克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽crustin5基因克隆及其表達(dá)分析
李博 王凱 于曉東 劉睿哲 藺思函 商靜 沈秀麗 杜志強(qiáng)

摘要:【目的】深入了解克氏原螯蝦先天免疫過(guò)程中抗菌肽的作用與功能,豐富先天免疫中抗菌肽的理論知識(shí),為克氏原螯蝦的病害機(jī)理研究及防控措施制定提供參考依據(jù)。【方法】從克氏原螯蝦肝胰腺組織提取總RNA,利用PCR擴(kuò)增crustin5基因全長(zhǎng)cDNA序列,運(yùn)用DNAMAN 6.0、ProtParam、ProtScale、SOPMA和SWISS-MODEL等在線軟件對(duì)其進(jìn)行生物信息學(xué)分析,并以實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR檢測(cè)crustin5基因在克氏原螯蝦各組織中的表達(dá)情況。【結(jié)果】克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因cDNA序列全長(zhǎng)954 bp,開(kāi)放閱讀框(ORF)為429 bp,共編碼167個(gè)氨基酸殘基,其編碼蛋白相對(duì)分子量為16485.42 Da,理論等電點(diǎn)為8.58,為不穩(wěn)定的疏水性蛋白。克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征,包括N端的信號(hào)肽,C端的WAP結(jié)構(gòu)域,以及二者間的半胱氨酸富集區(qū);其二級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)中α-螺旋、β-轉(zhuǎn)角、無(wú)規(guī)則卷曲和延伸鏈分別占20.36%、7.78%、58.08%和13.77%。crustin5基因在克氏原螯蝦血細(xì)胞、肝胰腺、鰓、腸道、肌肉和淋巴器官等6種組織中均有不同程度的表達(dá),以在血細(xì)胞中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量最高,淋巴器官次之,在肌肉組織中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量最少。【結(jié)論】克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽crustin5具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征,且主要分布在血細(xì)胞和淋巴器官中,說(shuō)明crustin5是在克氏原螯蝦的血淋巴中參與先天免疫并發(fā)揮抗菌作用。
關(guān)鍵詞: 克氏原螯蝦;抗菌肽;crustin5基因;先天免疫;表達(dá)差異
Abstract:【Objective】To understand the role and function of antimicrobial peptides in the innate immunity of Procambarus clarkii, and enrich the theoretical knowledge of antimicrobial peptides in innate immunity. It provided reference for the study on the mechanism of P. clarkii diseases and the formulation of prevention measures. 【Method】Total RNA was extracted from the liver and pancreas of P. clarkii , and crustin5 gene cDNA full-length sequence was amplified by PCR technology. And bioinformatics analysis was carried out on it by online softwares including DNAMAN 6.0, ProtParam, ProtScale, SOPMA and SWISS-MODEL. crustin5 gene expression in tissues of P. clarkiiwas detected by qRT- PCR. 【Result】 The study found that the crustin5 gene had a full-length cDNA of 954 bp, an open reading frame(ORF) of 429 bp, and encoded 167 amino acid residues. The predicted molecular weight of the protein was 16485.42 Da, and the theoretical isoelectric point was 8.58. The crustin5 protein was unstable hydrophobic protein. It had the characteristic structure of the crustins family, including the N-terminal signal peptide, the C-terminal WAP domain, and rich in hemicarboxy-lamine between them. The secondary structure of protein, alpha-helix, beta-corner, random curl and extension chain accounted for 20.36%, 7.78%, 58.08% and 13.77% respectively. The crustin 5 gene was expressed to different degrees in six tissues(hemocytes, hepatopancreas, gill, intestinal tract, muscle andlymphoid organs). The highest expression was in hemocytes, followed by lymphoid organs, andthe lowest in muscle. 【Conclusion】The crustin5 of P. clarkii antimicrobial peptide has the characteristic structure of crustins family, is mainly distributed in hemocytes and lymphatic organs. It suggests that crustin5 plays an antibacterial role in hemolymph and participate in the innate immunity of P. clarkii.
0 引言
【研究意義】近年來(lái),淡水養(yǎng)殖業(yè)發(fā)展勢(shì)頭迅猛,尤其是蝦類養(yǎng)殖,但同時(shí)遭受細(xì)菌和病毒等病原體的嚴(yán)重侵害。克氏原螯蝦(Procambarus clarkii)又稱淡水小龍蝦,其在感染細(xì)菌和病毒時(shí)主要依靠先天免疫進(jìn)行抵抗(韓珂珂,2019)。在先天免疫過(guò)程中,克氏原螯蝦會(huì)產(chǎn)生一種重要的免疫效應(yīng)因子,即抗菌肽(Crustin),其對(duì)細(xì)菌、真菌及病毒等病原體具有廣譜的抑制效果。抗菌肽對(duì)不同細(xì)菌均具有抑菌活性,尤其對(duì)革蘭氏細(xì)菌具有很強(qiáng)的殺傷作用(郭慧等,2013;馬春霞等,2017),同時(shí)兼具抗病毒作用、免疫調(diào)節(jié)作用(吳希,2006)及對(duì)真菌的殺傷作用(王顯偉,2012)。因此,加強(qiáng)克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽研究,豐富有關(guān)先天免疫中抗菌肽的理論知識(shí),對(duì)確保克氏原螯蝦養(yǎng)殖業(yè)持續(xù)健康發(fā)展具有重要意義。【前人研究進(jìn)展】抗菌肽是由DNA編碼合成于核糖體的多肽,不同類型的抗菌肽存在許多相似之處,一般為短肽(30~60個(gè)氨基酸),具有強(qiáng)陽(yáng)離子性[等電點(diǎn)(pI)8.9~10.7]等特點(diǎn)(Ferrer et al.,1996;Boulanger et al.,2006)。第一個(gè)抗菌肽是由瑞典科學(xué)家Boman等于1980年從蠟樣芽抱桿菌誘導(dǎo)的惜古比天蠶(Hyalophora cecropia)蛹淋巴液中分離獲得(Boman and Steiner,1981),即天蠶素(Cecropins)。此后,諸多學(xué)者開(kāi)始對(duì)抗菌肽研究產(chǎn)生興趣濃厚,并在海洋動(dòng)物中發(fā)現(xiàn)了多種新型的抗菌肽(王曉飛等,2019)。Acosta等(2014)在從羅非魚(yú)鰓組織分離出的魚(yú)素中鑒定獲得3種新的抗菌肽,分別是Orech-1、Orech-2和Orech-3;Doiron等(2018)在雪蟹(Chionoecetes opilio)水解產(chǎn)物中發(fā)現(xiàn)5種新的抗菌肽,分別是Arthrodial cuticle protein AMP6.0、I-connectin、Hyastatin、Vitellogenin和Slow-tonic S2 myosin heavy chain。隨著抗菌肽鑒定種類的增加,為抗菌肽家族的研究與發(fā)展奠定了基礎(chǔ)。此外,各種抗菌肽間具有相似的結(jié)構(gòu)和特點(diǎn)。Liao等(2013)、Zhong等(2013)分別在夏魯貽貝(Mytilus coruscus)和巴西蝸牛(Achatina fulica)黏液中發(fā)現(xiàn)新的抗菌肽,其共同特點(diǎn)是半胱氨酸含量較高;Qu等(2013)在石斑魚(yú)(Epinephiu scoioides)中發(fā)現(xiàn)一種抗菌肽亞型,也具有半胱氨酸含量較高的特點(diǎn);Park等(2018)發(fā)現(xiàn)的Rip-thanatin與Shenkarev等(2012)發(fā)現(xiàn)的Aurelin及Zhang等(2015)報(bào)道的蛤蜊抗菌肽具有相似結(jié)構(gòu),均包含2個(gè)α-螺旋區(qū)和3個(gè)二硫鍵交聯(lián)。最主要的共同特點(diǎn)是抗菌肽均具有較強(qiáng)抗菌活性,Wei等(2015)從海蛇中提取獲得的抗菌肽、Salger等(2016)在白鱸魚(yú)中發(fā)現(xiàn)的抗菌肽及Zhuang等(2017)從石斑魚(yú)中鑒定出的抗菌肽,均具有強(qiáng)大的廣譜抗菌活性:I類抗菌肽對(duì)細(xì)菌和纖毛原生動(dòng)物表現(xiàn)出廣譜抗菌活性,III類抗菌肽主要表現(xiàn)出抗原生動(dòng)物活性,II類抗菌肽的抗細(xì)菌和原生動(dòng)物活性則處于I類抗菌肽與III類抗菌肽之間。【本研究切入點(diǎn)】先天免疫是生物體在進(jìn)化過(guò)程中形成的一種天然防御機(jī)制,是生物體開(kāi)啟免疫應(yīng)答的基礎(chǔ)(高潔等,2016),對(duì)進(jìn)入生物體內(nèi)的抗原性物質(zhì)有無(wú)選擇性排斥和清除功能(杜欣軍,2007)。無(wú)脊椎動(dòng)物僅依靠先天免疫就能有效抵抗和防御復(fù)雜環(huán)境中的病原體侵染(孫晨,2011;徐鑫和劉忠淵,2014),抗菌肽是體液免疫中的重要效應(yīng)分子,但至今有關(guān)抗菌肽在克氏原螯蝦先天免疫過(guò)程中的作用機(jī)理鮮見(jiàn)報(bào)道。【擬解決的關(guān)鍵問(wèn)題】克隆克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽crustin5基因并進(jìn)行組織表達(dá)特性分析,旨在深入了解克氏原螯蝦先天免疫過(guò)程中抗菌肽的作用與功能,豐富先天免疫中抗菌肽的理論知識(shí),為克氏原螯蝦的病害機(jī)理研究及防控措施制定提供參考依據(jù)。
1 材料與方法
1. 1 試驗(yàn)材料
健康克氏原螯蝦購(gòu)自內(nèi)蒙古包頭市友誼水產(chǎn)市場(chǎng),在實(shí)驗(yàn)室無(wú)菌條件下采集其肝胰腺組織,快速置于液氮中保存,用于總RNA提取。總RNA提取試劑盒(TRIzol Total RNA Reagent)、cDNA第一鏈合成試劑盒(Thermo Scientific RevertAid First Stand cDNA Synthesis Kit)、PCR反應(yīng)套裝試劑盒、DNA純化回收試劑盒、質(zhì)粒DNA小量提取試劑盒及SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM II均購(gòu)自寶生物工程(大連)有限公司;DL2000 DNA Marker、DNA Ladder 1kb Marker和實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR引物購(gòu)自生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司。主要儀器設(shè)備:高速冷凍離心機(jī)(鹽城凱特實(shí)驗(yàn)儀器有限公司),PCR儀(北京線上生物科技有限公司),電泳儀(北京生東科技有限公司),ABI 7500實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR儀[英濰捷基(上海)貿(mào)易有限公司]。
1. 2 總RNA提取
將液氮中的克氏原螯蝦肝胰腺組織取出,利用TRIzol Total RNA Reagent提取總RNA,以1.5%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測(cè)其完整性,用滅菌DEPC雙蒸水稀釋后置于-80 ℃冰箱保存?zhèn)溆谩?/p>
1. 3 cDNA合成
根據(jù)Thermo Scientific RevertAid First Stand cDNA Synthesis Kit說(shuō)明,以O(shè)ligo(dT)18為引物,將提取獲得的總RNA反轉(zhuǎn)錄合成cDNA,-80 ℃冰箱保存?zhèn)溆谩?/p>
1. 4 目的基因PCR擴(kuò)增
依據(jù)本課題組前期的克氏原螯蝦轉(zhuǎn)錄組測(cè)序結(jié)果,并參照NCBI已公布的各物種抗菌肽基因序列,設(shè)計(jì)特異性引物(F:5'-CAGCAGGACGCTGAC GGC-3',R:5'-TTACCCTGAACAGGGCTG-3'),以cDNA為模板擴(kuò)增目的基因。PCR擴(kuò)增程序:94 ℃預(yù)變性5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,55 ℃ 45 s,72 ℃ 40 s,進(jìn)行35個(gè)循環(huán);72 ℃延伸10 min,4 ℃結(jié)束反應(yīng)。取3.0 ?L PCR擴(kuò)增產(chǎn)物進(jìn)行1.0%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測(cè)。
1. 5 重組載體構(gòu)建及序列測(cè)定
PCR擴(kuò)增產(chǎn)物經(jīng)1.0%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳驗(yàn)證后,利用DNA純化回收試劑盒進(jìn)行目的基因回收;用DNA小量提取試劑盒提取大腸桿菌pET-28a質(zhì)粒載體,以EcoRⅠ和XhoⅠ限制性內(nèi)切酶對(duì)目的基因和pET-28a質(zhì)粒載體進(jìn)行雙酶切,在T4連接酶作用下進(jìn)行酶聯(lián)反應(yīng),獲得的重組質(zhì)粒pET-28a-crustin5轉(zhuǎn)化大腸桿菌DH5α感受態(tài)細(xì)胞;同時(shí)提取重組質(zhì)粒pET-28a-crustin5,繼續(xù)轉(zhuǎn)化BL21(DE3)感受態(tài)細(xì)胞,篩選陽(yáng)性克隆送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司進(jìn)行測(cè)序。
1. 6 生物信息學(xué)分析
1. 6. 1 目的基因序列分析 使用BLAST對(duì)目的基因cDNA全長(zhǎng)序列進(jìn)行分析,并通過(guò)ExPASy將其翻譯成氨基酸序列。
1. 6. 2 氨基酸序列比對(duì)與系統(tǒng)進(jìn)化樹(shù)繪制 使用NCBI中的BLAST對(duì)目的基因序列和已知基因序列進(jìn)行對(duì)比,利用DNAMAN 6.0對(duì)克氏原螯蝦crus-tin5氨基酸序列與已知的crustin氨基酸序列進(jìn)行多序列對(duì)比分析,并以MEGA 6.0繪制系統(tǒng)發(fā)育進(jìn)化樹(shù),分析其進(jìn)化關(guān)系。
1. 6. 3 目的蛋白理化性質(zhì)分析 采用ProtParam(https://web.expasy.org/protparam/)對(duì)crustin5蛋白進(jìn)行理化性質(zhì)預(yù)測(cè)分析,包括相對(duì)分子量、理論等電點(diǎn)、氨基酸組成、蛋白不穩(wěn)定指數(shù)、脂肪系數(shù)及親水性平均系數(shù)等,并使用ExPASy中的ProtScale(https://web.expasy.org/protscale/)對(duì)crustin5蛋白進(jìn)行親/疏水性分析。
1. 6. 4 crustin 5蛋白二、三級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)預(yù)測(cè) 利用SOPMA(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html)和SWISS-MODEL(http://swissmodel.expasy.org/)分別預(yù)測(cè)crustin5蛋白二、三級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)。
1. 7 組織差異表達(dá)分析
隨機(jī)挑取暫養(yǎng)1周的健康克氏原螯蝦(3尾以上),解剖采集其血細(xì)胞、肝胰腺、鰓、腸道、肌肉和淋巴器官等6種組織。提取總RNA后反轉(zhuǎn)錄合成cDNA,使用SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM II在ABI 7500實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR儀進(jìn)行crustin5基因表達(dá)定量分析,以18S rRNA為內(nèi)參基因。實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR擴(kuò)增引物如表1所示,擴(kuò)增程序:95 ℃預(yù)變性30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 34 s,進(jìn)行40個(gè)循環(huán)。利用2-??Ct法換算crustin5基因在克氏原螯蝦各組織中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量。
2 結(jié)果與分析
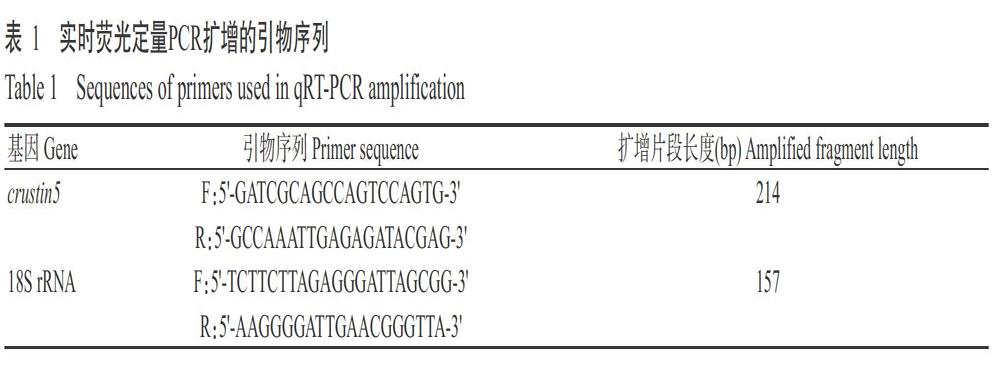
2. 1 克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因的PCR擴(kuò)增結(jié)果
PCR擴(kuò)增產(chǎn)物經(jīng)1.0%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測(cè),結(jié)果(圖1)顯示,在500 bp附近有一條單一、清晰的目的條帶,與預(yù)期結(jié)果(429 bp)相符,表明已成功擴(kuò)增獲得克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因。
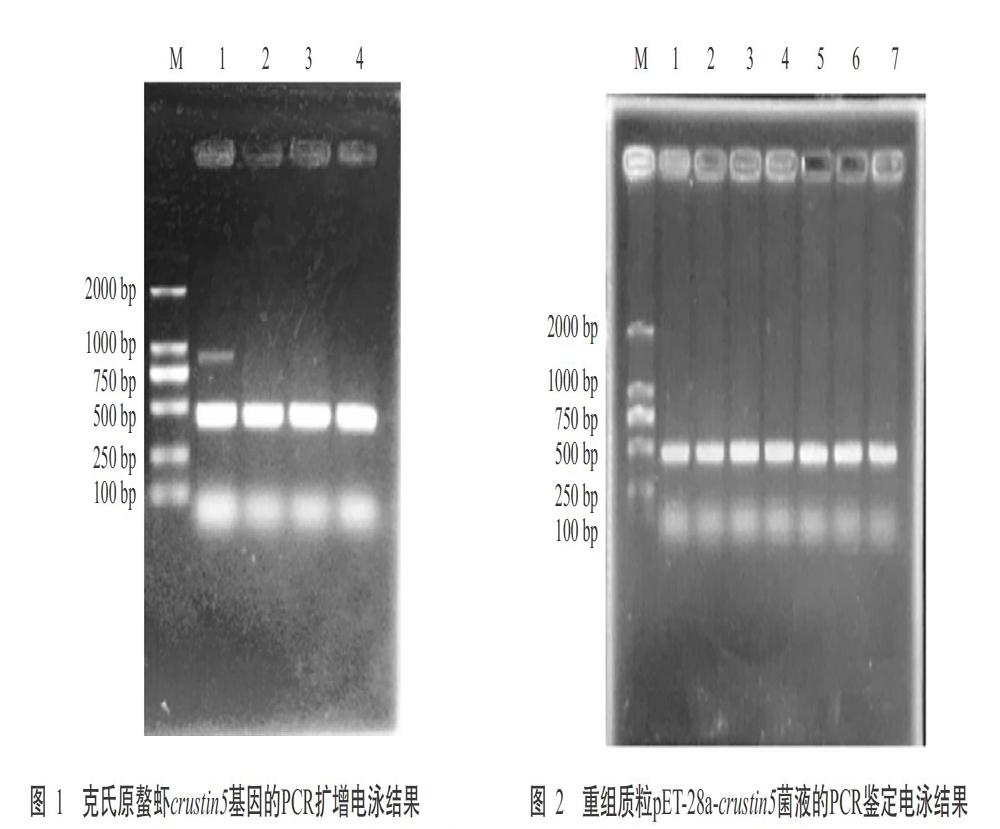
2. 2 重組質(zhì)粒菌液PCR鑒定結(jié)果
以重組質(zhì)粒pET-28a-crustin5轉(zhuǎn)化DH5α感受態(tài)細(xì)胞,經(jīng)擴(kuò)大培養(yǎng)后挑取陽(yáng)性菌落進(jìn)行PCR鑒定,采用1.0%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證,發(fā)現(xiàn)在500 bp附近出現(xiàn)一條清晰的目的條帶(圖2),與預(yù)期結(jié)果(429 bp)相符。提取重組質(zhì)粒pET-28a-crustin5后將其轉(zhuǎn)化BL21(DE3)感受態(tài)細(xì)胞,經(jīng)菌液PCR鑒定及1.0%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳檢測(cè),也獲得一條與預(yù)期結(jié)果相符的明亮條帶。
2. 3 克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因測(cè)序分析結(jié)果
重組質(zhì)粒pET-28a-crustin5轉(zhuǎn)化BL21(DE3)感受態(tài)細(xì)胞后,篩選出陽(yáng)性克隆送至生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司進(jìn)行測(cè)序,結(jié)果表明,克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因cDNA序列全長(zhǎng)954 bp,開(kāi)放閱讀框(ORF)為429 bp,共編碼167個(gè)氨基酸殘基(圖3)。crustin5蛋白具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征,包括N端的信號(hào)肽(圖中紅色字體部分),C端的WAP結(jié)構(gòu)域(灰色區(qū)域部分),以及二者間的半胱氨酸富集區(qū)。
2. 4 crustin5氨基酸序列同源性分析結(jié)果
根據(jù)NCBI中的BLAST對(duì)比分析結(jié)果,挑選出與克氏原螯蝦物種相近、基因序列同源性較高的crustin氨基酸序列,并利用DNAMAN 6.0進(jìn)行多序列對(duì)比分析,結(jié)果(圖4)發(fā)現(xiàn),克氏原螯蝦crustin5氨基酸序列與斑節(jié)對(duì)蝦Pm-crustin5氨基酸序列、小褐美對(duì)蝦Fs-crustin氨基酸序列、圣保羅對(duì)蝦Fp-crustin氨基酸序列、日本對(duì)蝦Pj-crustin2氨基酸序列、日本對(duì)蝦Pj-crustin4氨基酸序列和中國(guó)對(duì)蝦Fc-crustin氨基酸序列的同源性分別為28.65%、27.27%、26.86%、25.71%、23.46%和21.39%,與遠(yuǎn)海梭子蟹Pp-crustin氨基酸序列、鋸緣青蟹Ss-crustin氨基酸序列、紫螯青蟹St-crustin氨基酸序列和中華絨螯蟹Es-crustin1氨基酸序列的同源性分別為19.41%、18.24%、17.65%和17.34%。
2. 5 系統(tǒng)發(fā)育進(jìn)化樹(shù)分析結(jié)果
基于crustin氨基酸序列同源性構(gòu)建的系統(tǒng)發(fā)育進(jìn)化樹(shù)(圖5)顯示,克氏原螯蝦(crustin5)與小褐美對(duì)蝦(Fs-crustin)、圣保羅對(duì)蝦(Fp-crustin)、中華絨螯蟹(Es-crustin1)、斑節(jié)對(duì)蝦(Pm-crustin5)、遠(yuǎn)海梭子蟹(Pp-crustin)、鋸緣青蟹(Ss-crustin)、紫螯青蟹(St-crustin)、中國(guó)對(duì)蝦(Fc-crustin)、日本對(duì)蝦(Pj-crustin 2)和日本對(duì)蝦(Pj-crustin4)聚類在同一個(gè)進(jìn)化分支上,說(shuō)明其親緣關(guān)系較近,同源性較高。其中,克氏原螯蝦crustin5與中華絨螯蟹crustin1的親緣關(guān)系最近。
2. 6 克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白理化性質(zhì)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果
使用ProtParam對(duì)克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白進(jìn)行理化性質(zhì)預(yù)測(cè)分析,結(jié)果顯示,克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白分子式為C705H1089N213O222S12,相對(duì)分子量為16485.42 Da,理論等電點(diǎn)為8.58;從主要氨基酸組成及其含量可知,以甘氨酸(Gly)含量最高,占25.1%,絲氨酸(Ser)占7.2%,丙氨酸(Ala)占6.6%,半胱氨酸(Cys)、亮氨酸(Leu)、脯氨酸(Pro)和蘇氨酸(Thr)均占6.0%;克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白不穩(wěn)定指數(shù)為53.27(>40.00),屬于不穩(wěn)定蛋白;其脂肪系數(shù)為56.11。
2. 7 克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白親/疏水性預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果
利用ExPASy中的ProtScale對(duì)克氏原螯蝦crus-tin5蛋白親/疏水性進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè),其總平均親水性系數(shù)為-0.074。由圖6可看出,克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白的疏水性氨基酸多于親水性氨基酸,故屬于疏水性蛋白。
2. 8 克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白二、三級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果
利用SOPMA預(yù)測(cè)克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白二級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu),結(jié)果(圖7)顯示crustin5蛋白二級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)中的α-螺旋、β-轉(zhuǎn)角、無(wú)規(guī)則卷曲和延伸鏈分別占20.36%、7.78%、58.08%和13.77%。同時(shí)以SWISS-MODEL的自動(dòng)建模功能對(duì)克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白三級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行預(yù)測(cè),發(fā)現(xiàn)crustin5蛋白可能存在的三級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)如圖8所示,與其二級(jí)結(jié)構(gòu)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果一致。
2. 9 crustin5基因在克氏原螯蝦各組織中的分布情況
以18S rRNA為內(nèi)參基因,采用實(shí)時(shí)熒光定量PCR檢測(cè)crustin5基因在克氏原螯蝦血細(xì)胞、肝胰腺、鰓、腸道、肌肉和淋巴器官等6種組織中的表達(dá)分布情況,結(jié)果(圖9)顯示克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因在6種組織中均有不同程度的表達(dá),以在血細(xì)胞中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量最高,淋巴器官次之,在肌肉組織中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量最少。
3 討論
I型甲殼肽是信號(hào)肽序列與WAP結(jié)構(gòu)域間含一個(gè)半胱氨酸富含區(qū)的抗菌肽。于愛(ài)清(2014)從紅螯光殼螯蝦(Cherax quadricarinatus)血細(xì)胞中成功克隆獲得一個(gè)重要的抗菌肽,簡(jiǎn)稱為Cq-crustin,其氨基酸序列具有I型抗菌肽結(jié)構(gòu)。劉燕等(2018)從墨吉明對(duì)蝦(Fenneropenaeus merguiensis)中克隆獲得crustinⅡ基因,并證實(shí)其具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征。王月(2018)對(duì)從擬穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)鑒定獲得的2種抗菌肽(Sp-crus3和Sp-crus4)進(jìn)行比對(duì)分析,發(fā)現(xiàn)二者均屬于I型甲殼肽。此外,宋呈文(2013)在三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)中發(fā)現(xiàn)Pt-crustin2和Pt-crustin3氨基酸序列的N端均存在一段信號(hào)肽序列,C端則存在一個(gè)WAP結(jié)構(gòu)域,且二者間存在一個(gè)半胱氨酸富集區(qū)。本研究從克氏原螯蝦中成功克隆獲得一條新的crustin編碼基因序列,命名為crustin5。克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因cDNA序列全長(zhǎng)954 bp,共編碼167個(gè)氨基酸殘基,其編碼蛋白相對(duì)分子量為16485.42 Da,理論等電點(diǎn)為8.58。克氏原螯蝦crustin5蛋白結(jié)構(gòu)預(yù)測(cè)結(jié)果顯示,crustin5蛋白具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征,包括N端的信號(hào)肽,C端的WAP結(jié)構(gòu)域,以及二者間的半胱氨酸富集區(qū)。可見(jiàn),克氏原螯蝦crustin5與上述抗菌肽具有相似的結(jié)構(gòu)。
大多數(shù)抗菌肽蛋白都能在血淋巴細(xì)胞中高表達(dá)。柳峰松(2005)研究發(fā)現(xiàn),crustin基因在中國(guó)明對(duì)蝦(F. chinensis)的血細(xì)胞、鰓和腸道組織中均有表達(dá)。劉燕等(2018)采用熒光定量PCR檢測(cè)crustinⅡ基因在墨吉明對(duì)蝦體內(nèi)的表達(dá)分布情況,發(fā)現(xiàn)crustinⅡ基因在血細(xì)胞中高表達(dá),而在腸道、鰓、肝胰腺、尾部肌肉、胃、眼柄和心臟組織中的表達(dá)量非常低,且存在顯著差異。本研究結(jié)果表明,克氏原螯蝦crustin5基因在其血細(xì)胞和淋巴器官中的相對(duì)表達(dá)量也較高,故推測(cè)克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽crustin5是一種具有良好抗菌活性的抗菌肽分子,在先天免疫系統(tǒng)中發(fā)揮重要的抗菌作用。
4 結(jié)論
克氏原螯蝦抗菌肽crustin5具有典型的crustins家族結(jié)構(gòu)特征,且主要分布在血細(xì)胞和淋巴器官中,說(shuō)明crustin5是在克氏原螯蝦的血淋巴中參與先天免疫并發(fā)揮抗菌作用。
參考文獻(xiàn):
杜欣軍. 2007. 中國(guó)明對(duì)蝦先天免疫的模式識(shí)別與效應(yīng)分子[D]. 濟(jì)南:山東大學(xué). [Du X J. 2007. Pattern recognition and effector of innate immunity in Chinese shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis)[D]. Jinan:Shandong University.]
高潔,顧剛,陸林,王曉群. 2016. C1q腫瘤壞死因子相關(guān)蛋白4研究進(jìn)展[J]. 國(guó)際心血管病雜志,43(2):99-101. [Gao J,Gu G,Lu L,Wang X Q. 2016. Research progress of C1q tumor necrosis factor-associated protein 4[J]. International Journal of Cardiovascular Disease,43(2):99-101.]
郭慧,冼健安,畢建柱,葉超霞,王安利. 2013. 蝦類免疫因子的研究進(jìn)展[J]. 飼料工業(yè),34(22):42-46. [Guo H,Xian J A,Bi J Z,Ye C X,Wang A L. 2013. Research progress in immune factors of shrimp[J]. Feed Industry,34(22):42-46.]
韓珂珂. 2019. 克氏原螯蝦三個(gè)免疫相關(guān)基因Caspase-3C、Lectin和LGBP的功能研究[D]. 南京:南京師范大學(xué). [Han K K. 2019. Functional study of three immune-rela-ted genes,Caspase-3C,Lectin and LGBP in Procambarus clarkii[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Normal University.]
劉燕,張展雄,李曉筠,梁華芳,陳兆明. 2018. 墨吉明對(duì)蝦(Fenneropenaeus merguiensis)Crustin II型基因的克隆與原核重組表達(dá)[J]. 基因組學(xué)與應(yīng)用生物學(xué),37(1):229-237. [Liu Y,Zhang Z X,Li X Y,Liang H F,Chen Z M. 2018. Cloning and prokaryotic recombinant expression of Crustin II type gene in Fenneropenaeus merguiensis[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,37(1):229-237.]
柳峰松. 2005. 中國(guó)明對(duì)蝦(Fenneropenaeus chinensis)抗菌因子及模式識(shí)別蛋白的研究[D]. 北京:中國(guó)科學(xué)院. [Liu F S. 2005. Study on antimicrobial factor and pa-ttern recognition protein of Chinese shrimp,F(xiàn)ennerope-naeus chinensis[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Scien-ces.]
馬春霞,彭金霞,何蘋萍,雷愛(ài)瑩,馬寧,王瑞,黎銘. 2017. 凡納濱對(duì)蝦抗菌肽crunstinA在畢赤酵母菌中的表達(dá)[J]. 南方農(nóng)業(yè)學(xué)報(bào),48(7):1310-1316. [Ma C X,Peng J X,He P P,Lei A Y,Ma N,Wang R,Li M. 2017. Expression of Litopenaeus vannamei antimicrobial peptide crunstinA in Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,48(7):1310-1316.]
宋呈文. 2013. 三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)抗菌肽crustin的基因克隆和表達(dá)分析[D]. 北京:中國(guó)科學(xué)院大學(xué). [Song C W. 2013. Cloning and expression analysis of antimicrobial peptide crustin of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus[D]. Beijing:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.]
孫晨. 2011. 甲殼動(dòng)物抗菌肽及信號(hào)轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo)和轉(zhuǎn)錄激活因子(STAT)的基因克隆與功能分析[D]. 濟(jì)南:山東大學(xué). [Sun C. 2011. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of crustacean antimicrobial peptides and STAT(signal transducer and activator transcription)[D]. Jinan:Shandong University.]
王顯偉. 2012. 十足目甲殼動(dòng)物C型凝集素功能研究[D]. 濟(jì)南:山東大學(xué). [Wang X W. 2012. Functional study of C-type lectins from decapod crustaceans[D]. Jinan:Shandong University.]
王曉飛,彭會(huì),陳芳奕,張財(cái)亮,黃文樹(shù). 2019. 擬穴青蟹抗菌肽Crustin新變體的表達(dá)特性與抗菌功能[J]. 廈門大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào)(自然科學(xué)版),58(3):358-365. [Wang X F,Peng H,Chen F Y,Zhang C L,Huang W S. 2019. Characterization of expression and antimicrobial activity of a novel crustin isoform from Scylla paramamosain[J]. Journal of Xiamen University(Natural Science),58(3):358-365.]
王月. 2018. 擬穴青蟹甲殼肽(Crustin)的免疫功能研究[D]. 新鄉(xiāng):河南師范大學(xué). [Wang Y. 2018. Functional analyses of crustins in the innate immune system of Mud Crab,Scylla paramamosain[D]. Xinxiang:Henan Normal University.]
吳希. 2006. 重組家蠶抗菌肽CM4抗真菌作用機(jī)理的研究[D]. 南京:南京師范大學(xué). [Wu X. 2006. Antifungal mechanism of recombinant Bombyx mori antimicrobial peptide CM4[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Normal University.]
徐鑫,劉忠淵. 2014. 先天免疫系統(tǒng)中肽聚糖蛋白識(shí)別研究進(jìn)展[J]. 動(dòng)物醫(yī)學(xué)進(jìn)展,35(10):94-98. [Xu X, Liu Z Y. 2014. Progress on peptidoglycan recognition protein in innate immune system[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine,35(10):94-98.]
于愛(ài)清. 2014. 蝦蟹類免疫相關(guān)基因的研究[D]. 上海:華東師范大學(xué). [Yu A Q. 2014. Studies on immune-related genes of shrimp and crabs[D]. Shanghai:East China Normal University.]
Acosta J,Carpio Y,Valdés I,Velázquez J,Zamora Y,Morales R,Morales A,Rodríguez E,Estrada M P. 2014. Co-administration of tilapia alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides with subunit antigens boost immunogenicity in mice and tilapia(Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Vaccine,32(2):223-229.
Boman H G,Steiner H. 1981. Humoral immunity in Cecropia pupae[J]. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immuno-logy,95(4):75-91.
Boulanger N,Bulet P,Lowenberger C. 2006. Antimicrobial peptides in the interactions between insects and flagellate parasites[J]. Trends in Parasitology,22(6):262-268.
Doiron K,Beaulieu L,St-Louis R,Lemarchand K. 2018. Reduction of bacterial biofilm formation using marine natural antimicrobial peptides[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B:Biointerfaces,167:524-530.
Ferrer M,kapoor T M,Strassmaier T,Weissenhom W,Skehel J J,Oprian D,Schreiber S L,Wiley D C,Harrison S C.1996. Selection of gp41-mediated HIV-1 cell entry inhibitors from biased combinatorial libraries of non-natural binding elements[J]. Nature Structural Biology,6(10):953-960.
Liao Z,Wang X C,Liu H H,F(xiàn)an M H,Sun J J,Shen W. 2013. Molecular characterization of a novel antimicrobial peptide from Mytilus coruscus[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immu-nology,34(2):610-616.
Park K E,Jang S H,Lee J,Lee S A,Kikuchi Y,Seo Y S,Lee B L. 2018. The roles of antimicrobial peptide,rip-thanatin,in the midgut of Riptortus pedestris[J]. Developmental & Comparative Immunology,78:83-90.
Qu H,Chen B,Peng H,Wang K J. 2013. Molecular cloning,recombinant expression,and antimicrobial activity of EC-hepcidin3,a new four-cysteine hepcidin isoform from Epinephelus coioides[J]. Bioscience,Biotechnology,and Biochemistry,77(1):103-110.
Salger S A,Cassady K R,Reading B J,Noga E J. 2016. A diverse family of host-defense peptides(piscidins) exhibit specialized anti-bacterial and anti-protozoal activities in fishes[J]. PLoS One,11(8):e0159423.
Shenkarev Z O,Panteleev P V,Balandin S V,Gizatullina A K,Altukhov D A,F(xiàn)inkina E I,Kokryakov V N,Arseniev A S,Ovchinnikova T V. 2012. Recombinant expression and solution structure of antimicrobial peptide aurelin from jellyfish Aurelia aurita[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,429(1-2):63-69.
Wei L,Gao J,Zhang S,Wu S,Xie Z,Ling G,Kuang Y Q,Yang Y,Yu H,Wang Y. 2015. Identification and characterization of the first Cathelicidin from sea snakes with potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity and special mechanism[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,290(27):16633-16652.
Zhang L,Yang D,Wang Q,Yuan Z,Wu H,Pei D,Cong M,Li F,Ji C,Zhao J. 2015. A defensin from clam Venerupis philippinarum:Molecular characterization,localization,antibacterial activity,and mechanism of action[J]. Develop-mental & Comparative Immunology,51(1):29-38.
Zhong J,Wang W,Yang X,Yan X,Liu R. 2013. A novel cysteine-rich antimicrobial peptide from the mucus of the snail of Achatina fulica[J]. Peptides,39:1-5.
Zhuang Z R,Yang X D,Huang X Z,Gu H X,Wei H Y,He Y J,Deng L. 2017. Three new piscidins from orange-spotted grouper(Epinephelus coioides):Phylogeny,expression and functional characterization[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology,66:240-253.
(責(zé)任編輯 蘭宗寶)
 南方農(nóng)業(yè)學(xué)報(bào)2020年4期
南方農(nóng)業(yè)學(xué)報(bào)2020年4期
- 南方農(nóng)業(yè)學(xué)報(bào)的其它文章
- 海南地區(qū)油茶未成熟胚分生結(jié)節(jié)的植株再生
- 河南省小農(nóng)戶農(nóng)地經(jīng)營(yíng)權(quán)轉(zhuǎn)出影響因素實(shí)證分析
- 我國(guó)與東盟國(guó)家農(nóng)產(chǎn)品貿(mào)易影響因素及潛力分析
- 不同規(guī)格香港牡蠣殼形態(tài)性狀對(duì)重量性狀的影響
- 全雌吉富羅非魚(yú)家系選育及其生長(zhǎng)性能分析
- 鴨ChREBP基因表達(dá)載體構(gòu)建及其對(duì)原代肝細(xì)胞和PC3細(xì)胞脂質(zhì)性狀的影響
