杏褪綠卷葉植原體新疆分離物16SrDNA基因克隆與序列分析
艾克熱木·買買提 韓劍 羅明
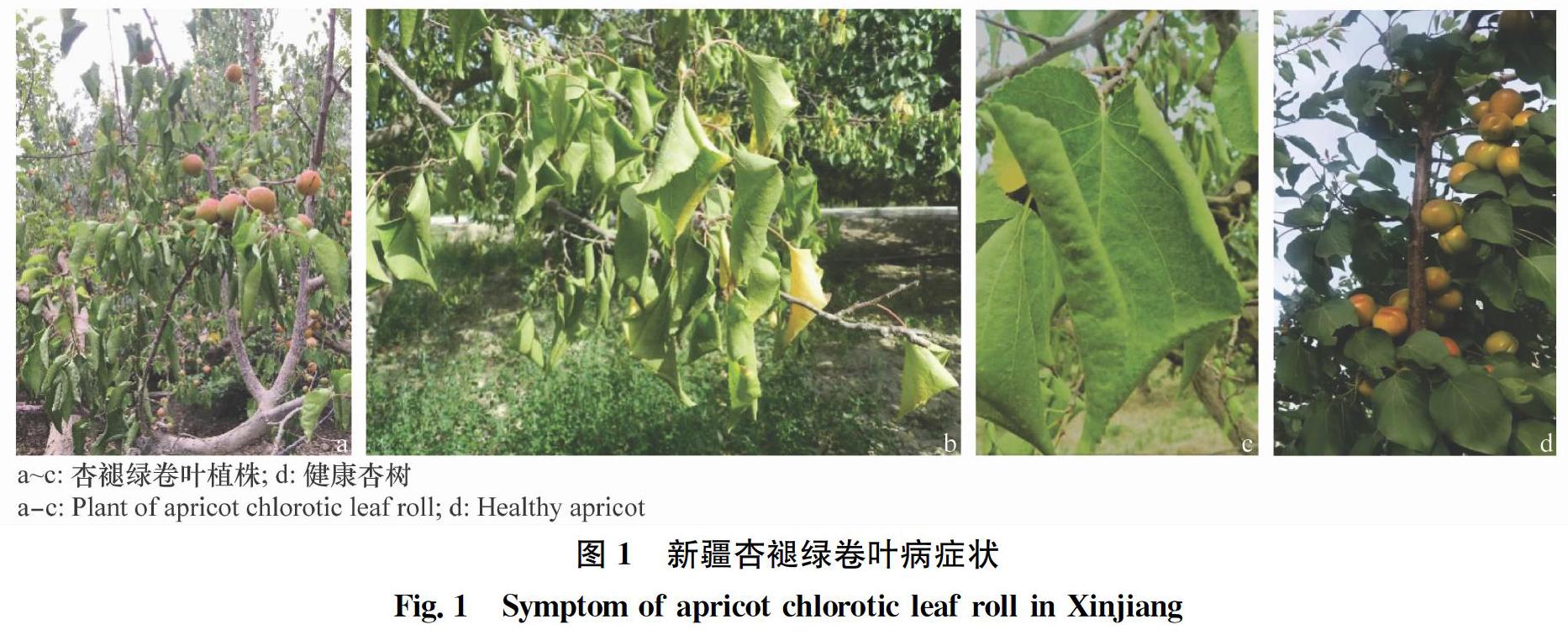

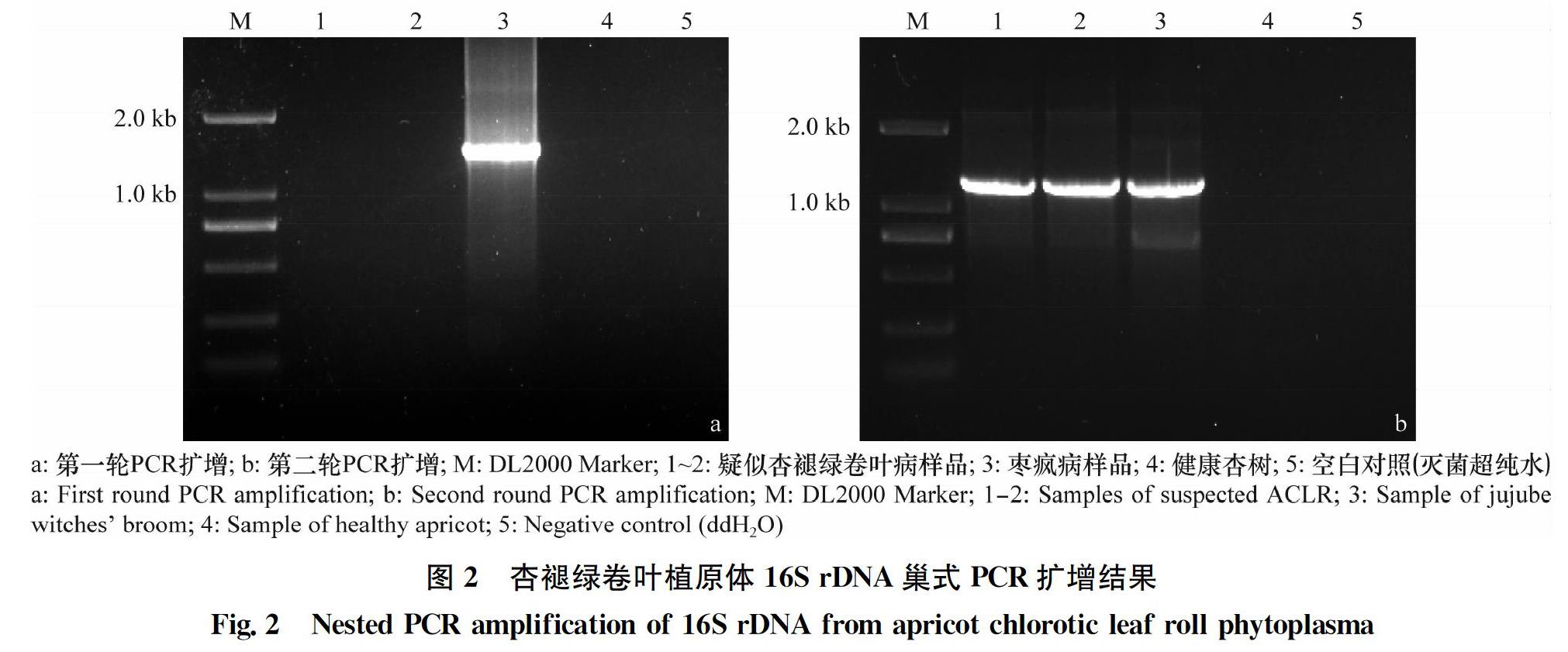
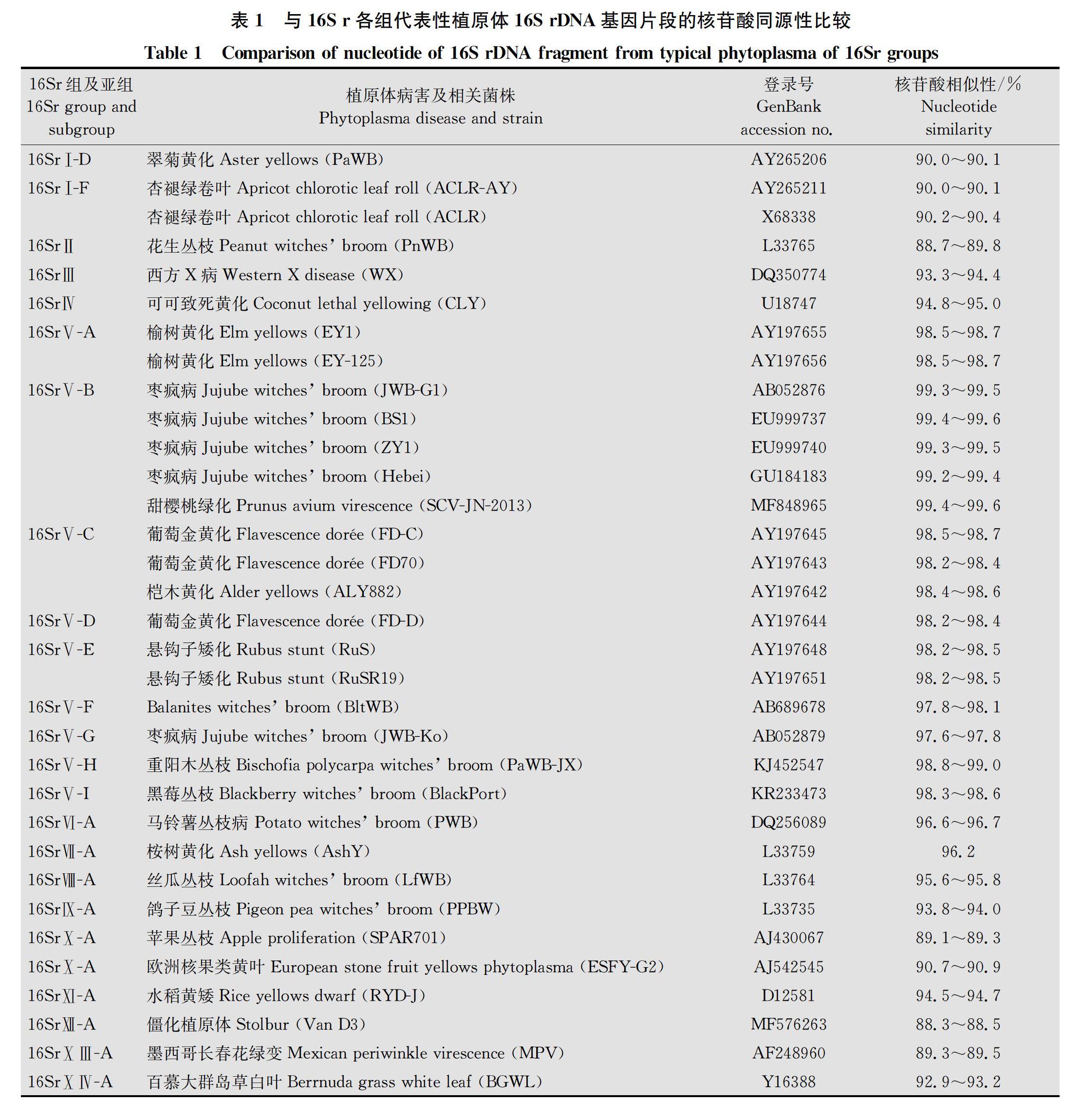
摘要 利用植原體16S rDNA基因通用引物對新疆輪臺縣疑似杏褪綠卷葉病植株總DNA進行巢氏PCR檢測,擴增出大小約1.2 kb的特異性條帶。對擴增產物克隆和測序,確定特異片段大小為1 248 bp。序列同源性比較和系統進化分析表明,新疆杏褪綠卷葉植原體不同分離株16S rDNA基因序列同源性極高,達到99.8%~100%。與16SrⅤ組成員的同源性達到98.2%以上,其中與16SrⅤ-B亞組的棗瘋病植原體山東寶山分離株,甜櫻桃綠化植原體山東分離株同源性最高,達到99.4%~99.6%。進一步虛擬RFLP分析,結果表明該植原體屬于榆樹黃化組(16SrⅤ)的一個新的亞組,與其相似性最高的是16SrⅤ-B亞組,相似系數為0.94。本研究首次報道了新疆杏褪綠卷葉植原體16S rDNA的序列,確定了其分類地位,為杏褪綠卷葉病的早期診斷和檢測提供了基礎。
關鍵詞 杏; 杏褪綠卷葉病; 植原體; 16S rDNA; 序列分析
中圖分類號: S 436.6 ?文獻標識碼: A ?DOI: 10.16688/j.zwbh.2019046
Abstract By using Nested-PCR, the 16S rDNA of phytoplasma of apricot chlorotic leaf roll (ACLR) in diseased sample from Luntai region in Xinjiang was amplified by the universal primer pairs, then a phytoplasma-specific 1.2 kb fragment were amplified by nested-PCR. The 16S rDNA gene was cloned by polymerase chain reaction from samples of ACLR, they were then sequenced. The result of sequencing showed that the ACLR strains from Xinjiang consists of 1 248 bp in 16S rDNA gene. The similarity and phylogenetic analysis showed that the six ACLR isolates sequenced from Luntai region are closely related to each other, displaying 99.8%-100% nucleotide sequence similarity, and the six isolates shared approximately 98.2% identity with 16SrⅤ group, the results of blast showed that the genetic distance of six isolates was closely to the 16SrⅤ-B subgroup,which shared the highest similarity (99.4%-99.6%) with the strains of prunus avium virescence phytoplasma (MF848965) from Shandong and jujube witches-broom phytoplasma (EU999737) from Shandong. Furthermore, virtual RFLP analysis showed that the phytoplasma belonged to a new subgroup within the elm yellows group(16SrⅤ), the most similar was the reference pattern of the 16Sr group Ⅴ, subgroup B (GenBank accession: AB05287), with a similarity coefficient of 0.94. This study reports 16S rDNA sequences of ACLR phytoplasmas and classified phytoplasma of ACLR in Xinjiang for the first time, it provides the base for early diagnosis and detection.
Key words apricot; apricot chlorotic leafroll; phytoplasma; 16S rDNA; sequence analysis
杏Armeniaca vulgaris為薔薇科杏屬植物,是中國栽培歷史最悠久的果樹之一。新疆作為杏的原生起源中心,擁有豐富的杏種質資源,其栽培面積和產量均居中國各省(區)之首。杏褪綠卷葉病(apricot chlorotic leaf roll disease)是危害杏樹的一種高致死性植原體病害。該病害于1973年首次在法國杏樹上發現,之后陸續在歐洲其他核果類樹種如扁桃、歐洲李、櫻桃、桃和油桃等多種果樹上發現,成為影響歐洲核果類果樹商業化栽培的主要病害。中國,歐洲和北美均將其列入進境植物檢疫危險性病害名錄[1-2]。1993年,趙京民對北京、河北、山西等地出現嚴重早期落葉的杏樹植株的組織切片進行了電鏡觀察,初步判斷可能是由類菌原體所致[3]。……

