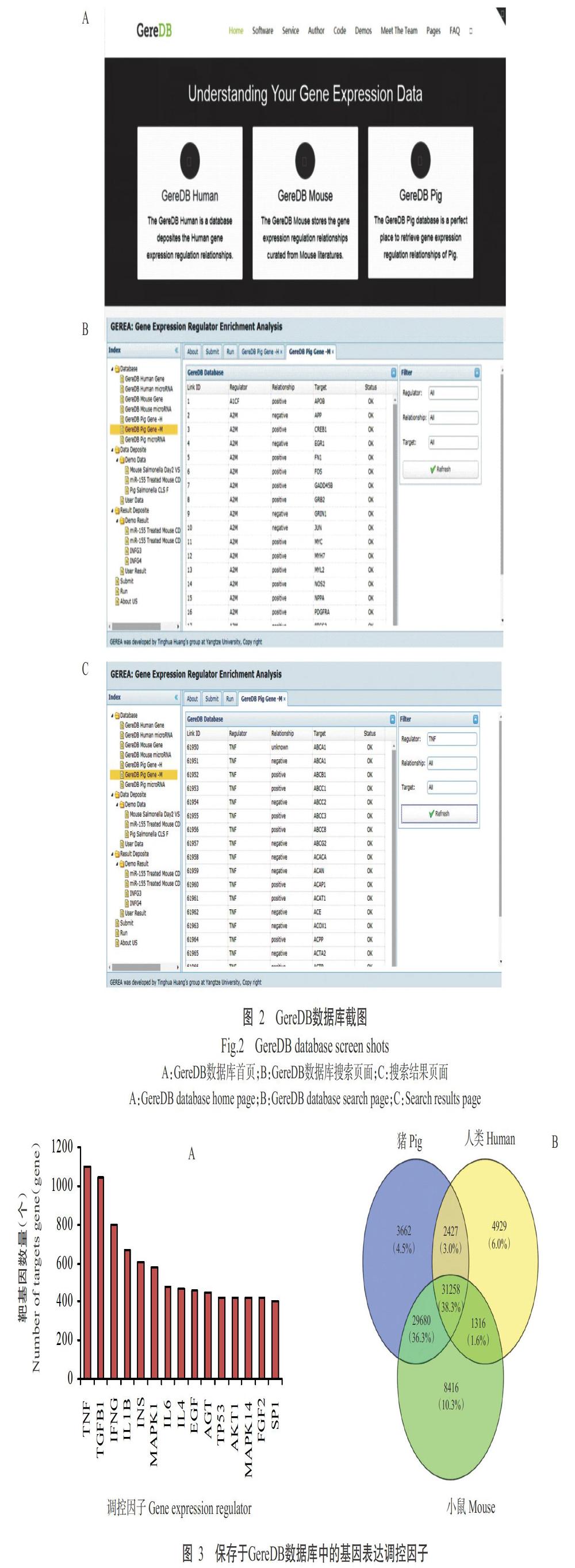
在GereDB數據庫首頁(http://www.thua45.cn/geredb-wp/)上可看到豬的基因表達數據在最右側(圖2-A),點擊進去后進入GereDB搜索頁面,可選擇搜索Regulator、Relationship或Target鏈接(圖2-B)。GereDB數據庫中的數據是根據基因組織,其鏈接搜索允許使用NCBI官方基因符號(基因名)檢索感興趣的數據。從Links搜索結果頁面(圖2-C)可獲得與基因表達調控因子相關的基因,包括調控基因和靶基因的官方基因符號,以及調控基因對每個靶基因的影響。
2. 4 GereDB數據庫是一種獨特的基因表達調控資源
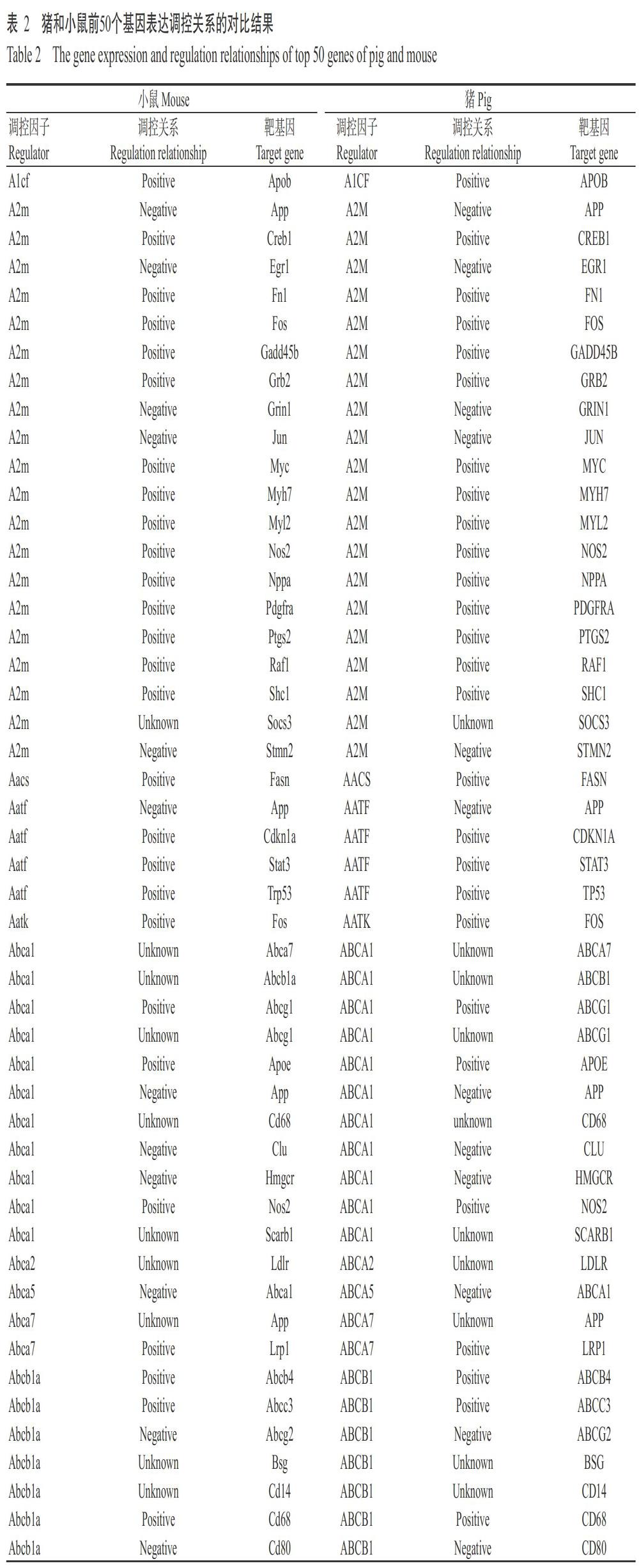
通過對GereDB數據庫中的調控關系進行分析,發現大量基因表達調控子網絡構成了基因表達調控網絡體系(Boyle et al.,2014)。圖3-A顯示靶基因數量最多的前15個網絡體系調控因子,若將基因表達調控網絡體系分解成單個子網絡時,即可查找調控基因表達的最主要調控因子。TNF可調控GereDB數據庫中的1103個基因,而TGFB1可調控1042個基因。GereDB數據庫中有116個調控因子可調控100多個基因,說明其在豬轉錄組調控中發揮重要作用。GereDB團隊也曾對小鼠和人類的基因表達調控關系進行整理,在GereDB數據庫中儲存的豬、小鼠及人類基因調控鏈接數如圖3-B所示。小鼠的基因調控鏈接數為70670條,人類的基因調控鏈接數為39930條,豬的基因調控鏈接數為67027條。其中,豬與小鼠的重疊數有60938條(重疊率為74.6%),與人類的重疊數有33685條(重疊率為41.3%),三者的重疊數有31258條,重疊率為38.3%。
2. 5 真實豬基因表達數據集測試GEREA生物信息學分析工具的結果
GEREA分析生物信息學工具運行70 s,結果(表3)顯示,與母豬分娩前14 d相比,分娩后1 d母豬乳腺中26個調控因子的靶基因顯著差異表達(FDR<0.05)。其中,乳腺組織中FGF2調控的靶基因有19個正調控上調表達、3個負調控上調表達,另有6個正調控下調表達、7個負調控下調表達,提示FGF2調控因子在母豬泌乳方面發揮重要作用。
3 討論
在人類生物醫學研究中,模式生物小鼠的研究在過去十幾年間已非常全面深入,尤其一些與疾病發生、生長繁殖及代謝有關的基因在小鼠中已得到深入研究(Vemula et al.,2019;Yamamoto et al.,2019;Yin et al.,2019)。為此,本研究借鑒和參照小鼠已獲得的基因表達調控信息,通過序列比對方式,研究相關基因在豬基因表達調控中的特性和功能,并對其進行詳細注釋,最后將比對結果及相關注釋信息儲存到專門的GereDB數據庫中,建立豬基因表達調控二級數據庫,為解釋豬的生長發育規律、遺傳育種和疾病防控等提供科學依據。
獲取基因功能信息的一種有效途徑是通過不同物種間序列相似性比對,利用相似性檢索分析對基因序列進行分析,推測其代表的基因結構和功能。該方法已成為一種常用的功能基因組研究方法,尤其在新的物種完成基因組測序后,利用其他物種中的已知基因功能信息對新測序物種中的基因進行注釋和分析,具有方便快捷且準確有效的特點,獲得的功能注釋信息可為后續的研究驗證提供重要線索(Vallenet et al.,2019)。本研究從NCBI上獲取豬和小鼠的基因組序列,通過序列相似性比對分析,以小鼠的基因表達調控信息為原材料,成功獲取豬基因表達調控關系數據。本研究構建的豬GereDB數據庫是豬專門化本地二級數據庫,基于其本地化BLAST檢索系統是通過整合由NCBI開發的數據庫搜索程序BLAST工具為用戶提供序列比對功能,通過一種局部的算法來獲得2個基因序列中的相似性序列,其分析過程與通過NCBI在線BLAST分析一致,參數選擇及最終結果也與NCBI在線分析結果的格式類似,但檢索速度和準確性得到明顯提高,是一套能迅速與大型公開數據庫(主要是蛋白數據庫或DNA數據庫)進行相似性序列比對,尋找相同或相似序列且相對準確而高效的分析工具。BLAST能接受用戶輸入的序列,通過在本地數據庫中進行捜索,然后將用戶輸入序列的同源序列返回給用戶,實現本地核苷酸與蛋白的同源性檢索。
GereDB數據庫是一個獨特、有效、方便的資源,尤其對于人類基因表達數據研究者來說,提供了一個可獲得較全面關系信息的平臺。對于豬基因的表達和調控,由于缺乏從文獻中提取相關數據的有效方法,通常難以獲得豬基因表達調控關系數據,而本研究構建的豬GereDB數據庫有助于探索高通量測序檢測到的差異表達基因是如何被某些調控因子所調控。此外,利用存儲于GereDB數據庫中豬基因表達與調控間的關系,以及GEREA的調控基因發現算法,能發現編排特定轉錄譜的調控因子。
4 結論
豬GereDB數據庫能提供豬基因表達和調控間關系的信息,且能利用GEREA生物信息學分析工具發掘豬基因表達調控數據,有助于揭示調控因子對高通量測序差異表達基因的調控機制,為從基因水平探究豬的生長發育及疾病防控提供數據信息。
參考文獻:
Arthur J S,Ley S C. 2013. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity[J]. Nature Reviews. Immunology,13(9):679-692.
Bolstad B M,Irizarry R A,Astrand M,Speed T P. 2003. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias[J]. Bioinformatics,19(2):185-193.
Bovolenta L A,Acencio M L,Lemke N. 2012. HTRIdb:An open-access database for experimentally verified human transcriptional regulation interactions[J]. BMC Genomics,13:405. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-405.
Boyle A P,Araya C L,Brdlik C,Cayting P,Cheng C,Cheng Y,Gardner K,Hillier L W,Janette J,Jiang L,Kasper D,Kawli T,Kheradpour P,Kundaje A,Li J J,Ma L,Niu W,Rehm E J,Rozowsky J,Slattery M,Spokony R,Terrell R,Vafeados D,Wang D,Weisdepp P,Wu Y C,Xie D,Yan K K,Feingold E A,Good P J,Pazin M J,Huang H,Bickel P J,Brenner S E,Reinke V,Waterston R H,Gerstein M,White K P,Kellis M,Snyder M. 2014. Comparative analysis of regulatory information and circuits across distant species[J]. Nature,512(7515):453-456.
Croft M,Siegel R M. 2017. Beyond TNF:TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic disea-ses[J]. Nature Reviews. Rheumatology,13(4):217-233.
Essaghir A,Demoulin J B. 2012. A minimal connected network of transcription factors regulated in human tumors and its application to the quest for universal cancer biomarkers[J]. PLoS One,7(6):e39666.
Essaghir A,Toffalini F,Knoops L,Kallin A,van Helden J,Demoulin J B. 2010. Transcription factor regulation can be accurately predicted from the presence of target gene signatures in microarray gene expression data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,38(11):e120.
Green D S,Young H A,Valencia J C. 2017. Current prospects of type II interferon gamma signaling and autoimmunity[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,292(34):13925-13933.
Gui J,Greene C S,Sullivan C,Taylor W,Moore J H,Kim C. 2015. Testing multiple hypotheses through IMP weighted FDR based on a genetic functional network with application to a new zebrafish transcriptome study[J]. BioData Mining,8:17. doi: 10.1186/s13040-015-0050-8.
Han H,Cho J W,Lee S,Yun A,Kim H,Bae D,Yang S,Kim C Y,Lee M,Kim E,Lee S,Kang B,Jeong D,Kim Y,Jeon H N,Jung H,Nam S,Chung M,Kim J H,Lee I. 2018. TRRUST v2:An expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions [J]. Nucleic Acids Research,46(D1):D380-D386.
Huang T,Huang X,Shi B,Yao M. 2019. GEREDB:Gene expression regulation database curated by mining abstracts from literature[J]. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology,17(4):1950024.
Huang T H,Uthe J J,Bearson S M,Demirkale C Y,Nettleton D,Knetter S,Christian C,Ramer-Tait A E,Wannemuehler M J,Tuggle C K. 2011. Distinct peripheral blood RNA responses to Salmonella in pigs differing in Salmonella shedding levels:Intersection of IFNG,TLR and miRNA pathways[J]. PLoS One,6(12):e28768.
Jones B. 2015. Gene expression:Layers of gene regulation[J]. Nature Reviews. Genetics,16(3):128-129.
Shojaie A,Michailidis G. 2010. Network enrichment analysis in complex experiments[J]. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology,9:Article22. doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1483.
Subramanian A,Tamayo P,Mootha V K,Mukherjee S,Ebert B L,Gillette M A,Paulovich A,Pomeroy S L,Golub T R,Lander E S,Mesirov J P. 2005. Gene set enrichment analysis:A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Ame-rica,102(43):15545-15550.
Sun S,Yu X. 2016. HMM-Fisher:Identifying differential methylation using a hidden Markov model and Fisher?s exact test[J]. Statistical Applications in Genetics and Molecular Biology,15(1):55-67.
Vallenet D,Calteau A,Dubois M,Amours P,Bazin A,Beuvin M,Burlot L,Bussell X,Fouteau S,Gautreau G,Lajus A,Langlois J,Planel R,Roche D,Rollin J,Rouy Z,Sabatet V,Médigue C. 2019. MicroScope:An integrated platform for the annotation and exploration of microbial gene functions through genomic,pangenomic and metabolic comparative analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,48(D1):D579-D589.
Vemula P,Jing Y,Zhang H,Hunt J B Jr,Sandusky-Beltran L A,Lee D C,Liu P. 2019. Altered brain arginine metabolism in a mouse model of tauopathy[J]. Amino Acids,51(3):513-528.
Wachter A. 2014. Gene regulation by structured mRNA elements[J]. Trends Genetics,30(5):172-181.
Yamamoto Y,Hirose N,Kamimura S,Wakayama S,Ito J,Ooga M,Wakayama T. 2019. Production of mouse offspring from inactivated spermatozoa using horse PLCζ mRNA[J]. The Journal of Reproduction and Development,66(1):67-73.
Yin C,Liu B,Wang P,Li X,Li Y,Zheng X,Tai Y,Wang C,Liu B. 2019. Eucalyptol alleviates inflammation and pain responses in a mouse model of gout arthritis[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,1779(9):2042-2057.
Zhao Y,Chen J,Freudenberg J M,Meng Q,Rajpal D K,Yang X. 2016. Network-based identification and prioritization of key regulators of coronary artery disease loci[J]. Arteriosclerosis,Thrombosis,and Vascular Biology,36(5):928-941.
(責任編輯 蘭宗寶)

