顱內靜脈竇血栓形成的臨床特點分析
郭傳佳 吳幼鑾 郭傳良
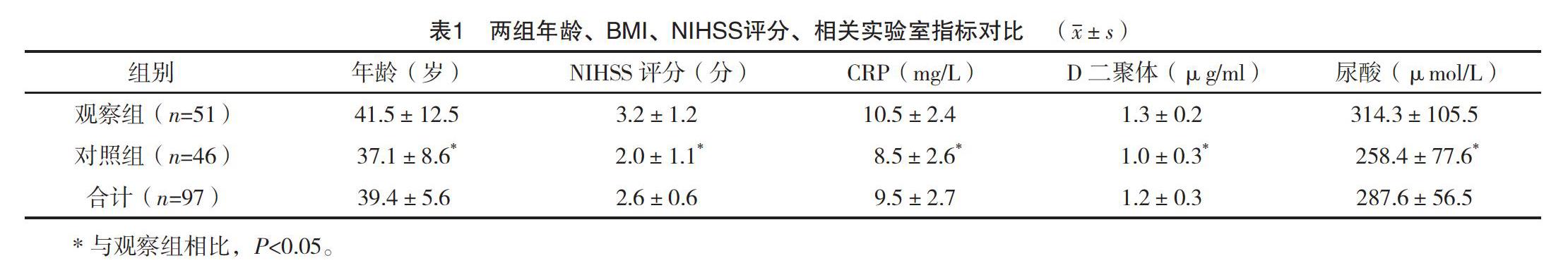
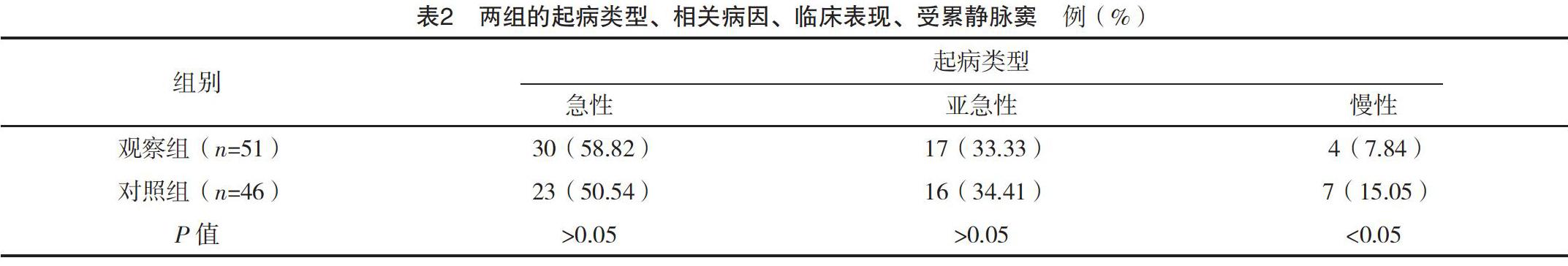
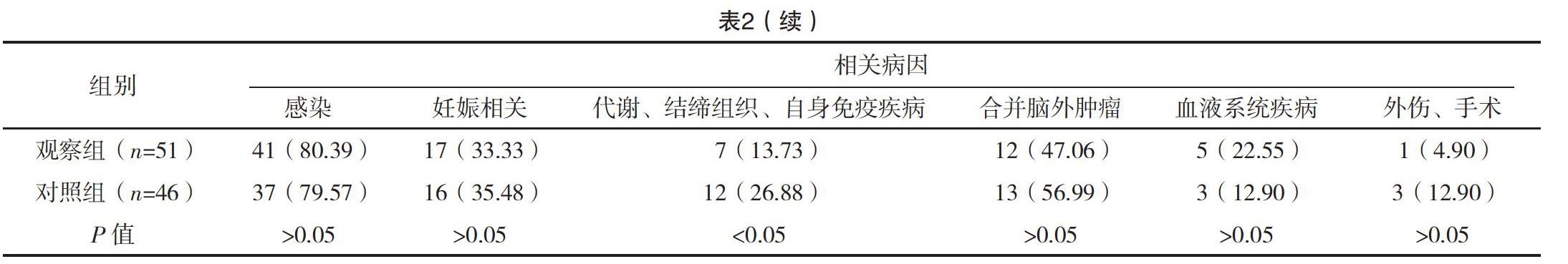
【摘要】 目的:分析顱內靜脈竇血栓形成的臨床特點,總結診治經驗。方法:納入顱內靜脈竇血栓形成97例,收集患者的臨床資料,并將首次CT/MR檢查為存在腦實質損傷的對象51例納入觀察組,其余對象46例納入對照組,進行對比分析。結果:觀察組年齡、NIHSS、CRP、D-二聚體、尿酸水平高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。觀察組患者起病類型為慢性者比例低于對照組,相關病因中代謝、結締組織、自身免疫疾病比例,臨床表現中其他神經功能缺損者及心肌梗死者低于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);兩組患者受累靜脈竇比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。觀察組進展性卒中發生率、癲癇發生率、復發率高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:顱內靜脈竇血栓形成表現比較復雜,其中影像學存在腦實質損傷的患者年齡、NIHSS等指標高于影像學陰性患者,更多出現顱內壓升高、意識障礙、語言障礙等神經功能缺損,血栓部位多為上矢狀竇或多發血栓形成,且進展性卒中發生率、癲癇發生率、復發率較高;而影像學陰性患者多為慢性起病,多合并代謝、結締組織、自身免疫疾病。
【關鍵詞】 顱內靜脈竇血栓形成 腦梗死 臨床分析
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.12.056 文獻標識碼 B 文章編號 1674-6805(2020)12-0-03
Clinical Characteristics of Intracranial Venous Sinus Thrombosis/GUO Chuanjia, WU Youluan, GUO Chuanliang. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(12): -135
[Abstract] Objective: To analyze the clinical features of intracranial venous thrombosis and to summarize the experience of diagnosis and treatment. Method: A total of 97 cases of intracranial venous thrombosis were included, the clinical data of the patients were collected, and the first CT/MR examination was performed in 51 subjects with brain parenchyma injury as observation group, and 46 of the other subjects were included in the control group for comparative analysis. Result: The age, NIHSS, CRP, D-dimer and uric acid level of the patient were higher than those of the control group (P<0.05). The proportion of patients with chronic disease was lower than that of control group, the proportion of metabolism, connective tissue, autoimmune disease, other neurological deficit in clinical manifestation and myocardial infarction were lower than those of control group (P<0.05). There was no difference between the two groups in affected venous sinus (P>0.05). The incidence of progressive stroke, the incidence of seizures and the recurrence rate in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion: The manifestation of intracranial venous sinus thrombosis is more complex, in which the age, NIHSS and other indexes of patients with cerebral parenchyma injury are higher than those of patients with negative imaging, more neurological deficit such as intracranial pressure elevation, disturbance of consciousness, language disorder, thrombus site is superior sagittal sinus or multiple thrombosis, and the incidence of progressive stroke, the incidence of epilepsy and recurrence rate are higher in patients with imaging negative than those with negative imaging. Chronic onset, multiple combined metabolism, connective tissue, autoimmune disease.
[Key words] Intracranial venous sinus thrombosis Cerebral infarction Clinical analysis
First-authors address: Datian County Hospital, Datian 366100, China
顱內靜脈竇血栓形成是一種腦卒中類型,占腦卒中的0.5%~1.0%,發生率約為5/100萬,發生率較低,極易被誤漏診,有報道顯示其早期誤漏診率高達50%[1-2]。深入分析顱內靜脈竇血栓形成的臨床特點,總結疾病診治經驗,有助于降低誤漏診風險。2010年1月-2018年1月,醫院共收治了顱內靜脈竇血栓形成97例,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
2010年1月-2018年1月,醫院共診治顱內靜脈竇血栓形成97例。納入標準:(1)臨床資料完整;(2)年齡≥15歲;(3)初次診斷。排除標準:(1)腦卒中病史;(2)既往或同時合并原發顱內其他病變,如顱內腫瘤。其中男55例,女42例,平均年齡(39.4±9.5)歲。
1.2 影像學方法
采用CT、MRI作為診斷技術,所有對象都采用CT檢查,82例聯合MRI檢查。MRI檢查采用1.5TMRI機,入院后2周內進行檢查,包括T1、T2加權、FLAIR序列、DWI序列掃描。T1加權包括TI Weighted Image,TR 1 750 ms,TE 24 ms。液體衰減反轉恢復脈沖序列參數,TR 7 800 ms,TE 140 ms。視野24 mm×24 mm,層厚5 mm,間隔5 mm,矩陣288×192。CT檢查采用64排多層螺旋CT機,電壓120 kV,電流280 mA。聯合會診進行診斷,一時無法明確診斷的對象,需要隨訪復查評估診斷[3-4]。……

