參附注射液調控大鼠心肌梗死模型microRNA-135a的表達機制
蘇天生 羅繼紅 盧靜 陳志斌 王志民 廖云海 林磊
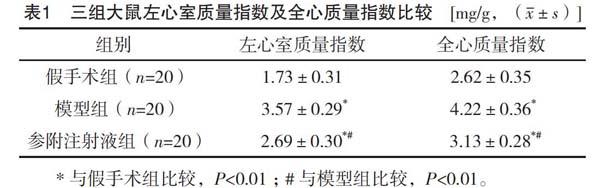
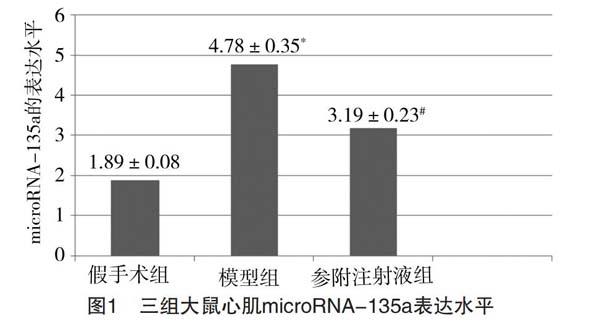
【摘要】 目的:研究參附注射液對大鼠心肌梗死模型microRNA-135a的調控機制。方法:將60只健康SD大鼠隨機分為三組,每組20只。模型組和參附注射液組行結扎冠狀動脈左前降支(LAD)術建立心肌梗死模型,假手術組冠狀動脈不做結扎。模型組和假手術組予以0.9%氯化鈉注射液6.0 ml/(kg·d)腹腔注射,參附注射液組予以參附注射液6.0 ml/(kg·d)腹腔注射,連續給藥12周。比較三組大鼠心肌質量指數。采用Realtime RT-PCR方法檢測大鼠心肌microRNA-135a的表達。結果:參附注射液組和模型組大鼠全心質量指數及左心室重量指數均明顯高于假手術組,且模型組高于參附注射液組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。與假手術組比較,模型組大鼠心肌microRNA-135a表達量上調,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);與模型組比較,參附注射液組大鼠心肌microRNA-135a表達量下調,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:microRNA-135a在心肌梗死中可能發揮重要作用,參附注射液可能通過抑制microRNA-135a的上調,抑制心肌梗死大鼠心室重構,從而改善大鼠心功能。
【關鍵詞】 參附注射液 心肌梗死 microRNA-135a
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.16.001 文獻標識碼 A 文章編號 1674-6805(2020)16-000-03
Mechanism of Shenfu Injection Regulating the Expression of MicroRNA-135a in Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction/SU Tiansheng, LUO Jihong, LU Jing, CHEN Zhibin, WANG Zhimin, LIAO Yunhai, LIN Lei. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(16): -3
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the regulation mechanism of Shenfu Injection on microRNA-135a in rat model of myocardial infarction. Method: A total of 60 healthy SD rats were randomly divided into three groups, with 20 rats in each group. The left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) was ligated in model group and Shenfu Injection group to establish myocardial infarction model, while the coronary artery in sham operation group was not ligated. Model group and sham operation group were given 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection 6.0 ml/ (kg·d) intraperitoneal injection, and Shenfu Injection group was given Shenfu Injection 6.0 ml/ (kg·d) intraperitoneal injection for 12 weeks. The myocardial mass index of the three groups was compared. The expression of microRNA-135a in rat myocardial was detected by Realtime RT-PCR. Result: The whole-heart mass index and left ventricular mass index of rats in Shenfu Injection group and model group were significantly higher than those in sham operation group, and the model group was significantly higher than that in Shenfu Injection group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.01). Compared with sham operation group, the expression level of microRNA-135a was up-regulated in the model group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Compared with the model group, the expression level of microRNA-135a in rat myocardial was down-regulated in Shenfu Injection group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: MicroRNA-135a may play an important role in myocardial infarction. Shenfu Injection may improve the cardiac function of rats by inhibiting the up regulation of microRNA-135a and inhibiting the ventricular remodeling of rats with myocardial infarction.
[Key words] Shenfu Injection Myocardial infarction MicroRNA-135a
First-authors address: The Second Peoples Hospital Affiliated to Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350003, China
急性心肌梗死(AMI)是指由于冠狀動脈急性狹窄或閉塞,供血持續減少或終止,所產生的心肌嚴重缺血壞死。其主要病理生理機制是在冠狀動脈粥樣硬化的基礎上,由于某些機械原因(如高血壓或冠狀動脈痙攣等)誘發了易損斑塊的破裂和血栓形成,產生了急性冠狀動脈嚴重狹窄或完全閉塞的結果。急性心肌梗死在中老年多發,起病急,發病兇險,死亡率高,預后差。急性心肌梗死發展為缺血性心肌病、心衰的核心病理生理機制是心室重構,梗死心肌細胞發生凋亡,導致左心室大小、組織結構發生改變[1]。阻止或逆轉心室重構是延緩心力衰竭發生的重要手段。參附注射液有保護心肌、抗休克、改善心功能和微循環等作用,在缺血性心臟病中應用廣泛,但其對心肌microRNA-135a影響如何,還未見報道。……

